What is “Neural Network”
Modern neuroscientists often discuss the brain as a type of computer. Neural networks aim to do the opposite: build a computer that functions like a brain.
Of course, we only have a cursory understanding of the brain’s complex functions, but by creating a simplified simulation of how the brain processes data, we can build a type of computer that functions vary from a standard one.
Computer processors process data (“in order”). They perform many operations on a set of data, one at a time. Parallel processing (“processing several streams at once”) speeds up the computer by using many processors in series.
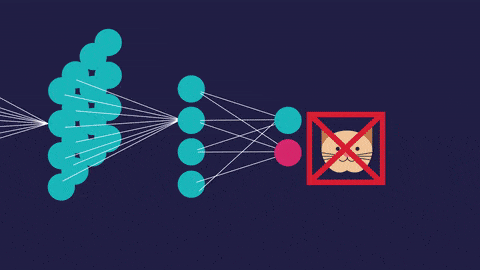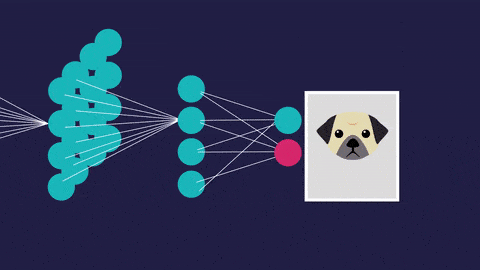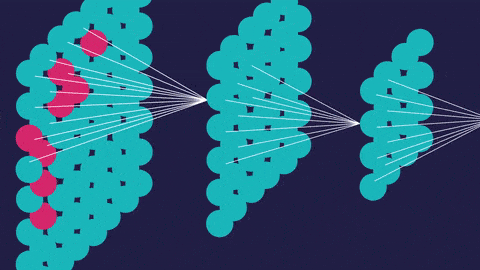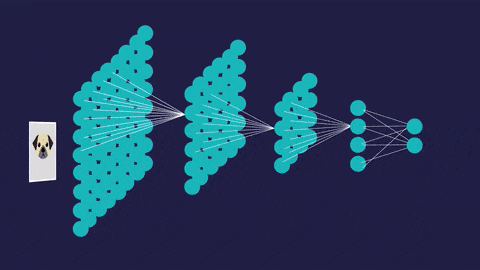
An artificial neural network (so called to distinguish it from the actual neural networks in the brain) has a different structure. It’s interconnected. This allows it to process data vary, learn from that data, and update its own internal structure to improve performance.
The high degree of interconnectedness, but, has some astounding effects. For example, neural networks are very good at recognizing obscure patterns in data.
Some historical facts about Neural Network
Although neural networks are massively innovative computer technologies, the idea goes back to 1943, with 2 prospectors from the Chicago Institute, Warren McCullough, a neurophysiologist and Walter Pitts, a student.
Their article “Logical calculation of thoughts immanent in angry business efficiency” was published for the first time in the journal Brain Theory, which explained the concept that the activation of a neuron is considered the main thing of brain energy. However, this act is largely related to the development of the cognitive doctrines of such a time, and 2 prospectors moved to the Massachusetts Scientific and Technical University, in 1952, to begin the first section of cognitive science.
In the 1950s, neural intrigues were a fertile field for studying computerized neural intrigues, including Perceptron, which provided visual definitions of images based on the difficult eye of a fly. In 1959, 2 prospectors from the Stanford Institute designed MADALINE (almost all ADAptive LINear Elements), with a neural network extending from beyond the theoretical and taking on an important issue. MADALINE was used to reduce the number of echoes on the telephone line, to increase the quality of the voice and was so successful, as if it remains in paid use for the current time. Despite the initial interest in the artificial origin of neural networks, the 1969 book from the Massachusetts Scientific and Technical University, Perceptrons: the introduction to computational geometry deserves interest. The creators showed their own skepticism in the artificial origin of neural networks and, as probably, it is probably considered a dead end in the search for the genuine artificial origin of the mind. Probably muffled this area for studies in the 1970s movement, both in terms of interest and in financing. Despite the fact that certain aspirations lasted, and in 1975 the first multi-layer network was invented, opening the way for the upcoming development in neural networks, an acquisition that some considered to be unfeasible less than in 10 years.
