scikit-learn 应用
首先是sklearn的官网:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/
在官网网址上可以看到很多的demo,下边这张是一张非常有用的流程图,在这个流程图中,可以根据数据集的特征,选择合适的方法。

2.sklearn使用的小例子

import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier iris=datasets.load_iris()
iris_X=iris.data
iris_y=iris.target print(iris_X[:2,:]) #输出数据的前2行,
print(iris_y) X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(iris_X,iris_y,test_size=0.3) #把数据集分为训练集和测试集两个部分一部分是训练集,一部分是测试集,其中测试集占了30%
print(y_train) knn=KNeighborsClassifier()
knn.fit(X_train,y_train)
print(knn.predict(X_test))
print(y_test)

3.sklearn数据集
在上边例子中,直接使用了sklearn的数据集,在这个包中还有很多其他的数据集,数据集的网址:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/classes.html#module-sklearn.datasets不仅可以使用数据集中的数据,还可以生成虚拟的数据,
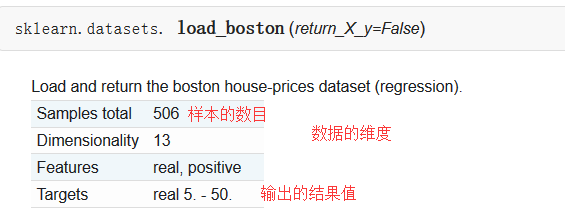
sklearn中自带的数据集,以房屋数据集为例:
sklearn可以生成的数据集,回归模型中使用的数据集为例:

| Parameters: |
n_samples : int, optional (default=100):The number of samples. n_features : int, optional (default=100):The number of features. n_informative : int, optional (default=10):The number of informative features, i.e., the number of features used to build the linear model used to generate the output. n_targets : int, optional (default=1):The number of regression targets, i.e., the dimension of the y output vector associated with a sample. By default, the output is a scalar. bias : float, optional (default=0.0):The bias term in the underlying linear model. effective_rank : int or None, optional (default=None) if not None:The approximate number of singular vectors required to explain most of the input data by linear combinations. Using this kind of singular spectrum in the input allows the generator to reproduce the correlations often observed in practice. if None:The input set is well conditioned, centered and gaussian with unit variance. tail_strength : float between 0.0 and 1.0, optional (default=0.5):The relative importance of the fat noisy tail of the singular values profile if effective_rank is not None. noise : float, optional (default=0.0):The standard deviation of the gaussian noise applied to the output. shuffle : boolean, optional (default=True):Shuffle the samples and the features. coef : boolean, optional (default=False):If True, the coefficients of the underlying linear model are returned. random_state : int, RandomState instance or None, optional (default=None):If int, random_state is the seed used by the random number generator; If RandomState instance, random_state is the random number generator; If None, the random number generator is the RandomState instance used by np.random. |
|---|---|
| Returns: |
X : array of shape [n_samples, n_features]:The input samples. y : array of shape [n_samples] or [n_samples, n_targets]:The output values. coef : array of shape [n_features] or [n_features, n_targets], optional:The coefficient of the underlying linear model. It is returned only if coef is True. |

from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #使用以后的数据集进行线性回归
loaded_data=datasets.load_boston()
data_X=loaded_data.data
data_y=loaded_data.target model=LinearRegression()
model.fit(data_X,data_y) print(model.predict(data_X[:4,:]))
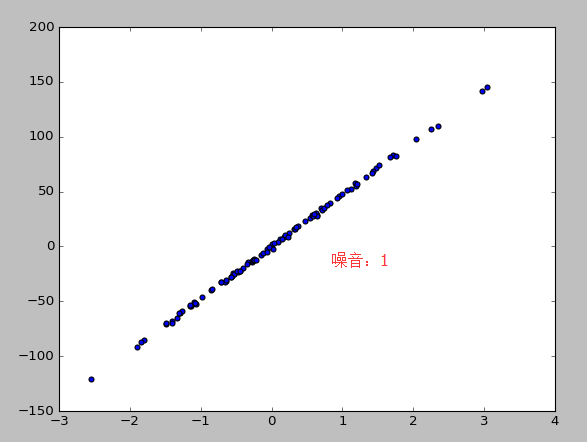
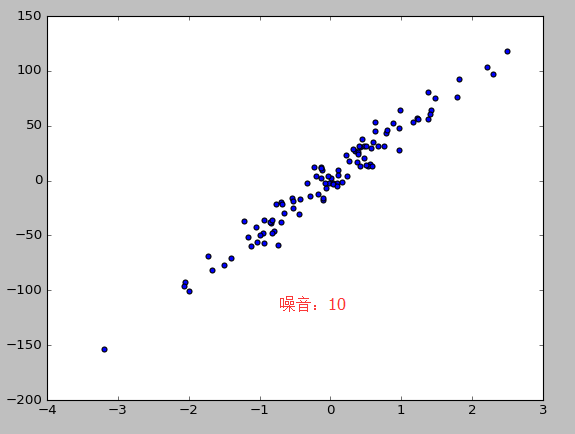
print(data_y[:4]) #使用生成线性回归的数据集,最后的数据集结果用散点图表示
X,y=datasets.make_regression(n_samples=100,n_features=1,n_targets=1,noise=10) #n_samples表示样本数目,n_features特征的数目 n_tragets noise噪音
plt.scatter(X,y)
plt.show()

