npm run serve/build 背后的真实操作
vue CLI 用起来的确很舒服,方便省事,但他经过层层封装很难明白,执行完那个npm run serve/build 后他都干了些什么,甚至不知道整个项目是怎么跑起来的,今天自己抽时间就去瞅瞅,为加深记录特此记录记录
【声明】纯属个人学习推敲,有不对的地方欢迎指正,我们一起讨论共同学习一起进步
文章目录
一、探寻npm run 背后的真实操作
1、看看 npm run serve
首选从npm run serve 开始,整个应该都很熟悉了,执行这命令后就是执行,package.json 的script 中key为serve后面的值
"scripts": {
"serve": "vue-cli-service serve",
"build": "vue-cli-service build",
"lint": "vue-cli-service lint"
},
其实真实的执行命令是这一个 npm run vue-cli-service serve 命令,那这个是个啥意思我们做个测试,添加个test 进行测试
"scripts": {
"serve": "vue-cli-service serve",
"build": "vue-cli-service build",
"lint": "vue-cli-service lint",
"test":"echo hello vue "
},
再来执行下命令 run , 看如下打印
D:\YLKJPro\fgzs>npm run test
> sdz@0.1.0 test D:\YLKJPro\fgzs
> echo hello vue
hello vue
其实就是执行了test 后面的echo , 那么 npm run vue-cli-service serve 后面的serve 是干啥的呢?再来看看
D:\YLKJPro\fgzs>npm run test serve
> sdz@0.1.0 test D:\YLKJPro\fgzs
> echo hello vue "serve"
hello vue "serve"
其实就是将后面的当成了参数
2、仿造一个serve
如果不信,我们再来做一个测试看看(仿造一个 serve)
"scripts": {
"serve": "vue-cli-service serve",
"build": "vue-cli-service build",
"lint": "vue-cli-service lint",
"test":"my-npm-test serve"
},
执行npm run test 输出如下
D:\YLKJPro\fgzs>npm run test > sdz@0.1.0 test D:\YLKJPro\fgzs
> my-npm-test serve serve
咦,奇怪了 , serve 怎么打印出来的呢,我并没有使用echo ?其实我是模仿了原来的脚本,
2-1. 创建测试文件夹
先在node_modules下创建一个mytest/bin目录,同时在该bin目录下创建一个测试的js,如下
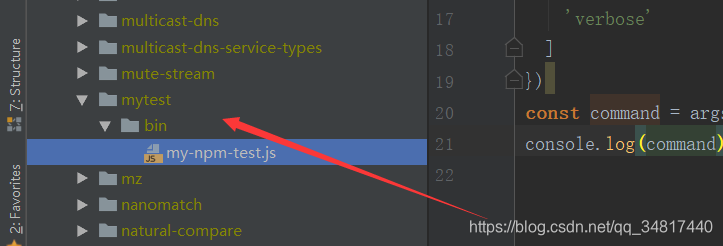
这个测试的js 也很简单就是把那个接收的参数打印出来,如下:
#!/usr/bin/env node const rawArgv = process.argv.slice(2) console.log(rawArgv[0])
2-2. 在 node_modules/.bin下创建测试脚本

添加了一个 linux 和 windows 的shell 脚本(my-npm-test和my-npm-test.cmd)
其实里面就一些目标js的路径
2-3. 添加my-npm-test
my-npm-test
#!/bin/sh
basedir=$(dirname "$(echo "$0" | sed -e 's,\\,/,g')") case `uname` in
*CYGWIN*) basedir=`cygpath -w "$basedir"`;;
esac if [ -x "$basedir/node" ]; then
"$basedir/node" "$basedir/../mytest/bin/my-npm-test.js" "$@"
ret=$?
else
node "$basedir/../mytest/bin/my-npm-test.js" "$@"
ret=$?