Enthusiasm by 1982 was renewed in neural networks, as soon as John Hopfield, Dr. of Princeton Institute, came up with an associative neural network; the innovation was contained in the fact that these had the opportunity to wander, as previously it was only unidirectional, and is also famous for its own inventor as the Hopfield Network. Moving forward, artificially derived neural wiles use great reputation and recovery.
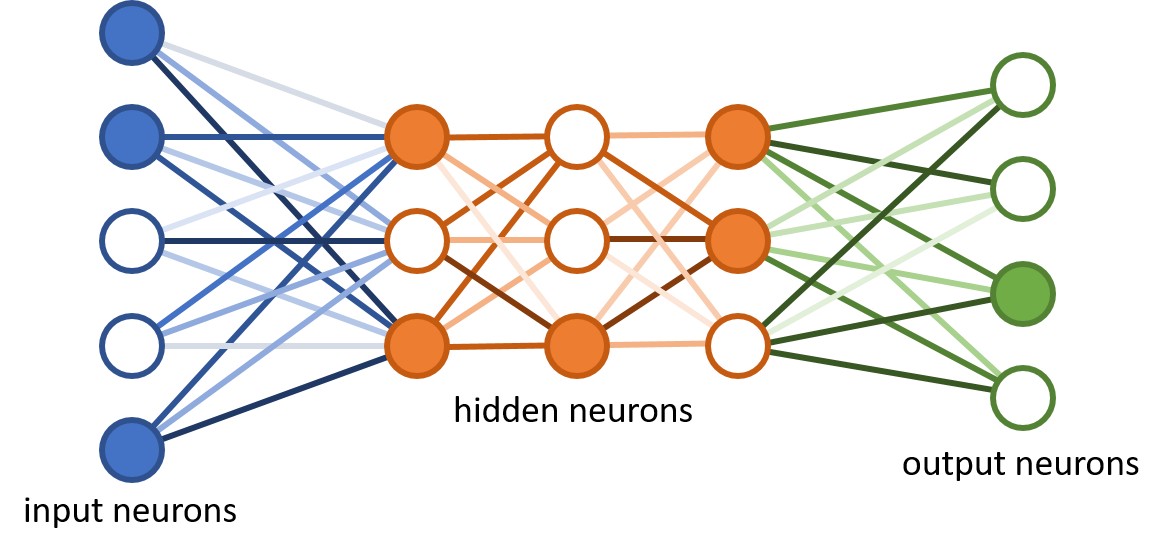
How neural networks learn
Unlike other algorithms, neural networks with their deepest learning do not have any chance of being programmed for the task. Faster, they have a need, like the developing brain of a baby, so that they need to find out the information. The learning strategies go through three methods
- Supervised learning: This learning strategy is the simplest, as there is a labeled dataset, which the computer goes through, and the algorithm gets modified until it can process the dataset to get the desired result.
- Unsupervised learning: This strategy gets used in cases where there is no labeled dataset available to learn from. The neural network analyzes the dataset, and then a cost function then tells the neural network how far off of target it was. The neural network then adjusts to increase the accuracy of the algorithm.
- Reinforced learning: In this algorithm, the neural network is reinforced for positive results, and punished for a negative result, forcing the neural network to learn over time.
