Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十七章:拾取
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十七章:拾取
代码工程地址:
https://github.com/jiabaodan/Direct12BookReadingNotes
学习目标
学习如何实现拾取算法,我们将它分解为下面几个步骤:
- 当点击屏幕上s点时,计算对应的透视窗口上的点p;
- 在视景坐标系下计算拾取射线;
- 将射线和要进行检测的模型变换到同一个坐标系下;
- 检测模型是否和射线相交,取深度值最小的那个。
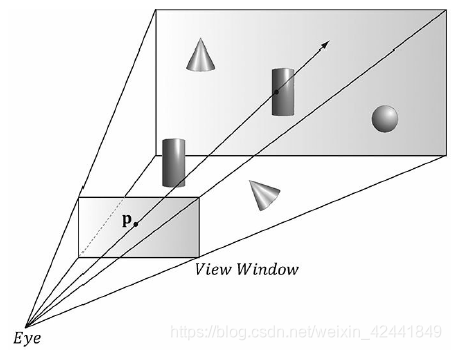
1 屏幕透视窗口的变换
第一个需要变换的是,从点击的屏幕变换到NDC,回顾之前从视景坐标系变换到NDC的变换矩阵:
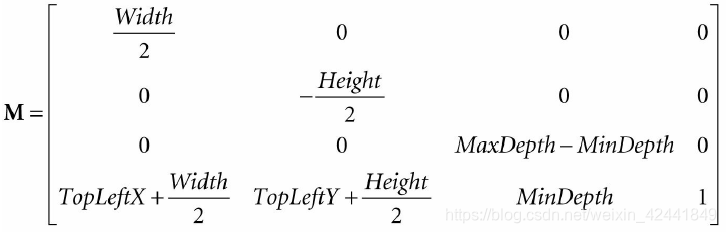
它是通过D3D12_VIEWPORT结构中的数据组成:
typedef struct D3D12_VIEWPORT
{
FLOAT TopLeftX;
FLOAT TopLeftY;
FLOAT Width;
FLOAT Height;
FLOAT MinDepth;
FLOAT MaxDepth;
} D3D12_VIEWPORT;
一般情况下视景是整个后置缓冲,深度缓冲范围是0~1,所以TopLeftX = 0, TopLeftY = 0, MinDepth = 0, MaxDepth = 1, Width = w, Height = h,那么变换矩阵可以简化为:
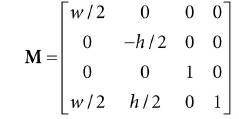
现在令pndc = (xndc, yndc, zndc, 1)是NDC的一个点(−1 ≤ xndc ≤ 1, −1 ≤ yndc ≤ 1, and 0 ≤ zndc ≤ 1),变换pndc到屏幕坐标系:
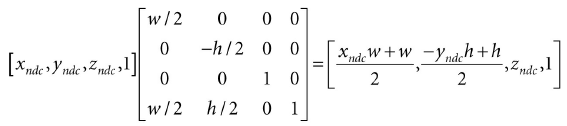
我们不修改Z值,因为拾取计算不关系深度值在哪个坐标系,那么2D屏幕上的点ps = (xs, ys)就对应于NDC下的pndc:
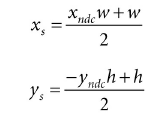
上面的方式通过NDC点找到了屏幕坐标系下的点ps,但是拾取算法中我们需要通过屏幕上的点找打NDC下的点:
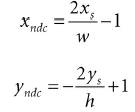
现在我们拥有了NDC下面的点,但是为了发射射线,我们需要得到视景坐标系下面的点,回顾第五章6.3.3,我们映射点从视景坐标系到NDC是通过x坐标除以宽高比r:
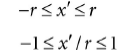
所以直接在X坐标上乘以宽高比即可:
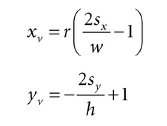
再回顾第五章6.3.1,透视窗口是距离原点d=(α2)d = (\frac{\alpha}{2} )d=(2α),其中a是竖直方向上的角度。那么我们就可以通过点(xv, yv, d )发射射线,只要计算出d:
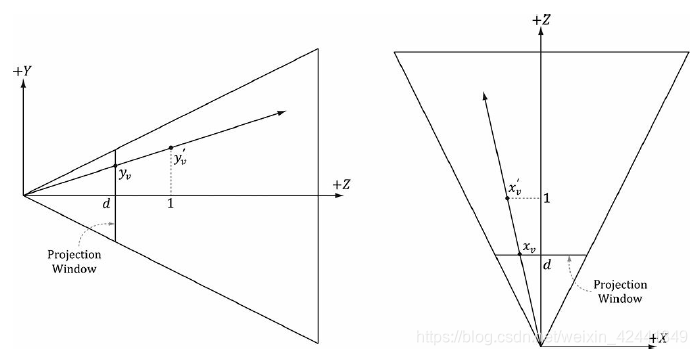
通过相似三角形:
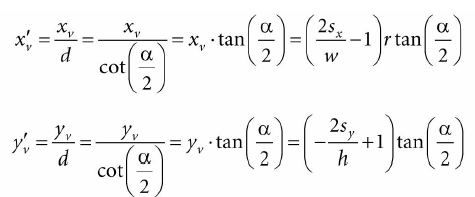
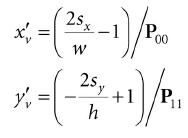
那么我们可以通过点(x′v, y′v, 1)发射射线,和(xv, yv, d )发射的射线是一样的,在视景坐标系下计算发射射线的代码如下:
void PickingApp::Pick(int sx, int sy)
{
XMFLOAT4X4 P = mCamera.GetProj4x4f();
// Compute picking ray in view space.
