【EF Core】框架是如何识别实体的属性和主键v
在上一篇水文中,老周生动形象地解释了 DbContext 是如何识别实体 Set 的,大伙伴们可能会产生新的疑惑:实体是识别了,但,实体的属性或字段列表,它是怎么识别并映射给数据表的列的呢?
用过 EF 的人都知道(废话),其实默认情况下,实体类中只要不是静态的属性和字段都会被映射到数据表中,就算你不重写 DbContext 类的 OnModelCreating 方法,EF 都能自动给你“造”个模型,这是啥机制。
老周知道,大伙们比魏公公还急,那就不绕关子了,先上结论。那是因为:EF Core 中有一种类叫做约定(Conventions),或者翻译为“规范”也可以。这些约定实际上是一系列接口,但当然了,接口是不干活的,你得实现它(相信你们是学过面向老婆,哦不,是面向对象的)。为了不使大伙看得雨里云里雪里雾里,老周简单列一下常见的约定接口。这堆接口很多,也不要求你全都明白它们是什么,毕竟,咱们不会都用上的,除非你打算把 EF 的功能全部重写一遍(这样造轮子不太优雅)。
1、IConvention:所有约定接口的 base,里面是空的,仅作为一个标志——你的类如果实现了它,那表示你是一个约定。
2、IEntityTypeAddedConvention:当某个实体被添加到模型中,就会调用。
3、IPropertyAddedConvention:为实体添加属性后,就会调用。
4、IKeyAddedConvention:向实体添加主键后被调用。
5、IKeyRemovedConvention:实体主键被删除后被调用。
6、IPropertyRemovedConvention:从实体中删除某个属性后被调用。
……
这时候你会想:咦?这尼马的怎么看着那么像事件回调啊?还真是呢,这些约定接口,只要你实现了并添加到框架中,当模型发生变更后就会被调用,这使得 EF Core 能够跟踪模型的改变,保证模型状态是最新的。注意了,这里跟踪的是模型的结构(如有几个实体,实体有哪些属性会映射到数据库,有几个主键等),不是数据。
在 EF Core 内部,在初始化时会添加一些“预制菜”以供框架自己食用。即预置的约定集合,它们由一个名为 ProviderConventionSetBuilder 类负责创建。此类实现了 IProviderConventionSetBuilder 接口,继而实现了 CreateConventionSet 方法。
public virtual ConventionSet CreateConventionSet()
{
var conventionSet = new ConventionSet(); conventionSet.Add(new ModelCleanupConvention(Dependencies)); conventionSet.Add(new NotMappedTypeAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new OwnedAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ComplexTypeAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new KeylessAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new EntityTypeConfigurationAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new NotMappedMemberAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new BackingFieldAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ConcurrencyCheckAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new DatabaseGeneratedAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new RequiredPropertyAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new MaxLengthAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new StringLengthAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new TimestampAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ForeignKeyAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new UnicodeAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new PrecisionAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new InversePropertyAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new DeleteBehaviorAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new NavigationBackingFieldAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new RequiredNavigationAttributeConvention(Dependencies)); conventionSet.Add(new NavigationEagerLoadingConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new DbSetFindingConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new BaseTypeDiscoveryConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ManyToManyJoinEntityTypeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new PropertyDiscoveryConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new KeyDiscoveryConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ServicePropertyDiscoveryConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new RelationshipDiscoveryConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ComplexPropertyDiscoveryConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ValueGenerationConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new DiscriminatorConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new CascadeDeleteConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ChangeTrackingStrategyConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ConstructorBindingConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new KeyAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new IndexAttributeConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ForeignKeyIndexConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ForeignKeyPropertyDiscoveryConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new NonNullableReferencePropertyConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new NonNullableNavigationConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new BackingFieldConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new QueryFilterRewritingConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new RuntimeModelConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ElementMappingConvention(Dependencies));
conventionSet.Add(new ElementTypeChangedConvention(Dependencies)); return conventionSet;
}
好家伙,这么多。这里面有几位明星跟咱们今天的主题相关(高亮显示,被锥光灯对着那几位)。下面老详细但不啰嗦地介绍一下约定集合 ConventionSet。
这个类里面,为上面所列的接口(当然上面只列了常用的)各自分配一个 List<T> 类型的属性。
public class ConventionSet
{
/// <summary>
/// Conventions to run to setup the initial model.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IModelInitializedConvention> ModelInitializedConventions { get; } = []; /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when model building is completed.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IModelFinalizingConvention> ModelFinalizingConventions { get; } = []; /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when model validation is completed.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IModelFinalizedConvention> ModelFinalizedConventions { get; } = []; ……
/// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when a type is ignored.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<ITypeIgnoredConvention> TypeIgnoredConventions { get; } = []; /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when an entity type is added to the model.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IEntityTypeAddedConvention> EntityTypeAddedConventions { get; } = []; /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when an entity type is removed.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IEntityTypeRemovedConvention> EntityTypeRemovedConventions { get; } = []; /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when a property is ignored.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IEntityTypeMemberIgnoredConvention> EntityTypeMemberIgnoredConventions { get; } = []; …… /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when a primary key is changed.