fi
exit $ret
2-4. 添加my-npm-test.cmd
my-npm-test.cmd 用于windows 端
@IF EXIST "%~dp0\node.exe" (
"%~dp0\node.exe" "%~dp0\..\mytest\bin\my-npm-test.js" %*
) ELSE (
@SETLOCAL
@SET PATHEXT=%PATHEXT:;.JS;=;%
node "%~dp0\..\mytest\bin\my-npm-test.js" %*
)
到这里总算对npm run 有些了解了;
其实 执行 npm help run 官方也有想对应的解释 如

2-5. 执行原理
使用npm run script执行脚本的时候都会创建一个shell,然后在shell中执行指定的脚本。
这个shell会将当前项目的可执行依赖目录(即node_modules/.bin)添加到环境变量path中,当执行之后之后再恢复原样。就是说脚本命令中的依赖名会直接找到node_modules/.bin下面的对应脚本,而不需要加上路径。
2-6. 举一反三探寻npm run serve
好吧到这了总算知道npm run 并不是那么神秘了,咦 好像搞了半天还没说到,npm run serve 相关的东西,其实这已经讲完了,仔细一想,npm run serve === npm run vue-cli-service serve ,那么node_modules/.bin下面一定有两个vue-cli-service的文件,找找。。。
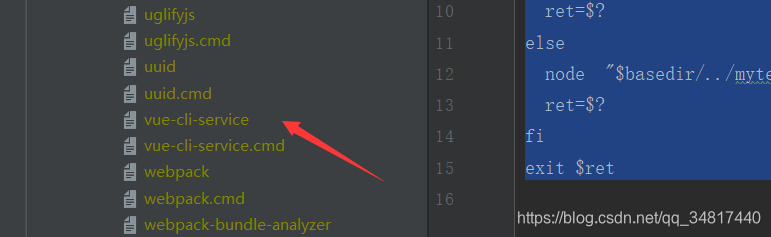
果不其然,再打开看看,他最终执行的js 是什么。打开文件
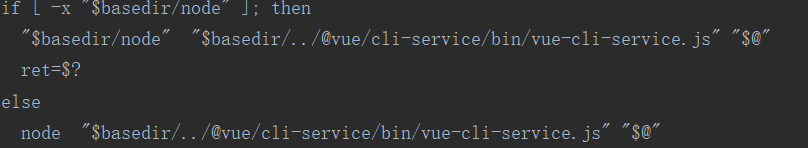
根据路径可以找到node_modules/@vue下对应的 js,
如下:
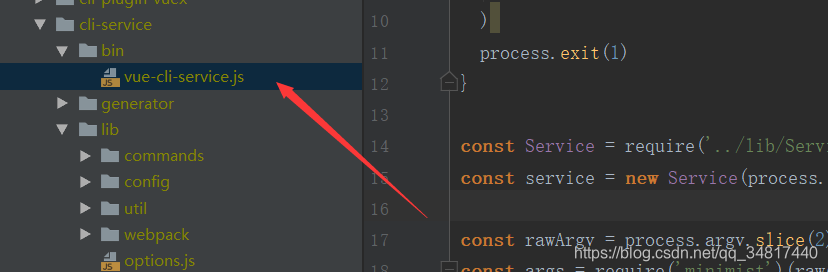
OK, 总算找到了真正的执行者,那这个文件又干了些什么呢,项目就这么启动了?
