JSR教程1——JSR 303 - Bean Validation介绍
1.Bean Validation
在任何时候,当你要处理一个应用程序的业务逻辑,数据校验是你必须要考虑和面对的事情。应用程序必须通过某种手段来确保输入进来的数据从语义上来讲是正确的。在通常的情况下,应用程序是分层的,不同的层由不同的开发人员来完成。很多时候同样的数据验证逻辑会出现在不同的层,这样就会导致代码冗余和一些管理的问题,比如说语义的一致性等。为了避免这样的情况发生,最好是将验证逻辑与相应的域模型进行绑定。
Bean Validation 为 JavaBean 验证定义了相应的元数据模型和 API。缺省的元数据是 Java Annotations,通过使用 XML 可以对原有的元数据信息进行覆盖和扩展。在应用程序中,通过使用 Bean Validation 或是你自己定义的 constraint,例如 @NotNull, @Max, @ZipCode, 就可以确保数据模型(JavaBean)的正确性。constraint 可以附加到字段,getter 方法,类或者接口上面。对于一些特定的需求,用户可以很容易的开发定制化的 constraint。Bean Validation 是一个运行时的数据验证框架,在验证之后验证的错误信息会被马上返回。
Bean Validation 中内置的 constraint
@NotNull/@Null
验证字段:引用数据类型
注解说明:注解元素必须是非空/空
@AssertTrue/@AssertFalse
验证字段:boolean
注解说明:注解元素必须是true/false
@Max(value)/@Min(value)
验证字段:byte、short、int、long及对应的包装类型以及BigDecimal、BigInteger
注解说明:验证值是否小于等于最大指定整数值/大于等于最小指定整数值
@DecimalMax(value)/@DecimalMin(value)
验证字段:byte、short、int、long及对应的包装类型以及BigDecimal、BigInteger、String
属性说明:验证值是否小于等于最大指定小数值/大于等于最小指定小数值
@Size(max, min)
验证字段:String、Collection、Map和数组
注解说明:验证元素大小是否在指定范围内
属性说明:max:最大长度,min:最小长度,message:提示信息,默认:{constraint.size}
@Digits(integer, fraction)
验证字段:byte、short、int、long及各自的包装类型以及BigDecimal、BigInteger、String
注解说明:验证数字构成是否合法
属性说明:integer:指定整数部分数字位数,fraction:指定小数部分数字位数
@Future/@Past
验证字段:java.util.Date,java.util.Calendar
注解说明:验证是否在当前系统时间之后/之前
@Pattern(value)
验证字段:String
注解说明:验证字符串是否匹配指定的正则表达式
属性说明:regexp:匹配的正则表达式,flags:指定Pattern.Flag的数值,表示正则表达式的选项
@Valid
验证字段:引用类型
属性说明:验证值是否需要递归调用
示例
@size (min=3, max=20, message="用户名长度只能在3-20之间")
@size (min=6, max=20, message="密码长度只能在6-20之间")
@pattern (regexp="[a-za-z0-9._%+-]+@[a-za-z0-9.-]+\.[a-za-z]{2,4}", message="邮件格式错误")
@NotNull(message = "用户名称不能为空")
