Light OJ 1199 - Partitioning Game (博弈sg函数)
Time Limit:4000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu
Description
Alice and Bob are playing a strange game. The rules of the game are:
- Initially there are n piles.
- A pile is formed by some cells.
- Alice starts the game and they alternate turns.
- In each tern a player can pick any pile and divide it into two unequal piles.
- If a player cannot do so, he/she loses the game.
Now you are given the number of cells in each of the piles, you have to find the winner of the game if both of them play optimally.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 1000), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case starts with a line containing an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100). The next line contains n integers, where the ith integer denotes the number of cells in the ith pile. You can assume that the number of cells in each pile is between 1 and 10000.
Output
For each case, print the case number and 'Alice' or 'Bob' depending on the winner of the game.
Sample Input
3
1
4
3
1 2 3
1
7
Sample Output
Case 1: Bob
Case 2: Alice
Case 3: Bob
题意:有n堆石子(1<=n<=100),每一堆分别有xi个石子(1<=xi<=10000),
一次操作可以使一堆石子变成两堆数目不相等的石子,
最后不能操作的算输,问先手胜还是后手胜。
思路:n堆石子相互独立,所以可以应用SG定理,只需要算出一堆石子的SG函数。
一堆石子(假设有x个)的后继状态可以枚举出来,分别是{1,x-1},{2,x-2},...,{(x-1)/2,x-(x-1)/2},
一堆石子分成的两堆石子又相互独立,再次应用SG定理。
所以SG(x) = mex{ SG(1)^SG(x-1), SG(2)^SG(x-2),..., SG((x-1)/2)^SG(x-(x-1)/2) },
最后的答案是SG(x1)^SG(x2)^...^SG(xn)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int sg[]= {};
bool vis[];
int t,cas=;
void get()
{
memset(sg,,sizeof(sg));
for(int i=; i<=; i++) //i=0相当于空石子堆 不符合题意
{
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
for(int j=; j+j<i; j++) //j=0相当于没分 j=i/2 相当于分成相等的两堆 这两种情况都是不可以的
vis[sg[j]^sg[i-j]]=;
for(int x=; x<=; x++)
if(!vis[x])
{
sg[i]=x;
break; //一定别忘了break
}
}
}
void pra()
{
printf("Case %d: Alice\n",cas++);
}
void prb()
{
printf("Case %d: Bob\n",cas++);
}
int main()
{
get();
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n,data,ans=;
cin>>n;
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
{
cin>>data;
ans^=sg[data]; //是sg[data]不是data 对于B来说每个都是0最好了
}
if(ans)
pra();
else
prb();
}
return ;
}
对sg函数的理解:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int sg[];
int hash[];
void getsg()
{
memset(sg,,sizeof(sg));
for(int i=;i<=;i++)
{
memset(hash,,sizeof(hash));
for(int j=;j+j<i;j++) //不相等的两堆
//注意是sg[j]不是sg[i]
hash[sg[j]^sg[i-j]]=; //sg[j]^sg[i-j] 是i的后继 i是从小到大跑的 所以不需要搜索直接用即可
//小的数是大的数的后继 sg[1]^sg[4]=0,sg[2]^sg[3]=1是sg[5]=2的后继
for(int x=;x<=;x++)//不是0的就是必胜点
//只要在上面的sg里能异或出来一个等于0的 就是后继里有一个是等于0的 这个点就是必胜点
//多个点异或和以前的思想一样 看成n个有向图
//i小的时候可以这么看
//根据题意 不能分的点比如1或者分了以后还能分一次的点比如4 就是必败点 sg值为0
//i的异或值就是i 分成两个数看他俩的异或值是多少 如果分成的两个数的异或值中存在0说明该点是胜的
if(!hash[x])
{
sg[i]=x;
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
getsg();
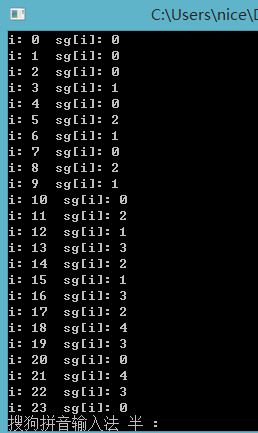
for(int i=;i<;i++)
cout<<"i: "<<i<<" sg[i]: "<<sg[i]<<endl;
/*int t,cas=1;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n,data,ans=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>data;
ans^=sg[data];
}
if(ans)
printf("Case %d: Alice\n",cas++);
else
printf("Case %d: Bob\n",cas++);
}*/
return ;
}
Light OJ 1199 - Partitioning Game (博弈sg函数)的更多相关文章
- LIGHT OJ 1199 - Partitioning Game
传送门 1199 - Partitioning Game PDF (English) problem=1199" style="color:rgb(79,107,114)&q ...
