Synchronous and Asynchronous I/O [Windows]
There are two types of input/output (I/O) synchronization: synchronous I/O and asynchronous I/O. Asynchronous I/O is also referred to as overlapped I/O.
In synchronous file I/O, a thread starts an I/O operation and immediately enters a wait state until the I/O request has completed. A thread performing asynchronous file I/O sends an I/O request to the kernel by calling an appropriate function. If the request is accepted by the kernel, the calling thread continues processing another job until the kernel signals to the thread that the I/O operation is complete. It then interrupts its current job and processes the data from the I/O operation as necessary.
The two synchronization types are illustrated in the following figure.
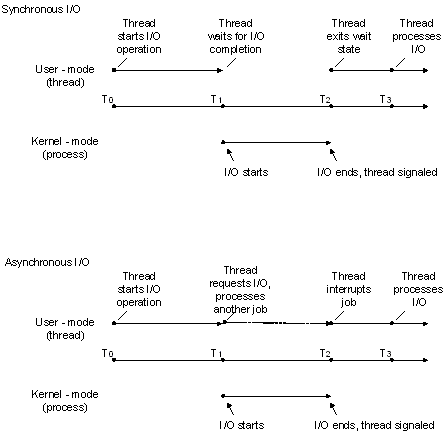
In situations where an I/O request is expected to take a large amount of time, such as a refresh or backup of a large database or a slow communications link, asynchronous I/O is generally a good way to optimize processing efficiency. However, for relatively fast I/O operations, the overhead of processing kernel I/O requests and kernel signals may make asynchronous I/O less beneficial, particularly if many fast I/O operations need to be made. In this case, synchronous I/O would be better. The mechanisms and implementation details of how to accomplish these tasks vary depending on the type of device handle that is used and the particular needs of the application. In other words, there are usually multiple ways to solve the problem.
Synchronous and Asynchronous I/O Considerations
If a file or device is opened for synchronous I/O (that is, FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED is not specified), subsequent calls to functions such as WriteFile can block execution of the calling thread until one of the following events occurs:
- The I/O operation completes (in this example, a data write).
- An I/O error occurs. (For example, the pipe is closed from the other end.)
- An error was made in the call itself (for example, one or more parameters are not valid).
- Another thread in the process calls the CancelSynchronousIo function using the blocked thread's thread handle, which terminates I/O for that thread, failing the I/O operation.
- The blocked thread is terminated by the system; for example, the process itself is terminated, or another thread calls the TerminateThread function using the blocked thread's handle. (This is generally considered a last resort and not good application design.)
In some cases, this delay may be unacceptable to the application's design and purpose, so application designers should consider using asynchronous I/O with appropriate thread synchronization objects such as I/O completion ports. For more information about thread synchronization, see About Synchronization.
A process opens a file for asynchronous I/O in its call to CreateFile by specifying the FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED flag in the dwFlagsAndAttributes parameter. If FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED is not specified, the file is opened for synchronous I/O. When the file has been opened for asynchronous I/O, a pointer to an OVERLAPPED structure is passed into the call to ReadFile and WriteFile. When performing synchronous I/O, this structure is not required in calls to ReadFile and WriteFile.
备注
If a file or device is opened for asynchronous I/O, subsequent calls to functions such as WriteFile using that handle generally return immediately but can also behave synchronously with respect to blocked execution. For more information, see https://support.microsoft.com/kb/156932.
Although CreateFile is the most common function to use for opening files, disk volumes, anonymous pipes, and other similar devices, I/O operations can also be performed using a handle typecast from other system objects such as a socket created by the socket or accept functions.
Handles to directory objects are obtained by calling the CreateFile function with the FILE_FLAG_BACKUP_SEMANTICS attribute. Directory handles are almost never used—backup applications are one of the few applications that will typically use them.
After opening the file object for asynchronous I/O, an OVERLAPPED structure must be properly created, initialized, and passed into each call to functions such as ReadFile and WriteFile. Keep the following in mind when using the OVERLAPPED structure in asynchronous read and write operations:
- Do not deallocate or modify the OVERLAPPED structure or the data buffer until all asynchronous I/O operations to the file object have been completed.
- If you declare your pointer to the OVERLAPPED structure as a local variable, do not exit the local function until all asynchronous I/O operations to the file object have been completed. If the local function is exited prematurely, the OVERLAPPED structure will go out of scope and it will be inaccessible to any ReadFile or WriteFile functions it encounters outside of that function.
You can also create an event and put the handle in the OVERLAPPED structure; the wait functions can then be used to wait for the I/O operation to complete by waiting on the event handle.
As previously stated, when working with an asynchronous handle, applications should use care when making determinations about when to free resources associated with a specified I/O operation on that handle. If the handle is deallocated prematurely, ReadFile or WriteFile may incorrectly report that the I/O operation is complete. Further, the WriteFile function will sometimes return TRUE with a GetLastError value of ERROR_SUCCESS, even though it is using an asynchronous handle (which can also return FALSE with ERROR_IO_PENDING). Programmers accustomed to synchronous I/O design will usually release data buffer resources at this point because TRUE and ERROR_SUCCESS signify the operation is complete. However, if I/O completion ports are being used with this asynchronous handle, a completion packet will also be sent even though the I/O operation completed immediately. In other words, if the application frees resources after WriteFile returns TRUE with ERROR_SUCCESS in addition to in the I/O completion port routine, it will have a double-free error condition. In this example, the recommendation would be to allow the completion port routine to be solely responsible for all freeing operations for such resources.
The system does not maintain the file pointer on asynchronous handles to files and devices that support file pointers (that is, seeking devices), therefore the file position must be passed to the read and write functions in the related offset data members of the OVERLAPPED structure. For more information, see WriteFile and ReadFile.
