【Static Program Analysis - Chapter 2】 代码的表征之控制流图
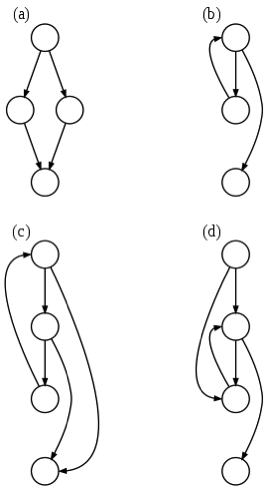
(a) an if-then-else
(b) a while loop
(c) a natural loop with two exits, e.g. while with an if...break in the middle; non-structured but reducible
(d) an irreducible CFG: a loop with two entry points, e.g. goto into a while or for loop
控制流图是代码的一种表征形式。
wiki:
Definition
In a control flow graph each node in the graph represents a basic block, i.e. a straight-line piece of code without any jumps or jump targets; jump targets start a block, and jumps end a block. Directed edges are used to represent jumps in the control flow. There are, in most presentations, two specially designated blocks: the entry block, through which control enters into the flow graph, and the exit block, through which all control flow leaves.[3]
Because of its construction procedure, in a CFG, every edge A→B has the property that:
The CFG can thus be obtained, at least conceptually, by starting from the program's (full) flow graph—i.e. the graph in which every node represents an individual instruction—and performing an edge contraction for every edge that falsifies the predicate above, i.e. contracting every edge whose source has a single exit and whose destination has a single entry. This contraction-based algorithm is of no practical importance, except as a visualization aid for understanding the CFG construction, because the CFG can be more efficiently constructed directly from the program by scanning it for basic blocks.[4]
Example
Consider the following fragment of code:
0: (A) t0 = read_num
1: (A) if t0 mod 2 == 0
2: (B) print t0 + " is even."
3: (B) goto 5
4: (C) print t0 + " is odd.” [jump targets]
5: (D) end program [jump targets]
In the above, we have 4 basic blocks:
A from 0 to 1, [entry block]
B from 2 to 3,
C at 4,
D at 5. [exit block]
A graph for this fragment has edges from A to B, A to C, B to D and C to D.
Reachability
Reachability is a graph property useful in optimization.
If a subgraph is not connected from the subgraph containing the entry block, that subgraph is unreachable during any execution, and so is unreachable code; under normal conditions it can be safely removed.
If the exit block is unreachable from the entry block, an infinite loop may exist. Not all infinite loops are detectable, see Halting problem. A halting order may also exist there.
Unreachable code and infinite loops are possible even if the programmer does not explicitly code them: optimizations like constant propagation and constant folding followed by jump threading can collapse multiple basic blocks into one, cause edges to be removed from a CFG, etc., thus possibly disconnecting parts of the graph.
Domination relationship
A block M dominates a block N if every path from the entry that reaches block N has to pass through block M. The entry block dominates all blocks.
In the reverse direction, block M postdominates block N if every path from N to the exit has to pass through block M. The exit block postdominates all blocks.
It is said that a block M immediately dominates block N if M dominates N, and there is no intervening block P such that M dominates P and P dominates N. In other words, M is the last dominator on all paths from entry to N. Each block has a unique immediate dominator.
Similarly, there is a notion of immediate postdominator, analogous to immediate dominator.
The dominator tree is an ancillary data structure depicting the dominator relationships. There is an arc from Block M to Block N if M is an immediate dominator of N. This graph is a tree, since each block has a unique immediate dominator. This tree is rooted at the entry block. The dominator tree can be calculated efficiently using Lengauer–Tarjan's algorithm.
A postdominator tree is analogous to the dominator tree. This tree is rooted at the exit block.
Special edges
A back edge is an edge that points to a block that has already been met during a depth-first (DFS) traversal of the graph. Back edges are typical of loops.
A critical edge is an edge which is neither the only edge leaving its source block, nor the only edge entering its destination block. These edges must be split: a new block must be created in the middle of the edge, in order to insert computations on the edge without affecting any other edges.
An abnormal edge is an edge whose destination is unknown. Exception handling constructs can produce them. These edges tend to inhibit optimization.
An impossible edge (also known as a fake edge) is an edge which has been added to the graph solely to preserve the property that the exit block postdominates all blocks. It cannot ever be traversed.
Loop management
A loop header (sometimes called the entry point of the loop) is a dominator that is the target of a loop-forming back edge. The loop header dominates all blocks in the loop body. A block may be a loop header for more than one loop. A loop may have multiple entry points, in which case it has no "loop header".
Suppose block M is a dominator with several incoming edges, some of them being back edges (so M is a loop header). It is advantageous to several optimization passes to break M up into two blocks Mpre and Mloop. The contents of M and back edges are moved to Mloop, the rest of the edges are moved to point into Mpre, and a new edge from Mpre to Mloop is inserted (so that Mpre is the immediate dominator of Mloop). In the beginning, Mpre would be empty, but passes like loop-invariant code motion could populate it. Mpre is called the loop pre-header, and Mloop would be the loop header.