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IEntityTypePrimaryKeyChangedConvention> EntityTypePrimaryKeyChangedConventions { get; } = []; /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when an annotation is set or removed on an entity type.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IEntityTypeAnnotationChangedConvention> EntityTypeAnnotationChangedConventions { get; } = []; /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when a property is ignored.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IComplexTypeMemberIgnoredConvention> ComplexTypeMemberIgnoredConventions { get; } = []; …… /// <summary>
/// Conventions to run when an annotation is changed on the element of a collection.
/// </summary>
public virtual List<IElementTypeAnnotationChangedConvention> ElementTypeAnnotationChangedConventions { get; } = [];
……
}
太长了,老周省略了部分代码,反正各位知道这个规律就行。当调用 Add 方法向集合添加约定时,它会根据你的约定类所实现的接口来分类,添加到对应的 List 中。
public virtual void Add(IConvention convention)
{
// 实现了 IModelInitializedConvention 接口的类,初始化模型时调用
if (convention is IModelInitializedConvention modelInitializedConvention)
{
ModelInitializedConventions.Add(modelInitializedConvention);
} // 实现了IModelFinalizingConvention接口的类,在模型初始化之前调用
if (convention is IModelFinalizingConvention modelFinalizingConvention)
{
ModelFinalizingConventions.Add(modelFinalizingConvention);
} // 初始化之后调用
if (convention is IModelFinalizedConvention modelFinalizedConvention)
{
ModelFinalizedConventions.Add(modelFinalizedConvention);
}
…… // 实体类型被添加到模型后调用
if (convention is IEntityTypeAddedConvention entityTypeAddedConvention)
{
EntityTypeAddedConventions.Add(entityTypeAddedConvention);
} // 实体从模型中删除后调用
if (convention is IEntityTypeRemovedConvention entityTypeRemovedConvention)
{
EntityTypeRemovedConventions.Add(entityTypeRemovedConvention);
} if (convention is IEntityTypeMemberIgnoredConvention entityTypeMemberIgnoredConvention)
{
EntityTypeMemberIgnoredConventions.Add(entityTypeMemberIgnoredConvention);
} ……
}
不管是“预制”的约定,还是咱们自己定义的,都可以添加到此集合中。
现在约定集合有了,怎么让它运作起来呢?EF Core 整了个调度器—— ConventionDispatcher,该类中公开一系列 OnXXXX 方法,对应着模型的各种行为。比如,OnModelInitialized 方法在模型完成初始化后被 Model 类调用,此方法会调用约定集合中所有实现了 IModelInitializedConvention 接口的约定类。
_modelBuilderConventionContext.ResetState(modelBuilder);
foreach (var modelConvention in conventionSet.ModelInitializedConventions)
{
modelConvention.ProcessModelInitialized(modelBuilder, _modelBuilderConventionContext);
if (_modelBuilderConventionContext.ShouldStopProcessing())
{
return _modelBuilderConventionContext.Result!;
}
}
当然,这里头很复杂,ConventionDispatcher 这些方法并非直接实现,而是嵌套了几个内部类,这些类实现 ConventionScope 抽象类。即 ImmediateConventionScope 和 DelayedConventionScope。这些类同样公开了 OnXXXX 方法。也就是说,ConventionDispatcher 类的 OnXXX 方法调用了这两个嵌套类的 OnXXXX 方法。
前文提到,OnModelInitialized 方法中通过 foreach 循环调用所有实现了 IModelInitializedConvention 接口的约定类。而 DbSetFindingConvention 类正是实现了该接口,在 ProcessModelInitialized 方法的实现中,通过 SetFinder 对象,进而将 DbContext 子类的 DbSet<T> 类型属性所对应的实体类添加到 Model 中。
public virtual void ProcessModelInitialized(
IConventionModelBuilder modelBuilder,
