C/C++语言读取SEGY文件(二)
SEGY IO (2D)
本文档将介绍SEGY的读取与写入过程,即SEGY文件的复制,并且在实现过程采用采样点×道数二维数组的形式读写。
新建头文件SegyDataIO2D.h与C++文件SegyDataIO2D.cpp,以及主程序main.cpp。
1 编写头文件SegyDataIO2D.h
1.1 程序描述、调用、声明、定义
/**********************************************************************
* Copyright(C) 2018,Company All Rights Reserved (1)版权说明
*
* @file : SegyDataIO2D.cpp (2) 文件名
*
* @brief : 实现地震数据的读、写操作 (3) 该文件主要功能简介
*
* @version : 1.0 (4) 版本信息
*
* @author : Fan XinRan (5) 创建作者
*
* @date : 2022/2/9 星期三 (6) 创建时间
*
* Others : (7) 备注、改动信息等
**********************************************************************/
//调用需要的C头文件
#include<stdio.h> //C Language header file
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
//调用需要的C++头文件
#include<iostream> // C++ header file
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//调用非标准库
#include"alloc.h" // 用于创建多维数组
#include"segy.h" // 包含segy与bhed结构体,用于提取卷头和道头中采集、存储的信息
#define PI 3.141592654 //Constant Number Definition
#define EPS 0.0000001
using namespace std; // 声明命名空间
1.2 声明函数
输入和输出均为文件指针。
bool copySeismicData2D(const char *filenameInput, const char *filenameOutput); //Copy seismic data from Inputfile to Outputfile
完整代码
/**********************************************************************
* Copyright(C) 2018,Company All Rights Reserved
*
* @file : SegyDataIO2D.cpp
*
* @brief : 实现地震数据的读、写操作
*
* @version : 1.0
*
* @author : Fan XinRan
*
* @date : 2022/2/9 星期三
*
* Others :
**********************************************************************/
//(1)调用需要的C头文件
#include<stdio.h> // C Language header file
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
//(2)调用需要的C++头文件
#include<iostream> // C++ header file
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//(3)调用需要的非标准库头文件
#include"alloc.h" // project header file
#include"segy.h"
//(4)定义全局常量
#define PI 3.141592654 // Constant Number Definition
#define EPS 0.0000001
//(5)声明命名空间
using namespace std;
//(6)声明函数名、输入、输出及其类型
bool copySeismicData2D(const char *filenameInput, const char *filenameOutput); //Copy seismic data from Inputfile to Outputfile
2 编写C++文件SegyDataIO2D.cpp
2.1 必要的说明
/*************************************************************************************************************
Function: copySeismicData2D (1)函数名
Description: copy segy file from input data to output data (2)简要描述其功能
Input:
const char *filenameInput [in] input filename (.segy) (3)输入变量及输入文件类型
Output:
const char *filenameOutput[out] output filename (.segy) (4)输出变量及输出文件类型
Return:
bool true program success
bool false program failed (5)返回值及其说明
Author: Fan XinRan (6)创建作者
Date : 2022/2/9 (7)创建时间
Others: (8)备注、改动信息等
*************************************************************************************************************/
2.2 定义读、写函数
#include "SegyDataIO2D.h"
bool copySeismicData2D(const char *filenameInput, const char *filenameOutput){
//实现代码
...
}
(1) 定义待使用的结构体变量、数值型变量
bhed 与 segy均为定义在segy.h中的结构体(structure),分别包含了二进制卷头信息与道头信息,使用成员访问运算符.获取其内容;
使用unsigned int 声明整型变量,使用long long 或__int64声明segy文件字节数、地震道字节数,防止数据量超出范围,并且尽可能初始化变量。
bhed fileheader; // file header 卷头
segy traceheader; // trace header 道头
unsigned int nt=0; // number of sample 采样点数
unsigned int sizefileheader=sizeof(fileheader); // size of fileheader;
unsigned int sizetraceheader=sizeof(traceheader); // size of traceheader;
unsigned int ncdp = 0; // number of cdp 道数
long long size_file = 0; //size of input file
long long size_trace = 0; //size of per-trace
(2)新建指针变量
在读、写地震道数据这一任务中,需要用到输入指针、输出指针、地震道数据指针以及道头指针,四个指针变量。与1-1 SEGY IO相比多定义了一个关于traceheader的指针变量,用于存放道头信息。
FILE *fpinput = NULL; // input file pointer
FILE *fpoutput = NULL; //output file pointer
float **dataInput = NULL; //input data pointer 注意此处**dataInput前有两个"*",表示的是二级指针
segy *traceheaderArray = NULL; //traceheader pointer
(3)打开输入、输出文件指针并判空
fpinput = fopen(filenameInput, "rb"); //open input file pointer
fpoutput = fopen(filenameOutput,"wb"); //open output file pointer
if(fpinput==NULL){ //如果文件指针为NULL
printf("Cannot open %s file\n", filenameInput); //打印“文件打开失败”
return false; //结束程序
}
if(fpoutput==NULL){
printf("Cannot open %s file\n", filenameOutput);
return false;
}
//读写操作
...
