day09作业
一.填空题
1.方法 2.堆内存 3.构造方法 4.this 5.this 6.static 7.使用类名进行访问 8.package import class 9.关键字 10.lang
二.选择题
1.D 2.B 3.D 4.AC 5.AC
三.判断题
1.√ 2.× 3.√ 4.× 5.√ 6.× 7.√
四.
1.构造方法的作用是给对象进行初始化。
特点:1.方法名与类名相同(大小写也一致)
2.没有返回值类型,连void也没有
3.没有具体的返回值return
注意事项:
1.如果我们没有给出构造方法,系统将自动给出一个无参构造方法。
2.如果我们给出了构造方法,系统将不会提供默认的无参构造方法。
可以不写return语句。
2.setXxx()方法和构造方法
3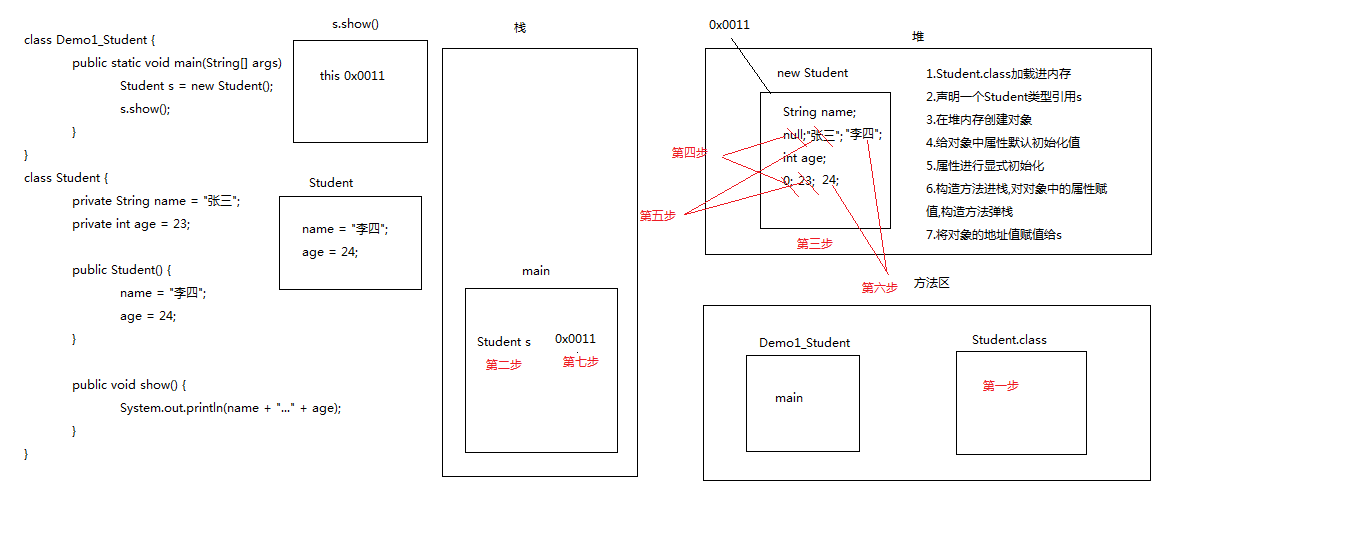
4.a. 随着类的加载而加载
b:优先于对象存在
c:被类的所有对象共享
d.可以通过类名调用
当对象出现共享数据时,该数据用static修饰。
5.public static void main(String[] args){}
public : 被jvm调用,所以权限要足够大
static : 被jvm调用,不需要创建对象,直接类名.调用即可
void : 被jvm调用,不需要有任何的返回值
main : 只有这样写才能被jvm识别,main不是关键字
String[] args : 以前是用来接收键盘录入的
class Test13_Vehicle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vehicle a = new Vehicle();
a.setSpeed(10);
a.setSize(10);
System.out.println(a.speedUp() + " " + a.speedDown());
}
}
class Vehicle {
private int speed;
private int size;
public Vehicle(){}
public Vehicle(int speed,int size){
this.speed = speed;
this.size = size;
}
public void setSpeed(int speed){
this.speed = speed;
}
public int getSpeed(){
return speed;
}
public void setSize(int size){
this.size = size;
}
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
public int speedUp(){
return speed += 1;
}
public int speedDown(){
return speed -= 1;
}
}
class Test10_Person {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p.setName("张三");
p.setAge(24);
p.display();
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("姓名:" + name + " " + "年龄:" + age);
}
}
class Test11_Circle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle c = new Circle(1.5);
System.out.println(c.getArea() + " " + c.getPerimeter());
}
}
class Circle {
private double radius;
public Circle(){}
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius(){
return radius;
}
public double getArea(){
return 3.14 * radius * radius;
}
public double getPerimeter(){
return 2 * 3.14 * radius;
}
}
class Test12_Network {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Network a = new Network("Mike","123456","123456");
System.out.println("用户ID:" + a.getId() + " " + "用户密码:" + a.getPassword() + " " + "用户邮箱:" + a.getEmail() + "@gameschool.com");
}
}
class Network {
private String id;
private String password;
private String email;
public Network(){}
public Network(String id,String password,String email){
this.id = id;
this.password = password;
this.email = email;
}
public void setId(String id){
this.id = id;
}
public String getId(){
return id;
}
public void setPassword(String password){
this.password = password;
}
public String getPassword(){
return password;
}
public void setEmail(String Email){
this.email = email;
}
public String getEmail(){
return email;
}
}
class Test14_Calculaion {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculaion n = new Calculaion(10);
System.out.println(n.add() + " " + n.sub() + " " + n.times() + " " + n.div());
