c++ why can't class template hide its implementation in cpp file?
类似的问题还有: why can't class template use Handle Class Pattern to hide its implementation? || why there are linker problems (undefined reference) to my class template?
我出现问题的源码(见main.cpp,Stack.h,Stack.cpp)(本来是准备用来展示Handle Class Pattern如何实现implementation-hiding),报错如下:
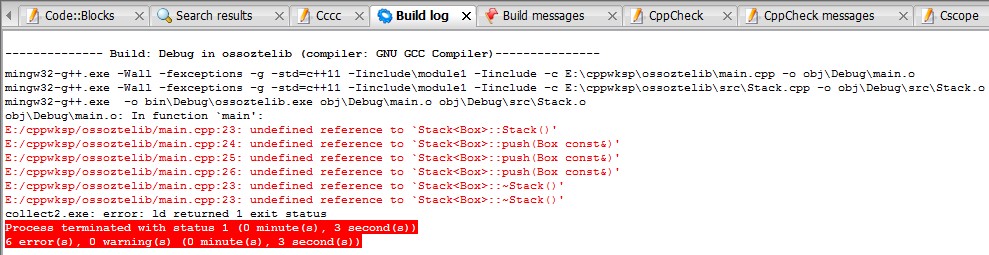
问题的本质&解决办法:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/8752837/undefined-reference-to-template-class-constructor
http://www.parashift.com/c++-faq-lite/templates-defn-vs-decl.html
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/5417465/separating-template-interface-and-implementation-in-c
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/18121071/hiding-template-implementation-details-from-doxygen
方法1:Explicitly instantiate the template, and its member definitions
方法2:Copy the implemtation code of the class template into its header file
总结:
虽然有2种解决办法,但是方法一显然“太笨”,而且“太不灵活”
So, if you plan to create your own class template, then you just don't need to consider enforcing implementation hiding as you do to normal classes, the only way to hide the implementation of a class template is not to provide its header.
On the other hand, if you decide to design something to be a class template, you must be sure there's nothing need to be hidden for that template, for example: encryption algorithm or other sensitive stuff.
Insight Comment:
The very goal of template is to create a "pattern" so that the compiler can generate classes and functions for a multitude of unrelated types. If you hide this pattern, how do you expect the compiler to be able to generate those classes and functions ?
代码:
main.cpp
#include "Stack.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Box {
public:
Box():data(), ID(num++) { cout << "Box" << ID << " cons" << endl; }
Box(const Box ©): data(copy.data), ID(num++) { cout << "Box" << ID << " copy cons" << endl; }
~Box() { cout << "Box" << ID << " des" << endl; }
int data;
private:
static int num;
const int ID;
};
int Box::num = ;
int main()
{
Box b1,b2,b3;
Stack<Box> bstack;
bstack.push(b1);
bstack.push(b2);
bstack.push(b3);
return ;
}
Stack.h
#ifndef STACK_H
#define STACK_H #include <cstddef> template <typename T>
class StackImpl; // Stack implementation (hidden), private part
// will not be seen by clients template <typename T>
class Stack
{
public:
Stack();
~Stack();
/**
Inserts a new element at the top of the stack,
above its current top element.
The content of this new element is
initialized to a copy of val.
@param val value to which the inserted element is initialized
*/
void push(const T &val);
/**
@return a reference to the top element in the stack
*/
T& top();
/**
@return a const reference to the top element in the stack
*/
const T& top() const;
/**
Removes the element on top of the stack.
This calls the removed element's destructor.
*/
void pop();
/**
@return the number of elements in the stack.
*/
size_t size();
private: StackImpl<T> *impl; // Stack implementation (hidden), private part
// will not be seen by clients }; #endif // STACK_H
Stack.cpp
#include "Stack.h" #include <stdexcept> using namespace std; template <typename T>
class Link {
public: T data;
Link *next; Link(const T &_data): data(_data), next(NULL) {}
Link(const T &_data, Link *_next): data(_data), next(_next) {}
~Link() {
next = NULL;
} }; template <typename T>
class StackImpl {
public: // even though they're public, but they're not in the header, thus it's safe Link<T> *head; size_t size; StackImpl(): head(NULL) {}
~StackImpl() {
Link<T> *ptr = head;
while (ptr != NULL) {
ptr = head->next;
delete head;
head = ptr;
}
size = ;
}
}; template <typename T>
Stack<T>::Stack(): impl(new StackImpl<T>()) {} template <typename T>
Stack<T>::~Stack() {
if (impl != NULL)
delete impl;
}
/**
Inserts a new element at the top of the stack,
above its current top element.
The content of this new element is
initialized to a copy of val.
