learning ext2 filesystem notes
reference: http://e2fsprogs.sourceforge.net/ext2intro.html
reference: http://www.nongnu.org/ext2-doc/index.html
reference: http://www.science.unitn.it/~fiorella/guidelinux/tlk/
Each file is represented by a structure, called an inode. Each inode contains the description of the file: file type, access rights, owners, timestamps, size, pointers to data blocks. The addresses of data blocks allocated to a file are stored in its inode. When a user requests an I/O operation on the file, the kernel code converts the current offset to a block number, uses this number as an index in the block addresses table and reads or writes the physical block.
Directories:
Directories are implemented as a special type of files. Actually, a directory is a file containing a list of entries. Each entry contains an inode number and a file name. When a process uses a pathname, the kernel code searchs in the directories to find the corresponding inode number. After the name has been converted to an inode number, the inode is loaded into memory and is used by subsequent requests.
what happend when a extern stroage was mounted:
When a filesystem is to be mounted, the appropriate mount function is called. This function is responsible for reading the superblock from the disk, initializing its internal variables, and returning a mounted filesystem descriptor to the VFS. After the filesystem is mounted, the VFS functions can use this descriptor to access the physical filesystem routines.
A mounted filesystem descriptor contains several kinds of data: informations that are common to every filesystem types, pointers to functions provided by the physical filesystem kernel code, and private data maintained by the physical filesystem code. The function pointers contained in the filesystem descriptors allow the VFS to access the filesystem internal routines.
Two other types of descriptors are used by the VFS: an inode descriptor and an open file descriptor. Each descriptor contains informations related to files in use and a set of operations provided by the physical filesystem code. While the inode descriptor contains pointers to functions that can be used to act on any file (e.g. create, unlink), the file descriptors contains pointer to functions which can only act on open files (e.g. read, write).
Note: When such a file is deleted, random data is written in the disk blocks previously allocated to the file. This prevents malicious people from gaining access to the previous content of the file by using a disk editor.
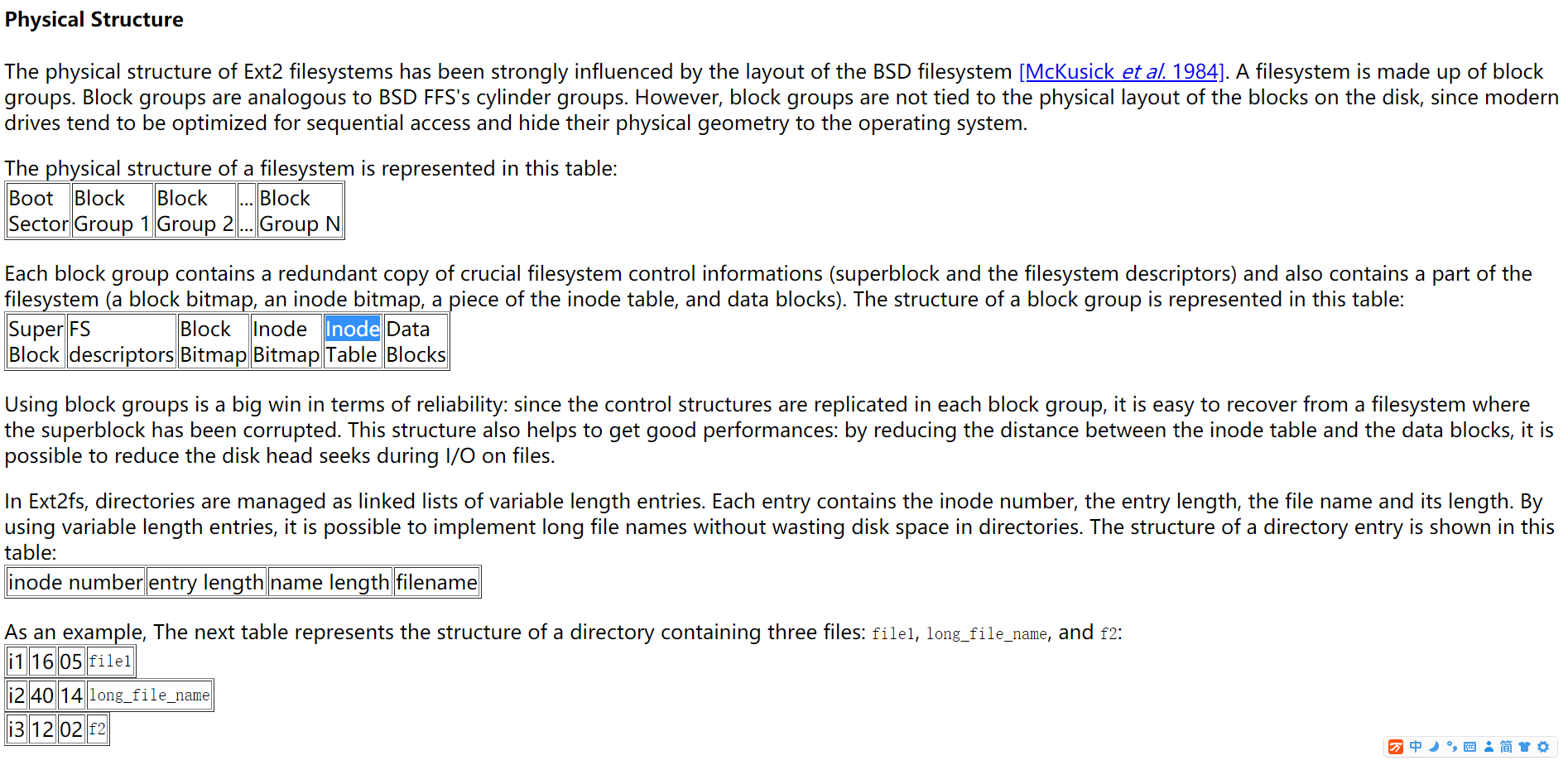
