算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-001选择排序法(Selection sort)
一、介绍
1.算法的时间和空间间复杂度

2.特点
Running time is insensitive to input. The process of finding the smallest item on one
pass through the array does not give much information about where the smallest item
might be on the next pass. This property can be disadvantageous in some situations.
For example, the person using the sort client might be surprised to realize that it takes
about as long to run selection sort for an array that is already in order or for an array
with all keys equal as it does for a randomly-ordered array! As we shall see, other algo-
rithms are better able to take advantage of initial order in the input.
Data movement is minimal. Each of the N exchanges changes the value of two array
entries, so selection sort uses N exchanges—the number of array accesses is a linear
function of the array size. None of the other sorting algorithms that we consider have
this property (most involve linearithmic or quadratic growth).
3.过程
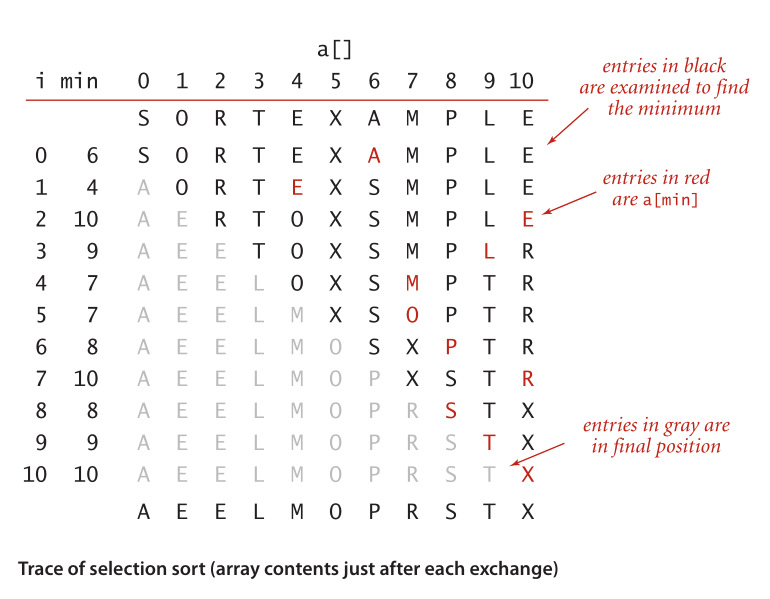
二、代码
package algorithms.elementary21; /******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac Selection.java
* Execution: java Selection < input.txt
* Dependencies: StdOut.java StdIn.java
* Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/21sort/tiny.txt
* http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/21sort/words3.txt
*
* Sorts a sequence of strings from standard input using selection sort.
*
* % more tiny.txt
* S O R T E X A M P L E
*
* % java Selection < tiny.txt
* A E E L M O P R S T X [ one string per line ]
*
* % more words3.txt
* bed bug dad yes zoo ... all bad yet
*
* % java Selection < words3.txt
* all bad bed bug dad ... yes yet zoo [ one string per line ]
*
******************************************************************************/ import java.util.Comparator; import algorithms.util.StdIn;
import algorithms.util.StdOut; /**
* The <tt>Selection</tt> class provides static methods for sorting an
* array using selection sort.
* <p>
* For additional documentation, see <a href="http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/21elementary">Section 2.1</a> of
* <i>Algorithms, 4th Edition</i> by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
*
* @author Robert Sedgewick
* @author Kevin Wayne
*/
public class Selection { // This class should not be instantiated.
private Selection() { } /**
* Rearranges the array in ascending order, using the natural order.
* @param a the array to be sorted
*/
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int N = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int min = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++) {
if (less(a[j], a[min])) min = j;
}
exch(a, i, min);
assert isSorted(a, 0, i);
}
assert isSorted(a);
} /**
* Rearranges the array in ascending order, using a comparator.
* @param a the array
* @param c the comparator specifying the order
*/
public static void sort(Object[] a, Comparator c) {
int N = a.length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int min = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < N; j++) {
if (less(c, a[j], a[min])) min = j;
}
exch(a, i, min);
assert isSorted(a, c, 0, i);
}
assert isSorted(a, c);
} /***************************************************************************
* Helper sorting functions.
***************************************************************************/ // is v < w ?
private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
} // is v < w ?
private static boolean less(Comparator c, Object v, Object w) {
return c.compare(v, w) < 0;
} // exchange a[i] and a[j]
private static void exch(Object[] a, int i, int j) {
Object swap = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = swap;
} /***************************************************************************
* Check if array is sorted - useful for debugging.