//fopen()与fclose()成对出现,在对文件的操作完成后切记关闭文件
fclose(fpinput); //close input file pointer
fclose(fpoutput); //close output file pointer
(4)读取/计算卷、道信息
fread(&fileheader,sizefileheader,1,fpinput); // 从输入流(fpinput)中读取卷头信息到指定地址---->fileheader
nt = fileheader.hns; //从卷头信息中获取采样点数
_fseeki64(fpinput,0,SEEK_END); // 从文件末尾偏移这个结构体0个长度给文件指针fpinput,即fpinput此时指向文件尾
size_file = _ftelli64(fpinput); // 返回当前文件位置,即文件总字节数
size_trace = nt*sizeof(float)+sizetraceheader; // 每一道的字节数 = 采样点字节数+道头字节数
ncdp = (size_file - (long long)sizefileheader)/size_trace; // 道数 = (文件总字节数 - 卷头字节数)/每一道的字节数
_fseeki64(fpinput,sizefileheader,SEEK_SET); // 从文件开头偏移sizefileheader(卷头字节数)个长度给指针fpinput,即fpinput此时指向第一道的开始
fwrite(&fileheader, sizefileheader, 1, fpoutput); // 先写入卷头
fread()从给定流读取数据到指针所指向的数组中;fread(*ptr, size, nmemb,*stream)- ptr -- 指向带有最小尺寸 size*nmemb 字节的内存块的指针;
- size -- 要读取的每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
- nmemb -- 元素的个数,每个元素的大小为 size 字节;
- stream -- 指向 FILE 对象的指针。
fwrite(*ptr, size, nmemb,*stream)参数与fread()相同,把ptr所指向的数组中的数据写入到给定流stream中;_fseeki64的用法与fseek相同,表示从文件指定位置偏移一定字节数;前者具有更高的兼容性;_ftelli64与ftell同理,返回给定流的当前文件位置;_fseeki64(*stream, offset, whence)stream -- 指向 FILE 对象的指针;
offset -- 相对 whence 的偏移量,以字节为单位;
whence -- 表示开始添加偏移 offset 的位置。一般定义为
SEEK_SET(文件开头)、SEEK_CUR(文件指针的当前位置)、SEEK_END(文件末尾)三类常量。
(5)遍历每一条地震道,读、写数据
dataInput=alloc2float(nt,ncdp); // 分配nt*ncdp(采样点数×道数)所需的内存空间,用来存放二维地震道数据
//其中,alloc2float是卸载alloc.h中的函数,创建一个float型的二维数组
//dataInput为二级指针,可简记为dataInput指向每一行的开头
memset(dataInput[0], 0, nt*ncdp * sizeof(float)); // 从第一行的开头开始,将内存块中nt*ncdp个字符赋值为0
// dataInput指向每行开头,而dataInput[0]则为整个二维数组的起始位置
// 在内存的动态存储区中分配ncdp个长度为sizetraceheader的连续空间
traceheaderArray = (segy*)calloc(ncdp,sizetraceheader);
//逐道读取道头与地震道数据
for(int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++){
fread(&traceheaderArray[itrace],sizetraceheader,1,fpinput); // &traceheaderArray[itrace]为第itrace道的地址,读取该道头信息
fread(dataInput[itrace],nt * sizeof(float),1,fpinput); // dataInput[itrace]指向列开头,并读取nt个采样点的信息
}//end for(int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++)
//逐道写入道头与地震道数据
for (int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++) {
fwrite(&traceheaderArray[itrace], sizetraceheader, 1, fpoutput); // 写入该道头信息
fwrite(dataInput[itrace], nt * sizeof(float), 1, fpoutput); // 写入nt个采样点的信息
}//end for(int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++)
// 在每个条件语句末尾的"}"添加备注,便于寻找和区分
//在写操作完成后释放内存
free(traceheaderArray); // free traceheader pointer
free2float(dataInput); // free data input pointer