4。模型的参数
sklearn 的 model 属性和功能都是高度统一的. 你可以运用到这些属性查看 model 的参数和值等等.

from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #使用以后的数据集进行线性回归
loaded_data=datasets.load_boston()
data_X=loaded_data.data
data_y=loaded_data.target model=LinearRegression()
model.fit(data_X,data_y) print(model.predict(data_X[:4,:]))
print(data_y[:4]) #参数
print(model.coef_) #如果y=0.1x+0.3 则此行输出的结果为0.1
print(model.intercept_) #此行输出的结果为0.3
print(model.get_params()) #模型定义时定义的参数,如果没有定义则返回默认值
print(model.score(data_X,data_y)) #给训练模型打分,注意用在LinearR中使用R^2 conefficient of determination打分

输出的结果:

[ 30.00821269 25.0298606 30.5702317 28.60814055]
[ 24. 21.6 34.7 33.4]
[ -1.07170557e-01 4.63952195e-02 2.08602395e-02 2.68856140e+00
-1.77957587e+01 3.80475246e+00 7.51061703e-04 -1.47575880e+00
3.05655038e-01 -1.23293463e-02 -9.53463555e-01 9.39251272e-03
-5.25466633e-01]
36.4911032804
{'fit_intercept': True, 'normalize': False, 'n_jobs': 1, 'copy_X': True}
0.740607742865

5.标准化:normalization
normalization 在数据跨度不一的情况下对机器学习有很重要的作用.特别是各种数据属性还会互相影响的情况之下. Scikit-learn 中标准化的语句是 preprocessing.scale() . scale 以后, model 就更能从标准化数据中学到东西.

from sklearn import preprocessing #进行标准化数据时,需要引入个包
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_classification
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt X,y=make_classification(n_samples=300,n_features=2,n_redundant=0,n_informative=2,random_state=22,n_clusters_per_class=1,scale=100) #X=preprocessing.minmax_scale(X,feature_range=(-1,1))
X=preprocessing.scale(X) #0.966666666667 没有 0.477777777778
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.3)
clf=SVC()
clf.fit(X_train,y_train)
print(clf.score(X_test,y_test)) plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y)
plt.show() a=np.array([[10,2.7,3.6],
[-100,5,-2],
[120,20,40]],dtype=np.float64) #每一列代表一个属性
print(a) #标准化之前a
print(preprocessing.scale(a)) #标准化之后的a

6.交叉验证 cross validation(1)
sklearn 中的 cross validation 交叉验证 对于我们选择正确的 model 和model 的参数是非常有帮助的. 有了他的帮助, 我们能直观的看出不同 model 或者参数对结构准确度的影响.

from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier iris=load_iris()
iris_X=iris.data
iris_y=iris.target #直接训练
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(iris_X,iris_y,random_state=4) #把数据集分为训练集和测试集两个部分一部分是训练集,一部分是测试集,其中测试集占了30%
knn=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn.fit(X_train,y_train)
print(knn.score(X_test,y_test)) #0.973684210526 #交叉验证
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score
knn=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
score=cross_val_score(knn,iris_X,iris_y,cv=5,scoring='accuracy') #c分成几组 scoring是准确度
print(score)
print(score.mean()) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
k_range=range(1,31)
k_score=[]
for k in k_range:
knn=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=k)
#score=cross_val_score(knn,iris_X,iris_y,cv=10,scoring='accuracy')#for classification 精度
loss=-cross_val_score(knn,iris_X,iris_y,cv=10,scoring='mean_squared_error') #for regression 损失函数
#k_score.append(score.mean())
k_score.append(loss.mean())
plt.plot(k_range,k_score)
plt.xlabel("Value of K for KNN")
plt.ylabel("Cross-validates Accuracy")
plt.show()

