论文:Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention-阅读总结
Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention-阅读总结
笔记不能简单的抄写文中的内容,得有自己的思考和理解。
一、基本信息
**\1.标题:**Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention
**\2.作者:**Kelvin Xu,Jimmy Lei Ba,Ryan Kiros,Kyunghyun Cho,Aaron Courville,Ruslan Salakhutdinov,Richard S. Zemel,Yoshua Bengio
**\3.作者单位:**UC Berkeley,University of Toronto,Google Research,New York University&Facebook AI Research,Université de Montréal,CMU,University of Toronto, University of Montreal
**\4.发表期刊/会议:**ICML
**\5.发表时间:**2015
二、看本篇论文的目的
to study the attention mechanism used in natural image caption algorithm.
三、场景和问题
scene: image caption, natural image, scene understanding
problem: how to train the model in a deterministic manner using standard backpropagation techniques and stochastically by maximizing a variational lower bound.
四、研究目标
Models with an attention mechanism can attend to the salient part of an image while generating its caption.
五、主要思路/创新
Main inspiration:
\1.one of the most curious facets of the human cisual system is the presence of attention.
\2.Using representations (such as those from the very top layer of a convnet) that distill information in image down to the most salient objects has one potential drawback of losing informaiton which could be useful for richer, more descriptive captions.
\3.It necessitates a powerful mechanism to steer the model to informaiton important to the task at hand when using lower-level representation.
\4.Recent advances in caption generation and recent successes in employing attention in machine translation and object recognition.
Main innovation:
\1.Two attention mechanism:
a "soft" deterministic attention mechanism trainable by standard back-propagation methods.
a "hard" stochastic attention mechanism trainable by maximizing an approximate variational lower bound or equivalently by REINFORCE.
\2.Show how to gain insight and interpret the results of the framework by visualizing "where" and "what" the attention focused on.
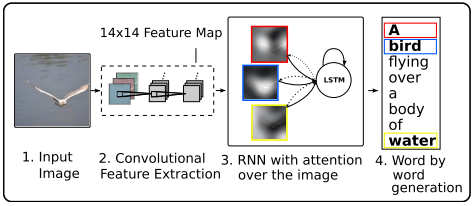
六、算法概述
\1.Encoder:
①.caption y is encoded as a sequence of 1-of-K encoded words:
y={\{\mathtt{y_1,\dots,y_C}\}},\mathtt{y_i}\in\mathbb{R}^K
\]
K is the size of the vocabulary and C is the length of the caption.
②.extractor (a convolutional neural network) produces L vectors, each of which is a D-dimensional representation corresponding to a part of the iamge:
a={\{\mathtt{a_1,\dots,a_L}\}},\mathtt{a_i}\in\mathbb{R}^D
\]
features are extracted from a lower convolutional layer, which allows the decoder to selectively focus on certain parts of an image by weighting a subset of all the feature vectors.
\2.Decoder:
①.LSTM network:
\begin{align*}
& \mathbf{i_t}=\sigma(W_iE\mathbf{y}_{t-1}+U_i\mathbf{h}_{t-1}+Z_i\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t+\mathbf{b}_i)\\
& \mathbf{f_t}=\sigma(W_fE\mathbf{y}_{t-1}+U_f\mathbf{h}_{t-1}+Z_f\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t+\mathbf{b}_f)\\
& \mathbf{c}_t=\mathbf{f}_t\mathbf{c}_{t-1}+\mathbf{i}_t\mathsf{tanh}(W_cE\mathbf{y}_{t-1}+U_c\mathbf{h}_{t-1}+Z_c\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t+\mathbf{b}_c)\\
& \mathbf{o}_t=\sigma(W_oE\mathbf{y}_{t-1}+U_o\mathbf{h}_{t-1}+Z_o\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t+\mathbf{b}_o)\\
&\mathbf{h}_t=\mathbf{o}_t\mathsf{tanh}(\mathbf{c}_t)
\end{align*}
\]
\(\mathbf{i_t,f_t,c_t,o_t,h_t}\) are the input, forget, memory, output and hidden state of the LSTM respectively. \(W_{\bullet},U_{\bullet},Z_{\bullet},\mathbf{b}_{\bullet}\) are learned weight matricies and biases.\(\mathbf{E}\in\mathbb{R}^{m\times K}\) is an embedding matrix. \(m\) and \(n\) denote the embedding and LSTM dimensionality. \(\sigma\) is the logistic sigmoid activation.
②.\(\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t\) is a dynamic representation of the relevant part of the image input at time t.
③.a mechanism \(\phi\) computes \(\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t\) from the annotation vectors \(\mathbf{a}_i,i=1,\dots,L\) corresponding to the features extracted at different image locations.
