用一维数组实现栈(C++编程思想 p120)
1 实现思路
向栈中插入4个元素后的状态
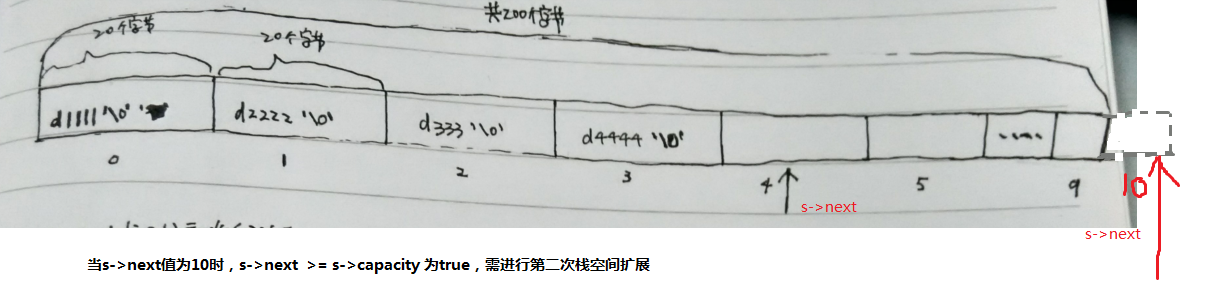
执行过程分析:

2 代码实现
clib.h 接口定义
typedef struct CStashTag
{
int ele_size; //栈中每个元素的占用的字节数
int capacity; //栈的容量,栈当前(不扩展)可容纳的元素的个数
int next; //相当于栈指针(标记下一个空位索引),栈中当前元素的个数
unsigned char* storage; //栈存储空间字符指针,动态分配的字节数组
} CStash; void initalize(CStash* s, int size);
void cleanup(CStash* s);
int add(CStash* s, const void* element);
void* fetch(CStash* s, int index);
int count(CStash* s);
void inflate(CStash* s, int increase = );
2 Clib.cpp 函数实现
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include "clib.h" using namespace std; void initalize(CStash* s, int sz)
{
s->ele_size = sz;
s->capacity = ;
s->next = ;
s->storage = ;
} int add(CStash* s, const void* element)
{
if (s->next >= s->capacity)
{
inflate(s);
}
int startBytes = s->next * s->ele_size;
unsigned char* e = (unsigned char*)element; for (int i=; i<s->ele_size; i++)
s->storage[startBytes + i] = e[i];
s->next++; return s->next - ;
} //取出索引index处的栈元素
void* fetch(CStash* s, int index)
{
assert( <= index);
if (index >= s->next)
{
return ;
}
return &(s->storage[index * s->ele_size]);
} //返回栈中元素的个数
int count(CStash* s)
{
return s->next;
} //扩展栈空间,增加increase个元素空间
void inflate(CStash* s, int increase)
{
printf("inflate increase %d\n", increase); assert(increase > ); //原栈长 + 增加的栈元素个数
int newCapacity = s->capacity + increase;
int newBytes = newCapacity * s->ele_size; //新的栈空间字节数
int oldBytes = s->capacity * s->ele_size; //旧的栈空间字节数 unsigned char* b = new unsigned char[newBytes]; //在堆上分配新的栈空间 if (oldBytes)
{
//拷贝旧的栈空间的内容到新的栈空间,并释放旧的栈空间
//把旧内存块中的数据拷贝到新分配的内存块
for (int i=; i<oldBytes; i++)
b[i] = s->storage[i];
delete [] (s->storage); //释放旧的内存块
} s->storage = b; //使栈存储空间字符指针s->storage指向新分配的内存块
s->capacity = newCapacity; //更新栈的容量
} //清理栈存储空间字符指针
void cleanup(CStash* s)
{
if (s->storage != )
{
cout<<"freeing storage"<<endl;
delete []s->storage;
}
} int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{ CStash stash; char str1[] = "d1111";
char str2[] = "d2222";
char str3[] = "d3333";
char str4[] = "d4444"; initalize(&stash, ); add(&stash, str1);
add(&stash, str2);
add(&stash, str3);
add(&stash, str4); unsigned char* result = (unsigned char*)fetch(&stash, );
printf("fetch result %s\n", result);
cleanup(&stash); return ;
}; 输出:
inflate increase 10
fetch result d3333
freeing storage
向栈中存放int型数据测试:
void intTest()
{
CStash intStash; initalize(&intStash, sizeof(int)); //栈中存放int型数据,所以栈元素占用int--4个字节 int i;
for (i=; i<; i++)
add(&intStash, &i); for (i=; i<count(&intStash); i++)
cout<< "fetch(&intStash, " << i << ") = " << *(int *) fetch(&intStash, i) <<endl;
cleanup(&intStash);
} 输出:
inflate increase 10
inflate increase 10
fetch(&intStash, 0) = 0
fetch(&intStash, 1) = 1
fetch(&intStash, 2) = 2
fetch(&intStash, 3) = 3
fetch(&intStash, 4) = 4
fetch(&intStash, 5) = 5
fetch(&intStash, 6) = 6
fetch(&intStash, 7) = 7
fetch(&intStash, 8) = 8
fetch(&intStash, 9) = 9
fetch(&intStash, 10) = 10
fetch(&intStash, 11) = 11
fetch(&intStash, 12) = 12
fetch(&intStash, 13) = 13
fetch(&intStash, 14) = 14
fetch(&intStash, 15) = 15
fetch(&intStash, 16) = 16
fetch(&intStash, 17) = 17
fetch(&intStash, 18) = 18
fetch(&intStash, 19) = 19
freeing storage
向栈中存放字符串(字符数组指针)测试:
void stringTest()
{
CStash stringStash; ifstream in; const int bufsize = ;
initalize(&stringStash, sizeof(char) * bufsize);
in.open("clib.h");
assert(in); string line;
while (getline(in, line))
{
add(&stringStash, line.c_str());
} char *cp;