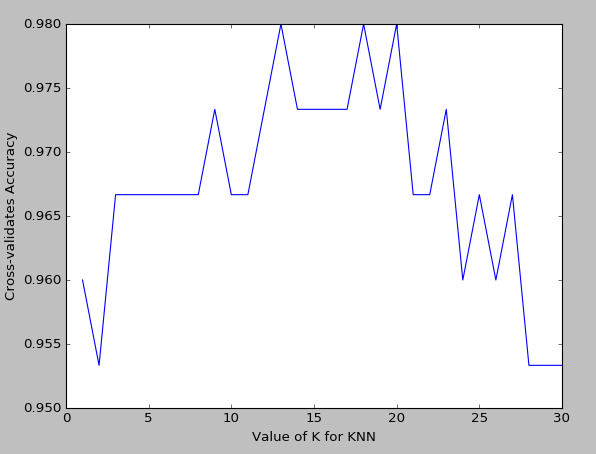
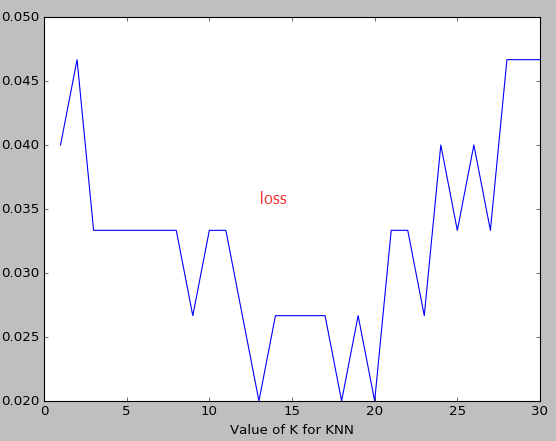
k越大越容易underfitting而不是overfitting
如果想要对不同的机器学习模型来计算,可能需要把knn的值换一下
7.交叉验证 cross validation(2)
sklearn.learning_curve 中的 learning curve 可以很直观的看出我们的 model 学习的进度,对比发现有没有 overfitting 的问题.然后我们可以对我们的 model 进行调整,克服 overfitting 的问题.

from sklearn.learning_curve import learning_curve #可视化学习的整个过程
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np digits=load_digits()
X=digits.data
y=digits.target
train_sizes,train_loss,test_loss=learning_curve(
SVC(gamma=0.1),X,y,cv=10,scoring="mean_squared_error",
train_sizes=[0.1,0.25,0.5,0.75,1]) #记录的点是学习过程中的10%,25%等等的点
train_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(train_loss,axis=1)
test_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(test_loss,axis=1) plt.plot(train_sizes,train_loss_mean,"o-",color="r",label="Training")
plt.plot(train_sizes,test_loss_mean,"o-",color="g",label="Cross-validation") plt.xlabel("Training examples")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()