}
}
class Calculaion {
private int num;
public Calculaion(){}
public Calculaion(int num){
this.num = num;
}
public void setNum(int num){
this.num = num;
}
public int getNum(){
return num;
}
public int add(){
return num += 2;
}
public int sub(){
return num -= 2;
}
public int times(){
return num *= 2;
}
public int div(){
return num /= 2;
}
}
class Test15_Draw {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Draw p = new Draw(10,3);
p.drawTrian();
p.drawRec();
p.drawPra();
}
}
class Draw {
private int count;
private int lines;
public Draw(){}
public Draw(int count,int lines){
this.count = count;
this.lines = lines;
}
public void setCount(){
this.count = count;
}
public int getCount(){
return count;
}
public void setLines(){
this.lines = lines;
}
public int getLines(){
return lines;
}
public void drawTrian(){
int m = 0;
a:for (int i = 0;i < lines ;i++ ) {
for (int k = 0;k < lines - i ;k++ ) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = 1;j <= 2 * i - 1 ;j++ ) {
System.out.print("*");
m++;
if (m == count) {
break a;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void drawRec(){
int row = count / lines;
int m = 0;
a:for (int i = 0;i < lines ;i++ ) {
for (int j = 0;j <= row ;j++ ) {
System.out.print("*");
m++;
if (m == count) {
break a;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public void drawPra(){
int row = count / lines;
int m = 0;
a:for (int i = 0;i < lines ;i++ ) {
for (int j = 1;j < i ;j++ ) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int k = 0;k <= row;k++ ) {
System.out.print("*");
m++;
if (m == count) {
break a;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class Test16_Fridge {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fridge f = new Fridge();
f.setBrand("海尔");
f.setHorsepower("100匹");
f.setTemperature("零下5℃");
f.heat();
f.refrigeration();
f.ventilate();
}
}
class Fridge {
private String brand;
private String horsepower;
private String temperature;
public Fridge(){}
public Fridge(String brand,String horsepower,String temperature){
this.brand = brand;
this.horsepower = horsepower;
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public void setBrand(String brand){
this.brand = brand;
}
public String getBrand(){
return brand;
}
public void setHorsepower(String horsepower){
this.horsepower = horsepower;
}
public String getHorsepower(){
return horsepower;
}
public void setTemperature(String temperature){
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public String getTemperature(){
return temperature;
}
public void heat(){
System.out.println("加热");
}
public void refrigeration(){
System.out.println("制冷");
}
public void ventilate(){
System.out.println("通风");
}
}
day09作业的更多相关文章
- python day09作业答案
2. def lst(input): lst2=[] count=0 for i in range(0,len(input)): if i %2!=0: lst2.append(input[i]) r ...