int i = ;
while ((cp = (char *) fetch(&stringStash, i++)) != )
{
cout<< "fetch(&stringStash, " << i << ") = " << cp << endl;
} cleanup(&stringStash);
} 输出:
inflate increase 10
inflate increase 10
fetch(&stringStash, 1) = typedef struct CStashTag
fetch(&stringStash, 2) = {
fetch(&stringStash, 3) = int ele_size; //栈中每个元素的占用的字节数
fetch(&stringStash, 4) = int capacity; //栈的容量,栈当前(不扩展)可容纳的元素的个数
fetch(&stringStash, 5) = int next; //相当于栈指针(标记下一个空位索引),栈中当前元素的个数
fetch(&stringStash, 6) = unsigned char* storage; //栈存储空间字符指针,动态分配的字节数组
fetch(&stringStash, 7) = } CStash;
fetch(&stringStash, 8) =
fetch(&stringStash, 9) = void initalize(CStash* s, int size);
fetch(&stringStash, 10) = void cleanup(CStash* s);
fetch(&stringStash, 11) = int add(CStash* s, const void* element);
fetch(&stringStash, 12) = void* fetch(CStash* s, int index);
fetch(&stringStash, 13) = int count(CStash* s);
fetch(&stringStash, 14) = void inflate(CStash* s, int increase = 10);
freeing storage
附C++实现:
1)Stash.h头文件
#ifndef STASH_H_INCLUDED
#define STASH_H_INCLUDED class Stash
{
int ele_size; //栈中每个元素的占用的字节数
int capacity; //栈的容量,栈当前(不扩展)可容纳的元素的个数
int next; //相当于栈指针(标记下一个空位索引),栈中当前元素的个数
unsigned char* storage; //栈存储空间字符指针,动态分配的字节数组
void inflate(int increase = ); public:
void initalize(int sz);
int add(const void* element);
void* fetch(int index);
int count();
void cleanup();
}; #endif // STASH_H_INCLUDED
2)Stash.cpp实现文件
#include "Stash.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert> using namespace std; void Stash::initalize(int sz)
{
ele_size = sz;
capacity = ;
next = ;
storage = ;
} int Stash::add(const void *element)
{
if (next >= capacity)
{
inflate();
} int startBytes = next * ele_size;
unsigned char *e = (unsigned char *) element; for (int i=; i<ele_size; i++)
{
storage[startBytes + i] = e[i];
}
next++; return next-;
} void Stash::inflate(int increase)
{
cout << "inflate increase: " << increase << endl; assert(increase > ); int newCapacity = capacity + increase;
int newBytes = newCapacity * ele_size;
int oldBytes = capacity * ele_size; unsigned char *b = new unsigned char[newBytes]; if (oldBytes)
{
for (int i=; i<oldBytes; i++)
b[i] = storage[i];
delete []storage;
} storage = b;
capacity = newCapacity;
} void* Stash::fetch(int index)
{
assert(index >= );
if (index > next)
return ;
return &(storage[index * ele_size]);
} int Stash::count()
{
return next;
} void Stash::cleanup()
{
if (storage != )
{
cout << "freeing storage .... " << endl;
delete []storage;
}
}
3)main.cpp测试类
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include "Stash.h" using namespace std; void intTest()
{
Stash intStash; intStash.initalize(sizeof(int)); //栈中存放int型数据,所以栈元素占用int--4个字节 int i;
for (i=; i<; i++)
intStash.add(&i); for (i=; i<intStash.count(); i++)
cout<< "intStash.fetch(" << i << ") = " << *(int *) intStash.fetch(i) <<endl;
intStash.cleanup();
} void stringTest()
{
Stash stringStash;
ifstream in;
const int bufsize = ; stringStash.initalize(sizeof(char) * bufsize);
in.open("Stash.h"); string line;
while (getline(in, line))
{
stringStash.add(line.c_str());
} char *cp;
int i = ;
while ((cp = (char *) stringStash.fetch(i++)) != )
{
cout<< "stringStash.fetch(" << i << ") = " << cp << endl;
} stringStash.cleanup();
} int main()
{ //intTest();
stringTest(); return ;
}
用一维数组实现栈(C++编程思想 p120)的更多相关文章
- 小马哥讲Spring栈核心编程思想 Spring IoC+Bean+Framework
小马哥出手的Spring栈核心编程思想课程,可以说是非常专业和权威的Spring课程.课程主要的方向与核心是Spring Framework总览,带领同学们重新认识重新认识IoC,Spring IoC ...