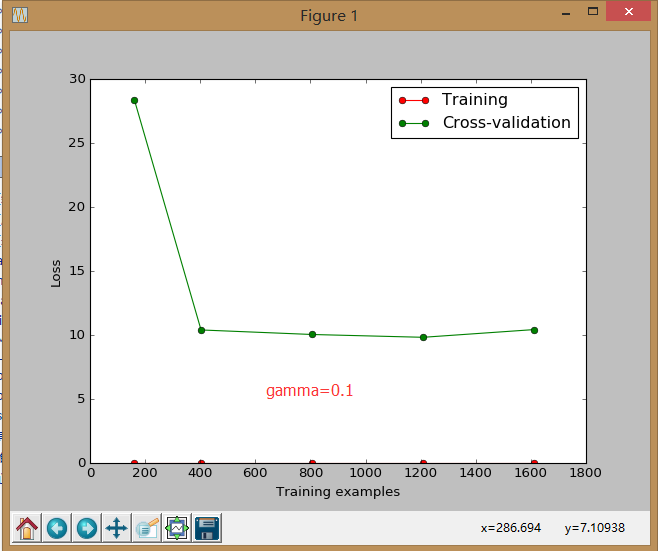
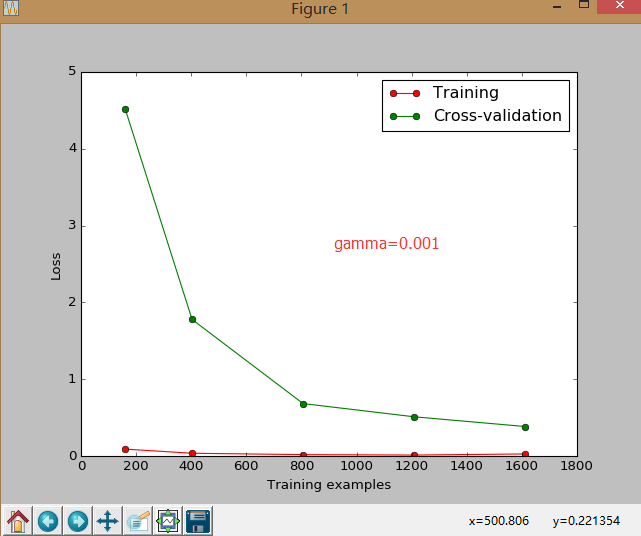
8.交叉验证 cross validation(3)
连续三节的 cross validation让我们知道在机器学习中 validation 是有多么的重要, 这一次的 sklearn 中我们用到了 sklearn.learning_curve 当中的另外一种, 叫做 validation_curve, 用这一种 curve 我们就能更加直观看出改变 model 中的参数的时候有没有 overfitting 的问题了.这也是可以让我们更好的选择参数的方法.

from sklearn.learning_curve import validation_curve #可视化学习的整个过程
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np digits=load_digits()
X=digits.data
y=digits.target
gamma_range=np.logspace(-6,-2.3,5)#从-6到-2.3取5个点
train_loss,test_loss=validation_curve(
SVC(),X,y,param_name="gamma",param_range=gamma_range,cv=10,scoring="mean_squared_error")
train_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(train_loss,axis=1)
test_loss_mean= (-1)*np.mean(test_loss,axis=1) plt.plot(gamma_range,train_loss_mean,"o-",color="r",label="Training")
plt.plot(gamma_range,test_loss_mean,"o-",color="g",label="Cross-validation") plt.xlabel("gamma")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()

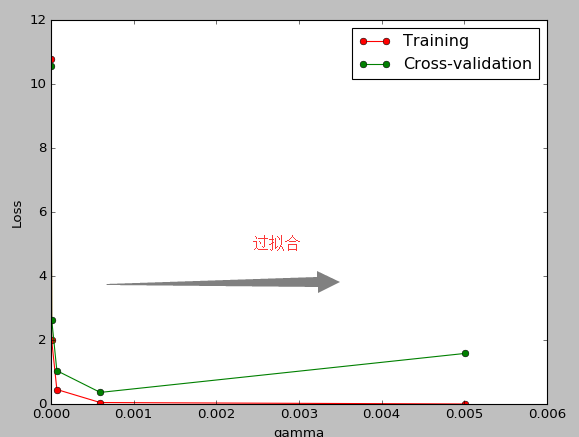
9,存储模型:
我们练习好了一个 model 以后总需要保存和再次预测, 所以保存和读取我们的 sklearn model 也是同样重要的一步.本文采用了两种方法来存储

from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets clf=svm.SVC()
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X,y=iris.data,iris.target
clf.fit(X,y) #method1:pickle
import pickle
#save
with open('save/clf.pickle','wb')as f:
pickle.dump(clf,f) #restore
with open('save/clf.pickle','rb') as f:
clf=pickle.load(f)
print(clf.predict(X[0:1])) #method2:joblib
from sklearn.externals import joblib
#save
joblib.dump(clf,'save/clf.pkl')
clf3=joblib.load('save/clf.pkl')
print(clf3.predict(X[0:1]))

