[LeetCode] 802. Find Eventual Safe States 找到最终的安全状态
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. If we reach a node that is terminal (that is, it has no outgoing directed edges), we stop.
Now, say our starting node is eventually safe if and only if we must eventually walk to a terminal node. More specifically, there exists a natural number K so that for any choice of where to walk, we must have stopped at a terminal node in less than K steps.
Which nodes are eventually safe? Return them as an array in sorted order.
The directed graph has N nodes with labels 0, 1, ..., N-1, where N is the length of graph. The graph is given in the following form: graph[i] is a list of labels j such that (i, j) is a directed edge of the graph.
Example:
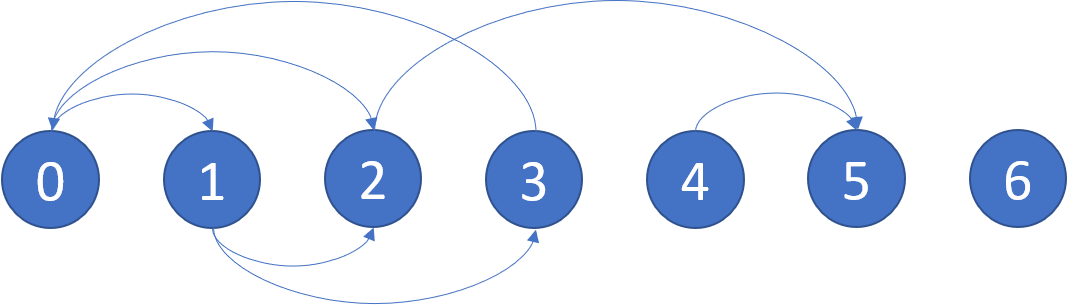
Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]]
Output: [2,4,5,6]
Here is a diagram of the above graph.
Note:
graphwill have length at most10000.- The number of edges in the graph will not exceed
32000. - Each
graph[i]will be a sorted list of different integers, chosen within the range[0, graph.length - 1].
在一个有向图中,如果从一个节点出发走过很多步之后到达了终点(出度为0的节点,无路可走了),则认为这个节点是最终安全的节点。如果根本停不下来,那就是在一个环上,就是不安全节点。要在自然数K步内停止,到达安全节点,返回满足要求的排序好的所有安全节点的索引值。实质是在一个有向图中找出不在环路上的节点。
解法:DFS,可采用染色的方法对节点进行分类:0表示该结点还没有被访问;1表示已经被访问过了,并且发现是safe的;2表示被访问过了,但发现是unsafe的。我们采用DFS的方法进行遍历,并返回该结点是否是safe的:如果发现它已经被访问过了,则直接返回是否是safe的标记;否则就首先将其标记为unsafe的,然后进行DFS搜索(此时该结点会处在DFS的路径上,所以后面的DFS一旦到了该结点,就会被认为是形成了环,所以直接返回false)。当整个DFS的搜索都已经结束,并且都没有发现该结点处在环上时,说明该结点是safe的,所以此时将其最终标记为safe即可。空间复杂度是O(n),时间复杂度是O(n)
解法2: 迭代,记录下每个节点的出度,如果出度为0那必然是环路外的节点,然后将该点以及指向该点的边删除,继续寻找出度为0的点
class Solution {
public List<Integer> eventualSafeNodes(int[][] graph) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(graph == null || graph.length == 0) return res;
int nodeCount = graph.length;
int[] color = new int[nodeCount];
for(int i = 0;i < nodeCount;i++){
if(dfs(graph, i, color)) res.add(i);
}
return res;
}
public boolean dfs(int[][] graph, int start, int[] color){
if(color[start] != 0) return color[start] == 1;
color[start] = 2;
for(int newNode : graph[start]){
if(!dfs(graph, newNode, color)) return false;
}
color[start] = 1;
return true;
}
}
Python:
def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
n = len(graph)
out_degree = collections.defaultdict(int)
in_nodes = collections.defaultdict(list)
queue = []
ret = []
for i in range(n):
out_degree[i] = len(graph[i])
if out_degree[i]==0:
queue.append(i)
for j in graph[i]:
in_nodes[j].append(i)
while queue:
term_node = queue.pop(0)
ret.append(term_node)
for in_node in in_nodes[term_node]:
out_degree[in_node] -= 1
if out_degree[in_node]==0:
queue.append(in_node)
return sorted(ret)
Python:
# Time: O(|V| + |E|)
# Space: O(|V|)
import collections class Solution(object):
def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
WHITE, GRAY, BLACK = 0, 1, 2 def dfs(graph, node, lookup):
if lookup[node] != WHITE:
return lookup[node] == BLACK
lookup[node] = GRAY
for child in graph[node]:
if lookup[child] == BLACK:
continue
if lookup[child] == GRAY or \
not dfs(graph, child, lookup):
return False
lookup[node] = BLACK
return True lookup = collections.defaultdict(int)
return filter(lambda node: dfs(graph, node, lookup), xrange(len(graph)))
Python:
class Solution(object):
def eventualSafeNodes(self, graph):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not graph: return [] n = len(graph)
# 用字段存储每个节点的父节点
d = {u:[] for u in range(n)}
degree = [0] * n
for u in range(n):
for v in graph[u]:
d[v].append(u)
degree[u] = len(graph[u]) Q = [u for u in range(n) if degree[u]==0]
res = []
while Q:
node = Q.pop()
res.append(node)
for nodes in d[node]:
degree[nodes] -= 1
if degree[nodes] == 0:
Q.append(nodes)
return sorted(res)
C++:
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> eventualSafeNodes(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
vector<int> res;
if (graph.size() == 0) {
return res;
}
int size = graph.size();
vector<int> color(size, 0); // 0: not visited; 1: safe; 2: unsafe.