- Java编程思想—八皇后问题(数组法、堆栈法)
Java编程思想-八皇后问题(数组法.堆栈法) 实验题目:回溯法实验(八皇后问题) 实验目的: 实验要求: 实验内容: (1)问题描述 (2)实验步骤: 数组法: 堆栈法: 算法伪代码: 实验结果: ...
- 《Java编程思想》笔记 第十六章 数组
1 数组 数组和容器比较,数组的优点也只剩访问效率高这一点了. 2 数组是第一级对象 数组也是一个对象,和其他普通对象一样在堆中创建, int[ ] arr arr是数组的引用. 可以隐式创建数组对 ...
- java数组实现买彩票(二个一维数组的比较思想)
/** 设计一个程序,模拟从彩球池里随机抽取5个彩球(彩球池里一共有11个彩球,编号为1~11), 要求在控制台打印出这5个被取出来的彩球的编号(注意编号不能重复). 思路: 1.创建一个int类型的 ...
- Java编程思想 笔记
date: 2019-09-06 15:10:00 updated: 2019-09-24 08:30:00 Java编程思想 笔记 1. 四类访问权限修饰词 \ 类内部 本包 子类 其他包 publ ...
- C++编程思想重点笔记(下)
上篇请看:C++编程思想重点笔记(上) 宏的好处与坏处 宏的好处:#与##的使用 三个有用的特征:字符串定义.字符串串联和标志粘贴. 字符串定义的完成是用#指示,它容许设一个标识符并把它转化为字符串, ...
- Java编程思想(11~17)
[注:此博客旨在从<Java编程思想>这本书的目录结构上来检验自己的Java基础知识,只为笔记之用] 第十一章 持有对象 11.1 泛型和类型安全的容器>eg: List<St ...
- Java编程思想读书笔记(一)【对象导论】
2018年1月7日15:45:58 前言 作为学习Java语言的经典之作<Java编程思想>,常常被人提起.虽然这本书出版十年有余,但是内容还是很给力的.很多人说这本书不是很适合初学者,我 ...
- Java编程思想(后)
Java编程思想(后) 持有对象 如果一个程序只包含固定数量的且其生命期都是已知的对象,那么这是一个非常简单的程序. Java中的库基本类型: List, Set, Queue和Map --- 称为集 ...
随机推荐
- 分布式--ActiveMQ 消息中间件(一) https://www.jianshu.com/p/8b9bfe865e38
1. ActiveMQ 1). ActiveMQ ActiveMQ是Apache所提供的一个开源的消息系统,完全采用Java来实现,因此,它能很好地支持J2EE提出的JMS(Java Message ...
- LeetCode --- Validate Binary Search Tree
题目链接 判断一颗二叉树是否是二叉搜索树(二叉排序树),也就是BST 如果该二叉树是BST, 那么对其中序遍历,所得序列一定是单调递增的(不考虑有重复数值的情况) 附上代码: /** * Defini ...
- API管理的五大规则
http://www.csdn.net/article/2012-12-18/2812929-5-Rules-For-API-Management 1. 设计 开发人员使用API访问各种不同的类,并且 ...
- maven的配置和使用
Maven 简介 1.1 Maven 是什么 翻译为“专家”,“内行” Maven是跨平台的项目管理工具.主要服务于基于Java平台的项目构建,依赖管理和项目信息管理. 1.2 为什么使用Maven ...
- nginx简单使用
nginx开启./nginx重启./nginx -s reload关闭./nginx -s stop或quit
- Docker Remote API使用准备
1 修改配置文件 CentOS: /etc/sysconfig/docker Ubuntu: /etc/init/docker.conf 1.添加: DOCKER_OPTS='-H tcp://0.0 ...
- 【JZOJ4359】【GDKOI2016】魔卡少女
题目描述 君君是中山大学的四年级学生.有一天在家不小心开启了放置在爸爸书房中的一本古书.于是,君君把放在书中最上面的一张牌拿出来观摩了一下,突然掀起一阵大风把书中的其她所有牌吹散到各地.这时一只看上去 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第五章:渲染流水线
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第五章:渲染流水线 学习目标 了解几个用以表达真实场景的标志和2D图像 ...
- GCD使用经验与技巧浅谈
前言 GCD(Grand Central Dispatch)可以说是Mac.iOS开发中的一大“利器”,本文就总结一些有关使用GCD的经验与技巧. dispatch_once_t必须是全局或stati ...
- 64位linux源码安装mysql
一:下载mysql http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/中的Generally Available(GA) Releases标签页,在MySQL Communit ...