youtube学习 :
周莫烦:https://www.youtube.com/user/MorvanZhou
个人主页:https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/
源码:https://github.com/MorvanZhou
scikit-learn 应用的更多相关文章
- scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类 (python代码)
scikit learn 模块 调参 pipeline+girdsearch 数据举例:文档分类数据集 fetch_20newsgroups #-*- coding: UTF-8 -*- import ...
- (原创)(三)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的线性回归模型初探
一.Scikit Learn中使用estimator三部曲 1. 构造estimator 2. 训练模型:fit 3. 利用模型进行预测:predict 二.模型评价 模型训练好后,度量模型拟合效果的 ...
- (原创)(四)机器学习笔记之Scikit Learn的Logistic回归初探
目录 5.3 使用LogisticRegressionCV进行正则化的 Logistic Regression 参数调优 一.Scikit Learn中有关logistics回归函数的介绍 1. 交叉 ...
- Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习
转自:http://my.oschina.net/u/175377/blog/84420#OSC_h2_23 Scikit Learn: 在python中机器学习 Warning 警告:有些没能理解的 ...
- Scikit Learn
Scikit Learn Scikit-Learn简称sklearn,基于 Python 语言的,简单高效的数据挖掘和数据分析工具,建立在 NumPy,SciPy 和 matplotlib 上.
- Linear Regression with Scikit Learn
Before you read This is a demo or practice about how to use Simple-Linear-Regression in scikit-lear ...
- 如何使用scikit—learn处理文本数据
答案在这里:http://www.tuicool.com/articles/U3uiiu http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/feature_extracti ...
- Query意图分析:记一次完整的机器学习过程(scikit learn library学习笔记)
所谓学习问题,是指观察由n个样本组成的集合,并根据这些数据来预测未知数据的性质. 学习任务(一个二分类问题): 区分一个普通的互联网检索Query是否具有某个垂直领域的意图.假设现在有一个O2O领域的 ...
- 机器学习框架Scikit Learn的学习
一 安装 安装pip 代码如下:# wget "https://pypi.python.org/packages/source/p/pip/pip-1.5.4.tar.gz#md5=83 ...
- Python第三方库(模块)"scikit learn"以及其他库的安装
scikit-learn是一个用于机器学习的 Python 模块. 其主页:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/. GitHub地址: https://github.com/ ...
随机推荐
- Nginx拓展功能合集
一:NGINX跨域解决方式 #是否允许请求带有验证信息 add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials true; #允许跨域访问的域名,可以是一个域的列表,也 ...
- 【Shiro】一、Apache Shiro简介
一.Apache Shiro简介 1.简介 一个安全性框架 特点:功能丰富.使用简单.运行独立 核心功能: Authentication(认证):你是谁? Authorization(授权):谁能干什 ...
- (转)Linux环境进程间通信----系统 V 消息队列列
转:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-ipc/part3/ 消息队列(也叫做报文队列)能够克服早期unix通信机制的一些缺点.作为早期unix通 ...
- TI低功耗蓝牙(BLE)介绍【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/ooakk/article/details/7302425 TI低功耗蓝牙(BLE)介绍 本文档翻译和修改自参考资料:CC2540Bluetooth L ...
- Java学习之集合(LinkedList链表集合)
一.什么是链表集合,通过图形来看,比如33只知道它下一个是55 如果:现在要删除33的话,就是把55赋值给45,这样看它操作集合速度会非常快. 二.LinkedList特有方法 1.添加 addFir ...
- arttemplate02
1.后台传来的数据 { "code": 200, "checkRecords": [ { "id": "402881e75cc80 ...
- 17、通过maven生成测试报告
目录如下: 通过Maven 生成报告 进入testngTest根目录,运行mvn test 命令 进入 testngTest\target\surefire-reports 路径查看测试报告
- laydate box-sizingCSS就会变形
*{-webkit-box-sizing:border-box;-moz-box-sizing:border-box;/* box-sizing:border-box; */} 解决:在/laydat ...
- vue-router 使用二级路由去实现子组件的显示和隐藏
在需求中有一个这样的情况:一个组件在主组件和另外的组件中引用,且点击主组件和这个组件分别有相应得切换事件. 一开始的时候我是没有划分组件,把它们放到主组件内,这样便于切换,但是主主件内有独立的部分需要 ...
- Tomcat Architect
Tomcat Architect Hierarchy of nested tag representing different components in server.xml. 1 <Serv ...