- python day09作业
- day09作业—函数进阶
# 2.写函数,接收n个数字,求这些参数数字的和.(动态传参) def func1(*args): sum = 0 for i in args: sum += i print(sum) func1(1 ...
- day09 作业
简述定义函数的三种方式 空函数.无参函数.有参函数 简述函数的返回值 函数内部代码经过一系列的逻辑处理返回的结果 函数没有返回值,默认返回None 函数可以通过return返回出返回值 return可 ...
- day09作业01用户登录与验证
import timeLoginTime = time.asctime( time.localtime(time.time()) )print ("time %s" % Login ...
- python 作业
Linux day01 计算机硬件知识整理 作业要求:整理博客,内容如下 编程语言的作用及与操作系统和硬件的关系 应用程序->操作系统->硬件 cpu->内存->磁盘 cpu与 ...
- DSB
Linux day01 计算机硬件知识整理 作业要求:整理博客,内容如下 编程语言的作用及与操作系统和硬件的关系 应用程序->操作系统->硬件 cpu->内存->磁盘 cpu与 ...
- Python异常处理和进程线程-day09
写在前面 上课第九天,打卡: 最坏的结果,不过是大器晚成: 一.异常处理 - 1.语法错误导致的异常 - 这种错误,根本过不了python解释器的语法检测,必须在程序运行前就修正: - 2.逻辑上的异 ...
- python开发学习-day09(队列、多路IO阻塞、堡垒机模块、mysql操作模块)
s12-20160312-day09 *:first-child { margin-top: 0 !important; } body>*:last-child { margin-bottom: ...
随机推荐
- 20135239 益西拉姆 linux内核分析 可执行程序的装载
益西拉姆 + 原创作品请勿转载 + <Linux内核分析>MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000 ” week 7 可 ...
- Tensorflow实战Google深度学习框架-总结-1
第一章:深度学习简介 1⃣️应用有 1.计算机视觉 2.语音识别 3.自然语言处理 4.人机博弈 2⃣️深度学习,机器学习,AI 的关系
- 梯度提升树GBDT算法
转自https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/29802325 本文对Boosting家族中一个重要的算法梯度提升树(Gradient Boosting Decison Tree, 简 ...
- PDF文本内容批量提取到Excel
QQ:231469242,版权所有 sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘 https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269 ...
- Android的taskAffinity对四种launchMode的影响
在Android系统中,一个application的所有Activity默认有一个相同的affinity(亲密关系,相似之处).也就是说同一个应用程序的的所有Activity倾向于属于同一个task. ...
- KVM管理概述
一.使用QEMU管理虚拟机 1.KVM指南 https://activedoc.opensuse.org/book/opensuse-virtualization-with-kvm/part-iii- ...
- 视音频数据处理入门:UDP-RTP协议解析
===================================================== 视音频数据处理入门系列文章: 视音频数据处理入门:RGB.YUV像素数据处理 视音频数据处理 ...
- 海思Hi3518A 海思Hi3518C 海思Hi3518E 这几个芯片都有什么区别么
在3518A.3518C的基础上深化完善,推出了Hi3518E.作为新一代IP民用摄像机SoC,Hi3518E集成新一代ISP,优化了编码前图像处理算法,采用新一代H.264编码器.同时采用业内领先的 ...
- Spyder简述
导言 想打造轮子, 就必须要有一套完善的造轮子的工具. 我在jupyter+sciTE的组合里转来转去, 最后还是打算放弃这个组合, 因为离开了自动完成/调用提示/随时随地的访问文档帮助, 前行之路太 ...
- Spring Data JPA原生SQL查询
package com.test.cms.dao.repository;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import javax.pe ...