@Max(value = 100, message = "年龄不能大于100岁")
@Min(value= 18 ,message= "必须年满18岁!" )
@AssertTrue(message = "bln4 must is true")
@AssertFalse(message = "blnf must is falase")
@DecimalMax(value="100",message="decim最大值是100")
DecimalMin(value="100",message="decim最小值是100")
@NotNull(message = "身份证不能为空")
@Pattern(regexp="\d{18,18}|\d{15,15}|(\d{17,17}[x|X])$", message="身份证格式错误")
2.Hibernate Validator
Hibernate Validator 是 Bean Validation 的参考实现 . Hibernate Validator 提供了 JSR 303 规范中所有内置 constraint 的实现,除此之外还有一些附加的 constraint。
Hibernate Validator 附加的 constraint
@Email
注解说明:被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址
@Length
注解说明:长度限制。被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内
@NotEmpty
注解说明:被注释的字符串的必须非空
@Range
注解说明:被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内
示例
@Email(message = "比如输入正确的邮箱")
@Length(min = 5, max = 20, message = "用户名长度必须位于5到20之间")
3.扩展自定义的constraint
一个 constraint 通常由 annotation 和相应的 constraint validator 组成,它们是一对多的关系。也就是说可以有多个 constraint validator 对应一个 annotation。在运行时,Bean Validation 框架本身会根据被注释元素的类型来选择合适的 constraint validator 对数据进行验证。
有些时候,在用户的应用中需要一些更复杂的 constraint。Bean Validation 提供扩展 constraint 的机制。可以通过两种方法去实现,一种是组合现有的 constraint 来生成一个更复杂的 constraint,另外一种是开发一个全新的 constraint
4.实战
通过创建一个虚构的订单管理系统(基于 JSP 的 web 应用)来演示如何在 Java 开发过程中应用 Bean Validation。
1>.系统设计和运用的技术
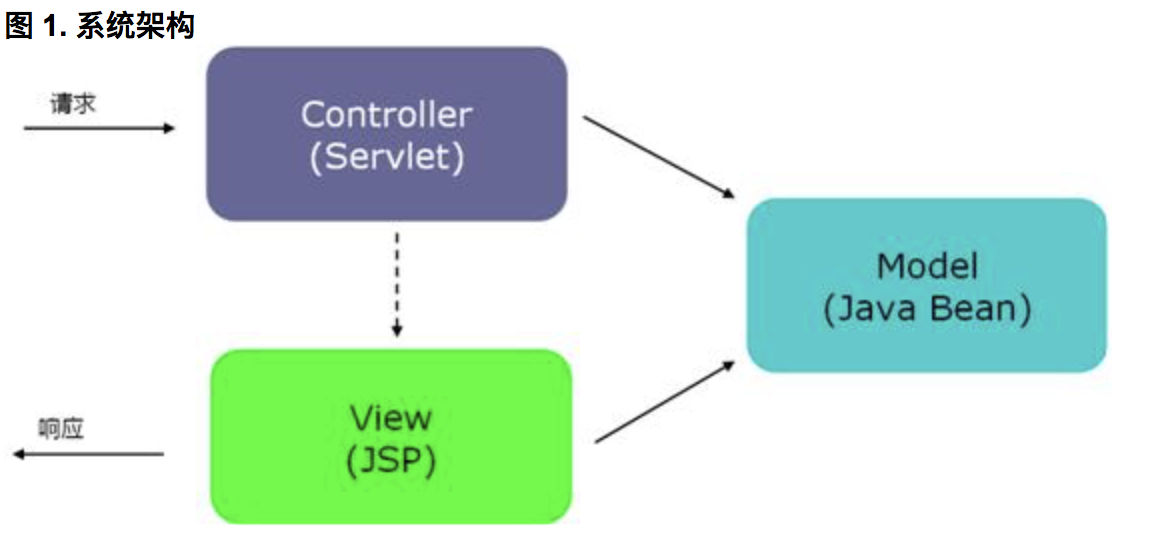 

2>.数据模型
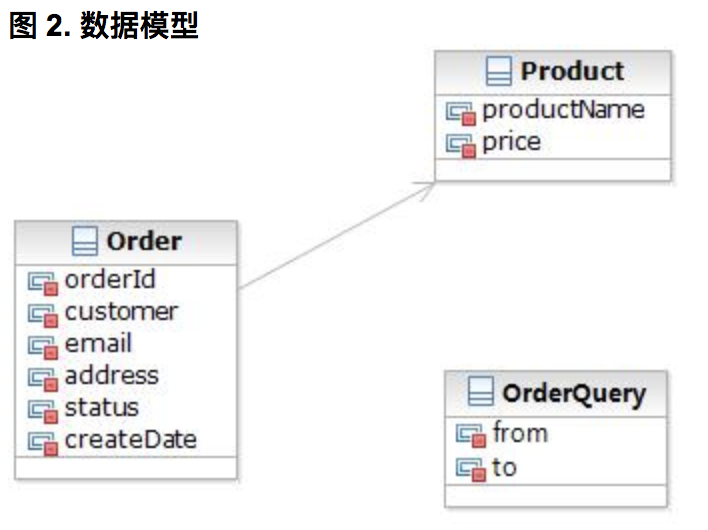 

3>.声明了 contraint 的 JavaBean
Order.java
```代码
package net.quickcodes.demo.domain;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
import javax.validation.constraints.Size;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created by mac.manon on 2016/10/20.