二、项目编译详解
我们打开这个vue-cli-service.js (代码就不行行详细讲解了,直接借助大佬博客https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000017876208)
1、关于vue-cli-service.js
const semver = require('semver')
const { error } = require('@vue/cli-shared-utils')
const requiredVersion = require('../package.json').engines.node
// 检测node版本是否符合vue-cli运行的需求。不符合则打印错误并退出。
if (!semver.satisfies(process.version, requiredVersion)) {
error(
`You are using Node ${process.version}, but vue-cli-service ` +
`requires Node ${requiredVersion}.\nPlease upgrade your Node version.`
)
process.exit(1)
}
// cli-service的核心类。
const Service = require('../lib/Service')
// 新建一个service的实例。并将项目路径传入。一般我们在项目根路径下运行该cli命令。所以process.cwd()的结果一般是项目根路径
const service = new Service(process.env.VUE_CLI_CONTEXT || process.cwd())
// 参数处理。
const rawArgv = process.argv.slice(2)
const args = require('minimist')(rawArgv, {
boolean: [
// build
'modern',
'report',
'report-json',
'watch',
// serve
'open',
'copy',
'https',
// inspect
'verbose'
]
})
const command = args._[0]
// 将我们执行npm run serve 的serve参数传入service这个实例并启动后续工作。(如果我们运行的是npm run build。那么接收的参数即为build)。
service.run(command, args, rawArgv).catch(err => {
error(err)
process.exit(1)
})
上面js 最后调用了../lib/Service 中的run来进行项目的构建 ,那再去看看 Service.js 又做了些什么
2、关于Service.js
// ...省略import
module.exports = class Service {
constructor (context, { plugins, pkg, inlineOptions, useBuiltIn } = {}) {
process.VUE_CLI_SERVICE = this
this.initialized = false
// 一般是项目根目录路径。
this.context = context
this.inlineOptions = inlineOptions
// webpack相关收集。不是本文重点。所以未列出该方法实现
this.webpackChainFns = []
this.webpackRawConfigFns = []
this.devServerConfigFns = []
//存储的命令。
this.commands = {}
// Folder containing the target package.json for plugins
this.pkgContext = context
// 键值对存储的pakcage.json对象,不是本文重点。所以未列出该方法实现
this.pkg = this.resolvePkg(pkg)
// **这个方法下方需要重点阅读。**
this.plugins = this.resolvePlugins(plugins, useBuiltIn)
// 结果为{build: production, serve: development, ... }。大意是收集插件中的默认配置信息
// 标注build命令主要用于生产环境。
this.modes = this.plugins.reduce((modes, { apply: { defaultModes }}) => {
return Object.assign(modes, defaultModes)
}, {})
}
init (mode = process.env.VUE_CLI_MODE) {
if (this.initialized) {
return
}
this.initialized = true
this.mode = mode
// 加载.env文件中的配置
if (mode) {
this.loadEnv(mode)
}
// load base .env
this.loadEnv()
// 读取用户的配置信息.一般为vue.config.js
const userOptions = this.loadUserOptions()
// 读取项目的配置信息并与用户的配置合并(用户的优先级高)
this.projectOptions = defaultsDeep(userOptions, defaults())
debug('vue:project-config')(this.projectOptions)
// 注册插件。
this.plugins.forEach(({ id, apply }) => {
apply(new PluginAPI(id, this), this.projectOptions)
})
// wepback相关配置收集
if (this.projectOptions.chainWebpack) {
this.webpackChainFns.push(this.projectOptions.chainWebpack)
}
if (this.projectOptions.configureWebpack) {
this.webpackRawConfigFns.push(this.projectOptions.configureWebpack)
}
}
resolvePlugins (inlinePlugins, useBuiltIn) {
const idToPlugin = id => ({
id: id.replace(/^.\//, 'built-in:'),
apply: require(id)
})
let plugins
// 主要是这里。map得到的每个插件都是一个{id, apply的形式}
// 其中require(id)将直接import每个插件的默认导出。
// 每个插件的导出api为
// module.exports = (PluginAPIInstance,projectOptions) => {
// PluginAPIInstance.registerCommand('cmdName(例如npm run serve中的serve)', args => {
// // 根据命令行收到的参数,执行该插件的业务逻辑
// })
// // 业务逻辑需要的其他函数
//}
// 注意着里是先在构造函数中resolve了插件。然后再run->init->方法中将命令,通过这里的的apply方法,
// 将插件对应的命令注册到了service实例。
const builtInPlugins = [
'./commands/serve',
'./commands/build',
'./commands/inspect',
'./commands/help',
// config plugins are order sensitive
'./config/base',
'./config/css',
'./config/dev',
'./config/prod',
'./config/app'
].map(idToPlugin)
// inlinePlugins与非inline得处理。默认生成的项目直接运行时候,除了上述数组的插件['./commands/serve'...]外,还会有
// ['@vue/cli-plugin-babel','@vue/cli-plugin-eslint','@vue/cli-service']。
// 处理结果是两者的合并,细节省略。
if (inlinePlugins) {
//...
