Codeforces 938.D Buy a Ticket
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Musicians of a popular band "Flayer" have announced that they are going to "make their exit" with a world tour. Of course, they will visit Berland as well.
There are n cities in Berland. People can travel between cities using two-directional train routes; there are exactly m routes, i-th route can be used to go from city vi to city ui (and from ui to vi), and it costs wi coins to use this route.
Each city will be visited by "Flayer", and the cost of the concert ticket in i-th city is ai coins.
You have friends in every city of Berland, and they, knowing about your programming skills, asked you to calculate the minimum possible number of coins they have to pay to visit the concert. For every city i you have to compute the minimum number of coins a person from city i has to spend to travel to some city j (or possibly stay in city i), attend a concert there, and return to city i (if j ≠ i).
Formally, for every 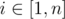 you have to calculate
you have to calculate 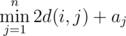 , where d(i, j) is the minimum number of coins you have to spend to travel from city i to city j. If there is no way to reach city j from city i, then we consider d(i, j) to be infinitely large.
, where d(i, j) is the minimum number of coins you have to spend to travel from city i to city j. If there is no way to reach city j from city i, then we consider d(i, j) to be infinitely large.
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105, 1 ≤ m ≤ 2·105).
Then m lines follow, i-th contains three integers vi, ui and wi (1 ≤ vi, ui ≤ n, vi ≠ ui, 1 ≤ wi ≤ 1012) denoting i-th train route. There are no multiple train routes connecting the same pair of cities, that is, for each (v, u) neither extra (v, u) nor (u, v) present in input.
The next line contains n integers a1, a2, ... ak (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1012) — price to attend the concert in i-th city.
Print n integers. i-th of them must be equal to the minimum number of coins a person from city i has to spend to travel to some city j (or possibly stay in city i), attend a concert there, and return to city i (if j ≠ i).
4 2
1 2 4
2 3 7
6 20 1 25
6 14 1 25
3 3
1 2 1
2 3 1
1 3 1
30 10 20
题目大意:每个点有点权a[i],定义d[i][j]为i到j的最短路.对于每一个i,求一个任意的j,使得2*d[i][j] + a[j]最小.
分析:这道题应该属于那种想一会就能想到的题.
题目让我们求的实际上是多源最短路.怎么求?floyd? 其实可以dijkstra来求.现将所有的点以及点权放到结构体里,并且加入到优先队列中.每扩展到一个点,这个点的答案就被确定了,因为是优先队列,每次都会找路径长度最小的扩展.然后再把这个点能扩展到的点以及路径长度放到优先队列中,不断处理,直到所有点的答案被确定.
这道题利用了dijkstra每次取最短距离的点更新和可以处理多源最短路的特点,以前做过的一道类似的题:hdu6166
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; typedef long long ll;
const ll maxn = ;
ll n,m,head[maxn],to[maxn * ],nextt[maxn * ],w[maxn * ],tot = ,vis[maxn],ans[maxn];
priority_queue <pair<ll,ll>,vector<pair<ll,ll> >,greater<pair<ll,ll> > > q; void add(ll x,ll y,ll z)
{
w[tot] = z;
to[tot] = y;
nextt[tot] = head[x];
head[x] = tot++;
} int main()
{
scanf("%I64d%I64d",&n,&m);
for (ll i = ; i <= m; i++)
{
ll a,b,c;
scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&a,&b,&c);
add(a,b,*c);
add(b,a,*c);
}
for (ll i = ; i <= n; i++)
{
ll t;
scanf("%I64d",&t);
q.push(make_pair(t,i));
}
while (!q.empty())
{
pair <ll,ll> u = q.top();
q.pop();
if (vis[u.second])
continue;
vis[u.second] = ;
ans[u.second] = u.first;
for (ll i = head[u.second];i;i = nextt[i])
{
ll v = to[i];
q.push(make_pair(u.first + w[i],v));
}
}
for (ll i = ; i <= n; i++)
printf("%I64d ",ans[i]); return ;
}
Codeforces 938.D Buy a Ticket的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 938 D. Buy a Ticket (dijkstra 求多元最短路)
题目链接:Buy a Ticket 题意: 给出n个点m条边,每个点每条边都有各自的权值,对于每个点i,求一个任意j,使得2×d[i][j] + a[j]最小. 题解: 这题其实就是要我们求任意两点的 ...