*/
public class Order {
// 必须不为 null, 大小是 10
@NotNull
@Size(min = 10, max = 10)
private String orderId;
// 必须不为空
@NotEmpty
private String customer;
// 必须是一个电子信箱地址
@Email
private String email;
// 必须不为空
@NotEmpty
private String address;
// 必须不为 null, 必须是下面四个字符串'created', 'paid', 'shipped', 'closed'其中之一
// @Status 是一个定制化的 contraint
@NotNull
@Status
private String status;
// 必须不为 null
@NotNull
private Date createDate;
// 嵌套验证
@Valid
private Product product;
public String getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public void setOrderId(String orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public String getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(String customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public Date getCreateDate() {
return createDate;
}
public void setCreateDate(Date createDate) {
this.createDate = createDate;
}
public Product getProduct() {
return product;
}
public void setProduct(Product product) {
this.product = product;
}
}
```
Product.java
```代码
package net.quickcodes.demo.domain;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.NotEmpty;
/**
* Created by mac.manon on 2016/10/20.
*/
public class Product {
// 必须非空
@NotEmpty
private String productName;
// 必须在 8000 至 10000 的范围内
// @Price 是一个定制化的 constraint
@Price
private float price;
public String getProductName() {
return productName;
}
public void setProductName(String productName) {
this.productName = productName;
}
public float getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(float price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
```
OrderQuery.java
package net.quickcodes.demo.domain;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created by mac.manon on 2016/10/20.
*/
// 'to'所表示的日期必须在'from'所表示的日期之后
// @QueryConstraint 是一个定制化的 constraint
@QueryConstraint
public class OrderQuery {
private Date from;
private Date to;
public Date getFrom() {
return from;
}
public void setFrom(Date from) {
this.from = from;
}
public Date getTo() {
return to;
}
public void setTo(Date to) {
this.to = to;
}
}
4>.定制化的 constraint
@Price是一个定制化的 constraint,由两个内置的 constraint 组合而成。
@Price 的 annotation 部分
package net.quickcodes.demo.domain;
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.Payload;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* Created by mac.manon on 2016/10/20.
*/
// @Max 和 @Min 都是内置的 constraint
@Max(10000)
@Min(8000)
@Constraint(validatedBy = {})
@Documented
@Target( { ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Price {
String message() default "错误的价格";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
@Status是一个新开发的 constraint.
@Status 的 annotation 部分
package net.quickcodes.demo.domain;
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import javax.validation.Payload;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* Created by mac.manon on 2016/10/20.
*/
@Constraint(validatedBy = {StatusValidator.class})
@Documented
@Target( { ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.FIELD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Status {
String message() default "不正确的状态 , 应该是 'created', 'paid', shipped', closed'其中之一";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
@Status 的 constraint validator 部分
package net.quickcodes.demo.domain;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created by mac.manon on 2016/10/20.