For each location \(i\), \(\phi\) generates a positive weight \(\alpha_i\) which can be interpreted either as the probability that location \(i\) is the right place to focus for producing the next word (stochastic attention mechanism), or as the relative importance to give to location \(i\) in blending the $ \mathbf_i$'s together (deterministic attention mechanism).
④.weight \(\alpha_i\) of each annotation vector \(a_i\) is computed by an \(attention\,model\,f_{att}\) (a multilayer perceptron conditioned on the previous hidden state \(\mathbf{h}_{t-1}\))
\begin{align*}
&e_{ti}=f_{att}({\mathbf{a}_i},\mathbf{h}_{t-1})\\
&\alpha_{ti}=\frac{exp(e_{ti})}{\sum^L_{k=1}exp(e_{tk})}
\end{align*}
\]
once the wrights (which sum to one) are computed, the context vector \(\hat{z}_t\) is computed by:
\mathbf{\hat{z}_t}=\phi(\{\mathbf{a}_i\},\{\alpha_i\})
\]
⑤.The initial memory state and hidden state of the LSTM:
\mathbf{c}_0=f_{init,c}\left(\frac{1}{L}\sum^L_i\mathbf{a}_i\right),\mathbf{h}_0=f_{init,h}\left({\frac{1}{L}\sum^L_i\mathbf{a}_i}\right)
\]
⑥.a deep output layer computes the output word probability from the image (the context vector), the previously generated word, and the decoder state (\(h_t\)):
p(\mathbf{y}_t|\mathbf{a},\mathbf{y}_1^{t-1})\propto exp(\mathbf{L}_o(\mathbf{Ey_{t-1}}+\mathbf{L}_h\mathbf{h}_t+\mathbf{L}_z\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t))
\]
\(\mathbf{L}_o\in \mathbb{R}^{K\times m},\mathbf{L}_h\in \mathbb{R}^{m\times n},\mathbf{L}_z\in \mathbb{R}^{m\times D}\,and\,\mathbf{E}\) are learned parameters initialized randomly.
七、两种Attention机制实现细节
Stochastic "Hard" Attention:
\1.location variable \(s_{t,i}\), an indicator one-hot variable which is set to 1 if the \(i\)-th location (out of \(L\)) is the one used to extract visual features for generating the \(t\)-th word.
\2.Assign a multinoulli distribution parametrized by \(\{\alpha_i \}\) to treat the attention locations as intermediate latent variables, and \(\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t\) can be viewed as a random variable:
理解:multinoulli distribution explanation
\begin{align*}
&p(s_{t,i}=1|s_{j<t},\mathbf{a})=\alpha_{t,i}\\
&\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t=\sum_is_{t,i}\mathbf{a}_i
\end{align*}
\]
\3.a new objective function \(L_s\):
\begin{align*}
L_s & =\sum_s\,p(s|\mathbf{a})\mathsf{log}\, p(\mathbf{y}|s,\mathbf{a})\\
&\leq \mathsf{log\sum_s}\, p(s|\mathbf{a})p(\mathbf{y}|s,\mathbf{a})\\
&=\mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|\mathbf{a})
\end{align*}
\]
\(\mathbf{y}\) the sequence of words, \(\mathbf{a}\) the given image features, So parameters \(W\) of the models can be derived by directly optimizing.
\4.\(L_s\)'s gradient:
\frac{\partial L_s}{\partial W}=\sum_s\,p(s|\mathbf{a})\left[\frac{\partial\,\mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|s,\mathbf{a})}{\partial W}+\mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|s,\mathbf{a})\frac{\partial\,\mathsf{log}\,p(s|\mathbf{a})}{\partial W}\right]
\]
the gradient of \(L_s\) is approximated by a Monte Carlo method:
\frac{\partial L_s}{\partial W}\approx \frac{1}{N}\sum_s^N\left[\frac{\partial\,\mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|\tilde{s}^n,\mathbf{a})}{\partial W}+\mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|\tilde{s}^n,\mathbf{a})\frac{\partial\,\mathsf{log}\,p(\tilde{s}^n|\mathbf{a})}{\partial W}\right]\\
\tilde{s}^n_t \sim \mathbf{Multinoulli}(\{\ \alpha_i^n \})
\]
\(\tilde{s}^n=(s^n_1,s^n_2,\dots)\) is a sequence of sampled attention locations from a multinouilli distribution.
