Linux System Programming 学习笔记(九) 内存管理
1. 进程地址空间
2. 动态内存
/* obtaining dynamic memory */
#include <stdlib.h>
void * malloc (size_t size);
/* returns a pointer to a block of memory suitable for holding an array of nr elements, each of size bytes */
#include <stdlib.h>
void * calloc (size_t nr, size_t size);
/* resizing (making larger or smaller) existing allocations */
#include <stdlib.h>
void * realloc (void *ptr, size_t size);
3. 数据对齐
/* actual allocation size of the chunk of memory pointed to by ptr */
#include <malloc.h>
size_t malloc_usable_size (void *ptr);
4. 管理数据段
#include <unistd.h>
int brk (void *end);
void * sbrk (intptr_t increment);
5. 匿名内存映射
void *p;
p = mmap (NULL, /* do not care where */
* , /* 512 KB */
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, /* read/write */
MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_PRIVATE, /* anonymous, private */
−, /* fd (ignored) */
); /* offset (ignored) */
if (p == MAP_FAILED)
perror ("mmap");
else
/* 'p' points at 512 KB of anonymous memory... */
6. 基于栈的动态内存分配
/* make a dynamic memory allocation from the stack */
#include <alloca.h>
void * alloca (size_t size);
7. 变长数组 Variable-Length Arrays
for (i = ; i < n; ++i) {
char foo[i + ];
/* use 'foo'... */
}
8. 选择内存分配机制
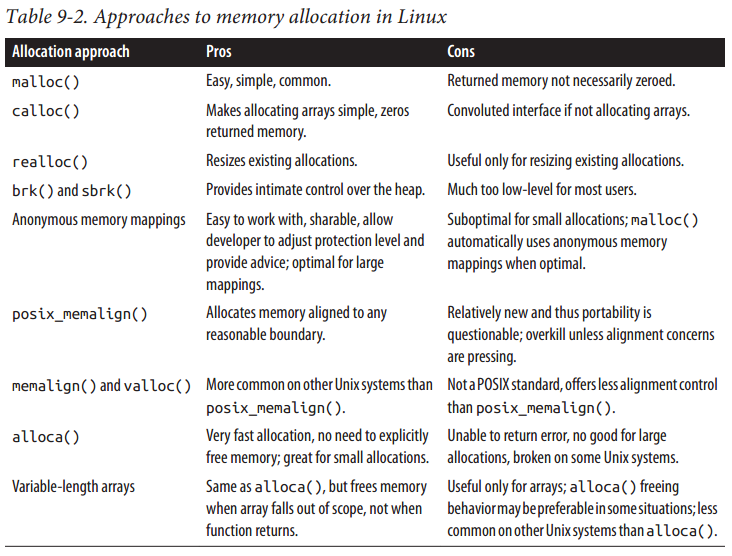
9. 内存操作
/* memset() sets the n bytes starting at s to the byte c and returns s */
#include <string.h>
void * memset (void *s, int c, size_t n);
/* compares two chunks of memory for equivalence */
#include <string.h>
int memcmp (const void *s1, const void *s2, size_t n);
因为结构体通常涉及到数据对齐,所以使用memcmp来比较两个结构体是不安全的
/* are two dinghies identical? (BROKEN) */
int compare_dinghies (struct dinghy *a, struct dinghy *b)
{
return memcmp (a, b, sizeof (struct dinghy));
}
上述代码不安全,应该分别比较每个结构体成员:
/* are two dinghies identical? */
int compare_dinghies (struct dinghy *a, struct dinghy *b)
{
int ret;
if (a->nr_oars < b->nr_oars)
return −;
if (a->nr_oars > b->nr_oars)
return ;
ret = strcmp (a->boat_name, b->boat_name);
if (ret)
return ret;
/* and so on, for each member... */
}
/* copies the first n bytes of src to dst, returning dst */
#include <string.h>
void * memmove (void *dst, const void *src, size_t n);
memmove可以正确处理内存区重叠的情况(部分dst位于src之内)
#include <string.h>
void * memcpy (void *dst, const void *src, size_t n)
memcpy在内存区出现重叠时 属于未定义行为
/* scans the n bytes of memory pointed at by s for the character c */
#include <string.h>
void * memchr (const void *s, int c, size_t n);
10. 锁定内存
/* “locking”one or more pages into physical memory, ensuring that they are never paged out to disk */
#include <sys/mman.h>
int mlock (const void *addr, size_t len);
mlock() locks the virtual memory starting at addr and extending for len bytes into physical memory
/* mlockall() locks all of the pages in the current process's address space into physical memory. */
