linux-多线程
一、什么是线程?
线程是进程的一个实体,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,它是比进程更小的能独立执行的基本单位。线程自己基本上不拥有系统资源,仅仅拥有一点在执行中不可缺少的资源(如程序计数器,一组寄存器和栈),可是它可与同属一个进程的其它的线程共享进程所拥有的所有资源。
二、什么时候使用多线程?
三、线程的创建
#include<pthread.h>
int pthread_create (pthread_t *__restrict __newthread,//新创建的线程ID
__const pthread_attr_t *__restrict __attr,//线程属性
void *(*__start_routine) (void *),//新创建的线程从start_routine開始运行
void *__restrict __arg)//运行函数的參数
返回值:成功-0,失败-返回错误编号,能够用strerror(errno)函数得到错误信息
四、线程的终止
- 线程从运行函数返回,返回值是线程的退出码
- 线程被同一进程的其它线程取消
- 调用pthread_exit()函数退出。这里不是调用exit,由于线程调用exit函数,会导致线程所在的进程退出。
一个小样例:
启动两个线程,一个线程对全局变量num运行加1操作,运行五百次,一个线程对全局变量运行减1操作,相同运行五百次。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h> int num=0;
void *add(void *arg) {//线程运行函数,运行500次加法
int i = 0,tmp;
for (; i <500; i++)
{
tmp=num+1;
num=tmp;
printf("add+1,result is:%d\n",num);
}
return ((void *)0);
}
void *sub(void *arg)//线程运行函数,运行500次减法
{
int i=0,tmp;
for(;i<500;i++)
{
tmp=num-1;
num=tmp;
printf("sub-1,result is:%d\n",num);
}
return ((void *)0);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) { pthread_t tid1,tid2;
int err;
void *tret;
err=pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,add,NULL);//创建线程
if(err!=0)
{
printf("pthread_create error:%s\n",strerror(err));
exit(-1);
}
err=pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,sub,NULL);
if(err!=0)
{
printf("pthread_create error:%s\n",strerror(err));
exit(-1);
}
err=pthread_join(tid1,&tret);//堵塞等待线程id为tid1的线程,直到该线程退出
if(err!=0)
{
printf("can not join with thread1:%s\n",strerror(err));
exit(-1);
}
printf("thread 1 exit code %d\n",(int)tret);
err=pthread_join(tid2,&tret);
if(err!=0)
{
printf("can not join with thread1:%s\n",strerror(err));
exit(-1);
}
printf("thread 2 exit code %d\n",(int)tret);
return 0;
}
使用g++编译该文件(g++ main.cpp -o main)。此时会报错undefined reference to `pthread_create'。
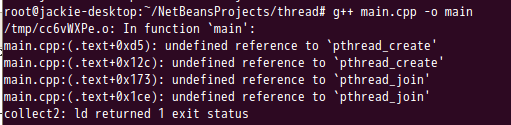
报这个错误的原因是:pthread库不是linux默认的库,所以在编译时候须要指明libpthread.a库。
解决方法:在编译时,加上-lpthread參数。
运行结果:
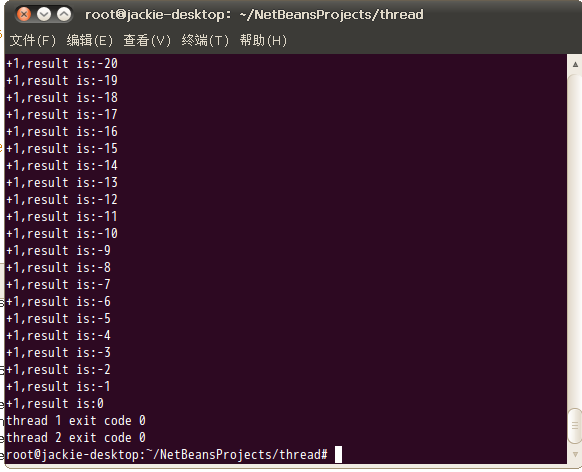
乍一看,结果是对的,加500次,减500次,最后结果为0。可是细致看全部的输出,你会发现有异样的东西。
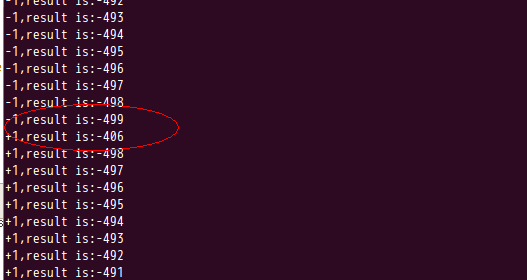
导致这个不和谐出现的原因是,两个线程能够对同一变量进行改动。假如线程1运行tmp=50+1后,被系统中断,此时线程2对num=50运行了减一操作,当线程1恢复,在运行num=tmp=51。而正确结果应为50。所以当多个线程对共享区域进行改动时,应该採用同步的方式。
五、线程同步
1、相互排斥量
#include<pthread.h>
int pthread_mutex_init (pthread_mutex_t *__mutex,
__const pthread_mutexattr_t *__mutexattr);
int pthread_mutex_destroy (pthread_mutex_t *__mutex);
返回值:成功-0,失败-错误编号
#include<pthread.h>
int pthread_mutex_lock (pthread_mutex_t *__mutex);
int pthread_mutex_unlock (pthread_mutex_t *__mutex);
使用相互排斥量改动上一个程序(改动部分用红色标出):
void *add(void *arg) {
int i = 0,tmp;
for (; i <500; i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mylock);
tmp=num+1;
num=tmp;
printf("+1,result is:%d\n",num);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mylock);
}
return ((void *)0);
}
void *sub(void *arg)
{
int i=0,tmp;
for(;i<500;i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mylock);
tmp=num-1;
num=tmp;