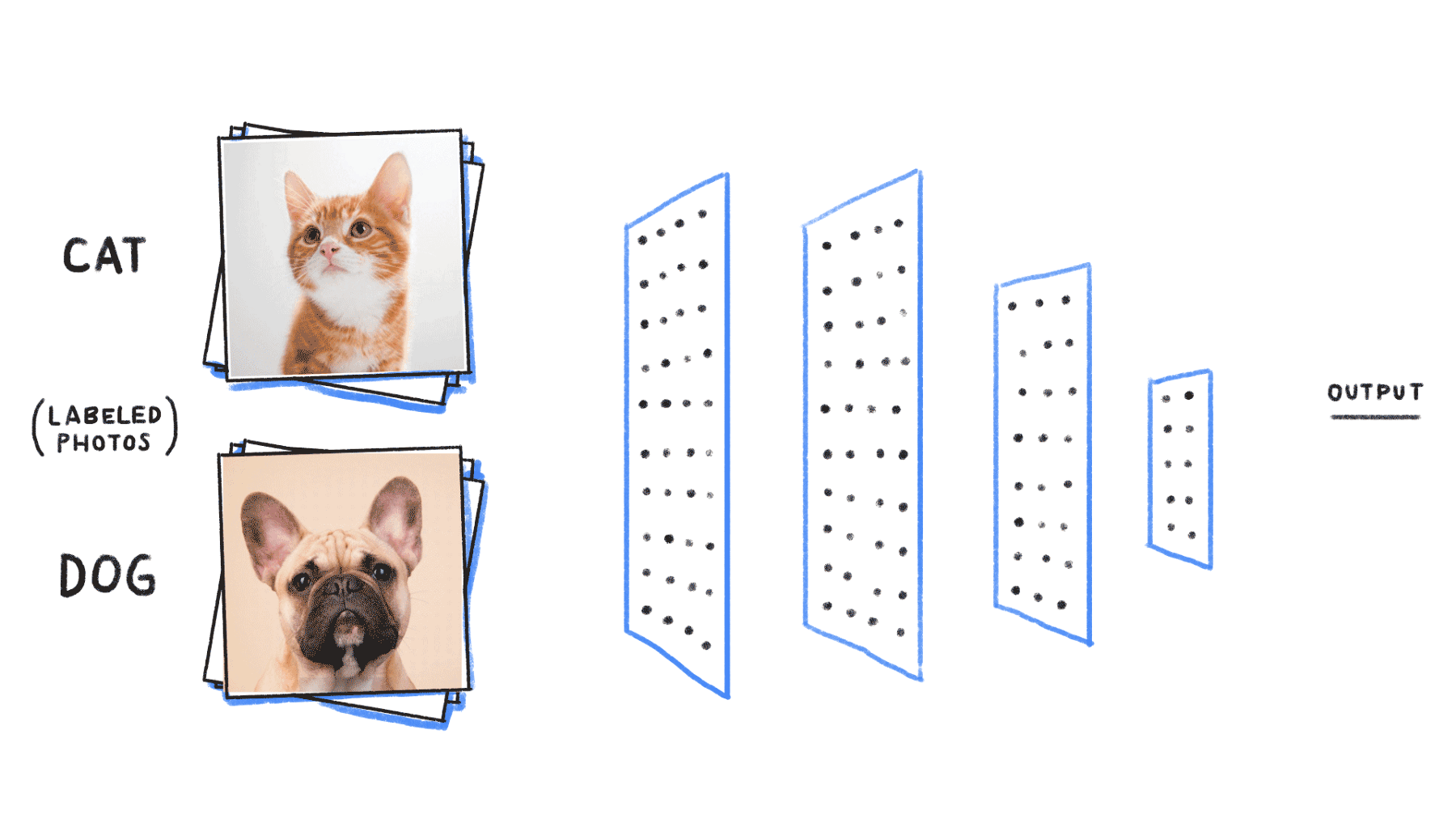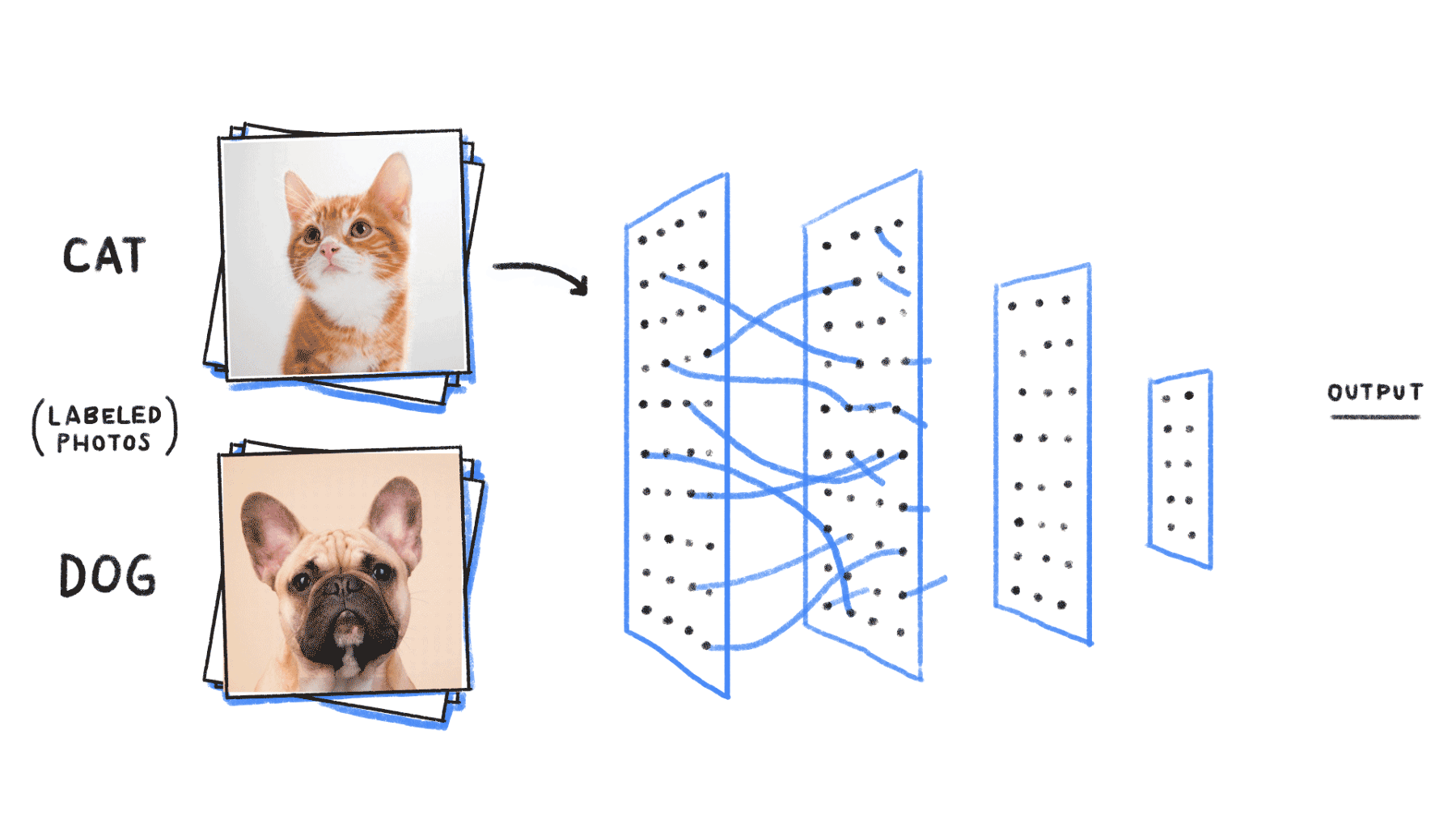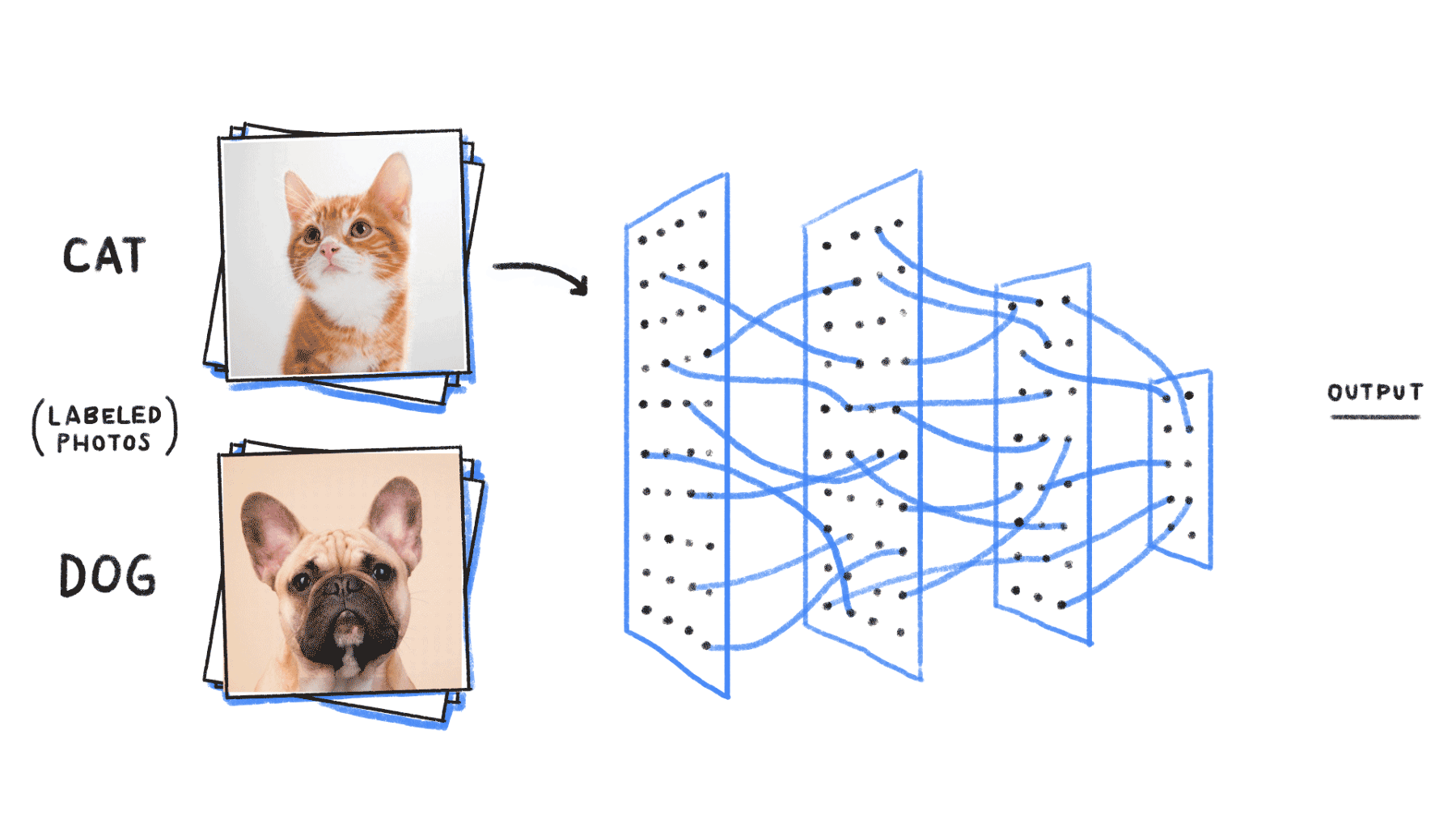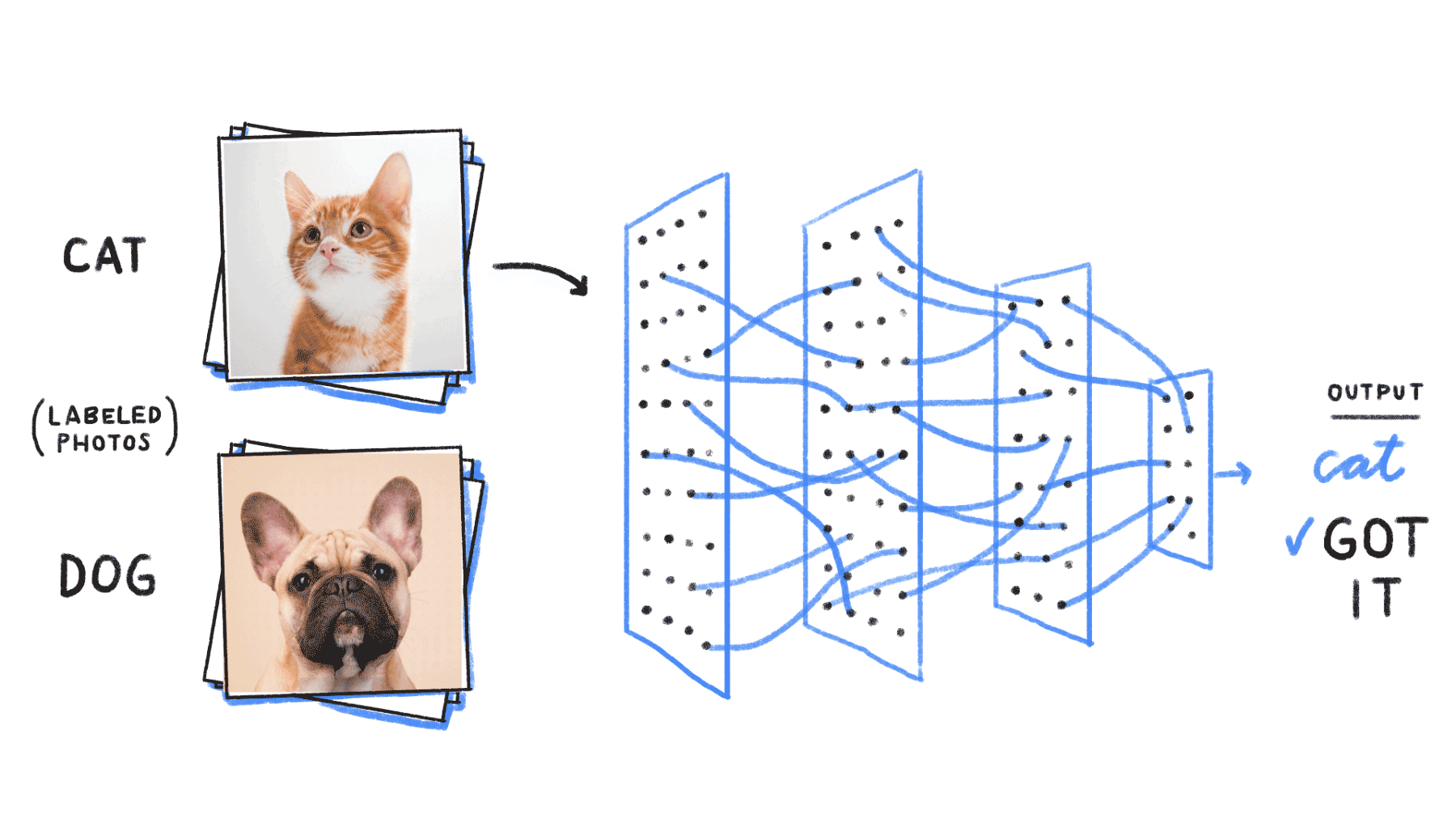
Application of Neural Networks
Neural networks are used, with applications for financial operations, enterprise planning, trading, business analytics, and product maintenance. Neural networks have also gained widespread adoption in business applications such as forecasting and marketing research solutions, fraud detection and risk assessment.
A neural network evaluates price data and unearths opportunities for making trade decisions based on data analysis. The networks can distinguish subtle nonlinear interdependencies and patterns other methods of technical analysis cannot. But, a 10 percent improvement in efficiency is all an investor can ask for from a neural network. There will always be data sets and task classes that a better analyzed by using before developed algorithms. It is not so much the algorithm that matters; it is the well-prepared input data on the targeted indicator that determines the level of success of a neural network.
