James Munkres Topology: Sec 22 Exer 6
Exercise 22.6 Recall that \(\mathbb{R}_{K}\) denotes the real line in the \(K\)-topology. Let \(Y\) be the quotient space obtained from \(\mathbb{R}_K\) by collapsing the set \(K\) to a point; let \(p: \mathbb{R}_K \rightarrow Y\) be the quotient map.
(a) Show that \(Y\) satisfies the \(T_1\) axiom, but is not Hausdorff.
(b) Show that \(p \times p: \mathbb{R}_K \times \mathbb{R}_K \rightarrow Y \times Y\) is not a quotient map.
Comment This exercise shows that the product map of two quotient maps is not necessarily a quotient map.
Proof: (a) At first, we will clarify the forms of open sets in the quotient space \(Y\), which are defined as the images of saturated open sets in \(\mathbb{R}_K\) under the quotient map \(p\). Assume the set \(K\) coalesces to \(\alpha\), \(Y\) can be written as: \(Y = (\mathbb{R} - K) \cup \{\alpha\}\). For any \(x\) in \(\mathbb{R} - K\), \(p^{-1}(x) = x\) and \(p^{-1}(\alpha) = K\). Then the saturated open sets in \(\mathbb{R}_K\) have the following two forms:
- open set \(U\) of \(\mathbb{R}_K\) which contains \(K\);
- \(U - K\) with \(U\) being arbitrary open set in \(\mathbb{R}_K\).
Then their images under the quotient map \(p\) are
- \((U - K) \cup \{\alpha\}\) with \(K \subsetneq U\)
- \(U - K\)
which comprise the quotient topology on \(Y\). To prove \(Y\) satisfies the \(T_1\)-axiom, by referring to Theorem 17.8, we only need to show that one-point set \(\{x_0\}\) is closed. Then finite union of such closed singletons is also closed. To achieve this, there are two cases to be discussed.
If \(x_0 = \alpha\), for any point \(x \in Y\) and \(x \neq x_0\), i.e. \(x \in \mathbb{R} - K\), there exists an open set \(U - K\) in \(Y\) containing \(x\), which does not contain \(x_0\). Therefore, for all \(x \in \mathbb{R} - K\), it does not belong to the closure of \(\{\alpha\}\). Hence \(\{\alpha\}\) is closed.
If \(x_0 \in \mathbb{R} - K\), there are further two sub-cases:
For any \(x \in \mathbb{R} - K\) and \(x \neq x_0\), because \(\mathbb{R}_K\) is Hausdorff, there exists open sets \(U\) and \(V\) in \(\mathbb{R}_K\), such that \(x_0 \in U\), \(x \in V\) and \(U \cap V = \Phi\). Then \(x_0 \in (U - K)\), \(x \in (V - K)\) and \((U - K) \cap (V - K) = \Phi\), where both \(U - K\) and \(V - K\) are open in \(Y\). Hence \(\{x_0\} \cap (V - K) = \Phi\).
For \(x = \alpha\), the open set containing \(x\) has the form \((U - K) \cup \{\alpha\}\) where \(U\) is an open set in \(\mathbb{R}_K\) containing \(K\). Then,
- when \(x_0 \in (-\infty, 0]\), let \(U = (0, 2)\);
- when \(x_0 \in (0, 1]\), let \(U = (0,x_0) \cup (x_0, \frac{3}{2})\);
- when \(x_0 \in (1, +\infty)\), let \(U = (0,x_0)\),
such that \(K \subset U\) and \(\{x_0\} \cap ((U - K) \cup \{\alpha\}) = \Phi\).
Combining the above two sub-cases, we have for any \(x \neq x_0\) in \(Y\), it does not belong to the closure of \(\{x_0\}\). Hence \(\{x_0\}\) is closed.
Summarize the above cases, one-point set in \(Y\) is closed. Hence \(Y\) satisfies the \(T_1\)-axiom.
Next, we will show \(Y\) is not Hausdorff.