} else {
//...默认走这条路线
plugins = builtInPlugins.concat(projectPlugins)
}
// Local plugins 处理package.json中引入插件的形式,具体代码省略。
return plugins
}
async run (name, args = {}, rawArgv = []) {
// mode是dev还是prod?
const mode = args.mode || (name === 'build' && args.watch ? 'development' : this.modes[name])
// 收集环境变量、插件、用户配置
this.init(mode)
args._ = args._ || []
let command = this.commands[name]
if (!command && name) {
error(`command "${name}" does not exist.`)
process.exit(1)
}
if (!command || args.help) {
command = this.commands.help
} else {
args._.shift() // remove command itself
rawArgv.shift()
}
// 执行命令。例如vue-cli-service serve 则,执行serve命令。
const { fn } = command
return fn(args, rawArgv)
}
// 收集vue.config.js中的用户配置。并以对象形式返回。
loadUserOptions () {
// 此处代码省略,可以简单理解为
// require(vue.config.js)
return resolved
}
}
2-1. command 中的fn
看到上面说的
// 执行命令。例如vue-cli-service serve 则,执行serve命令。
const { fn } = command
return fn(args, rawArgv)
其实还是不明吧,command中他究竟执行了个什么操作,那不妨来个console
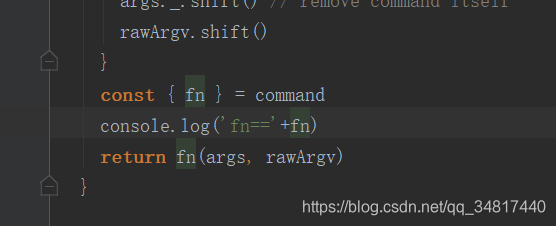
我们再运行下 run build 来看究竟,一执行屏幕就打印了一异步函数
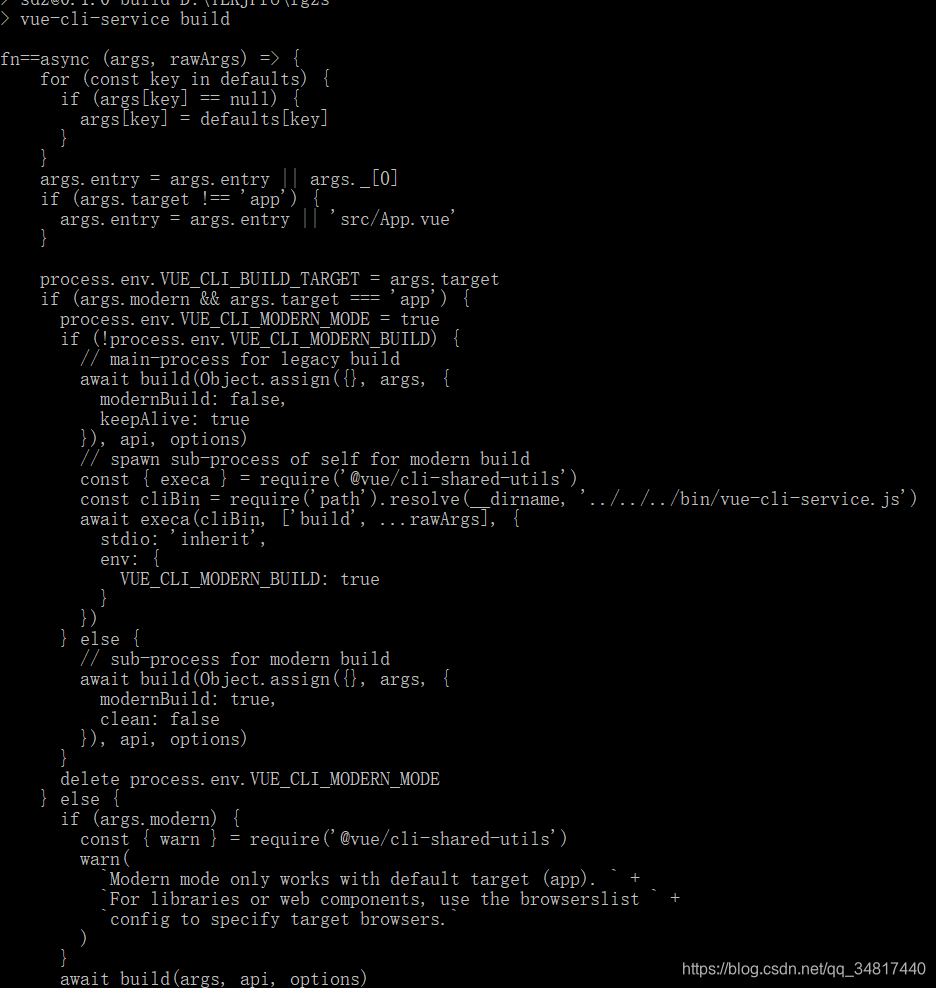
咦这是哪里的,不要忘记了,上面说的在运行npm run build 时我们给他传入了一个build的参数
而在代码的解析中我们知道,在constructor构造时就将其所需外部plugin编译到了command中
所以根据builtInPlugins这里的操作,我们就能找到这个异步函数是在commands/build/index.js中, 到该文件一看就都明白了
接下来还有一个是 PluginAPI 进行插件编译的js
3、关于PluginAPI
class PluginAPI {
constructor (id, service) {
this.id = id
this.service = service
}