IConventionContext<IConventionModelBuilder> context)
{
foreach (var setInfo in Dependencies.SetFinder.FindSets(Dependencies.ContextType))
{
modelBuilder.Entity(setInfo.Type, fromDataAnnotation: true);
}
}
注意上面的 Dependencies.SetFinder.FindSets,咱们看看它里面是如何获得实体类型信息的。
public virtual IReadOnlyList<DbSetProperty> FindSets(Type contextType)
=> _cache.GetOrAdd(contextType, FindSetsNonCached); private static DbSetProperty[] FindSetsNonCached(Type contextType)
{
var factory = ClrPropertySetterFactory.Instance; return contextType.GetRuntimeProperties()
.Where(
p => !p.IsStatic()
&& !&& p.DeclaringType != typeof&&&& p.PropertyType.GetGenericTypeDefinition() == typeof(DbSet<>))
.OrderBy(p => p.Name)
.Select(
p => new DbSetProperty(
p.Name,
p.PropertyType.GenericTypeArguments.Single(),
p.SetMethod == null ? null : factory.Create(p)))
.ToArray();
}
其实就是从 DbContext 的子类中查找符合以下条件的属性:
1、非静态成员;
2、非索引;
3、属性的类型是泛型;
4、这个泛型类是 DbSet<>。
老周就不继续套了,不然大伙们会头晕的,这里老周直接简单说一下这个调用链:
--> DbContext以及数据库提供者初始化
--> DbContextServices从服务容器中被提取
--> 访问 DbContextServices的 Model 或 DesignTimeModel 属性以获得 Model 对象
--> 如果 Model 未实例化则调用 CreateModel 方法
--> 先从 DbContextOptions 中找 Model(实际通过 CoreOptionsExtension 类的 Model 属性获取);
--> DbContextOptions 中未找到 Model,则从 DbContext 子类所在的程序集中查找 DbContextModelAttribute 特性,此特应用在程序集上,用于描述自定义 Model 的类型(也就是说你可以自己实现 IModel 接口,把整个 EF Core 框架的模型管理机制替换掉);
--> 如果在 DbContext 子类所在的程序集还是找不到 Model,那就用 ModelSource 类去找;
--> ModelSource 先从缓存的对象中查查有没有现成的 Model;
--> 缓存中找不到现存的 Model,认栽了,那就 new 一个;
--> new 一个 ModelConfigurationBuilder 实例;
--> 调用 DbContext 子类的 ConfigureConventions 方法。这个方法是虚的,默认是空。你在继承 DbContext 类时可以重写此方法,添加自定义的约定类;
--> new 一个 ModelBuilder 实例,调用 DbContext 子类的 OnModelCreating 方法。你在继承 DbContext 类时可以重写此方法,自己去定义模型结构。这个相信大伙伴很常用也很熟悉的套路了;
--> 最后通过 ModelBuilder.Model 属性就能获取到 Model 实例了。
在以上过程中,各种预置的约定类会被调用,当然包括 DbSetFindingConvention 类啦。
现在,大伙大概知道 DbContext 公开 DbSet<T>,到这些 DbSet 被添加到模型的原理。既然实体类型是通过 DbSetFindingConvention 约定类添加到模型中的,那么咱们可以推测到,实体类的属性也是通过约定自动添加到模型中的,对应的约定就是 PropertyDiscoveryConvention 类。
啊,What the KAO!前面讲了这么多铺垫的话,终于轮到主角出场了。PropertyDiscoveryConvention 类的默认实现中,只要实体类中非静态的属性和字段都会被添加到模型中,从而会被映射到数据库中。
如果我们不希望某个属性被映射,最简单的方法是在这个属性(或字段,甚至整个实体类)上应用 NotMappedAttribute 就行了。不过,如果被排除的属性是具有共性的呢,总不能你每个实体类中都放一次 NotMapped 特性吧。为了好理解,老周下面用示例来说明。假设咱们的项目有这么一条规则:实体类中不管是属性还是字段,凡是带下画线开头的都不能映射到数据库中,即,如 _What、__What 之类命名的都被排除。这种情况下,一个个地做模型配置会很麻烦,就得用上约定了,只要向模型添加新实体,约定就会自动运行,排除下画线开头的成员。
咱们不需要全新造轮子,所以,最好的方案是从 PropertyDiscoveryConvention 派生。PropertyDiscoveryConvention 类公开一个虚方法叫 DiscoverPrimitiveProperties,分析属性(或字段)时否要添加到模型的逻辑都在该方法中实现的。所以,老周这里不用官方文档的方法(官方示例重写了多个方法,并且有的代码是从基类拷贝过去的),而是直接重写 DiscoverPrimitiveProperties 方法,找到下画线开头的属性,然后忽略掉即可。
public class CustPropertyDiscoveryConvention : PropertyDiscoveryConvention
{
// 注意,基类构造函数需要 ProviderConventionSetBuilderDependencies 类型的参数,所以我们要定义这个构造函数
public CustPropertyDiscoveryConvention(ProviderConventionSetBuilderDependencies deps)
:base(deps)
{
} protected override void DiscoverPrimitiveProperties(IConventionTypeBaseBuilder structuralTypeBuilder, IConventionContext context)
{
// 获取CLR类型
Type clrtype = structuralTypeBuilder.Metadata.ClrType;
// 找出带“_”开头的属性