printf("-1,result is:%d\n",num);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mylock);
}
return ((void *)0);
}
2、读写锁
同意多个线程同一时候读,仅仅能有一个线程同一时候写。适用于读的次数远大于写的情况。
#include<pthread.h>
int pthread_rwlock_init (pthread_rwlock_t *__restrict __rwlock,
__const pthread_rwlockattr_t *__restrict
__attr);
int pthread_rwlock_destroy (pthread_rwlock_t *__rwlock);
返回值:成功--0,失败-错误编号
int pthread_rwlock_rdlock (pthread_rwlock_t *__rwlock)
写加锁:
int pthread_rwlock_wrlock (pthread_rwlock_t *__rwlock)
解锁用同一个函数:
int pthread_rwlock_unlock (pthread_rwlock_t *__rwlock)
3、条件变量
int pthread_cond_init (pthread_cond_t *__restrict __cond,
__const pthread_condattr_t *__restrict
__cond_attr);
int pthread_cond_destroy (pthread_cond_t *__cond);
条件等待
pthread_cond_wait (pthread_cond_t *__restrict __cond,
pthread_mutex_t *__restrict __mutex)
这里须要注意的是,调用pthread_cond_wait传递的相互排斥量已锁定,pthread_cond_wait将调用线程放入等待条件的线程列表,然后释放相互排斥量,在pthread_cond_wait返回时,再次锁定相互排斥量。
int pthread_cond_signal (pthread_cond_t *__cond); int pthread_cond_broadcast (pthread_cond_t *__cond)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#define DEBUG 1 int num=0;
pthread_mutex_t mylock=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t qready=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
void * thread_func(void *arg)
{
int i=(int)arg;
int ret;
sleep(5-i);//线程睡眠,然最先生成的线程,最后苏醒
pthread_mutex_lock(&mylock);//调用pthread_cond_wait前,必须获得相互排斥锁
while(i!=num)
{
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("thread %d waiting\n",i);
#endif
ret=pthread_cond_wait(&qready,&mylock);//该函数把线程放入等待条件的线程列表,然后对相互排斥锁进行解锁,这两部都是原子操作。而且在pthread_cond_wait返回时,相互排斥量再次锁住。
if(ret==0)
{
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("thread %d wait success\n",i);
#endif
}else
{
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("thread %d wait failed:%s\n",i,strerror(ret));
#endif
}
}
printf("thread %d is running \n",i);
num++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mylock);//解锁
pthread_cond_broadcast(&qready);//唤醒等待该条件的全部线程
return (void *)0;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) { int i=0,err;
pthread_t tid[4];
void *tret;
for(;i<4;i++)
{
err=pthread_create(&tid[i],NULL,thread_func,(void *)i);
if(err!=0)
{
printf("thread_create error:%s\n",strerror(err));
exit(-1);
}
}
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
err = pthread_join(tid[i], &tret);
if (err != 0)
{
printf("can not join with thread %d:%s\n", i,strerror(err));
exit(-1);
}
}
return 0;
}
在非DEBUG模式,运行结果如图所看到的:
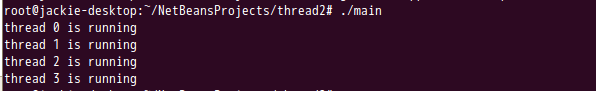

在DEBUG模式能够看出,线程3先被唤醒,然后运行pthread_cond_wait(输出thread 3 waiting),此时在pthread_cond_wait中先解锁相互排斥量,然后进入等待状态。这是thread 2加锁相互排斥量成功,进入pthread_cond_wait(输出thread 2 waiting) ,相同解锁相互排斥量,然后进入等待状态。直到线程0,全局变量与线程參数i一致,满足条件,不进入条件等待,输出thread 0 is running。全局变量num运行加1操作,解锁相互排斥量,然后唤醒全部等待该条件的线程。thread
3 被唤醒,输出thread 3 wait success。可是不满足条件,再次运行pthread_cond_wait。如此运行下去,满足条件的线程运行,不满足条件的线程等待。
linux-多线程的更多相关文章
- Linux多线程服务端编程一些总结
能接触这本书是因为上一个项目是用c++开发基于Linux的消息服务器,公司没有使用第三方的网络库,卷起袖子就开撸了.个人因为从业经验较短,主 要负责的是业务方面的编码.本着兴趣自己找了这本书.拿到书就 ...
