[Git] An efficient GIT workflow for mid/long term projects
reference : http://fle.github.io/an-efficient-git-workflow-for-midlong-term-projects.html
Our full-web project has been going on for nearly two years and is running in production for over 18 months. I think it's my first project without any headache about our codebase and VCS management. So, I'll present our GIT workflow which has proven to be very effective for now.
Context
- Several developers
- Several staging/pre-production servers, several (non-synchronous) production servers
- Monthly releases (more or less) with delivery on staging, then on production servers
- On servers, basecode is directly pulled from the GIT repository with fabric
Rules
To handle this, we have set some simple rules:
- One (and only one) maintainer, who manage GIT repository and releases
- Never commit directly on master
- Never rebase master on any branch
- Do not get out of planned workflow
Workflow
Master branch
Our branch master is the common trunk and simply contains all the codebase of the next release. Since we don't work directly on it, it evolves mainly with merges.
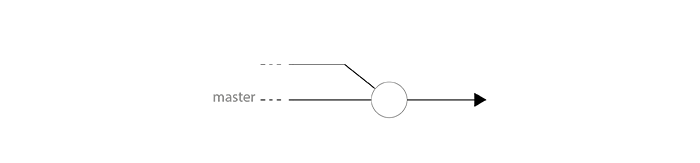
Development branches
When a developer starts a new feature or a bugfix, he creates a new branch from master HEAD
$ (master) git checkout -b featureA
$ (featureA) git commit -a -m "featureA part 1"
$ (featureA) git commit -a -m "featureA part 2"
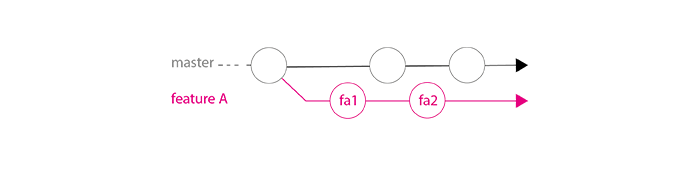
He follows branch master evolution and regularly ensures his code still works, by rebasing his branch featureA on branch master.
$ (featureA) git rebase master
When his developments are done (commits fa1 / fa2 in schema below), he does a last rebase. Thanks to this:
- he ensures that the maintainer will be able to merge easily (maintainer should not need to read code deeply and search why there are conflicts)
- if tests pass on development branch after rebase, they should pass on master after merge, so we ensure that branch ``master`` is always working well
Possibly, it will be the good time to clean the development branch to let it neat just when it is finished.
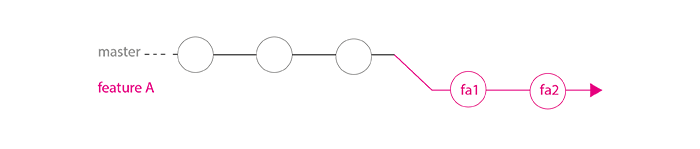
The maintainer can now merge this branch in master peacefully, without big conflict troubles. As the maintainer, I like to use no-ff option to force a merge commit, so history can stay really readable (we easily see where the branch has started and where it has been merged).
$ (master) git merge --no-ff featureA
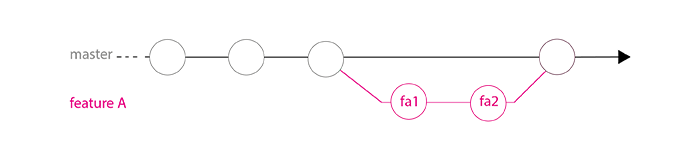
Now that the branch has been merged, the developer should remove his development branch.
$ (master) git branch -d featureA
$ (master) git push origin :featureA
Stable branches
When we prepare a release, we update CHANGELOG (with our workflow, a git log --oneline should be quite clear to do that) and tag the branch master (optional), then we start a stable branch.
$ (master) git tag 1.0
$ (master) git checkout -b stable1.0
$ (stable1.0) git push origin stable1.0
This branch is deployed on different servers.
While development goes on, we possibly have to do some hotfixes (for example: commit hf1 in schema below), that must be sent in production quickly. These hotfixes are done directly on concerned stable branch.
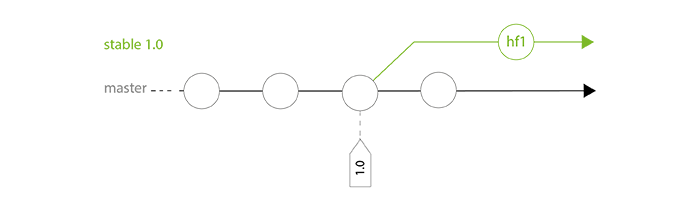
Regularly, the maintainer merges stable branch in master to bring back these commits. This action is particularly important before the next release.
$ (master) git merge --no-ff stable1.0
We found this method really useful because:
- each stable branch has its own life and doesn't take care of branch master evolution, so we can hotfix stable branche freely and without stress
- we ensure that no hotfix commit has been lost before next release (avoid regressions)
A complete history example
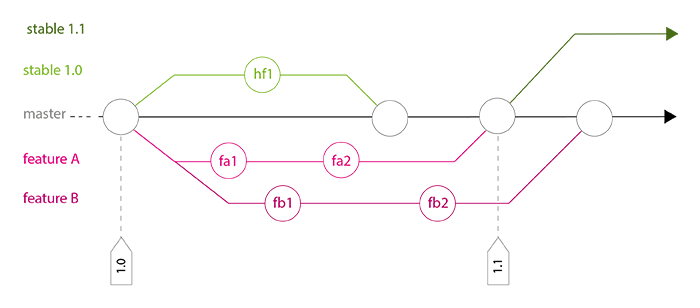
Conclusion
Of course, there are several GIT workflows which can be very efficient, but we found many advantages in working with this method, and no real issue:
- Branch master is always clean and working well
- Developers don't care about GIT whole workflow
- We can fix stable branch without asking ourselves what happened on master since last release
- We ensure that each stable release contains new features and possible fixes
- Always working with branches and using``-no-ff``option make history really clear !