Let \(x_1, x_2 \in Y\), \(x_1 = \alpha\) and \(x_2 = 0\). For any open set in \(Y\) containing 0 but not \(\alpha\), it must have the form \(V - K\) with \(V\) being open in \(\mathbb{R}_K\). Then there exists an open interval \((a_2, b_2)\) with \(a_2 < 0\) and \(b_2 > 0\) such that \(0 \in (a_2, b_2)\) and \((a_2, b_2) \subset V\). We can find an \(n_0 \in \mathbb{Z}_+\) such that \(\frac{1}{n_0} < b_2\) and hence \(\frac{1}{n_0} \in (a_2, b_2)\). Meanwhile, any open set containing \(\alpha\) has the form \((U - K ) \cup \{\alpha\}\) with \(U\) being open in \(\mathbb{R}_K\) and \(K \subsetneq U\). Then there exists an open interval \((a_1,b_1)\) such that \(\frac{1}{n_0} \in (a_1, b_1)\) and \((a_1, b_1) \subset U\). Therefore, \((a_1,b_1) \cap (a_2,b_2) \neq \Phi\) and \(U \cap V \neq \Phi\), especially, \((U-K)\cap(V-K)\neq\Phi\). Hence, \(((U-K)\cup\{\alpha\}) \cap (V-K) \neq \Phi\). Therefore, for any open set containing 0, there is no open set containing \(\alpha\) which has no intersection with it. So \(Y\) is not Hausdorff.
(b) To prove this part, Exercise 13 in Section 17 should be adopted, which is presented below:
\(X\) is Hausdorff if and only if the diagonal \(\Delta = \{x \times x \vert x \in X \}\) is closed in \(X \times X\).
- If \(X\) is Hausdorff, for any \(x_1, x_2 \in X\) and \(x_1 \neq x_2\), there exist \(U\) and \(V\) open in \(X\) such that \(x_1 \in U\), \(x_2 \in V\) and \(U \cap V = \Phi\). Because \(U\) and \(V\) have no common points, \((U \times V) \cap \Delta = \Phi\). Then according to Theorem 17.5, \((x_1, x_2)\) does not belong to the closure of \(\Delta\). Because \(x_1\) and \(x_2\) are arbitrary two different points in \(X\), \(\Delta\) is closed.
- On the contrary, if \(\Delta\) is closed, for all \(x_1, x_2 \in X\) and \(x_1 \neq x_2\), there exists an open set \(W\) in \(X \times X\) containing \((x_1,x_2)\) such that \(W \cap \Delta = \Phi\). Then there exists a basis element \(U \times V\) in \(X \times X\) such that \((x_1, x_2) \subset U \times V \subset W\). Hence \(x_1 \in U\) and \(x_2 \in V\). Because \((U \times V) \cap \Delta = \Phi\), \(U \cap V = \Phi\). Because \(x_1\) and \(x_2\) are arbitrary two different points in \(X\), \(X\) is Hausdorff.
With the proved S17E13 and the obtained conclusion in part (a) that \(Y\) is no Hausdorff, we know that the diagonal set \(\Delta\) is not closed in \(Y \times Y\). Meanwhile, because its preimage \((p \times p)^{-1}(\Delta) = \{x \times x \vert x \in \mathbb{R}\}\) is closed in \(\mathbb{R}_K \times \mathbb{R}_K\), the product map \(p \times p\) is not a quotient map.
Finally, the following figure illustrates the original space \(\mathbb{R}_K\) and the quotient space \(Y\). The transformation from \(\mathbb{R}_K\) to \(Y\) can be considered as merging a countable number of knots on a rope.
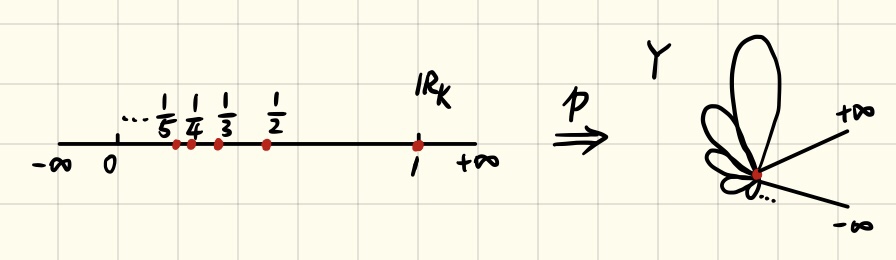
PS: Because the world we are living in is Hausdorff, Diagon Alley is always closed.
