CodeForces 916E Jamie and Tree(树链剖分+LCA)
To your surprise, Jamie is the final boss! Ehehehe.
Jamie has given you a tree with n vertices, numbered from 1 to n. Initially, the root of the tree is the vertex with number 1. Also, each vertex has a value on it.
Jamie also gives you three types of queries on the tree:
1 v — Change the tree's root to vertex with number v.
2 u v x — For each vertex in the subtree of smallest size that contains u and v, add x to its value.
3 v — Find sum of values of vertices in the subtree of vertex with number v.
A subtree of vertex v is a set of vertices such that v lies on shortest path from this vertex to root of the tree. Pay attention that subtree of a vertex can change after changing the tree's root.
Show your strength in programming to Jamie by performing the queries accurately!
The first line of input contains two space-separated integers n and q (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ q ≤ 105) — the number of vertices in the tree and the number of queries to process respectively.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an ( - 108 ≤ ai ≤ 108) — initial values of the vertices.
Next n - 1 lines contains two space-separated integers ui, vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n) describing edge between vertices ui and vi in the tree.
The following q lines describe the queries.
Each query has one of following formats depending on its type:
1 v (1 ≤ v ≤ n) for queries of the first type.
2 u v x (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, - 108 ≤ x ≤ 108) for queries of the second type.
3 v (1 ≤ v ≤ n) for queries of the third type.
All numbers in queries' descriptions are integers.
The queries must be carried out in the given order. It is guaranteed that the tree is valid.
For each query of the third type, output the required answer. It is guaranteed that at least one query of the third type is given by Jamie.
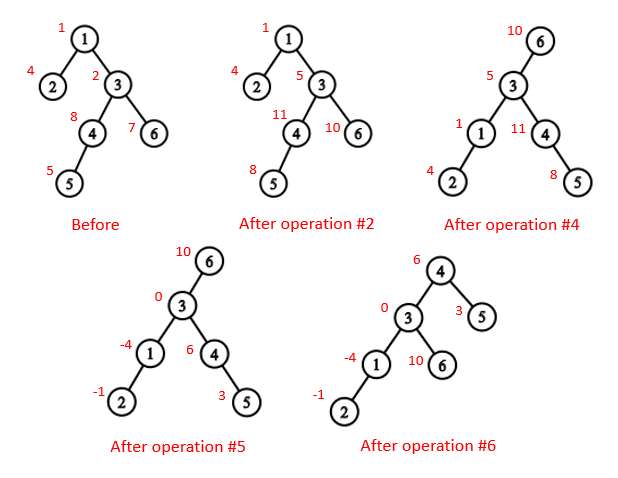
6 7
1 4 2 8 5 7
1 2
3 1
4 3
4 5
3 6
3 1
2 4 6 3
3 4
1 6
2 2 4 -5
1 4
3 3
27
19
5
4 6
4 3 5 6
1 2
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 3
2 2 4 3
1 1
2 2 4 -3
3 1
18
21
The following picture shows how the tree varies after the queries in the first sample.
题意(来自mangoyang大佬)
有一棵n个节点的有根树,标号为1-n,你需要维护一下三种操作
1.给定一个点v,将整颗树的根变为v
2.给定两个点u, v,将lca(u, v)所在的子树都加上x
3.给定一个点v,你需要回答以v所在的子树的权值和
题解:
这道题大概有以下几个难点
首先是换根情况下的子树权值和查询,但如果你做过洛谷P3979遥远的国度这道题,而且你还是用树链剖分写的,你大致就会做这个东西了。
维护一个LCA,然后从根节点跳到当前这个子树根节点的儿子所处的深度,记这个点为A,如果A点的父亲是我们询问的子树根节点,那么根节点在子树中,此时当前的新子树就是除了A点和A点的原子树以外的所有点,否则的话就是子树根节点的原子树,当然也要特判一下,如果根节点刚好是要查询的子树根节点,那么查询范围就是全部节点
修改也是同理的
然后是包括u和v的最小子树,画一下图就可以知道子树的根节点应该是u到根节点的路径与v到根节点的路径的第一个交点
这个交点可以通过对根和u,根和v,v和u两两取LCA后取深度最大的点获得,挺简单的想法,可以自行模拟体会一下
假设我们已经获得了这个根节点,那么之后的操作就是换根情况下子树的权值修改了,这在上面已经提到过了,就不再赘述了。
CodeForces 916E Jamie and Tree(树链剖分+LCA)的更多相关文章
- Bzoj 2588 Spoj 10628. Count on a tree(树链剖分LCA+主席树)
2588: Spoj 10628. Count on a tree Time Limit: 12 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MB Description 给定一棵N个节点的树,每个点 ...
