《MIDINET: A CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORK FOR SYMBOLIC-DOMAIN MUSIC GENERATION》论文阅读笔记
出处 arXiv.org (引用量暂时只有3,too new)2017.7
SourceCode:https://github.com/RichardYang40148/MidiNet
Abstract
以前的音乐生成工作多基于RNN,受DeepMind提出的WaveNet的启发,作者尝试用CNN来生成音乐,确切地说,用GAN来生成音乐,模型称为MidiNet。与Google的MelodyRNN(magenta)相比,在realistic和pleasant上旗鼓相当,yet MidiNet’s melodies are reported to be much more interesting。
Introduction
1989年[1]就开始研究用神经网络来谱曲,最近几年才形成气候(这里列举了一堆神经网络生成音乐的参考paper),主要还是基于RNN来生成。接着重点介绍了WaveNet[2],WaveNet证实了用CNN来生成音乐的可能性,并且CNN在训练的速度和并行性上都优于RNN[3]。作者这样描述所做的工作:Following this light, we investigate in this paper a novel CNN-based model for symbolic-domain generation, focusing on melody generation. Instead of creating a melody sequence continuously, we propose to generate melodies one bar (measure) after another, in a successive manner. This allows us to employ convolutions on a 2-D matrix representing the presence of notes over different time steps in a bar. We can have such a score-like representation for each bar for either a real or a generated MIDI.
借助于transposed convolution[4],G将噪音z生成为2-D scorelike representation,D判断2-D scorelike representation的真假。这套gan结构没有考虑bar与bar之间的temporal依赖,作者将前面生成bar作为条件,输入到下个G的生成过程中(conditioner CNN)。这样MidiNet模型既可以从scratch(不带前置条件的z noise)从生成旋律,也能从任一表示为scorelike representation的前置音乐片段中生成旋律.借助于[5]中提出的feature matching(既然 G 和 D 的训练不够稳定,常常 D 太强,G 太弱,那么不如就把 D 网络学到的特征直接“传”给 G,让 G 不仅能知道 D 的输出,还能知道 D 是基于什么输出的),模型可以控制当前bar与前面生成的bar之间的相似度。
Related Work
Google的MelodyRNN(magenta)[6]是当前最著名的symbolic-domain神经网络音乐生成器,作为基准参考。Song from PI [7]多轨道RNN生成音乐,需要提供一些先验的配置信息(?)。Sony的DeepBach[8]也是基于RNN。C-RNN-GAN[9]是目前作者已知的唯一基于GAN的模型,与本文模型相比,缺乏条件生成机制,因此不能给定前置音乐来进行生成。DeepMind的WaveNet[10]是基于waveform的形式而不是symbolic-domain的。

Method

Symbolic Representation for Convolution: MiDi数据依然是被分为bars,固定时间长度,一个track的数据矩阵被表示为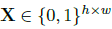 ,h是note数量,w是一个bar中的time_step,这里忽略了音符的力度。多个X就组织成了多个track的数据。这个矩阵无法分辨长拍音符和短拍连续按键音符,作者留到未来工作去处理。
,h是note数量,w是一个bar中的time_step,这里忽略了音符的力度。多个X就组织成了多个track的数据。这个矩阵无法分辨长拍音符和短拍连续按键音符,作者留到未来工作去处理。
Generator CNN and Discriminator CNN:作者使用了feature matching 和 one-sided label 来优化GAN: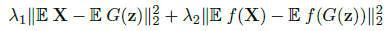 ,f是D的第一层输出(为什么只要第一层呢?)
,f是D的第一层输出(为什么只要第一层呢?)
Conditioner CNN:额外输入的condition分为1D和2D。1D condition是一个n维tensor,被reshape后concatenate在CNN的各个中间层的featuremap上,reshape规则为duplicate the values ab times to get a tensor of shape a-by-b-by-n,,(a,b)是中间层的shape。2D condition是h-by-w matrix(可以是multiple),对于D来说,可以直接加到D的输入层,影响后面整个的网络,对G来说,需要构建一个Condition CNN,架构近似于reverse of the generator CNN,将h*w的矩阵依次生成为对应于G的中间层的shape的矩阵并concatenate(与G使用了相同的filter参数,训练时使用与G相同的梯度来训练)。
对于Creativity的控制,采用了两种方式(1)对条件condition的控制只应用到G的部分卷积层中,让G有一定自由度 (2)在feature matching的公式中控制$\lamda1$和$\lamda2$的值,以控制生成的歌和训练集中歌曲的相似度。
IMPLEMENTATION
Dataset:从TheoryTab(https://www.hooktheory.com/theorytab)爬取了1,022 首MIDI tab,只有两个track:melody和chord。为了简化,过滤出了规整的12个大调和弦和12个小调和弦。每8个bars做一个切分,并将melody和chord分开,每个bar被定义为16个音符的长度(w=16)。数据中不许存在pause,存在pause就将前面的音符(或后面的)拉长,这个规则太不灵活了吧,同时将三十二分音符等都exclude掉了。notes数量被限定为C4 to B5两个8度,忽略掉音符的按键力度。虽然只有24个音符有效,但在数据表示中还是使用了h=128。和弦使用了13维的vector,12维表示和弦名,1维表示大小调。一个bar限制为一个和弦。限制真多。