var props = clrtype.GetRuntimeProperties()
.Where(p => p.Name.StartsWith("_"));
foreach(PropertyInfo p in props)
{
// 这些属性忽略
// 再调用基类成员,执行“预制”的约定,这时,被忽略的成员不再添加到模型
base.DiscoverPrimitiveProperties(structuralTypeBuilder, context);
}
}
然后,咱们定义一个实体类来测试一下。
public class Person
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public int? Age { get; set; }
public string? _WhatIsThis { get; set; }
}
注意那个 _WhatIsThis 属性,按照本例规则,它无缘映射到数据库。
从 DbContext 类派生一个类。
public class TestDbContext : DbContext
{
/// <summary>
/// 用户访问实体
/// </summary>
public DbSet<Person> Persons { get; set; } protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
// 配置数据库连接
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Data Source=(localdb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;Initial Catalog=Demo;Integrated Security=True;Trust Server Certificate=True");
} protected override void ConfigureConventions(ModelConfigurationBuilder configurationBuilder)
{
configurationBuilder.Conventions.Replace<PropertyDiscoveryConvention>(sp =>
{
// 1、获取 ProviderConventionSetBuilderDependencies 服务实例,因为构造函数需要它
var deps = sp.GetRequiredService<ProviderConventionSetBuilderDependencies>();
// 2、返回自定义属性发现约定的实例
return new CustPropertyDiscoveryConvention(deps);
});
}
}
这里老周调用了 Replace 方法,注意泛型参数一定要指定基类 PropertyDiscoveryConvention,因为 EF Core 默认注册的类型是 PropertyDiscoveryConvention,而不是咱们自定义的 CustPropertyDiscoveryConvention。这里就是把默认的约定替换成咱们自己的。另外,你也可能不调用 Replace 方法,而是 Add 方法直接添加一个新的约定。这样做也是可以的,只不过 PropertyDiscoveryConvention 的 DiscoverPrimitiveProperties 方法会处理两次。其实影响也不大。
最后,咱们实例化数据库上下文,并创建一个数据库。
using (var dc = new TestDbContext())
{
dc.Database.EnsureCreated();
// 输出模型的调试信息
Console.WriteLine(dc.Model.ToDebugString(MetadataDebugStringOptions.ShortDefault));
}
运行程序代码,看到输出的模型信息中未包含 _WhatIsThis 属性。
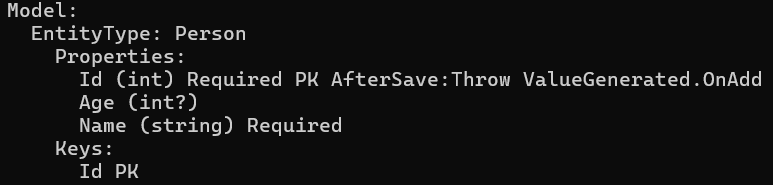
再看看创建的数据库,表中也是没有下画线开头的列。
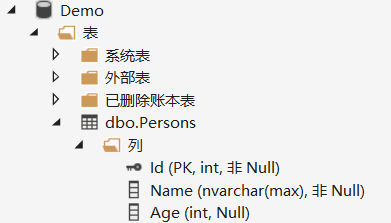
这就表明咱们自己的约定类被成功执行了。
咱们知道,EF Core 不仅会自动发现实体的属性,同时也会根据属性的命名自动识别主键。如你的实体类名为 Song,如果你的实体中有个属性叫 Id,或叫 SongId,类型是Guid、int 之类的类型,那这个属性会被自动标记为主键。
有了上面的认知,咱们也很快猜出来,还是预置约定干的活。对的,它叫 KeyDiscoveryConvention。如果你要对自动发现主键做定制化处理,为了便于批量应用于实体,也可以从 KeyDiscoveryConvention 派生一个类来搞搞,然后替换或添加到约定集合中即可。就像上面的示例一样,如法炮制,套路都一样的。
【EF Core】框架是如何识别实体的属性和主键v的更多相关文章
- Entity Framework中的实体类添加复合主键
使用Code First模式实现给实体类添加复合主键,代码如下: using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Compon ...
- WebApi EF Core 2.1 Code First 设置导航属性,外键
Nuget: Microsoft.AspNetCore.All Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore//Include 导航属性在此空间 Microsoft.EntityFram ...
- ASP.NET Core教程【三】实体字段属性、链接标签、并发数据异常、文件上传及读取
前文索引:ASP.NET Core教程[二]从保存数据看Razor Page的特有属性与服务端验证ASP.NET Core教程[一]关于Razor Page的知识 实体字段属性 再来看看我们的实体类 ...
- (19)ASP.NET Core EF创建模型(包含属性和排除属性、主键、生成的值)
1.什么是Fluent API? EF中内嵌的约定将POCO类映射到表.但是,有时您无法或不想遵守这些约定,需要将实体映射到约定指示外的其他对象,所以Fluent API和注解都是一种方法,这两种方法 ...
- EF中更新操作 ID自增但不是主键 ;根据ViewModel更新实体的部分属性
//ID自增但不是主键的情况 public int Update_join<TEntity>(TEntity entity) where TEntity : class { dbconte ...
- 【Hibernate】--实体状体与主键生成策略
一.Hibernate三种状态 (1).瞬时状态(只存在Hibernate容器中,数据库中没有与之对应的记录) A.通过new实例化的实体,在没有执行save方法时. B.持久状态调用delete方法 ...