root@IoTP:~# dumpe2fs /dev/mmcblk1p2
dumpe2fs 1.42.13 (17-May-2015)
Filesystem volume name: rootfs
Last mounted on: /
Filesystem UUID: 69277f59-15ba-4705-95eb-b6200ad095dc
Filesystem magic number: 0xEF53
Filesystem revision #: 1 (dynamic)
Filesystem features: has_journal ext_attr resize_inode dir_index filetype needs_recovery sparse_super large_file
Filesystem flags: unsigned_directory_hash
Default mount options: user_xattr acl
Filesystem state: clean
Errors behavior: Continue
Filesystem OS type: Linux
Inode count: 236176
Block count: 944384
Reserved block count: 47219
Free blocks: 753105
Free inodes: 204057
First block: 0
Block size: 4096
Fragment size: 4096
Reserved GDT blocks: 230
Blocks per group: 32768
Fragments per group: 32768
Inodes per group: 8144
Inode blocks per group: 509
Filesystem created: Wed Jan 16 05:11:41 2019
Last mount time: Wed Jan 16 06:05:42 2019
Last write time: Wed Jan 16 06:05:42 2019
Mount count: 6
Maximum mount count: -1
Last checked: Wed Jan 16 05:11:41 2019
Check interval: 0 (<none>)
Lifetime writes: 666 MB
Reserved blocks uid: 0 (user root)
Reserved blocks gid: 0 (group root)
First inode: 11
Inode size: 256
Required extra isize: 28
Desired extra isize: 28
Journal inode: 8
First orphan inode: 173330
Default directory hash: half_md4
Directory Hash Seed: 32104d28-8e90-4157-9c6a-3a5950fc100a
Journal backup: inode blocks
Journal features: journal_incompat_revoke
Journal size: 64M
Journal length: 16384
Journal sequence: 0x000000a8
Journal start: 9
Group 0: (Blocks 0-32767)
Primary superblock at 0, Group descriptors at 1-1
Reserved GDT blocks at 2-231
Block bitmap at 232 (+232), Inode bitmap at 233 (+233)
Inode table at 234-742 (+234)
8123 free blocks, 8134 free inodes, 1 directories
Free blocks: 752-783, 792-815, 824-847, 856-879, 887-911, 943-975, 1024-1039, 1044-1055, 1057-1073, 1216-1231, 1281-1311, 1327-1359, 1369-1391, 1440-1455, 1497-1503, 1521-1551, 1570-1615, 1618-1647, 1696-1711, 1736-1759, 1780-1807, 1856-1871, 1886-1887, 1898-1935, 1954-1999, 2030-2063, 2094-2127, 2135-2159, 2194-2223, 2228-2255, 2259-2287, 2336-2351, 2356-2367, 2388-2415, 2427-2447, 2484-2511, 2516-2543, 2592-2607, 2725-2751, 2766-2799, 2831-2863, 2870-2895, 2900-2927, 2970-2991, 3022-3055, 3104-3119, 3181-3199, 3214-3247, 3252-3277, 3296-3311, 3328-3347, 3387-3391, 3417-3439, 3455-3514, 3536-3599, 3626-3663, 3712-3791, 3840-3903, 3968-3983, 4124-4223, 4326-4528, 4608-4623, 4813-4847, 5088-5103, 5105-5167, 5200-5215, 5760-5775, 5887, 5910-5935, 5952-5967, 5969-5999, 6291-6303, 6335, 6366-6383, 6385-6418, 6675-6703, 6720-6735, 6757-6799, 6836-6863, 6900-6927, 6962-6991, 7040-7055, 