float vx = (+2.0f*sx / mClientWidth - 1.0f) / P(0, 0);
float vy = (-2.0f*sy / mClientHeight + 1.0f) / P(1, 1);
// Ray definition in view space.
XMVECTOR rayOrigin = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
XMVECTOR rayDir = XMVectorSet(vx, vy, 1.0f, 0.0f);
2 世界/局部坐标系拾取射线
如果rv(t) = q + tu是世界坐标系下的拾取射线,V是世界坐标系到视景坐标系的变换矩阵,那么世界坐标系下的拾取射线为:
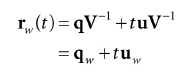
世界坐标系拾取射线对于在世界坐标系下定义的物体比较有用,但是大部分情况下,物体是在它自己的局部坐标系下定义的。如果W是局部坐标系到世界坐标系的变换矩阵,那么局部坐标系下的射线为:
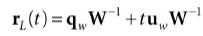
如果在世界坐标系下做检测,就需要将物体都变换到世界坐标系下;通常情况下物体拥有很多顶点,都变换过去的计算量非常大,所以只把射线变换到每个物体的局部坐标系下做检测就比较高效。
下面的代码展示了将一个射线变换到一个物体的局部坐标系:
// Assume nothing is picked to start, so the picked render-item is invisible.
mPickedRitem->Visible = false;
// Check if we picked an opaque render item. A real app might keep a separate
// "picking list" of objects that can be selected.
for(auto ri : mRitemLayer[(int)RenderLayer::Opaque])
{
auto geo = ri->Geo;
// Skip invisible render-items.
if(ri->Visible == false)
continue;
XMMATRIX V = mCamera.GetView();
XMMATRIX invView = XMMatrixInverse(&XMMatrixDeterminant(V), V);
XMMATRIX W = XMLoadFloat4x4(&ri->World);
XMMATRIX invWorld = XMMatrixInverse(&XMMatrixDeterminant(W), W);
// Tranform ray to vi space of Mesh.
XMMATRIX toLocal = XMMatrixMultiply(invView, invWorld);
rayOrigin = XMVector3TransformCoord(rayOrigin, toLocal);
rayDir = XMVector3TransformNormal(rayDir, toLocal);
// Make the ray direction unit length for the intersection tests.
rayDir = XMVector3Normalize(rayDir);
XMVector3TransformNormal和XMVector3TransformCoord函数都是传入3D向量,但是XMVector3TransformNormal里w = 0,XMVector3TransformCoord里w=1,所以XMVector3TransformNormal用来变换向量,XMVector3TransformCoord用来变换点。
3 射线/网格的相交检测
下面的代码展示了射线和三角形的相交检测,如果有多个三角形相交,取最近的那个三角形:
// If we hit the bounding box of the Mesh, then we might have
// picked a Mesh triangle, so do the ray/triangle tests.
//
// If we did not hit the bounding box, then it is impossible that we hit
// the Mesh, so do not waste effort doing ray/triangle tests.
float tmin = 0.0f;
if(ri->Bounds.Intersects(rayOrigin, rayDir, tmin))
{
// NOTE: For the demo, we know what to cast the vertex/index data to.
// If we were mixing formats, some metadata would be needed to figure
// out what to cast it to.
auto vertices = (Vertex*)geo->VertexBufferCPU->GetBufferPointer();
auto indices = (std::uint32_t*)geo->IndexBufferCPU->GetBufferPointer();
UINT triCount = ri->IndexCount / 3;
// Find the nearest ray/triangle intersection.
tmin = MathHelper::Infinity;
for(UINT i = 0; i < triCount; ++i)
{
// Indices for this triangle.