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
if (dfs(graph, i, color)) { // the i-th node is safe
res.push_back(i);
}
}
return res;
}
private:
bool dfs(vector<vector<int>> &graph, int start, vector<int> &color) {
if (color[start] != 0) {
return color[start] == 1;
}
color[start] = 2; // mark it as unsafe because it is on the path
for (int next : graph[start]) {
if (!dfs(graph, next, color)) {
return false;
}
}
color[start] = 1; // mark it as safe because no loop is found
return true;
}
};
All LeetCode Questions List 题目汇总
[LeetCode] 802. Find Eventual Safe States 找到最终的安全状态的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] Find Eventual Safe States 找到最终的安全状态
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. ...
- LeetCode 802. Find Eventual Safe States
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/find-eventual-safe-states/ 题目: In a directed graph, we start a ...
- 【LeetCode】802. Find Eventual Safe States 解题报告(Python)
[LeetCode]802. Find Eventual Safe States 解题报告(Python) 作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemi ...
- LC 802. Find Eventual Safe States
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. ...
- 【leetcode】802. Find Eventual Safe States
题目如下: 解题思路:本题大多数人采用DFS的方法,这里我用的是另一种方法.我的思路是建立一次初始值为空的safe数组,然后遍历graph,找到graph[i]中所有元素都在safe中的元素,把i加入 ...
- 802. Find Eventual Safe States
https://leetcode.com/problems/find-eventual-safe-states/description/ class Solution { public: vector ...
- Java实现 LeetCode 802 找到最终的安全状态 (DFS)
802. 找到最终的安全状态 在有向图中, 我们从某个节点和每个转向处开始, 沿着图的有向边走. 如果我们到达的节点是终点 (即它没有连出的有向边), 我们停止. 现在, 如果我们最后能走到终点,那么 ...
- [Swift]LeetCode802. 找到最终的安全状态 | Find Eventual Safe States
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. ...
- LeetCode 277. Find the Celebrity (找到明星)$
Suppose you are at a party with n people (labeled from 0 to n - 1) and among them, there may exist o ...
随机推荐
- 微信小程序和APP优劣势大对比
小程序的优势: 1. 无需下载,随走随关 2. 功能丰富,体验更简便 3. 接口众多,可以进行不断的开发 4. 流量入口大,背靠日活9.6亿的微信 5. 有强大的微信生态环境 小程序对比APP的好处: ...
- P1197 [JSOI2008]星球大战[并查集+图论]
题目来源:洛谷 题目描述 很久以前,在一个遥远的星系,一个黑暗的帝国靠着它的超级武器统治着整个星系. 某一天,凭着一个偶然的机遇,一支反抗军摧毁了帝国的超级武器,并攻下了星系中几乎所有的星球.这些星球 ...
- 如何使用git,进行项目的管理
1.首先,现在git上个创建一个项目, 2.然后在本地创建一个springboot工程 3.使用git命令 git init 将这个springboot项目交给git进行管理 4.创建一个dev分 ...
- luoguP2768: 珍珠项链(矩阵乘法优化DP)
题意:有K种珍珠,每种N颗,求长度为1~N的项链,包含K种珍珠的项链种类数.N<=1e9, K<=30; 思路:矩阵快速幂,加个1累加前缀和即可. #include<bits/std ...
- 基于C+OpenCV4.0的LineSegmentDetector算法实现
简单记录LSD算法的实现过程,当做备忘录用,如有问题欢迎指出和讨论 LSD的基本实现流程是计算出图像的梯度和场方向,然后对梯度进行排序,然后从大到小进行区域增长,之后对增长得到的区域求最小外接矩形,如 ...
- 使用docker 实现MySQL主从同步/读写分离
1. 利用 docker 实现 mysql 主从同步 / 读写分离 为了保证数据的完整和安全,mysql 设计了主从同步,一个挂掉还可以用另个.最近重构论坛,想来改成主从吧.担心失误,就先拿 dock ...
- learning scala akka actorySystem create and close
package com.example import akka.actor.ActorSystem import scala.util.{Failure, Success} import scala. ...
- dinoql 使用graphql 语法查询javascript objects
dinoql 是一个不错的基于graphql 语法查询javascript objects 的工具包,包含以下特性 graphql 语法(很灵活) 安全的访问(当keys 不存在的时候,不会抛出运行时 ...
- Mongo 安装及基本操作
一. 安装 Mongo文档: https://docs.mongodb.com/v3.6/administration/install-enterprise-linux/ Linux mongo的配置 ...
- 【luoguP1414]】又是毕业季II
题目链接 \(solution\) 暴力求每个数有多少个倍数,从大到小,数\(i\)的倍数有\(f_i\)个,那么选\(1\)~\(f_i\)个同学的答案可以为\(i\),取第一次更新的答案最大 #i ...