alloc2float(nt,ncdp):创建nt*ncdp个元素的二维数组,并分配内存;memset(),将某一块内存中的内容全部设置为指定值, 通常为新申请的内存做初始化工作。void memset(void *ptr, int c, size_t n),复制字符c(一个无符号字符)到参数ptr所指向的字符串的前n个字符;- str -- 指向要填充的内存块;
- c -- 要被设置的值;
- n -- 要被设置为该值的字符数。
完整代码
/*****************************************************************************
Function: copySeismicData2D
Description: copy segy file from input data to output data
Input:
const char *filenameInput [in] input filename (.segy)
Output:
const char *filenameOutput[out] output filename (.segy)
Return:
bool true program success
bool false program failed
Author: Fan XinRan
Date : 2022/2/9
Others:
*****************************************************************************/
#include "SegyDataIO2D.h"
bool copySeismicData2D(const char *filenameInput, const char *filenameOutput){
bhed fileheader; // file header
segy traceheader; // trace header
unsigned int nt=0; // number of sample
unsigned int sizetraceheader=sizeof(traceheader); // size of traceheader;
unsigned int sizefileheader=sizeof(fileheader); // size of fileheader;
unsigned int ncdp = 0; // number of cdp
long long size_file = 0; //size of input file
long long size_trace = 0; //size of per-trace
FILE *fpinput = NULL; // input file pointer
FILE *fpoutput = NULL; //output file pointer
float *dataInput = NULL; //input data pointer
segy *traceheaderArray = NULL; //traceheader pointer
fpinput = fopen(filenameInput, "rb"); //open input file pointer
fpoutput = fopen(filenameOutput,"wb"); //open output file pointer
if(fpinput==NULL){
printf("Cannot open %s file\n", filenameInput);
return false;
}
if(fpoutput==NULL){
printf("Cannot open %s file\n", filenameOutput);
return false;
}
fread(&fileheader,sizefileheader,1,fpinput);
nt = fileheader.hns;
_fseeki64(fpinput,0,SEEK_END);
size_file = _ftelli64(fpinput);
size_trace = nt*sizeof(float)+sizetraceheader;
ncdp = (size_file - (long long)sizefileheader)/size_trace;
_fseeki64(fpinput,sizefileheader,SEEK_SET);
fwrite(&fileheader, sizefileheader, 1, fpoutput);
dataInput = alloc2float(nt,ncdp);
memset(dataInput[0], 0, nt*ncdp * sizeof(float));
traceheaderArray = (segy*)calloc(ncdp,sizetraceheader);
for(int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++){
fread(&traceheaderArray[itrace],sizetraceheader,1,fpinput);
fread(dataInput[itrace],nt*sizeof(float),1,fpinput);
}//end for(int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++)
for (int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++) {