@param val value to which the inserted element is initialized
*/
template <typename T>
void Stack<T>::push(const T &val)
{
impl->head = new Link<T>(val, impl->head);
++(impl->size);
}
/**
@return a reference to the top element in the stack
*/
template <typename T>
T& Stack<T>::top()
{
if (impl->head == NULL)
throw runtime_error("empty stack");
return impl->head->data; }
/**
@return a const reference to the top element in the stack
*/
template <typename T>
const T& Stack<T>::top() const
{
if (impl->head == NULL)
throw runtime_error("empty stack");
return impl->head->data;
}
/**
Removes the element on top of the stack.
This calls the removed element's destructor.
*/
template <typename T>
void Stack<T>::pop()
{
if (impl->head == NULL)
throw runtime_error("empty stack");
Link<T> *ptr = impl->head->next;
delete impl->head;
impl->head = ptr;
--(impl->size);
} /**
@return the number of elements in the stack.
*/
template <typename T>
size_t Stack<T>::size() {
return impl->size;
}
c++ why can't class template hide its implementation in cpp file?的更多相关文章
- C++中template的.h文件和.cpp文件的问题
在C++中,用到类模板时,如果类似一般的类声明定义一样,把类声明放在.h文件中,而具体的函数定义放在.cpp文件中的话,会发现编译器会报错.如类似下面代码: //test.h文件 #ifndef TE ...
- c++模板类的使用,编译的问题
1,模板类编译的问题 前两天在写代码时,把模板类的声明和分开放在两个文件中了,类似于下面这样: stack.hpp: #ifndef _STACK_HPP #define _STACK_HPP tem ...
- 增强采样软件PLUMED的安装与使用
技术背景 增强采样(Enhanced Sampling)是一种在分子动力学模拟中常用的技术,其作用是帮助我们更加快速的在时间轴上找到尽可能多的体系结构及其对应的能量.比如一个氢气的燃烧反应,在中间过程 ...
- c++ simple class template example: Stack
main.cpp #include "Stack.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Box { pub ...
- 模板函数(template function)出现编译链接错误(link error)之解析
总的结论: 将template function 或者 template class的完整定义直接放在.h文件中,然后加到要使用这些template function的.cpp文件中. 1. 现 ...
- 用T4 Template生成代码
1 T4语法 T4的语法与ASP.NET的方式比较类似.主要包括指令.文本块.控制块. 1.1 指令 指令主要包括template, output, assembly, import, incl ...
- A Simple C++ Template Class that Matches a String to a Wildcard Pattern
A recently implemented enhanced wildcard string matcher, features of which including, Supporting wil ...
- How to organize the Template Files in C++
Normally you put class definitions in a header file and method definitions in a source file. Code th ...
- idea: Unable to parse template "class"
使用idea创建文件时,报“Cannot Create Class”.具体错误为: Unable to parse template "Class" error meesage: ...
随机推荐
- Qcon
http://2017.qconbeijing.com/?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral
- How to enable Hibernate option in windows 2008 R2 server?
http://velshare.blogspot.com/2013/02/how-to-enable-hibernate-option-in.html 1) To enable the Hiberna ...
- redis秒杀系统数据同步(保证不多卖)
东西不多卖 秒杀系统需要保证东西不多卖,关键是在多个客户端对库存进行减操作时,必须加锁.Redis中的Watch刚好可以实现一点.首先我们需要获取当前库存,只有库存中的食物小于购物车的数目才能对库存进 ...
- Android Studio Emulator 提示 “/dev/kvm is not found” 解决办法
重新安装HAXM即可解决 1.确定已经安装HAXM SDK Manager -> Extras -> Intel x86 Emulator Accelerator (HAXM instal ...
- jenkins如何在一台机器上开启多个slave
1.一台机器不是jenkins的master分支 2.另一台机器部署多个slave分支 3.部署多台slave分支的机器其实只需要在多个目录放置多个slave.jar就可以了,然后进行一些配置即可
- Python中调用其他程序的方式
前言 在Python中,可以方便地使用os模块来运行其他脚本或者程序,这样就可以在脚本中直接使用其他脚本或程序提供的功能,而不必再次编写实现该功能的代码.为了更好地控制运行的进程, 可以使用win32 ...
- Oracle OS认证 口令文件 密码丢失处理
Oracle OS认证 口令文件 密码丢失处理 分类: Oracle Basic Knowledge2009-10-19 14:24 5031人阅读 评论(9) 收藏 举报 oracleos数据库sq ...
- 表单提交时上传图片 表单ajax提交
页面 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery.form.js"></script>& ...
- rails delegate机制
Delegate是一种应用composite来代替extend的机制,可以有效地降低代码的耦合性. Rails 2.2增加了delegate方法,可以十分方便地实现delegate机制. 01.def ...
- Stack Exchange 的架构
近日,Stack Exchange系统管理员blog上发布了一篇关于Stack Exchange的架构一瞥,其包括了Stack Overflow, Server Fault 和 Super User的 ...