【Static Program Analysis - Chapter 2】 代码的表征之控制流图的更多相关文章
- 【Static Program Analysis - Chapter 2】 代码的表征之抽象语法树
抽象语法树:AbstractSyntaxTrees 定义(wiki): 在计算机科学中,抽象语法树(abstract syntax tree或者缩写为AST),或者语法树(syntax tree),是 ...
- 【Static Program Analysis - Chapter 4】格理论(Lattice Theory)与程序分析
# 从一个例子说起, **任务:给定这样一段代码,假设我们想分析出这段代码中,每个数值型变量和表达式的符号,即正数,负数或0.** 此外,还有可能出现两种情况就是: 1.我们无法分析出结果,即我们无法 ...
- 【Static Program Analysis - Chapter 3】Type Analysis
类型分析,个人理解就是(通过静态分析技术)分析出代码中,哪些地方只能是某种或某几种数据类型,这是一种约束. 例如,给定一个程序: 其中,我们可以很直接地得到一些约束: 最后,经过简化可以得到: 对 ...
- 【Static Program Analysis - Chapter 1】 Introduction
Regarding correctness, programmers routinely use testing to gain confidence that their programs work ...
- The Ultimate List of Open Source Static Code Analysis Security Tools
https://www.checkmarx.com/2014/11/13/the-ultimate-list-of-open-source-static-code-analysis-security- ...
- Top 40 Static Code Analysis Tools
https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/tools/top-40-static-code-analysis-tools/ In this article, I have ...
- 静态时序分析(static timing analysis)
静态时序分析(static timing analysis,STA)会检测所有可能的路径来查找设计中是否存在时序违规(timing violation).但STA只会去分析合适的时序,而不去管逻辑操作 ...
- static timing analysis 基础
此博文依据 特权同学在电子发烧友上的讲座PPT进行整理而成. static timing analysis 静态时序分析基础 过约束:有不必要的约束,或者是约束不能再某一情况下满足.——约束过头了 ...
- Soot生成代码控制流图
Soot可以对代码进行分析,提供了多种字节码分析和变换功能,通过它可以进行过程内和过程间的分析优化,以及程序流图的生成,还能通过图形化的方式输出. http://www.brics.dk/SootGu ...
随机推荐
- 使用Logstash filter grok过滤日志文件
Logstash提供了一系列filter过滤plugin来处理收集到的log event,根据log event的特征去切分所需要的字段,方便kibana做visualize和dashboard的da ...
- linux 时间同步的2种方法(转)
linux 时间同步的2种方法 张映 发表于 2012-10-23 分类目录: 服务器相关 标签:linux, ntp, 同步, 时间服务器 由于硬件的原因,机器或多或少的根标准时间对不上,一个月的误 ...
- CSS元素定位
使用 CSS 选择器定位元素 CSS可以通过元素的id.class.标签(input)这三个常规属性直接定位到,而这三种编写方式,在HTML中编写style的时候,可以进行标识如: #su ...
- Django REST framework 中的序列化器
在此之前定义一个序列化工具: views中的的代码 from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet from .models import B ...
- Linux命令第二篇
作业二: 1) 在用户的主目录下创建目录test,进入test创建空文件file1 # ls /home/test file 2) 以长格式形式显示文件信息,注意文件的权限和所属用户和组 # ...
- Servlet(7)—ServletConfig接口和SevletContext接口
ServletConfig接口 1. 可以获取当前Servlet在web.xml中的配置信息(用的不多) 2. 在不使用"硬编码"的情况下,将部署状态信息传递给Servlet.这个 ...
- MSSQL 调用C#程序集 实现C#字符串到字符的转化
10多年前用过MSSQL 调用C#程序集来实现数据的加密和解密,也搞过通过字符偏移实现简单的加密和解密.这次就总结一下吧: C#如下: public class CLRFunctions { /// ...
- android:Android中用文件初始化sqlite数据库(zz)
很多时候在应用安装初始化时,需要创建本地数据库,同时为数据库添加数据,之后再从数据库中读取数据. 这里有2个思路 1.先在本地创建一个能支持android使用的sqlite数据库文件,启动时, ...
- ajax跨域请求调用webservice接口
1.WebService 接口编写 步骤:新建web项目=>添加web service=>编写方法接口=>然后发布(本地测试可以直接把这个web service运行起来). 关键如何 ...
- SSE图像算法优化系列九:灵活运用SIMD指令16倍提升Sobel边缘检测的速度(4000*3000的24位图像时间由480ms降低到30ms)。
这半年多时间,基本都在折腾一些基本的优化,有很多都是十几年前的技术了,从随大流的角度来考虑,研究这些东西在很多人看来是浪费时间了,即不能赚钱,也对工作能力提升无啥帮助.可我觉得人类所谓的幸福,可以分为 ...