#include <sys/mman.h>
int mlockall (int flags);
Linux System Programming 学习笔记(九) 内存管理的更多相关文章
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(五) 进程管理
1. 进程是unix系统中两个最重要的基础抽象之一(另一个是文件) A process is a running program A thread is the unit of activity in ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(八) 文件和目录管理
1. 文件和元数据 每个文件都是通过inode引用,每个inode索引节点都具有文件系统中唯一的inode number 一个inode索引节点是存储在Linux文件系统的磁盘介质上的物理对象,也是L ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(一) 介绍
1. Linux系统编程的三大基石:系统调用.C语言库.C编译器 系统调用:内核向用户级程序提供服务的唯一接口.在i386中,用户级程序执行软件中断指令 INT n 之后切换至内核空间 用户程序通过寄 ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(七) 线程
1. Threading is the creation and management of multiple units of execution within a single process 二 ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(四) 高级I/O
1. Scatter/Gather I/O a single system call to read or write data between single data stream and mu ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(十一) 时间
1. 内核提供三种不同的方式来记录时间 Wall time (or real time):actual time and date in the real world Process time:the ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(十) 信号
1. 信号是软中断,提供处理异步事件的机制 异步事件可以是来源于系统外部(例如用户输入Ctrl-C)也可以来源于系统内(例如除0) 内核使用以下三种方法之一来处理信号: (1) 忽略该信号.SIG ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(六) 进程调度
1. 进程调度 the process scheduler is the component of a kernel that selects which process to run next. 进 ...
- Linux System Programming 学习笔记(二) 文件I/O
1.每个Linux进程都有一个最大打开文件数,默认情况下,最大值是1024 文件描述符不仅可以引用普通文件,也可以引用套接字socket,目录,管道(everything is a file) 默认情 ...
随机推荐
- vue跨域处理(vue项目中baseUrl设置问题)
1.开发环境: 2.生产环境: 然后 const instance = axios.create({ baseURL: process.env.API })
- JavaScript——图片懒加载
前言 有一个朋友问我这个问题,刚好有时间,现在就简单的写个Demo~ github | https://github.com/wangyang0210/bky/tree/picLoadLazy 内容 ...
- css文件和js文件后面带一个问号----2015-1103
经常看一些网站页面源代码中的css文件和js文件后面带一个问号,后面跟着一连串数字或字符,这是干什么用的? 这个方法我也用过,而且很好用?,它的作用有两个:1.作为版本号,让自己方便记忆.查找:2.作 ...
- JavaScript递归实现对象深拷贝
let personOne = { name:"张三", age:18, sex:"male", children:{ first:{ name:"z ...
- 【上下界网络流 二分】bzoj2406: 矩阵
感觉考试碰到上下界网络流也还是写不来啊 Description Input 第一行两个数n.m,表示矩阵的大小. 接下来n行,每行m列,描述矩阵A. 最后一行两个数L,R. Output 第一行,输出 ...
- 【启发式拆分】bzoj4059: [Cerc2012]Non-boring sequences
这个做法名字是从武爷爷那里看到的…… Description 我们害怕把这道题题面搞得太无聊了,所以我们决定让这题超短.一个序列被称为是不无聊的,仅当它的每个连续子序列存在一个独一无二的数字,即每个子 ...
- 如何用纯 CSS 创作一组昂首阔步的圆点
效果预览 在线演示 按下右侧的"点击预览"按钮可以在当前页面预览,点击链接可以全屏预览. https://codepen.io/comehope/pen/ejrMKe 可交互视频 ...
- Laravel中chunk组块结果集处理
如果你需要处理成千上万个 Eloquent 结果,可以使用 chunk 命令.chunk 方法会获取一个“组块”的 Eloquent 模型,并将其填充到给定闭包进行处理.使用 chunk 方法能够在处 ...
- Python基础——字符串操作
运算符 加(+) str2="hello"+"python" print(str2) 乘(*) str1="hello python" ...
- LeetCode(190) Reverse Bits
题目 Reverse bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer. For example, given input 43261596 (represented ...