*/
public class StatusValidator implements ConstraintValidator<Status, String> {
private final String[] ALL_STATUS = {"created", "paid", "shipped", "closed"};
public void initialize(Status status) {
}
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if(Arrays.asList(ALL_STATUS).contains(value))
return true;
return false;
}
}
5>.界面
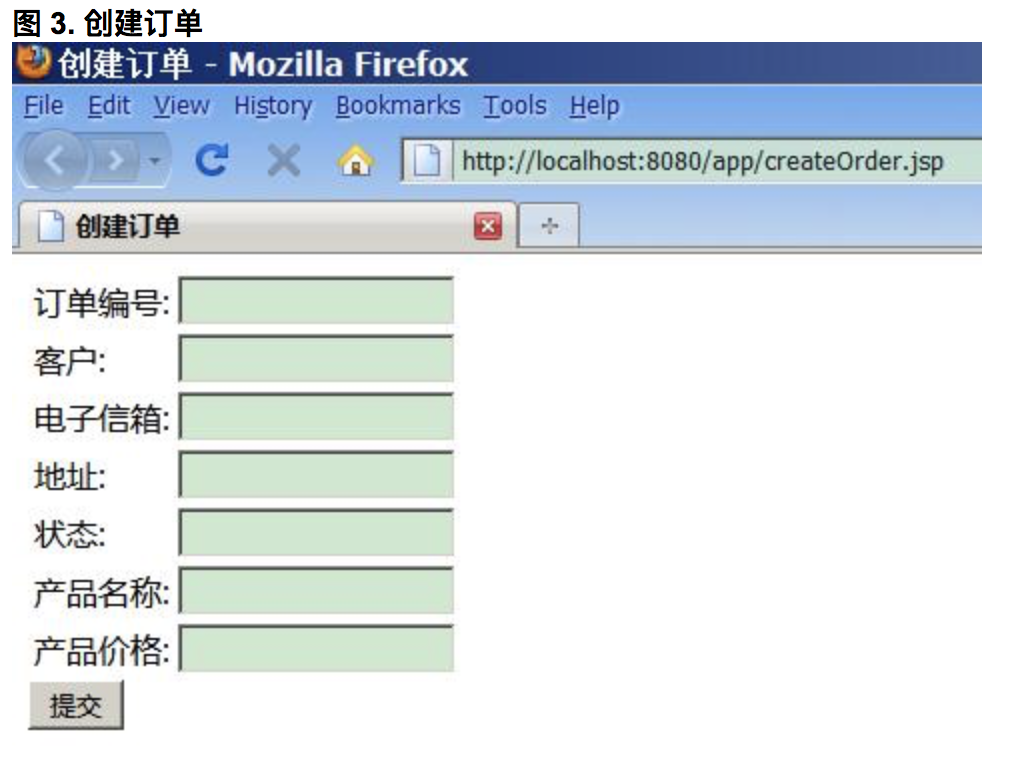 

6>.使用 Bean Validation API对这些信息的校验
关键代码:
Order order = new Order();
ValidatorFactory factory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = factory.getValidator();
Set> violations = validator.validate(order);
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 从 request 中获取输入信息
String orderId = (String) req.getParameter("orderId");
String customer = (String) req.getParameter("customer");
String email = (String) req.getParameter("email");
String address = (String) req.getParameter("address");
String status = (String) req.getParameter("status");
String productName = (String) req.getParameter("productName");
String productPrice = (String) req.getParameter("productPrice");
// 将 Bean 放入 session 中
Order order = new Order();
order.setOrderId(orderId);
order.setCustomer(customer);
order.setEmail(email);
order.setAddress(address);
order.setStatus(status);
order.setCreateDate(new Date());
Product product = new Product();