- EF 传递的主键值的数量必须与实体上定义的主键值的数量匹配 原因
主要是该数据表没有定义主键造成的
- Hibernate逍遥游记-第13章 映射实体关联关系-002用主键映射一对一(<one-to-one constrained="true">、<generator class="foreign">)
1. <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hi ...
- EF Core怎么只Update实体的部分列数据
下面是EF Core中的一个Person实体: public partial class Person { public int Id { get; set; } public string Code ...
- 跟我一起学.NetCore之EF Core 实战入门,一看就会
前言 还记得当初学习数据库操作时,用ADO.NET一步一步地进行数据操作及查询,对于查询到的数据还得对其进行解析,然后封装返回给应用层:遇到这种重复而繁琐的工作,总有一些大神或团队对其进行封装,从而出 ...
随机推荐
- 如何使用 MySQL 的 EXPLAIN 语句进行查询分析?
如何使用 MySQL 的 EXPLAIN 语句进行查询分析? EXPLAIN 是 MySQL 提供的分析 SQL 查询执行计划的工具,用于了解查询语句的执行过程,帮助优化查询性能. 1. EXPLAI ...
- kette介绍-Step之Merge Join
Merge Join介绍 需要配合Sort rows使用,对关联字段进行排序 关联两个step数据,可以是两个不同的数据库表数据,也可以是一张表,一个文件,输出字段为两张表所有字段 注意将小数据集作为 ...
- robotframework之数据驱动
用robotframework做接口自动化时,如果执行用例条数比较多时,需要把用例存到表格当中,通过数据驱动读取表格内容. 一.引入第三方库 数据驱动的第三方库:DataDriver 直接在setti ...
- Cursor怎么使用,3分钟上手Cursor:比ChatGPT更懂需求,用聊天的方式写代码,GPT4、Claude 3.5等先进LLM辅助编程
前言 在人工智能工具井喷的今天,大家早已习惯用AI辅助编程,但大多数工具要么停留在"问答式"交互,要么对复杂代码逻辑束手无策.而Cursor--这款专为开发者设计的AI编程工具,凭 ...
- jwt的个人理解
概念: jwt全名json web token,是一种web登录验证和授权技术 官网debug:#debug 应用场景: 授权这是使用JWT最常见的场景.一旦用户登录,每个后续请求将包括JWT,允许用 ...
- 2025dsfz集训Day2:二分与三分
DAY2:二分与三分 \[Designed\ By\ FrankWkd\ -\ Luogu@Lwj54joy,uid=845400 \] 特别感谢 此次课的主讲 - Kwling 二分概述 二分法,在 ...
- 8.6K star!完全免费+本地运行+无需GPU,这款AI搜索聚合神器绝了!
嗨,大家好,我是小华同学,关注我们获得"最新.最全.最优质"开源项目和高效工作学习方法 FreeAskInternet是一款革命性的开源项目,它完美结合了多引擎搜索和智能语言模型, ...
- Sentinel——热点规则
目录 热点规则 配置热点规则 API配置热点规则 热点规则 热点规则是用于实现热点参数限流的规则.热点参数限流指的是,在流控规则中指定对某方法参数的 QPS 限流后,当所有对该资源的请求URL中携带有 ...
- 【工具】JS脚本|网页任意视频倍速播放(包括MOOC、本地视频、其他的视频)
实际发布时间:2022-12-14 22:54:52. csdn禁止浏览器脚本相关博客了,就只能重新发到这儿了. 2024/12/14更新:更新了常见问题Q&A,可以配合食用. 只要浏览器 ...
- Linux下安装Flume
摘要 flume是由cloudera软件公司产出的可分布式日志收集系统,后于2009年被捐赠了apache软件基金会,为hadoop相关组件之一.尤其近几年随着flume的不断被完善以及升级版本的逐一 ...