fwrite(&traceheaderArray[itrace], sizetraceheader, 1, fpoutput);
fwrite(dataInput[itrace], nt * sizeof(float), 1, fpoutput);
}//end for(int itrace = 0; itrace < ncdp; itrace++)
free(traceheaderArray);
free(dataInput); // free data input pointer
fclose(fpinput); //close input file pointer
fclose(fpoutput); //close output file pointer
return true;
}
3 主函数main.cpp及运行结果
#include"ReadSeismic.h"
void main(){
copySeismicData2D("Demo.segy","Output2.segy");
}
运行主函数后,程序会读入Demo.segy,再写入到Output2.segy,从而完成对SEGY文件的复制。
附录
I 二维数组的动态内存分配方法
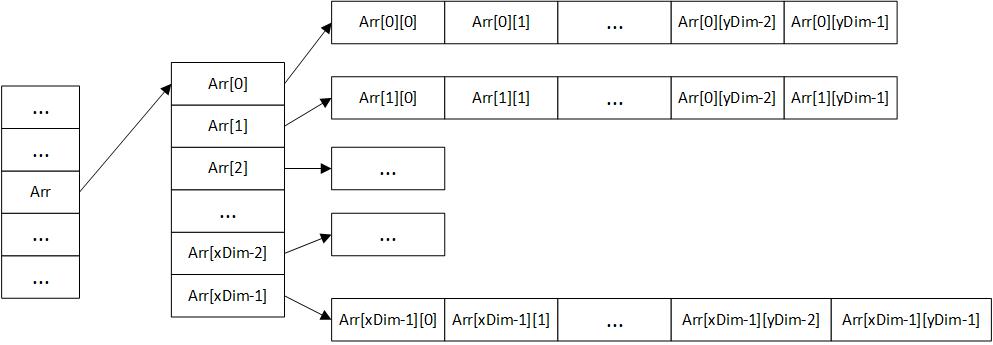
a.非连续分配
首先arr是一个二级指针,为arr分配xDim空间,每一维都是一个指向数组的指针,且每个数组内部的地址空间是连续的,但是数组之间的地址空间没有连续性。
void malloc2D_1(int **&a)
{
a = new int*[xDim]; // new的作用与malloc类似,分配一个一维数组的内存块
for(int i=0;i<xDim;i++)
a[i] = new int[yDim]; // 对一维数组的每一个元素继续分配内存块
assert(a!=NULL);
}
int main()
{
int **arr = NULL; // 声明一个二级指针
malloc2D_1(arr); // 执行分配内存操作
}
释放
需要逐个数组释放
void free2D_1(int **a)
{
for(int i=0;i<xDim;i++)
free(a[i]);
}
b.连续分配
void malloc2D_2(int **&a)
{
a = (int **)malloc( xDim * sizeof(int *) ); // 分配xDim字符的内存用来存放一级指针
a[0] = (int *)malloc( xDim * yDim * sizeof(int) ); // 分配xDim * yDim个元素所需的内存空间
for(int i=1;i<xDim;i++)
{
a[i] = a[i-1] + yDim; // 例如a[0]指向二维数组起始位置,a[1]=a[0]+yDim,则指向下一行(第一行)的开头,以此类推...
}
assert(a!=NULL);
}
int main()
{
int **arr = NULL;
malloc2D_2(arr);
}
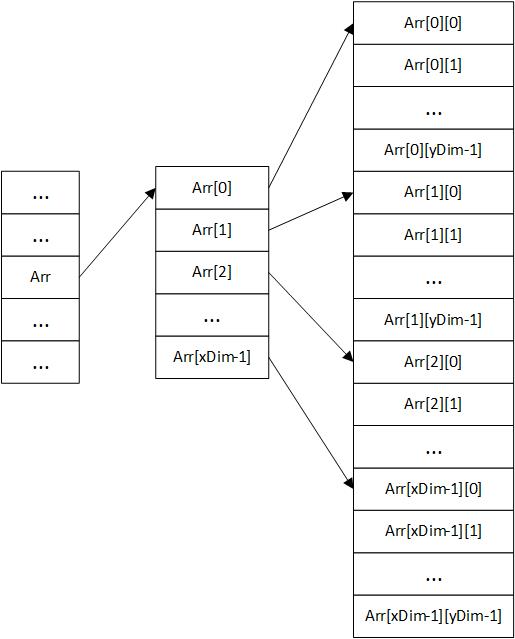
释放
只需要释放两个分配内存的指针即可
void free2D_2(int **a)
{
free(a[0]);
free(a);
}
II 两种索引方法
假设创建一个100×100的二维数组,并且每一行的数值等于其行号:
| 行号\列号 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ... | 97 | 98 | 99 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ||||
| 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 | 98 |
| 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
以此为例,分别介绍两种索引方法。
a.以一维数组方式索引
int nrow = 100;
int ncol = 100; // 声明行号和列号
float *a1 = (float*)calloc(nrow*ncol,sizeof(float));// 分配nrow*ncol个元素所需的内存空间,将起始地址指向a1
for (int irow = 0; irow < nrow; irow++) // 遍历行
{
for(int icol = 0; icol < ncol; icol++){ // 遍历列
a1[irow*ncol + icol] = irow; // 在一维数组上依据行、列计算索引,为指定地址赋值
}
}
b.以二维数组方式索引
float **a2 = alloc2float(ncol, nrow); // 利用alloc2float函数分配nrow*ncol个元素所需的内存空间,a2指向每行的起始位置
memset(a2[0],0,ncol*nrow*sizeof(float)); // 数组初始化为0
for (int irow = 0; irow < nrow; irow++)
{
for (int icol = 0; icol < ncol; icol++) {
a2[irow][icol] = irow; // 以二维数组的方式定位行、列
printf("%f\n", a2[irow][icol]);
}
}
C/C++语言读取SEGY文件(二)的更多相关文章
- C/C++语言读取SEGY文件笔记(一)
SEGY IO 推荐采用的IDE为Visual studio(VS),本文档将介绍SEGY文件的读取与写入过程,即SEGY文件的复制. 因此,新建头文件ReadSeismic.h与C++文件ReadS ...