***************************************************************************/ // is the array a[] sorted?
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
return isSorted(a, 0, a.length - 1);
} // is the array sorted from a[lo] to a[hi]
private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
for (int i = lo + 1; i <= hi; i++)
if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) return false;
return true;
} // is the array a[] sorted?
private static boolean isSorted(Object[] a, Comparator c) {
return isSorted(a, c, 0, a.length - 1);
} // is the array sorted from a[lo] to a[hi]
private static boolean isSorted(Object[] a, Comparator c, int lo, int hi) {
for (int i = lo + 1; i <= hi; i++)
if (less(c, a[i], a[i-1])) return false;
return true;
} // print array to standard output
private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
StdOut.println(a[i]);
}
} /**
* Reads in a sequence of strings from standard input; selection sorts them;
* and prints them to standard output in ascending order.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
Selection.sort(a);
show(a);
}
}
算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-001选择排序法(Selection sort)的更多相关文章
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-007归并排序(自下而上)
一. 1. 2. 3. 二.代码 package algorithms.mergesort22; import algorithms.util.StdIn; import algorithms.uti ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-006归并排序(Mergesort)
一. 1.特点 (1)merge-sort : to sort an array, divide it into two halves, sort the two halves (recursivel ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-005插入排序的改进版
package algorithms.elementary21; import algorithms.util.StdIn; import algorithms.util.StdOut; /***** ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-004希尔排序法(Shell Sort)
一.介绍 1.希尔排序的思路:希尔排序是插入排序的改进.当输入的数据,顺序是很乱时,插入排序会产生大量的交换元素的操作,比如array[n]的最小的元素在最后,则要经过n-1次交换才能排到第一位,因为 ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-002插入排序法(Insertion sort)
一.介绍 1.时间和空间复杂度 运行过程 2.特点: (1)对于已排序或接近排好的数据,速度很快 (2)对于部分排好序的输入,速度快 二.代码 package algorithms.elementar ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-008排序算法的复杂度(比较次数的上下限)
一. 1. 2.
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-2.1Elementary Sortss-003比较算法及算法的可视化
一.介绍 1. 2. 二.代码 1. package algorithms.elementary21; /*********************************************** ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-001递归
一. 方法可以调用自己(如果你对递归概念感到奇怪,请完成练习 1.1.16 到练习 1.1.22).例如,下面给出了 BinarySearch 的 rank() 方法的另一种实现.我们会经常使用递归, ...
- 算法Sedgewick第四版-第1章基础-1.3Bags, Queues, and Stacks-001可变在小的
1. package algorithms.stacks13; /******************************************************************* ...
随机推荐
- 打印a*a的乘法表
/*利用for循环打印 9*9 表? 1*1=1 1*2=2 2*2=4 1*3=3 2*3=6 3*3=9 1*4=4 2*4=8 3*4=12 4*4=16 1*5=5 2*5=10 3*5=15 ...
- @angular/cli项目构建--组件
环境:nodeJS,git,angular/cli npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org cnpm instal ...
- hdoj-3791-二叉搜索树(二叉搜索树模板题)
#include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> using namespace std; type ...
- Codeforces Round #242 (Div. 2)C(找规律,异或运算)
一看就是找规律的题.只要熟悉异或的性质,可以秒杀. 为了防止忘记异或的规则,可以把异或理解为半加运算:其运算法则相当于不带进位的二进制加法. 一些性质如下: 交换律: 结合律: 恒等律: 归零律: 典 ...
- jquery 获取所有父元素
最终结果: 代码: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> b, span, p, html body { padd ...
- HDU4416Good Article Good sentence(后缀自动机)
Problem Description In middle school, teachers used to encourage us to pick up pretty sentences so t ...
- C++中rand()函数的用法
1.rand()不需要参数,它会返回一个从0到最大随机数的任意整数,最大随机数的大小通常是固定的一个大整数. 2.如果你要产生0~99这100个整数中的一个随机整数,可以表达为:int num = r ...
- 使用POI导出excel进阶篇
进阶篇就是涉及到合并单元格了.就是某一列相同的单元格需要合并为一个,并分为多个sheet. 效果如图: 直接上代码,需要提供的数据自己搞,传到工具类里面就好. JcExcelVoSuper.java ...
- Linux查找/扫描局域网打印机IP
假设在 192.168.10.* 有一台网络打印机,但是我们不知道它的地址.一种笨方法就是在浏览器中依次输入 192.168.10.1 到 192.168.10.254,看是否出现管理页面. 另一种思 ...
- 第四篇 PHP的成长路线
学PHP开发这么久,进步不大,个人进行了分析.认为是我自己没有设定目标,就是对于自己要学成什么样没有清晰的认识. 今天特别了解了一下PHP的成长参考路线,以便自己以后迷失方向.PHP主要应该基于MYS ...