- LightOJ 1199 Partitioning Game(sg函数)题解
题意:可以把一堆石子分成不相等的两堆,不能操作为败 思路:把一个石子拆成两个,变成了两个独立的游戏,mex里加上两者的sg异或.sg打表. 代码: #include<set> #inclu ...
- S-Nim HDU 1536 博弈 sg函数
S-Nim HDU 1536 博弈 sg函数 题意 首先输入K,表示一个集合的大小,之后输入集合,表示对于这对石子只能去这个集合中的元素的个数,之后输入 一个m表示接下来对于这个集合要进行m次询问,之 ...
- Light OJ 1199:Partitioning Game(SG函数模板)
Alice and Bob are playing a strange game. The rules of the game are: 1. Initially there are n p ...
- Light OJ 1296 - Again Stone Game (博弈sg函数递推)
F - Again Stone Game Time Limit:2000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu ...
- hdu 3032(博弈sg函数)
题意:与原来基本的尼姆博弈不同的是,可以将一堆石子分成两堆石子也算一步操作,其它的都是一样的. 分析:由于石子的堆数和每一堆石子的数量都很大,所以肯定不能用搜索去求sg函数,现在我们只能通过找规律的办 ...
- HDU-4678 Mine 博弈SG函数
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4678 题意就不说了,太长了... 这个应该算简单博弈吧.先求联通分量,把空白区域边上的数字个数全部求出 ...
- light oj 1007 Mathematically Hard (欧拉函数)
题目地址:light oj 1007 第一发欧拉函数. 欧拉函数重要性质: 设a为N的质因数.若(N % a == 0 && (N / a) % a == 0) 则有E(N)=E(N ...
- (转)博弈 SG函数
此文为以下博客做的摘要: https://blog.csdn.net/strangedbly/article/details/51137432 ---------------------------- ...
随机推荐
- mysql中的having
from子句后面可以用where选择行,group by子句后面可以用having子句选择行, having中条件的定义和where中很相似,但是having中可以直接用聚合函数,但是where中不能 ...
- TCP和Http的区别
相信不少初学手机联网开发的朋友都想知道Http与Socket连接究竟有什么区别,希望通过自己的浅显理解能对初学者有所帮助. 1.TCP连接 手机能够使用联网功能是因为手机底层实现了TCP/IP协议,可 ...
- 初试visual studio2012的新型数据库LocalDB
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhangran/archive/2012/08/21/2649200.html 今天在vs2012里面打开以前的mvc3项目,结果弹出警告说在vs201 ...
- POI读写Excel简述之读取
一.POI读取Excel文件(以Excel2003版为例,2007版就是根据文件扩展名xlsx将HSSFWorkbook换为XSSFWorkbook,及其Sheet.Row.Cell也相应替换) // ...
- Linux下使用popen()执行shell命令
转载 http://www.cnblogs.com/caosiyang/archive/2012/06/25/2560976.html 简单说一下popen()函数 函数定义 #include < ...
- linux 定时 svn 代码更新,配置文件不修改
普通参数: 普通参数为正常的传参数: 例子: f1("111") 指定参数: 指定参数为指定哪个参数给函数方法里面某个形式参数专用,优点:不受传参数的位置约束. 例子: ...
- swift中文文档- 类型转换
未翻译完 待续(英语烂,求斧正) Type Casting 类型转换 Type casting is a way to check the type of an instance, and/or to ...
- 使用多种方式实现遍历HashMap
今天讲解的主要是使用多种方式来实现遍历HashMap取出Key和value,首先在java中如果想让一个集合能够用for增强来实现迭代,那么此接口或类必须实现Iterable接口,那么Iterable ...
- Item 表单页面的 Select2 相关业务逻辑
Select2 插件官网:https://select2.github.io/ Select2 初始化说明: 代码在 public/javascripts/subchannel_items.js 中的 ...
- 疯狂抨击ie6下各种扭曲行为
从开始接触ie6就被它强大的力量给震住了,虽然它很可怕,但是我总归得想方设法把它给扼杀在摇篮外.以下是我在ie6下面碰到的一些扭曲行为,弱弱的把它给干掉!!! 1.浮动下margin翻倍问题(很典型, ...