7100-7103, 7136-7151, 7731-7762, 7791-7823, 7872-7887, 7916-7935, 7966-7983, 7988-8015, 8020-8047, 8062-8079, 8159-8175, 8839-8863, 8894-8911, 8933-8964, 9029-9071, 9141-9151, 9183-9199, 9215-9231, 9278-9295, 9344-9359, 9401-9407, 9440-9455, 9536-9551, 9622-9631, 9664-9679, 9744-9759, 9780-9807, 9856-9871, 9936-9951, 9970-9999, 10043-10063, 10098-10127, 10171-10191, 10235-10255, 10296-10319, 10363-10383, 10427-10447, 10496-10511, 10632-10663, 10690-10735, 10784-10799, 10885-10911, 10944-10959, 11002-11007, 11040-11055, 11146-11167, 11200-11215, 11315-11327, 11352-11375, 11404-11439, 11488-11503, 11574-11583, 11616-11631, 11739-11759, 11784-11807, 11840-11855, 12000-12015, 12049-12080, 12145-12159, 12177-12207, 12282-12313, 12368-12399, 12436-12463, 12512-12527, 12603-12623, 12672-12687, 12738-12767, 12800-12815, 12866-12895, 12920-12943, 12978-13007, 13046-13071, 13106-13135, 13179-13199, 13236-13263, 13305-13327, 13376-13391, 13445-13471, 13504-13519, 13647-13679, 13713-13744, 13809-13823, 13829-13871, 13920-13935, 14040-14063, 14088-14111, 14144-14159, 14304-14319, 14341-14372, 14405-14447, 14491-14495, 14528-14543, 14590-14607, 14656-14671, 14726-14751, 14775-14799, 14848-14863, 14900-14911, 14934-14959, 15008-15023, 15123-15135, 15168-15183, 15192-15199, 15235-15279, 15328-15343, 15403-15423, 15442-15471, 15520-15535, 15629-15647, 15672-15695, 15697-15727, 15758-15791, 15822-15855, 15899-15919, 15959-15983, 15993-16015, 16045-16079, 16128-16143, 16170-16191, 16224-16239, 16243-16255, 16320-16335, 16375-16383, 16507-16527, 16534-16559, 16561-16591, 16632-16655, 16660-16687, 16736-16767, 16817-17051, 17132-17151, 17163-17407, 25600-26623, 27329-28671
Free inodes: 11-8144
learning ext2 filesystem notes的更多相关文章
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(3)--Learning Theory
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 本系列文章是Andrew Ng 在斯坦福的机器学习课程 CS 22 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(2)--Supervised Learning
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 本系列文章是Andrew Ng 在斯坦福的机器学习课程 CS 22 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(1)--Introduction
Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes 高雪松 @雪松Cedro Microsoft MVP 目 录 1 Introduction 1 1.1 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(6)—遗忘的数学知识
机器学习中遗忘的数学知识 最大似然估计( Maximum likelihood ) 最大似然估计,也称为最大概似估计,是一种统计方法,它用来求一个样本集的相关概率密度函数的参数.这个方法最早是遗传学家 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(5)—Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning 对于控制决策问题的解决思路:设计一个回报函数(reward function),如果learning agent(如上面的四足机器人.象棋AI程序)在决定 ...