- Hdu 5274 Dylans loves tree (树链剖分模板)
Hdu 5274 Dylans loves tree (树链剖分模板) 题目传送门 #include <queue> #include <cmath> #include < ...
- POJ3237 Tree 树链剖分 边权
POJ3237 Tree 树链剖分 边权 传送门:http://poj.org/problem?id=3237 题意: n个点的,n-1条边 修改单边边权 将a->b的边权取反 查询a-> ...
- Codeforces Round #200 (Div. 1) D Water Tree 树链剖分 or dfs序
Water Tree 给出一棵树,有三种操作: 1 x:把以x为子树的节点全部置为1 2 x:把x以及他的所有祖先全部置为0 3 x:询问节点x的值 分析: 昨晚看完题,马上想到直接树链剖分,在记录时 ...
- Codeforces Round #200 (Div. 1) D. Water Tree 树链剖分+线段树
D. Water Tree time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- CodeForces 343D water tree(树链剖分)
Mad scientist Mike has constructed a rooted tree, which consists of n vertices. Each vertex is a res ...
- Water Tree(树链剖分+dfs时间戳)
Water Tree http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/343/D time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit ...
- Query on a tree——树链剖分整理
树链剖分整理 树链剖分就是把树拆成一系列链,然后用数据结构对链进行维护. 通常的剖分方法是轻重链剖分,所谓轻重链就是对于节点u的所有子结点v,size[v]最大的v与u的边是重边,其它边是轻边,其中s ...
- 【BZOJ-4353】Play with tree 树链剖分
4353: Play with tree Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: 31 Solved: 19[Submit][Status][ ...
随机推荐
- 【Python】 Web开发框架的基本概念与开发的准备工作
Web框架基本概念 现在再来写这篇文章显然有些马后炮的意思.不过正是因为已经学习了Flask框架, 并且未来计划学习更加体系化的Django框架,在学习过程中碰到的很多术语等等,非常有必要通过这样一篇 ...
- 缺少libssl.so.4文件
1.报错代码: /usr/local/pureftpd/sbin/pure-ftpd: error while loading shared libraries: libssl.so.4: wrong ...
- 大数据 --> Spark与Hadoop对比
Spark与Hadoop对比 什么是Spark Spark是UC Berkeley AMP lab所开源的类Hadoop MapReduce的通用的并行计算框架,Spark基于map reduce算法 ...
- 如何图形化创建oracle数据库
需要注意的几点 1.如果用oracle客户端访问服务器的话必须把服务器的主机名写成(计算机的名称)Oracle创建数据库的方法 2.navigate如何远程oracle数据库 E:\app\lenov ...
- lua对多个精灵执行一系列动作,延时失效
function MainPlayerCards:sendCards() local winSize = cc.Director:getInstance():getWinSize() local nS ...
- Python读取配置文件,并连接数据库SQL Server
用配置文件保存固定的连接数据,改的话比较方便. 1.新建一个配置文件:SQlconfig.config,以数据库为例. 内容如下,当然也可以添加多个 [Database1] database=db_t ...
- C语言第三次博客作业—循环结构
一.PTA实验作业 题目1 1.实验代码 int N,i; //N为用户数 char sex; //sex表示性别 double High; //Hight表示身高 scanf("%d&qu ...
- 201621123043 《Java程序设计》第6周学习总结
1.1 面向对象学习暂告一段落,请使用思维导图,以封装.继承.多态为核心概念画一张思维导图或相关笔记,对面向对象思想进行一个总结. 注1:关键词与内容不求多,但概念之间的联系要清晰,内容覆盖面向对象的 ...
- 自主学习之RxSwift(一) -----Driver
对于RxSwift,我也是初学者,此系列来记录我学习RxSwift的历程! (一) 想必关于Drive大家一定在RxSwift的Demo中看到过,也一定有些不解,抱着一起学习的态度,来了解一下Driv ...
- MySQL搭建主从数据库 实现读写分离
首先声明,实际生产中,网站为了提高用户体验,性能等,将数据库实现读写分离是有必要的,我们让主数据库去写入数据,然后当用户查询的时候,然后在从数据库读取数据,故能减轻数据库的压力,实现良好的用户体验! ...