// 在service的init方法中
// 该函数会被调用,调用处如下。
// // apply plugins.
// 这里的apply就是插件暴露出来的函数。该函数将PluginAPI实例和项目配置信息(例如vue.config.js)作为参数传入
// 通过PluginAPIInstance.registerCommand方法,将命令注册到service实例。
// this.plugins.forEach(({ id, apply }) => {
// apply(new PluginAPI(id, this), this.projectOptions)
// })
registerCommand (name, opts, fn) {
if (typeof opts === 'function') {
fn = opts
opts = null
}
this.service.commands[name] = { fn, opts: opts || {}}
}
}
module.exports = PluginAPI
这些文件所有的操作加起来就完成了我们vue项目的构建,直接浏览器输入地址就可以看见效果了(一步步操作看完,是否感觉还是蛮复杂的呢- -哪有什么岁月静好,不过是有人替你负重前行罢了),欢迎加群一起交流
npm run serve/build 背后的真实操作的更多相关文章
- npm run dev/build/serve
1.ERR引发的思考 npm run dev npm ERR! missing script: dev npm ERR! A complete log of this run can be found ...
- npm run dev 和 npm run serve
1.ERR引发的思考 创建好的 vue 项目直接执行 vue run dev 报错?运行 vue run serve 就可以启动...如下 npm run dev npm ERR! missing s ...
- 在终端输入npm run serve时出现npm ERR! code ELIFECYCLE npm ERR! errno 1 npm ERR! test_vue_0613@1.0.0 dev: 错误的解决方法
在vscode终端使用命令 npm run serve 的时候报错 错误原因在于由于文件 node_modules 太大,在项目上传时有些人会删掉 导致我们下载的项目中缺少这个文件 在尝试把自己项目的 ...
- npm run serve 报错问题 (npm ERR! code ELIFECYCLE)
运行 npm cache clean --force删除 node_modules删除 package-lock.json运行 npm install最后 npm run serve
- vue工程npm run serve/start/dev启动时,node_modules文件报:Cannot read property 'range' of null 错误
改问题是"babel-eslint"版本更新问题导致的: 给大家一个最简单粗暴的解决方案: 在项目里找到对应的工程:直接删除里面的node_modules文件夹,然后重新npm i ...