UINT i0 = indices[i * 3 + 0];
UINT i1 = indices[i * 3 + 1];
UINT i2 = indices[i * 3 + 2];
// Vertices for this triangle.
XMVECTOR v0 = XMLoadFloat3(&vertices[i0].Pos);
XMVECTOR v1 = XMLoadFloat3(&vertices[i1].Pos);
XMVECTOR v2 = XMLoadFloat3(&vertices[i2].Pos);
// We have to iterate over all the triangles in order to find
// the nearest intersection.
float t = 0.0f;
if(TriangleTests::Intersects(rayOrigin, rayDir, v0, v1, v2, t))
{
if(t < tmin)
{
// This is the new nearest picked triangle.
tmin = t;
UINT pickedTriangle = i;
// Set a render item to the picked triangle so that
// we can render it with a special "highlight" material.
mPickedRitem->Visible = true;
mPickedRitem->IndexCount = 3;
mPickedRitem->BaseVertexLocation = 0;
// Picked render item needs same world matrix as object picked.
mPickedRitem->World = ri->World;
mPickedRitem->NumFramesDirty = gNumFrameResources;
// Offset to the picked triangle in the mesh index buffer.
mPickedRitem->StartIndexLocation = 3 * pickedTriangle;
}
}
}
}
上面的算法中,我们先进行了物体的包围体的检测,这样可以对性能进行很大的优化;因为只有通过包围体检测的物体,才进行逐三角形的相交检测。
观察上面的拾取,我们使用系统内存拷贝保存网格几何数据在MeshGeometry类中。这是因为我们无法读取vertex/index缓冲。
3.1 射线/AABB的相交检测
DirectX碰撞检测库中BoundingBox::Intersects函数可以用来检测,返回true就代表已经相交:
bool XM_CALLCONV BoundingBox::Intersects(
FXMVECTOR Origin, // ray origin
FXMVECTOR Direction, // ray direction (must be unit length)
float& Dist ); const // ray intersection parameter
给出射线r(t) = q + tu,最后一个参数就是t0计算出点P:
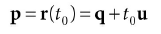
3.2 射线/球体的相交检测
DirectX碰撞检测库中的函数:
bool XM_CALLCONV BoundingSphere::Intersects(
FXMVECTOR Origin,
FXMVECTOR Direction,
float& Dist ); const
3.3 射线/三角形的相交检测
DirectX碰撞检测库中的函数:
bool XM_CALLCONV TriangleTests::Intersects(
FXMVECTOR Origin, // ray origin
FXMVECTOR Direction, // ray direction (unit length)
FXMVECTOR V0, // triangle vertex v0
GXMVECTOR V1, // triangle vertex v1
HXMVECTOR V2, // triangle vertex v2
float& Dist ); // ray intersection parameter
4 Demo应用
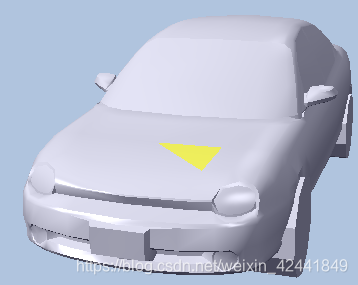
本例子中渲染了一个小车,可以让用户使用右键拾取网格中的三角形。为了实现拾取的三角形的高亮显示,本例中的Render-Item和以前的有些不同,只能部分在初始化中填充。我们添加了一个Visible属性,不可见的Render-Item将不绘制。下面的代码展示了如何根据拾取设置Render-Item属性:
// Cache a pointer to the render-item of the picked
// triangle in the PickingApp class.
RenderItem* mPickedRitem;
if(TriangleTests::Intersects(rayOrigin, rayDir, v0, v1, v2, t))
{
if(t < tmin)
{
// This is the new nearest picked triangle.
tmin = t;
UINT pickedTriangle = i;
// Set a render item to the picked triangle so that
// we can render it with a special "highlight" material.
mPickedRitem->Visible = true;
mPickedRitem->IndexCount = 3;
mPickedRitem->BaseVertexLocation = 0;
// Picked render item needs same world matrix as object picked.
mPickedRitem->World = ri->World;
mPickedRitem->NumFramesDirty = gNumFrameResources;
// Offset to the picked triangle in the mesh index buffer.