- Machine Learning Algorithms Study Notes(4)—无监督学习(unsupervised learning)
1 Unsupervised Learning 1.1 k-means clustering algorithm 1.1.1 算法思想 1.1.2 k-means的不足之处 1 ...
- Deep Learning Workbench Installation Notes
1. ROS Indigo (30 min) Just flow ROSWiki: http://wiki.ros.org/indigo/Installation/Ubuntu NOW simply ...
- lua: Learning Official Doc notes
dynamically typed vars: basic types: nil, boolean, number, string, function, userdata, thread & ...
- Ext FileSystem Family、Ext2、Ext3
catalog . 简介 . Ext2文件系统 . Ext3文件系统 . 小结 1. 简介 VFS虚拟文件系统接口和数据结构构成了一个框架,各个文件系统的实现都必须在框架内运转,但这并不要求每个文件系 ...
随机推荐
- 20145334赵文豪《网络对抗》-逆向及Bof基础实践
本次实践的对象是一个名为pwn1的linux可执行文件. 该程序正常执行流程是:main调用foo函数,foo函数会简单回显任何用户输入的字符串. 该程序同时包含另一个代码片段,getShell,会返 ...
- ArrayList初始化的4种方法
In the last post we discussed about class ArrayList in Javaand it’s important methods. Here we are s ...
- MySQL命令行导出、导入数据库,备份数据库表
MySQL导出数据库/数据表 1.首先,将你MySQL安装目录,例如C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.7\bin添加到你的系统环境变量PATH中: 2.导出数 ...
- POJ 2449 Remmarguts' Date(第K短路 + A* + 最短路)题解
题意:找出第k短路,输出长度,没有输出-1 思路:这题可以用A*做.A*的原理是这样,我们用一个函数:f = g + h 来表示当前点的预期步数,f代表当前点的预期步数,g代表从起点走到当前的步数,h ...
- JVM类加载机制总结
1.运行时加载优点 提高灵活性,可以在运行时动态加载,连接.例子:面向接口编程,动态绑定实现类(但C++也有动态绑定,说明动态绑定不一定通过运行时加载Class字节码实现,也可能是机器码支持的) 2. ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 南京赛区网络预赛 E AC Challenge 状压DP
题目链接: https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/30994 Dlsj is competing in a contest with n (0 < n \le 20)n(0& ...
- HDU 5873 Football Games(竞赛图兰道定理)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5873 题意: 现在有比赛,所有队伍两两进行比赛,赢的积2分,输的积0分,如果平局的话就各自都积1分,现在给出每只 ...
- python enumerate用法总结--转载
enumerate()说明 enumerate()是python的内置函数 enumerate在字典上是枚举.列举的意思 对于一个可迭代的(iterable)/可遍历的对象(如列表.字符串),enum ...
- Thunder团队Final版本控制
Final版本控制报告 团队介绍:Thunder Check in次数 :6次. check in log(时间.人员.message.动机.其他解释) 代码贡献量.代码贡献比例以及代码作用 git链 ...
- RabbitMQ入门_06_深入了解ack
A. Delivery Tag 参考资料:https://www.rabbitmq.com/confirms.html 仔细查看一下 Consumer 的回调方法: public void handl ...