- npm run serve修改为npm run dev
找到package.json文件,打开文件找到 "serve": "vue-cli-service serve" 这一行,把前面的 serve 修改 dev ...
- npm run build 时的 warning
entrypoint size limit: The following entrypoint(s) combined asset size exceeds the recommended limit ...
- React项目配置npm run build命令分环境打包
使用create-react-app脚手架创建的项目默认隐藏了webpack等配置文件信息,使用npm run eject命令暴露这些隐藏的配置文件信息 项目默认有两个环境:开发环境(npm star ...
- npm run dev 报错:missing script:dev
一.问题: 今天在运行vue项目时,在mac终端输入npm run dev,结果报错: 翻译是: npm错误:缺少script:dev npm错误:完整路径见:users/mymac/ .npm/_l ...
- 三面面试官:运行 npm run xxx 的时候发生了什么?
事情是这样的,直接开讲 面试官:npm run xxx的时候,发生了什么?讲的越详细越好. 我(心想,简单啊): 首先,DNS 解析,将域名解析成 IP 地址,然后 TCP 连接,TCP 三次握手.. ...
随机推荐
- 《程序员的自我修养》学习笔记——不一样的hello world【第四弹】
不一样的hello world Linux 的系统调用 通过glibc提供的库函数 glibc 是 Linux 下使用的开源的标准 C 库,它是 GNU 发布的 libc 库,即运行时库.glibc ...
- 第四朵“云”!全托管的时序数据云平台 TDengine Cloud 正式支持阿里云
3 月 13 日,全托管的时序数据处理云服务平台 TDengine Cloud 正式支持阿里云,这是继 Microsoft Azure.AWS.Google Cloud 后 TDengine Clou ...
- C# 动态创建类,动态创建表,支持多库的数据库维护方案
1.创建表 SqlSugar支持了3种模式的建表,非常的灵活,可以MYSQL MSSQL ORACLE等用同一语法创建数据库,不需要考虑数据库的兼容性 中间标准: string 大文本 5.1.3. ...
- unable to find Qt5Core.dll on PATH(已解决,超简单)
不久之前我在引用PyQt5库的时候总是出现unable to find Qt5Core.dll on PATH的错误,错误如下: 百度上都是说什么打包的时候出错,然后加上一句话,我试过以后也不行,后来 ...
- 基于Admin.NET框架的前端的一些改进和代码生成处理(1)
Admin.NET 是一套基于Furion/.NET 6实现的通用管理平台,模块插件式开发,框架包含了常规的权限管理.字典等管理模块,以及一些Vue3的Demo案例,框架前后端分离.后端基于基于Fur ...
- flask-sqlalchemy入门
Flask-SQLAlchemy 是一个为 Flask 应用增加 SQLAlchemy 支持的扩展.它致力于简化在 Flask 中 SQLAlchemy 的使用.SQLAlchemy 是目前pytho ...
- pywin32获取键盘状态,附带键位码
import win32apiimport win32con win32con.VK_CAPITAL # 20获取Caps Lock键编码 win32api.GetKeyState(win32con. ...
- [Java SE/JDK]Intellij IDEA中设置JDK版本
1 Intellij IDEA 修改JDK版本 第1步:配置JDK环境变量 装好JDK之后,要添加一个环境变量:JAVA_HOME 第2步:修改Idea配置 由Maven决定的版本 <build ...
- Unity学习笔记01 —— 编辑器
场景Scene 基本操作 按下鼠标滚轮拖动场景,滑动滚轮缩放场景. 鼠标右键旋转场景,点击""后,通过左键移动场景. 点击右键同时按下W/S/A/D/Q/E键可实现场景漫游. 在S ...
- Notion AI:门槛更低的ChatGPT Plus
[2023年3月27日]由于接口成本的问题,如今的大部分应用应该都只会建立在GPT-3/ChatGPT接口的基础上,所以想要体验GPT-4,还是得尊贵的ChatGPT Plus. 前段日子体验了Not ...