mPickedRitem->StartIndexLocation = 3 * pickedTriangle;
}
}
这个render-item是在绘制完不透明render-item后绘制的,使用一个高亮度的PSO。需要注意的是深度测试使用的是D3D12_COMPARISON_FUNC_LESS_EQUAL,因为如果使用D3D12_COMPARISON_FUNC_LESS会导致深度测试失败而不绘制:
DrawRenderItems(mCommandList.Get(), mRitemLayer[(int)RenderLayer::Opaque]);
mCommandList->SetPipelineState(mPSOs["highlight"].Get());
DrawRenderItems(mCommandList.Get(), mRitemLayer[(int)RenderLayer::Highlight]);
5 总结
- 拾取技术是判定用户在屏幕上点击的2D投射的物体,与之对应的3D物体;
- 拾取射线是从视景坐标系的原点发射出的一条射线,经过透视窗口上与用户点击屏幕的点对应的点;
- 我们可以用过变换射线的原点和方向向量来变换射线所在的坐标系(顶点w = 1,向量w = 0);
- 为了判定射线和物体是否相交,我们对物体的每一个三角形进行射线/三角形判定,如果有多个三角形相交,我们选择最近的那一个;
- 为了优化考虑,我们先进行物体包围体检测,只有检测通过的物体再遍历每个三角形检测。
6 练习
调查八叉树,优化拾取检测;之前提到的截头锥体剔除,也可以优化拾取检测。
(物理和碰撞也同理)
Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十七章:拾取的更多相关文章
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十三章:角色动画
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十三章:角色动画 学习目标 熟悉蒙皮动画的术语: 学习网格层级变换 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十一章:环境光遮蔽(AMBIENT OCCLUSION)
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第二十一章:环境光遮蔽(AMBIENT OCCLUSION) 学习目标 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十三章:计算着色器(The Compute Shader)
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十三章:计算着色器(The Compute Shader) 代码工程 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十一章:模板测试
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第十一章:模板测试 代码工程地址: https://github.co ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第七章:在Direct3D中绘制(二)
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第七章:在Direct3D中绘制(二) 代码工程地址: https:/ ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第六章:在Direct3D中绘制
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第六章:在Direct3D中绘制 代码工程地址: https://gi ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第五章:渲染流水线
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第五章:渲染流水线 学习目标 了解几个用以表达真实场景的标志和2D图像 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第四章:Direct 3D初始化
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第四章:Direct 3D初始化 学习目标 对Direct 3D编程在 ...
- Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第三章:变换
原文:Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 12 学习笔记之 --- 第三章:变换 学习目标 理解如何用矩阵表示线性变换和仿射变换: 学习在 ...
随机推荐
- 你真的会用Action的模型绑定吗?
在QQ群或者一些程序的交流平台,经常会有人问:我怎么传一个数组在Action中接收.我传的数组为什么Action的model中接收不到.或者我在ajax的data中设置了一些数组,为什么后台还是接收不 ...
- Leetcode82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II删除排序链表中的重复元素2
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现 的数字. 示例 1: 输入: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5 输出: 1-&g ...
- Redis源码解析:12AOF持久化
除了RDB持久化功能之外,Redis还提供了AOF(AppendOnly File)持久化功能.与RDB持久化通过保存数据库中的键值对来记录数据库状态不同,AOF持久化是通过保存Redis服务器所执行 ...
- 洛谷P4022 熟悉的文章
题意:给定一个串集合s,每次给定一个串t,询问一个最大的L,使得存在一种划分能把t划分成若干个子串, 其中好的子串总长不小于0.9|t|.好的子串定义为长度不小于L且是s中某一个串的子串. 解:发现这 ...
- bzoj 1179 [Apio2009]Atm——SCC缩点+spfa
题目:https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1179 显然SCC缩点. 然后准备倒着拓扑序推到st,结果WA. 听TJ说dj求最长路会发生不 ...
- PHP的安全性问题,你能说得上几个?
一.SQL注入 所谓SQL注入,就是通过把SQL命令插入到Web表单提交或输入域名或页面请求的查询字符串,最终达到欺骗服务器执行恶意的SQL命令.具体来说,它是利用现有应用程序,将(恶意)的SQL命令 ...
- SpringBoot集成lombook让代码更简洁
1)添加lombok依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>l ...
- nginx链接末尾自动补全斜杠
放在locaation里边就行 if (-d $request_filename){ rewrite ^(.*[^/])$ $/ permanent;#加斜杠 } 这样,nginx就会进行判断了,如果 ...
- round 469
第一次打codeforces,还是太菜了 代码全部来自大神void_f C #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <c ...
- 2019.8.10 NOIP模拟测试16 反思总结【基本更新完毕忽视咕咕咕】
一如既往先放代码,我还没开始改… 改完T1滚过来了,先把T1T2的题解写了[颓博客啊] 今天下午就要走了,没想到还有送行的饯别礼,真是欣喜万分[并没有] 早上刚码完前面的总结,带着不怎么有希望的心情开 ...