Types of neural networks
There are different kinds of deep neural networks – and each has advantages and disadvantages, depending on the use. Examples include:
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) contain five types of layers: input, convolution, merge, connect and output. Any layer owns a certain target, for example, summation, inclusion or activation. Convolutional neural intrigues explained the classification of images and the detection of objects. However, CNN is still used in other areas, such as natural language processing and prediction.
- Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) apply consistent information, such as data with a time stamp from a sensor device or a pronounced instruction consisting of a sequence of definitions. Unlike conventional neural grids, all inputs to the recurrent neural network are not dependent on each other, and the output for each element depends on the calculations of its past elements. RNNs are used in forecasting and timeline applications, mood analysis and other text applications.
- Feedforward neural networks, in which each perceptron in one layer is connected to every perceptron from the next layer. Information is fed forward from one layer to the next in the forward direction only. There are no feedback loops.
- Autoencoder neural networks are used to create abstractions called encoders, created from a given set of inputs. Although like more classical neural networks, autoencoders seek to model the inputs themselves, and thus the method is considered unsupervised. The premise of autoencoders is to desensitize the irrelevant and sensitize the relevant. As layers are added, further abstractions are formulated at higher layers (layers closest to the point at which a decoder layer is introduced). These abstractions can then be used by linear or nonlinear classifiers.
Why are neural networks important?
Neural networks are also suited to help people solve complex problems in real-life situations. They can learn and model the relationships between inputs and outputs that are nonlinear and complex; make generalizations and inferences; reveal hidden relationships, patterns, and predictions; and model volatile data (such as financial time series data) and variances needed to predict rare events (such as fraud detection). As a result, neural networks can improve decision processes in areas such as:
- Credit card and Medicare fraud detection.
- Optimization of logistics for transportation networks.
- Character and voice recognition, also known as natural language processing.
- Medical and disease diagnosis.
- Targeted marketing.
- Financial predictions for stock prices, currency, options, futures, bankruptcy and bond ratings.
- Robotic control systems.
- Electrical load and energy demand forecasting.
- Process and quality control.
- Chemical compound identification.
- Ecosystem evaluation.
- Computer vision to interpret raw photos and videos (for example, in medical imaging and robotics and facial recognition).

Neural Networks & Artificial Intelligence
In some circles, neural networks are thought of as “brute force” AI, because they start with a blank slate and hammer their way through to an accurate model. They are effective but to some eyes inefficient in their approach to modeling, which can’t make assumptions about functional dependencies between output and input.
That said, gradient descent is not recombining every weight with every other to find the best match – its method of pathfinding shrinks the relevant weight space, and thus the number of updates and required computation, by many orders of size.
What is “Neural Network”的更多相关文章
- Recurrent Neural Network系列1--RNN(循环神经网络)概述
作者:zhbzz2007 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhbzz2007 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 本文翻译自 RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS T ...
- Neural Network Toolbox使用笔记1:数据拟合
http://blog.csdn.net/ljp1919/article/details/42556261 Neural Network Toolbox为各种复杂的非线性系统的建模提供多种函数和应用程 ...
- 《Neural Network and Deep Learning》_chapter4
<Neural Network and Deep Learning>_chapter4: A visual proof that neural nets can compute any f ...
- How to implement a neural network
神经网络的实践笔记 link: http://peterroelants.github.io/posts/neural_network_implementation_part01/ 1. 生成训练数据 ...
- CS224d assignment 1【Neural Network Basics】
refer to: 机器学习公开课笔记(5):神经网络(Neural Network) CS224d笔记3--神经网络 深度学习与自然语言处理(4)_斯坦福cs224d 大作业测验1与解答 CS224 ...