三种模型:
Melody generator, no chord condition--- condition是melody of the previous bar,将此2D condition分散输入到G的各中间层中,不输入到D中。the first bar was composed of a real, priming melody sampled from our dataset; the
generation of the second bar was made by G, conditioned by this real melody; starting from the third bar, G had to use the (artificial) melody it generated previously for the last bar as the 2-D condition. This process repeated until
we had all the eight bars.
Melody generator with chord condition,stable mode----chord作为1D condition(13维向量,每个bar一个chord)应用在G的每一个卷积层上,为了突出和弦的贡献,2-D previous-bar condition只被应用在G的最后一层卷积上。
Melody generator with chord condition,creative mode---同上面一样,只是2-D previous-bar condition被应用在G所有的卷积层上,G可以在某些时候突破chord的限制,向上一个bar产生的旋律靠拢。这种模式的产出音乐,有不和谐的风险也有创新的可能性。
FutureWork
(1) multi-track + velocity + pause
(2)reinforcement learning with music theory[11]
(3)genre recognition[12], emotion recognition[13]
[1]Peter M. Todd. A connectionist approach to algorithmic composition. Computer Music Journal, 13(4):27– 43.
[2]A¨aron van den Oord, Sander Dieleman, Heiga Zen, Karen Simonyan, Oriol Vinyals, Alex Graves, Nal Kalchbrenner, Andrew Senior, and Koray Kavukcuoglu. WaveNet: A generative model for raw audio. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.03499, 2016.
[3]A¨aron van den Oord, Nal Kalchbrenner, Lasse Espeholt, Oriol Vinyals, Alex Graves, et al. Conditional image generation with pixelCNN decoders. In Proc. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,pages 4790–4798, 2016.
[4]Vincent Dumoulin and Francesco Visin. A guide to convolution arithmetic for deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.07285, 2016.
[5]Tim Salimans, Ian J. Goodfellow, Wojciech Zaremba,Vicki Cheung, Alec Radford, and Xi Chen. Improved techniques for training GANs. In Proc. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 2226–2234, 2016.
[6]Elliot Waite, Douglas Eck, Adam Roberts, and Dan Abolafia. Project Magenta: Generating longterm structure in songs and stories, 2016. https://magenta.tensorflow.org/blog/2016/07/15/lookback-rnn-attention-rnn/
[7] Hang Chu, Raquel Urtasun, and Sanja Fidler. Song from PI: A musically plausible network for pop music generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.03477, 2016.
[8]Ga¨etan Hadjeres and Franc¸ois Pachet. DeepBach: a steerable model for bach chorales generation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.01010, 2016
[9]Olof Mogren. C-RNN-GAN: Continuous recurrent neural networks with adversarial training. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.09904, 2016.
[10] Tom Le Paine, Pooya Khorrami, Shiyu Chang, YangZhang, Prajit Ramachandran, Mark A. Hasegawa-Johnson, and Thomas S. Huang. Fast WaveNet generation algorithm. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.09482,2016.
[11]Natasha Jaques, Shixiang Gu, Richard E. Turner, and Douglas Eck. Tuning recurrent neural networks with reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1611.02796, 2016.
[12]Keunwoo Choi, George Fazekas, Mark B. Sandler, and Kyunghyun Cho. Convolutional recurrent neural networks for music classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.04243, 2016.
[13]Yi-Hsuan Yang and Homer H. Chen. Music Emotion Recognition. CRC Press, 2011.
代码解析:
数据
因为没有拿到dataset,所以数据的格式只能猜测为主。
data_x 从npy文件中读取 ,猜测应该是一个nX1XhXw的tensor,n为长度,在训练时被截取为batch_size,1猜测为单track,h为note数量(128),w为time_step(16)
prev_x猜测和data_x同形,时序上比data_x领先,作为模型输入的2D_condition
data_y 作为模型输入的1D_condition
猜测因为卷积的时候要求输入tensor的shape为[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels],所以作者为之量身定做了4维的X矩阵
构建模型:


这里代码与paper有不一致的地方,D中只输入了1D_condition,没有把前期的条件矩阵2D_condition(prev_x)输入进来
Loss函数:
标准GAN的loss,使用单边平滑0.9

feature matching和L2 loss

综合起来:

模型搭建:
G:
首先将prev_x进行一系列卷积,也就是模型中的Condition CNN,每一层featureMap被加入到后面的生成层中

其后的deconv反卷积层中,都将结果与上面的prev_x的featuremap及y进行连接。
D:
D没有像论文中提及那样将prev_x作为输入条件在初始层进行连接,只在每一层将Y做了连接。
《MIDINET: A CONVOLUTIONAL GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORK FOR SYMBOLIC-DOMAIN MUSIC GENERATION》论文阅读笔记的更多相关文章
- 《MuseGAN: Multi-track Sequential Generative Adversarial Networks for Symbolic Music Generation and Accompaniment》论文阅读笔记
出处:2018 AAAI SourceCode:https://github.com/salu133445/musegan abstract: (写得不错 值得借鉴)重点阐述了生成音乐和生成图片,视频 ...
- (转)Introductory guide to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and their promise!
Introductory guide to Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and their promise! Introduction Neural ...
- 生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks,GAN)初探
1. 从纳什均衡(Nash equilibrium)说起 我们先来看看纳什均衡的经济学定义: 所谓纳什均衡,指的是参与人的这样一种策略组合,在该策略组合上,任何参与人单独改变策略都不会得到好处.换句话 ...
- 生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks, GAN)
生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks, GAN)是一种深度学习模型,是近年来复杂分布上无监督学习最具前景的学习方法之一. GAN 主要包括了两个部分,即 ...
- StackGAN: Text to Photo-realistic Image Synthesis with Stacked Generative Adversarial Networks 论文笔记
StackGAN: Text to Photo-realistic Image Synthesis with Stacked Generative Adversarial Networks 本文将利 ...
- 论文笔记之:Semi-Supervised Learning with Generative Adversarial Networks
Semi-Supervised Learning with Generative Adversarial Networks 引言:本文将产生式对抗网络(GAN)拓展到半监督学习,通过强制判别器来输出类 ...
- 《Self-Attention Generative Adversarial Networks》里的注意力计算
前天看了 criss-cross 里的注意力模型 仔细理解了 在: https://www.cnblogs.com/yjphhw/p/10750797.html 今天又看了一个注意力模型 < ...
- Paper Reading: Perceptual Generative Adversarial Networks for Small Object Detection
Perceptual Generative Adversarial Networks for Small Object Detection 2017-07-11 19:47:46 CVPR 20 ...
- SalGAN: Visual saliency prediction with generative adversarial networks
SalGAN: Visual saliency prediction with generative adversarial networks 2017-03-17 摘要:本文引入了对抗网络的对抗训练 ...
- Generative Adversarial Networks,gan论文的畅想
前天看完Generative Adversarial Networks的论文,不知道有什么用处,总想着机器生成的数据会有机器的局限性,所以百度看了一些别人 的看法和观点,可能我是机器学习小白吧,看完之 ...
随机推荐
- [HDU2896]病毒侵袭(AC自动机)
传送门 题目中文描述,赞! 除了val记录id以外就是模板. 注意:每次数组都要清0.0 ——代码 #include <cstdio> #include <queue> #in ...
- hdu3306:Another kind of Fibonacci
A(0)=A(1)=1,A(i)=X*A(i-1)+Y*A(i-2),求S(n)=A(0)^2+A(1)^2+A(2)^2+A(3)^2+……+A(n)^2. 这个矩阵有点毒.. #include&l ...
- APP后端处理视频的方案
在当前的app应用中,到处都能看到视频的身影,例如,在社交类的app上,用户可以拍摄属于自己的小视频,并发布到相应得栏目,增加和好友们互动的机会. 后台常见的视频处理有以下几种: · ...
- Palindrome--poj 1159(最长公共子字符串+滚动数字)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1159 题目大意: 给你一个n 代表n个字符 第二行给你一个字符串 求使这个字符串变成回文字符串 最少需要添加多少个字符 分析: 原 ...
- Java实验--统计字母出现频率及其单词个数
本周的实验要求在之前实现统计单词的基础之上(可以见之前博客的统计单词的那个实验),对其进行修改成所需要的格式,统计字母出现频率的功能,并按照一定的格式把最终结果的用特定的格式在文本中显示出来 统计过程 ...
- openstack swift middleware开发
首先MiddleWare核心代码,这段代码卸载swift的源代码目录下,~/swift/swift/common/middleware下新建deletionpreventing.py: import ...
- linux定时重启节约内存
linux服务器上运行的一些程序,比较消耗内存,需要定时重启,进行内存定期释放 0 2 * * * sudo /sbin/reboot && echo $(date) '重启成功' ...
- IOS开发 ios7适配
ios7控制器试图默认为全屏显示,导航栏的不同设置会产生不同的效果. 首先判断系统的的版本,区别: if (floor(NSFoundationVersionNumber) <= NSFound ...
- vi和vim上查找字符串
方法/步骤 1 我们以samba的配置文件为例,搜索一个user的字符串. vim /etc/samba/smb.conf 打开smb.conf 2 命令模式下,输入/user "/&quo ...
- Android开发——本地验证码的简易实现
0. 前言 验证码无处不在.有人问我,你知道达芬奇password以下是什么吗,对.答案就是达芬奇验证码. 验证码一个最基本的作用就是防止恶意暴力破解登录,防止不间断的登录尝试,事实上能够在se ...