product.setName(productName);
if(productPrice != null && productPrice.length() > 0)
product.setPrice(Float.valueOf(productPrice));
order.setProduct(product);
session.setAttribute("order", order);
ValidatorFactory factory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = factory.getValidator();
Set<ConstraintViolation<Order>> violations = validator.validate(order);
if(violations.size() == 0) {
session.setAttribute("order", null);
session.setAttribute("errorMsg", null);
resp.sendRedirect("creatSuccessful.jsp");
} else {
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer();
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages");
for(ConstraintViolation<Order> violation: violations) {
buf.append("-" + bundle.getString(violation.getPropertyPath().toString()));
buf.append(violation.getMessage() + "<BR>\n");
}
session.setAttribute("errorMsg", buf.toString());
resp.sendRedirect("createOrder.jsp");
}
}
如果用户不填写任何信息提交订单,相应的错误信息将会显示在页面上
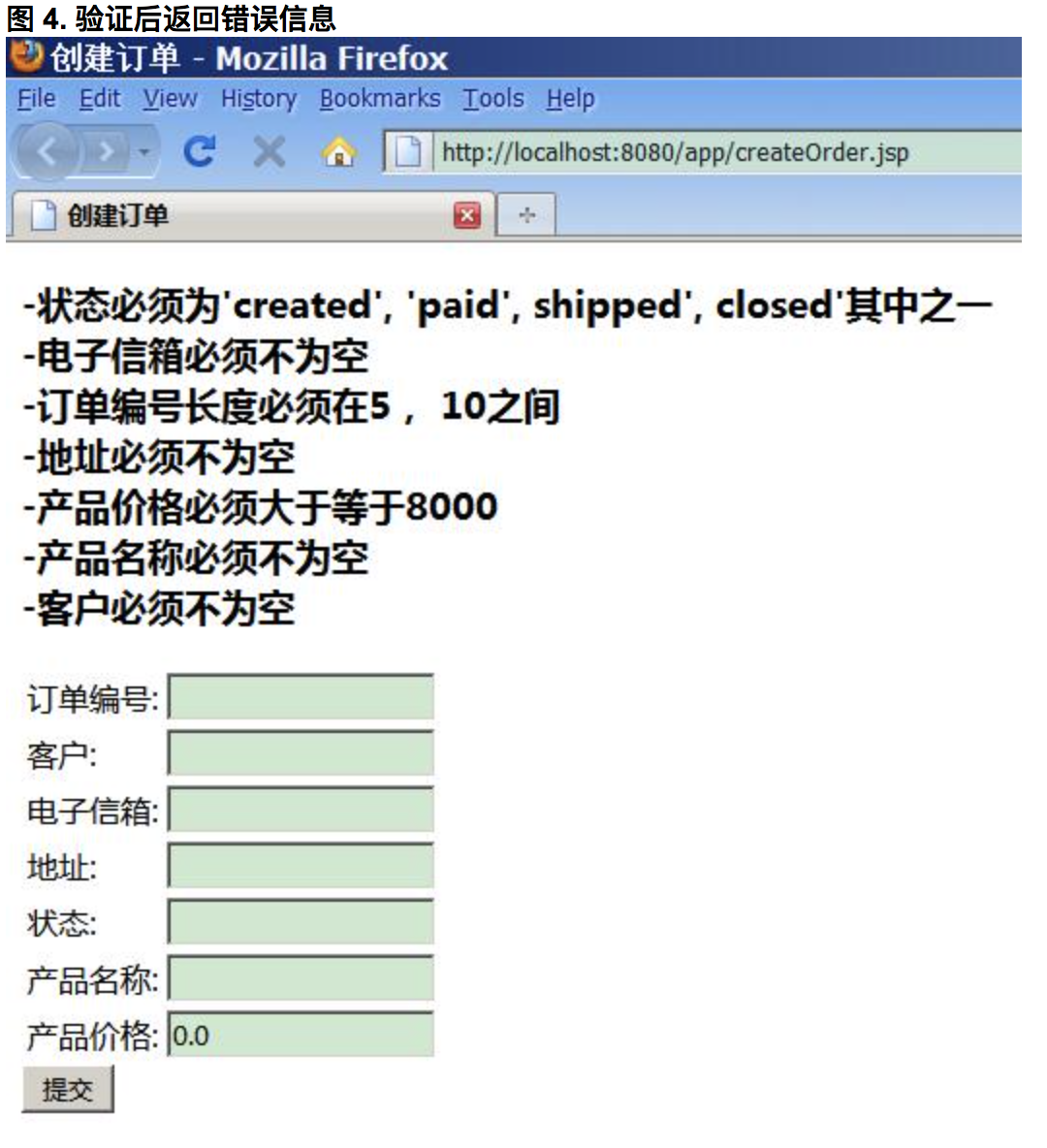 

JSR教程1——JSR 303 - Bean Validation介绍的更多相关文章
- JSR 303 - Bean Validation 介绍及最佳实践
JSR 303 - Bean Validation 介绍及最佳实践 JSR 303 – Bean Validation 是一个数据验证的规范,2009 年 11 月确定最终方案.2009 年 12 月 ...
- JSR 303 - Bean Validation 介绍及最佳实践(转)
JSR 303 – Bean Validation 是一个数据验证的规范,2009 年 11 月确定最终方案.2009 年 12 月 Java EE 6 发布,Bean Validation 作为一个 ...