- This workflow is scalable (number of developers or branches doesn't really matter)
[Git] An efficient GIT workflow for mid/long term projects的更多相关文章
- git项目实战常用workflow和命令
一个从无到有的项目大体经历-创建项目目录,创建repo,配置过滤集,配置git user,导入已有基础代码入库,将库放到central去,建立分支,修改代码,checkin代码,分支上 测试验证代码, ...
- Git基本命令 -- 创建Git项目
在这里下载git:https://git-scm.com/ 安装的时候, 如果是windows系统的话, 可以勾选unix的命令行工具, 这样在windows命令行下会多出很多命令, 例如ls. Gi ...
- git push and git pull
原文链接 git push 通常对于一个本地的新建分支,例如git checkout -b develop, 在develop分支commit了代码之后,如果直接执行git push命令,develo ...
- git init和git init -bare区别
1 Git init 和 git init –bare 的区别 用"git init"初始化的版本库用户也可以在该目录下执行所有git方面的操作.但别的用户在将更新push上来的 ...
- 小丁带你走进git世界一-git简单配置
小丁带你走进git世界一-git简单配置 1.github的简单配置 配置提交代码的信息,例如是谁提交的代码之类的. git config –global user.name BattleHeaer ...
- Git(远程仓库:git@oschina)-V2.0
1.注册git@osc(也就是“码云”) 这里会提示注册密码==push密码,反正一定要记住的东西. 2.安装git 这里要设置个人信息 git config --list //查看git信息 g ...
- git pull和git fetch的区别
Git中从远程的分支获取最新的版本到本地有这样2个命令:1. git fetch:相当于是从远程获取最新版本到本地,不会自动merge Git fetch origin master git log ...
- [.net 面向对象程序设计进阶] (26) 团队开发利器(五)分布式版本控制系统Git——图形化Git客户端工具TortoiseGit
[.net 面向对象程序设计进阶] (26) 团队开发利器(五)分布式版本控制系统Git——图形化Git客户端工具TortoiseGit 读前必备: 接上篇: 分布式版本控制系统Git——使用GitS ...
- Git:Git初体验——Git安装配置
作为即将成为一个程序员的男人,一直在听别人说Git多好多好,之前也随便了解了一些,但是始终没有决心去学会.现在大四了,只有毕设和一门开学六七周只去过一次课的全员必修课外,也没有什么事情做,何不去做这些 ...
随机推荐
- spring boot 之使用mapstruct
最近在阅读swagger源码,当看到 springfox.documentation.swagger2.mappers.ModelMapper 类时,无意中看到该类上面使用的 org.mapstruc ...
- openfire 部署后报错: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: interface xx is not visible from class loader
该异常是创建代理时加载接口的类加载器与创建时传入的不一致. 在本地eclipse做openfire二次开发,本地运行没错,部署到服务器上后报异常: java.lang.IllegalArgument ...
- Failed to load JavaHL Library. SVN
以前使用的电脑是32位的,安装的svn可以正常使用,但是现在的电脑室64位的,安装好svn后,把项目提交到svn的过程中,总是弹出来一个错误的对话框: Failed to load JavaHL Li ...
- customPage.class.php可添加js事件的分页类
用于ajax动态加载数据的分页类,分页事件可以动态添加,去除了a链接中的href地址. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ...
- 安卓代码混淆(Android Studio)
Proguard是安卓提供的方便开发者对代码和apk进行保护和精简的工具,可在SDK/tools文件夹下找到. proguard的作用 : 1,代码混淆 2,精简代码,删掉没有用到的代码,减小ap ...
- JDK源码分析(五)——HashSet
目录 HashSet概述 内部字段及构造方法 存储元素 删除元素 包含元素 总结 HashSet概述 从前面开始,已经分析过集合中的List和Map,今天来介绍另一种集合元素:Set.这是JDK对 ...
- POJ1222 EXTENDED LIGHTS OUT 高斯消元 XOR方程组
http://poj.org/problem?id=1222 在学校oj用搜索写了一次,这次写高斯消元,haoi现场裸xor方程消元没写出来,真实zz. #include<iostream> ...
- 鸟哥的私房菜:Bash shell(五)-数据流重导向
数据流重定向 数据流重导向就是将某个指令执行后应该要出现在屏幕上的数据, 给他传输到其它的地方,例如档案或者是装置 (例如打印机之类的!)!这玩意儿在 Linux 的文字模式底下可重要的! 尤其是如果 ...
- hdu 5301 Buildings (2015多校第二场第2题) 简单模拟
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5301 题意:给你一个n*m的矩形,可以分成n*m个1*1的小矩形,再给你一个坐标(x,y),表示黑格子 ...
- 【51nod-1239&1244】欧拉函数之和&莫比乌斯函数之和 杜教筛
题目链接: 1239:http://www.51nod.com/onlineJudge/questionCode.html#!problemId=1239 1244:http://www.51nod. ...