- Codeforces 938D Buy a Ticket (转化建图 + 最短路)
题目链接 Buy a Ticket 题意 给定一个无向图.对于每个$i$ $\in$ $[1, n]$, 求$min\left\{2d(i,j) + a_{j}\right\}$ 建立超级源点$ ...
- Codeforces 938D Buy a Ticket
Buy a Ticket 题意要求:求出每个城市看演出的最小费用, 注意的一点就是车票要来回的. 题解:dijkstra 生成优先队列的时候直接将在本地城市看演出的费用放入队列里, 然后直接跑就好了, ...
- Buy the Ticket{HDU1133}
Buy the TicketTime Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total ...
- 【HDU 1133】 Buy the Ticket (卡特兰数)
Buy the Ticket Problem Description The "Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire" will be on sh ...
- 【高精度练习+卡特兰数】【Uva1133】Buy the Ticket
Buy the Ticket Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) T ...
- Buy the Ticket(卡特兰数+递推高精度)
Buy the Ticket Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Tota ...
- hdu 1133 Buy the Ticket(Catalan)
Buy the Ticket Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) T ...
- HDUOJ---1133(卡特兰数扩展)Buy the Ticket
Buy the Ticket Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)To ...
随机推荐
- javascript 强制转换规则 boolean 布尔值类型
摘自 <你不知道的Javascript(中卷)> p55 一句话简述, 假值表以外的值均可以认为是真值,部分浏览器可能自定义了假值表以外的假值,并不符合W3C规范,需要特殊对待. 首先也是 ...
- 【转】AOE机制的DSL及其实际运用
AOE这个词的意思,我相信玩过WOW的人都不陌生,包括玩过LoL的也不会陌生,说穿了就是一个区域内发生效果(Area of effect).这里我们要讨论的就是关于一个适合于几乎所有游戏的AOE机制, ...
- 高可用Kubernetes集群-2. ca证书与秘钥
四.CA证书与秘钥 kubernetes集群安全访问有两种方式:"基于CA签名的双向数字证书认证"与"基于BASE或TOKEN的简单认证",生产环境推荐使用&q ...
- 从零开始的Python爬虫速成指南
序 本文主要内容:以最短的时间写一个最简单的爬虫,可以抓取论坛的帖子标题和帖子内容. 本文受众:没写过爬虫的萌新. 入门 0.准备工作 需要准备的东西: Python.scrapy.一个IDE或者随便 ...
- CQOI2018 游记 再见OI,既是反思,也是祝福
哎,怎么说呢? 时运不齐,命途多舛? 从头开始说吧. 今年的NOIP大家考的都不尽人意,每个人都有或多或少的失误,全部都几十分几十分地丢.最后大家剩下的觉得可能冲击一下省队的人一共只有7个. 伙伴们变 ...
- CF 1008B Turn the Rectangles(水题+贪心)
There are n rectangles in a row. You can either turn each rectangle by 90 degrees or leave it as it ...
- 单源最短路——Bellman-Ford算法
1.Dijkstra的局限性 Dijkstra算法是处理单源最短路径的有效算法,但它局限于边的权值非负的情况,若图中出现权值为负的边,Dijkstra算法就会失效,求出的最短路径就可能是错的. 列如以 ...
- scrum立会报告+燃尽图(第二周第七次)
此作业要求参见:https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/nenu/2018fall/homework/2252 一.小组介绍 组名:杨老师粉丝群 组长:乔静玉 组员:吴奕瑶.公冶 ...
- Thunder团队第七周 - Scrum会议4
Scrum会议4 小组名称:Thunder 项目名称:i阅app Scrum Master:翟宇豪 工作照片: 宋雨在照相,所以不在相片中. 参会成员: 王航:http://www.cnblogs.c ...
- 20162316刘诚昊 第八周实验报告:实验二 Java面向对象程序设计
实验内容 初步掌握单元测试和TDD 理解并掌握面向对象三要素:封装.继承.多态 初步掌握UML建模 熟悉S.O.L.I.D原则 了解设计模式 实验要求 1.没有Linux基础的同学建议先学习<L ...