File pointer position for a synchronous handle is maintained by the system as data is read or written and can also be updated using the SetFilePointer or SetFilePointerEx function.
An application can also wait on the file handle to synchronize the completion of an I/O operation, but doing so requires extreme caution. Each time an I/O operation is started, the operating system sets the file handle to the nonsignaled state. Each time an I/O operation is completed, the operating system sets the file handle to the signaled state. Therefore, if an application starts two I/O operations and waits on the file handle, there is no way to determine which operation is finished when the handle is set to the signaled state. If an application must perform multiple asynchronous I/O operations on a single file, it should wait on the event handle in the specific OVERLAPPED structure for each I/O operation, rather than on the common file handle.
To cancel all pending asynchronous I/O operations, use either:
- CancelIo—this function only cancels operations issued by the calling thread for the specified file handle.
- CancelIoEx—this function cancels all operations issued by the threads for the specified file handle.
Use CancelSynchronousIo to cancel pending synchronous I/O operations.
The ReadFileEx and WriteFileEx functions enable an application to specify a routine to execute (see FileIOCompletionRoutine) when the asynchronous I/O request is completed.
Synchronous and Asynchronous I/O [Windows]的更多相关文章
- Java Messages Synchronous and Asynchronous
//The Consumer Class Consumes Messages in a Synchronous Manner public class Consumer { public static ...
- 操作系统OS - 阻塞(Blocking)非阻塞(Non-Blocking)与同步(Synchronous)异步(Asynchronous)
参考: http://blog.jobbole.com/103290/ https://www.zhihu.com/question/19732473/answer/23434554 http://b ...
- Asynchronous Disk I/O Appears as Synchronous on Windows
Summary File I/O on Microsoft Windows can be synchronous or asynchronous. The default behavior for I ...
- Should I expose asynchronous wrappers for synchronous methods?
Lately I've received several questions along the lines of the following, which I typically summarize ...
- 磁盘异步I / O在Windows上显示为同步
概要 Microsoft Windows上的文件I / O可以是同步或异步的.I / O的默认行为是同步的,其中调用I / O函数并在I / O完成时返回.异步I / O允许I / O函数立即将执行返 ...
- C#的多线程——使用async和await来完成异步编程(Asynchronous Programming with async and await)
https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/mt674882.aspx 侵删 更新于:2015年6月20日 欲获得最新的Visual Studio 2017 RC ...
- Testing for the End of a File (Windows 的异步 IO)
The ReadFile function checks for the end-of-file condition (EOF) differently for synchronous and asy ...
- Async/Await - Best Practices in Asynchronous Programming
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/jj991977.aspx Figure 1 Summary of Asynchronous Programming ...
- Async/Await - Best Practices in Asynchronous Programming z
These days there’s a wealth of information about the new async and await support in the Microsoft .N ...
随机推荐
- 美国NOAA/AVHRR遥感数据
1.美国国家海洋和大气管理局(National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration,NOAA) 美国国家海洋和大气管理局隶属于美国商业部下属的科技部门,主要关 ...
- Unity引擎入门——制作第一个2D游戏(2)角色移动与动画
在上一节的内容里,我们已经创建出了一个主角,也搭建了一个简单的场景. 传送门:https://www.cnblogs.com/zny0222/p/12653088.html 既然有了主角,要怎样才能让 ...
- flink 一分钟入门篇
1. 业务说:“…… bulabula……,这个需求很简单,怎么实现我不管?” 面对霸气侧漏的业务需求,由于没有大数据知识储备,咱心里没底,咱也不敢问,咱也不敢说,只能静下来默默储备.默默寻觅解决方案 ...
- Java数组模拟队列
队列 先进先出 什么意思呢? 我的理解:队列就是一个数组(不包含链表),然后我们给它施加一个存数据和取数据的规则 当只允许从一端存数据,从另一端取数据的数组,就是队列,我们要做的就是给这个数组施加我们 ...
- Kubernetes Pod钩子
目录 1.Pod容器钩子最终目的 2.何为Pod容器钩子 3.基于PostStart演示 4.基于PreStop演示 5.优雅停止Java应用 1.Pod容器钩子最终目的 之前在生产环境中使用dubb ...
- Genetic CNN: 经典NAS算法,遗传算法的标准套用 | ICCV 2017
论文将标准的遗传算法应用到神经网络结构搜索中,首先对网络进行编码表示,然后进行遗传操作,整体方法十分简洁,搜索空间设计的十分简单,基本相当于只搜索节点间的连接方式,但是效果还是挺不错的,十分值得学习 ...
- Git 常见问题 冲突原因分析及解决方案
仅结合本人使用场景,方法可能不是最优的 1. 忽略本地修改,强制拉取远程到本地 主要是项目中的文档目录,看的时候可能多了些标注,现在远程文档更新,本地的版本已无用,可以强拉 git fetch --a ...
- SpringBoot事件监听机制源码分析(上) SpringBoot源码(九)
SpringBoot中文注释项目Github地址: https://github.com/yuanmabiji/spring-boot-2.1.0.RELEASE 本篇接 SpringApplicat ...
- python教程:使用 async 和 await 协程进行并发编程
python 一直在进行并发编程的优化, 比较熟知的是使用 thread 模块多线程和 multiprocessing 多进程,后来慢慢引入基于 yield 关键字的协程. 而近几个版本,python ...
- 如何使用python在短时间内寻找完数
完数:完全数(Perfect number),又称完美数或完备数,是一些特殊的自然数.它所有的真因子(即除了自身以外的约数)的和(即因子函数),恰好等于它本身.如果一个数恰好等于它的因子之和,则称该数 ...