- 《Linux 多线程服务端编程:使用 muduo C++ 网络库》电子版上市
<Linux 多线程服务端编程:使用 muduo C++ 网络库> 电子版已在京东和亚马逊上市销售. 京东购买地址:http://e.jd.com/30149978.html 亚马逊Kin ...
- [转载]赖勇浩:推荐《Linux 多线程服务器端编程》
推荐<Linux 多线程服务器端编程> 赖勇浩(http://laiyonghao.com) 最近,有一位朋友因为工作需要,需要从网游的客户端编程转向服务器端编程,找我推荐一本书.我推荐了 ...
- 《Linux多线程服务端编程:使用muduo C++网络库》上市半年重印两次,总印数达到了9000册
<Linux多线程服务端编程:使用muduo C++网络库>这本书自今年一月上市以来,半年之内已经重印两次(加上首印,一共是三次印刷),总印数达到了9000册,这在技术书里已经算是相当不错 ...
- linux多线程下载工具mwget
linux多线程下载工具mwget 经常使用wget进行文件下载,然而wget的处理速度并不如人意.遇到一些国外的站点,经常慢得像蜗牛一般.然而为了解决这个问题,便有了mwget:m表示multi多线 ...
- Linux多线程实例练习 - pthread_cancel()
Linux多线程实例练习 - pthread_cancel 1.代码 xx_pthread_cancel.c #include <pthread.h> #include <stdio ...
- Linux多线程实例练习 - pthread_exit() 与 pthread_join()
Linux多线程实例练习 - pthread_exit 与 pthread_join pthread_exit():终止当前线程 void pthread_exit(void* retval); pt ...
- Linux多线程实例练习 - pthread_create()
Linux多线程实例练习 pthread_create():创建一个线程 int pthread_create(pthread_t *tidp, const pthread_attr_t *attr, ...
- [转]一个简单的Linux多线程例子 带你洞悉互斥量 信号量 条件变量编程
一个简单的Linux多线程例子 带你洞悉互斥量 信号量 条件变量编程 希望此文能给初学多线程编程的朋友带来帮助,也希望牛人多多指出错误. 另外感谢以下链接的作者给予,给我的学习带来了很大帮助 http ...
- linux多线程同步pthread_cond_XXX条件变量的理解
在linux多线程编程中,线程的执行顺序是不可预知的,但是有时候由于某些需求,需要多个线程在启动时按照一定的顺序执行,虽然可以使用一些比较简陋的做法,例如:如果有3个线程 ABC,要求执行顺序是A-- ...
随机推荐
- 李洪强漫谈iOS开发[C语言-018]-scanf函数
- 冒泡排序BubbleSort
/** * * @author Administrator * 功能:交换式排序之冒泡排序 */ package com.test1; import java.util.Calendar; publi ...
- ANDROID_MARS学习笔记_S01原始版_007_Handler及线程的简单使用
一.运行结果 一.代码1.xml(1)activity_main.xml <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.c ...
- Qt中如何写一个model(自定义一个RowNode,我没有碰到过)
在qt中,用到最多就是model/view的结构来表示数据层及表示层的关系.model用于给view提供数据.那如何来实现一个简单的树形model呢. 实现一个自己的model需要重载以下的方法: Q ...
- Ember.js demo2
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script src="http://code.jquery.com/jquery-1 ...
- 存储过程系列之存储过程sql数据库调用和程序代码调用
1.存储过程,无参数的存储过程 创建无参数存储存储过程 Create Procedure DCEMREMR_TEMPLATEAs SELECT TOP 10 [FILENAME],[FILETITLE ...
- Cannot Create Supplier Site (Address) (文档 ID 1069032.1)
Error Address and Site Creation - Unable to create address and sites because of the following error ...
- 转自 Because of you 的总结
上下界网络流的问题严格的分,可以分为四类吧. 1:无源汇可行流 sgu 194 2:有源汇可行流 poj 2396 这题比较好,我建图建了将近200行 3:有源汇最大流 zoj 3496 这 ...
- [NYOJ 15] 括号匹配(二)
括号匹配(二) 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:6 描述 给你一个字符串,里面只包含"(",")","[&qu ...
- 深入理解c语言_从编译器的角度考虑问题_纪念Dennis Ritchie先生
开源中国: Dennis Ritchie教授过世了,他发明了C语言,一个影响深远并彻底改变世界的计算机语言.一门经历40多年的到今天还长盛不训的语言,今天很多语言都受到C的影 响,C++,Java,C ...