James Munkres Topology: Sec 22 Exer 6的更多相关文章
- James Munkres Topology: Sec 22 Exer 3
Exercise 22.3 Let \(\pi_1: \mathbb{R} \times \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}\) be projection on th ...
- James Munkres Topology: Sec 18 Exer 12
Theorem 18.4 in James Munkres “Topology” states that if a function \(f : A \rightarrow X \times Y\) ...
- James Munkres Topology: Sec 37 Exer 1
Exercise 1. Let \(X\) be a space. Let \(\mathcal{D}\) be a collection of subsets of \(X\) that is ma ...
- James Munkres Topology: Sec 22 Example 1
Example 1 Let \(X\) be the subspace \([0,1]\cup[2,3]\) of \(\mathbb{R}\), and let \(Y\) be the subsp ...
- James Munkres Topology: Lemma 21.2 The sequence lemma
Lemma 21.2 (The sequence lemma) Let \(X\) be a topological space; let \(A \subset X\). If there is a ...
- James Munkres Topology: Theorem 20.3 and metric equivalence
Proof of Theorem 20.3 Theorem 20.3 The topologies on \(\mathbb{R}^n\) induced by the euclidean metri ...
- James Munkres Topology: Theorem 20.4
Theorem 20.4 The uniform topology on \(\mathbb{R}^J\) is finer than the product topology and coarser ...
- James Munkres Topology: Theorem 19.6
Theorem 19.6 Let \(f: A \rightarrow \prod_{\alpha \in J} X_{\alpha}\) be given by the equation \[ f( ...
- James Munkres Topology: Theorem 16.3
Theorem 16.3 If \(A\) is a subspace of \(X\) and \(B\) is a subspace of \(Y\), then the product topo ...
随机推荐
- 配置webpack.config.js中的文件
webpack.config.js文件中,主要包括 entry:入口文件 output:出口文件 module:模块 plugins:插件 这几部分 1.基本配置 运行 webpack 这一命令可以将 ...
- Ajax简述
AJAX即“Asynchronous Javascript And XML”(异步JavaScript和XML),是指一种创建交互式网页应用的网页开发技术.AJAX = 异步 JavaScript和X ...
- Hexo博客部署-使用github作为保存中转仓库
本篇是在VPS上搭建Hexo静态博客的第一篇博文,写本篇的目的一是纪念一下,二是作为一个部署文档保留. 博客地址 相关描述 VPS环境是在搬瓦工上安装的centos6(x86),1核,512MB,10 ...
- IDEA中debug启动tomcat报错。Error running t8:Unable to open debugger port(127.0.0.1:49225):java.net.BindException"Address alread in use:JVM_Bind"
解决办法: 1,如下图打开项目配置的tomcat的“Edit Configurations...” 2,打开“Startup/Connection”--------"Debug"- ...
- CSS white-space属性详解
概述 CSS的white-space属性用于指定如何处理容器中的空白字符,例如:空格( ).换行(\n).缩进(\t)等. white-space出自CSS1,适用于块状元素,具有继承性,支持IE 5 ...
- 认识Modbus协议
1.什么是Modbus? Modbus协议是应用于电子控制器上的一种通用语言.通过此协议,控制器相互之间,控制器经由网络(例如以太网)和其它设备之间可以通信.Modbus协议定义了一个控制器能认识使用 ...
- vue组件中data为什么必须是个函数
<body> <div id="app"> <counter></counter> </div> <templat ...
- 「HNOI 2019」白兔之舞
一道清真的数论题 LOJ #3058 Luogu P5293 题解 考虑$ n=1$的时候怎么做 设$ s$为转移的方案数 设答案多项式为$\sum\limits_{i=0}^L (sx)^i\bin ...
- java 中类的方法
object类,即所有类的父类, getClass() 返回对象执行时的Class实例, getClass().getName();// 返回类的名字 toString();// equals();/ ...
- 二分查找算法的java实现
1.算法思想: 二分查找又称折半查找,它是一种效率较高的查找方法. 时间复杂度:O(nlogn) 二分算法步骤描述: ① 首先在有序序列中确定整个查找区间的中间位置 mid = ( low + ...