- JSR 303 - Bean Validation 是什么?
关于 Bean Validation JSR 303 - Bean Validation 是jree6 中的一项子规范,JSR 303 - Bean Validation着重解决以下实际问题: 在任何 ...
- JSR 303 - Bean Validation 模型验证
类是转载的,不知道转的哪里的. 此类依赖 JSR 303 – Bean Validation, Hibernate Validator. 代码不能直接运行.意会一下.自己改改. import com. ...
- JSR 303 - Bean Validation 简单介绍及用法
一.JSR-303简单介绍 JSR-303 是 JAVA EE 6 中的一项子规范.叫做 Bean Validation,官方參考实现是Hibernate Validator. 此实现与 Hibern ...
- spring 3.1 配置 JCR 303 Bean Validation
A) 导入Hibernate-Validator 要使用JSR303 校验框架, 需要加入框架的具体实现Hibernate-Validator, 在soureforge上下载最新的Hibernate ...
- JSR-303 Bean Validation 介绍及 Spring MVC 服务端参数验证最佳实践
任何时候,当要处理一个应用程序的业务逻辑,数据校验是你必须要考虑和面对的事情. 应用程序必须通过某种手段来确保输入参数在上下文来说是正确的. 分层的应用很多时候同样的数据验证逻辑会出现在不同的层,这样 ...
- JSR-303 Bean Validation 介绍及 Spring MVC 服务端验证最佳实践
任何时候,当要处理一个应用程序的业务逻辑,数据校验是你必须要考虑和面对的事情. 应用程序必须通过某种手段来确保输入参数在上下文来说是正确的. 分层的应用在很多时候,同样的数据验证逻辑会出现在不同的层, ...
- JSR 303 - Bean Validation 简介及使用方法
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/xlgen157387/article/details/46848507 自己写的验证: /** * * @ClassName: BeanValida ...
随机推荐
- emWin 使用 GUIBuilder 放置标题 TEXT 注意
@2018-7-10 13:27:16 emWin 使用 GUIBuilder 放置标题 “Scroll Compressor”,有居中显示要求,为了内容可在程序中方便更改且能达到自适应,应将其属性大 ...
- GDKOI2018发烧记
偏远小渔村NOIP螺旋升天选手又一次来到了广州参加GDKOI...金实的初三爷们也来啦?要被碾啦T T Day 0 跟HR Lao爷拼(biao)车到了高铁站,上了高铁居然没有颓颓颓吃吃吃(雾),安心 ...
- 解题:HAOI 2015 按位或
题面 Min-Max容斥:对于集合S $min(S)=\sum_{s∈S}(-1)^{|s|+1}max(s)$ $max(S)=\sum_{s∈S}(-1)^{|s|+1}min(s)$ 那么这个题 ...
- 洛谷P1445 樱花
题意:求 1/x + 1/y = 1/(n!)的正整数解个数. 解:神仙...... 设(n!) = t 打表发现 x ∈ [t+1 , 2t] 反正就是拿到式子以后乱搞一通然后发现得到了这个很美观的 ...
- (转)Java随机数
1 随机数的三种产生方式 本章先讲解Java随机数的几种产生方式,然后通过示例对其进行演示. 广义上讲,Java中的随机数的有三种产生方式: (01). 通过System.currentTimeMil ...
- Spark记录-Scala异常与处理
Scala try-catch语句 Scala提供try和catch块来处理异常.try块用于包含可疑代码.catch块用于处理try块中发生的异常.可以根据需要在程序中有任意数量的try...cat ...
- bzoj千题计划211:bzoj1996: [Hnoi2010]chorus 合唱队
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1996 f[i][j][0/1] 表示已经排出队形中的[i,j],最后一个插入的人在[i,j]的i或j ...
- Splay模板讲解及一些题目
普通平衡树模板以及文艺平衡树模板链接. 简介 平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree)具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二 ...
- Swagger文档化restful接口
1.注解 @Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用. @ApiOperation:注解来给API增加方法说明. @ApiImplicitParams : 用在方法上包含一组参数说明. @ApiImplici ...
- lucene简介——(一)
0.概念性东西 1.数据分类