- XiangBai——【AAAI2017】TextBoxes_A Fast Text Detector with a Single Deep Neural Network
XiangBai--[AAAI2017]TextBoxes:A Fast Text Detector with a Single Deep Neural Network 目录 作者和相关链接 方法概括 ...
- 论文阅读(Weilin Huang——【TIP2016】Text-Attentional Convolutional Neural Network for Scene Text Detection)
Weilin Huang--[TIP2015]Text-Attentional Convolutional Neural Network for Scene Text Detection) 目录 作者 ...
- 论文阅读(Xiang Bai——【PAMI2017】An End-to-End Trainable Neural Network for Image-based Sequence Recognition and Its Application to Scene Text Recognition)
白翔的CRNN论文阅读 1. 论文题目 Xiang Bai--[PAMI2017]An End-to-End Trainable Neural Network for Image-based Seq ...
- (转)The Neural Network Zoo
转自:http://www.asimovinstitute.org/neural-network-zoo/ THE NEURAL NETWORK ZOO POSTED ON SEPTEMBER 14, ...
- (转)LSTM NEURAL NETWORK FOR TIME SERIES PREDICTION
LSTM NEURAL NETWORK FOR TIME SERIES PREDICTION Wed 21st Dec 2016 Neural Networks these days are th ...
随机推荐
- VS2017、VS2019没有Setup安装项目(Visual Studio Installer)_解决方案
前言: VS2010中有一个自带的安装部署项目,叫:Visual Studio Installer ,我们通常称为:setup项目,是一个用于自定义安装部署的项目方案.但是在VS2017,VS2019 ...
- spring framework体系结构及内部各模块jar之间的maven依赖关系
很多人都在用spring开发java项目,但是配置maven依赖的时候并不能明确要配置哪些spring的jar,经常是胡乱添加一堆,编译或运行报错就继续配置jar依赖,导致spring依赖混乱,甚至下 ...
- kubernetes 客户端KubeClient使用及常用api
KubeClient是kubernetes 的C#语言客户端简单易用,KubeClient是.NET Core(目标netstandard1.4)的可扩展Kubernetes API客户端, gith ...
- C# 字符串转byte数组
public static byte[] HexstringToByte(string InString) { string[] ByteStrings; ByteStrings = InString ...
- python爬虫–爬取煎蛋网妹子图片
前几天刚学了python网络编程,书里没什么实践项目,只好到网上找点东西做. 一直对爬虫很好奇,所以不妨从爬虫先入手吧. Python版本:3.6 这是我看的教程:Python - Jack -Cui ...
- 《白帽子讲Web安全》- 学习笔记
一.为何要了解Web安全 最近加入新公司后,公司的官网突然被Google标记为了不安全的诈骗网站,一时间我们信息技术部门成为了众矢之的,虽然老官网并不是我们开发的(因为开发老官网的前辈们全都跑路了). ...
- 前端笔记之JavaScript面向对象(三)初识ES6&underscore.js&EChart.js&设计模式&贪吃蛇开发
一.ES6语法 ES6中对数组新增了几个函数:map().filter().reduce() ES5新增的forEach(). 都是一些语法糖. 1.1 forEach()遍历数组 forEach() ...
- 强化学习(七)时序差分离线控制算法Q-Learning
在强化学习(六)时序差分在线控制算法SARSA中我们讨论了时序差分的在线控制算法SARSA,而另一类时序差分的离线控制算法还没有讨论,因此本文我们关注于时序差分离线控制算法,主要是经典的Q-Learn ...
- EF获取多个数据集以及MySQL分页数据查询优化
背景:MySQL分页查询语句为 ,10; 一般页面还会获取总条数,这时候还需要一条查询总条数语句 , 这样数据库需要执行两次查询操作.MySQL提供了SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS追踪总条数的 ...
- js获取url 中的值,并跳转相应页面
实现方法:一:获取URL带QUESTRING参数的JAVASCRIPT客户端解决方案,相当于asp的request.querystring,PHP的$_GET1.函数: <Script lang ...