- C/C++读取SEGY文件(三)
SEGY IO (IBM&PC) 本文档将介绍SEGY的读取与写入过程,其中包括IBM与PC两种数据格式的转换. 程序将调用IEEE2IBM.cpp文件完成IBM与PC格式的互相转换. 新建头 ...
- R语言读取excel文件的3种方法
R读取excel文件中数据的方法: 电脑有一个excel文件,原始的文件路径是:E:\R workshop\mydata\biom excel数据为5乘2阶矩阵,元素为 ...
- C语言读取PE文件信息(一)
接下来的内容来源于对该博客文章http://www.pediy.com/kssd/pediy06/pediy7006.htm的解析. 一.打印Sections信息.下面的程序打印出Windows_Gr ...
- R语言读取EXCEL文件的各种方法
路径问题 原始文件路径C:\Users\air\Desktop\1.txt R中有两种方法读取该路径 C:\\Users\\air\\Desktop\\1.txt C:/Users/air/Deskt ...
- R语言读取本地文件注意事项
R里面应该用/,而不是\ ,或者用两个\\ R区分大小写,所以应该用C:,而不是c:
- c语言读取一个文件夹下的全部文件(jpg / png 文件)
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <unistd.h> #include<dirent.h> ...
- C语言读取写入CSV文件 [一]基础篇
本系列文章目录 [一] 基础篇 [二] 进阶篇--写入CSV [三] 进阶篇--读取CSV 什么是CSV? CSV 是一种以纯文本形式存储的表格数据,具体介绍如下(来自维基百科): 逗号分隔值(Com ...
- R语言读取文件
1.R语言读取文件,文件类型为.txt 直接使用read.table()即可,若不知道当前的工作目录,可以使用函数getwd()来查看 2.R语言读取文件,文件类型为.xlsx 方法一:可以把excl ...
随机推荐
- 截取一段时间内的log日志
可以使用sed命令对log文件进行抽取操作:1,sed查看某时间段到现在的系统日志:sed -n '/May 20 17/,$p' /var/log/messages | less2,sed 截选时间 ...
- CentOS下搭建自动化测试基础框架:Jenkins+Maven+TestNG+ReportNG
1. 安装JDK 1.1 卸载系统默认已安装的open-jdk rpm -qa|grep java 查出来openjdk相关的应用,把查出来的所有都要通过下面的命令给卸载掉 rpm -e --node ...
- Java开发调试技巧及Eclipse快捷键使用方法
1. 快捷键 syso 通过打印输出来调试,println可接受object型的参数,能输出任何类型 Syso输出的是黑色字体,代表的是Debug的信息 Syse,输出的是红色字体,代表错误的输出信息 ...
- 接口里的default,static方法
我们都知道接口里的变量默认隐含类型是public static final,也是就是说是常量.而方法默认类型是public abstract,所以接口的方法都是抽象方法,但是事实真的是这样吗? 我的P ...
- Kubectl —— 基本命令
Kubectl -- 基本命令 1.kubectl 基本命令 2.项目的生命周期 3.声明式管理方法 service的类型: ClusterIP:提供一个集群内部的虚拟IP以供Pod访问( servi ...
- TCP的报文详细解读
这张图好像挺有名的,其实一开始我看见的时候是一脸懵逼的,但是通过翻书(大学时代最害怕的计算机网络),查阅他人博客等等办法,最后终于有了一个系统的了解,当然,这里知识点多而杂,大家可以多看几遍,结合上面 ...
- 详解xpath定位
xpath定位 1.通过开发者工具直接copy 右击copy-copy xpath 2.串联的方式定位元素 from selenium import webdriverfrom time import ...
- Solution -「Gym 102956B」Beautiful Sequence Unraveling
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 求长度为 \(n\),值域为 \([1,m]\) 的整数序列 \(\lang a_n\rang\) 的个数,满足 \(\not\ ...
- Diary -「CSP 2019 J/S」 游记
\(\text{Day 0}\) 试机, 总体感觉不错, 至少不像初一时候的紧张, 毕竟是中青年选手了 ( ? ) 当晚睡得挺好, 虽然是冲着一等奖去的, 但还是没有给自己过多的思想包 ...
- 论文解读(AGCN)《 Attention-driven Graph Clustering Network》
Paper Information Title:<Attention-driven Graph Clustering Network>Authors:Zhihao Peng, Hui Li ...