\5.Moving average baseline technique -- to reduce the variance of the estimator:
b_k = 0.9\times b_{k-1} + 0.1\times \mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|\tilde{s}_k,\mathbf{a})
\]
to further reduce the estimator variance, the gradient of the entropy \(H[s]\) of the multinouilli distribution is added to the RHS of Eq.(7), final learning rule for the model:
\begin{align*}
\frac{\partial L_s}{\partial W}&\approx \frac{1}{N}\sum_{n=1}^N\left[\frac{\partial\,\mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|\tilde{s}^n,\mathbf{a})}{\partial W}+\\
\lambda_r(\mathsf{log}\,p(\mathbf{y}|\tilde{s}^n,\mathbf{a})-b)\frac{\partial\,\mathsf{log}\,p(\tilde{s}^n|\mathbf{a})}{\partial W}+\lambda_e\frac{\partial H[\tilde{s}^n]}{\partial W}\right]
\end{align*}
\]
\(\lambda_r\) and \(\lambda_e\) are two hyper-parameters set by cross-validation.
\6.to further improve the robustness fo the learning rule, with probability 0.5 for a given image, the sampled attention location \(\tilde{s}\) is set to its expected value \(\alpha\) (equivalent to the deterministic attention).
the formulation is equivalent to the \(\mathbf{RENIFORCE}\) learning rule, where the reward for the attention choosing a sequence of actions is a real value proportional to the log likelihood of the target sentence under the sampled attention trajectory.
Deterministic "Soft" Attention:
\1.Instead of sampling the attention location \(s_t\) each time, it just take the expectation of the context vector \(\hat{z}_t\) directly:
\mathbb{E}_{p(s_t|a)}[\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t]=\sum_{i=1}^L\, \alpha_{t,i}\mathbf{a}_i
\]
the soft attention weighted annotation vector is computed by : \(\phi(\{\mathbf{a_i}\},\{\alpha_i\})=\sum^L_i\alpha_i\mathbf{a}_i\), which corresponds to feeding in a soft \(\alpha\) weighted context into the system.
\2.\(\mathbf{n}_{t,i}\) is denoted as \(\mathbf{n}\) in Eq.(2) with \(\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t\) set to \(\mathbf{a}_i\). The normalized weighted geometric mean (NWGM) of the softmax of \(k\)-th word prediction:
\begin{align*}
\mathbf{NWGM}[p(y_t=k|\mathbf{a})]&=\frac{\prod_i\mathsf{exp}(n_{t,k,i})^{p(s_{t,i}=1|a)}}{\sum_j\prod_i\mathsf{exp}(n_{t,j,i})^{p(s_{t,i} = 1|a)}}\\
&=\frac{\mathsf{exp}(\mathbb{E}_{p(s_t|a)}[n_{t,k}])}{\sum_j\mathsf{exp}(\mathbb{E_{p(s_t|a)}}[n_{t,j}])}
\end{align*}
\]
This implies that the NWGM of the word prediction can be well approximated by using the expected context vector \(\mathbb{E}[\mathbf{\hat{z}}_t]\), instead of the sampled context vector \(\mathbf{a}_i\). Furthermore, the \(\mathbf{NWGM}\) can be computed by a single feedforward computation approximates the expection \(\mathbb{E}[p(y_t=k|\mathbf{a})]\) of the output over all possible attention locations induced by random variable \(s_t\).
Suggesting that the proposed deterministic attention model approximately maximizes the marginal likelihood over all possible attention locations.
\3.①.In training the deterministic model, a doubly stochastic regularization encourages the model to pay equal attention to every part of the image.
The attention \(\sum_i\alpha_{ti} = 1\) makes it possible for the decoder to ignore some parts of the input image, and encourage \(\sum_t\alpha_{ti}\approx \tau,\tau \ge \frac{L}{D}\). This penalty quantitatively improves overall performance and it qualitatively leads to more descriptive captions.
②.the soft attention model predicts a gating scalar \(\beta\) from previous hidden state \(\mathbf{h}_{t-1}\) at each time step t, such that, \(\phi(\{\mathbf{a_i}\},\{\alpha_i\})=\beta\sum_i^L\alpha_i\mathbf{a}_i\), \(\beta_t=\sigma(f_{\beta}(\mathbf{h}_{t-1}))\). This gating variable lets the decoder decide whether to put more emphasis on language modeling or on the context at each time step.
③.The soft attention model is trained end-to-end by minimizing the penalized negative log-likelihood:
L_d=-log(p(\mathbf{y}|\mathbf{a}))+\lambda\sum_i^L(1-\sum^C_t\alpha_{ti})^2
\]
\(\tau\) is simply fixed to 1.
八、采用的数据集&评价指标
Datasets:
Flickr8k, Flickr30k,(each image has 5 reference captions),MS COCO(discarding caption in excess of 5 to maintain a same number of references between the datasets).
Metrics:
BLEU (from 1 to 4 without a brevity penalty), METEOR (because of the criticism of BLEU)
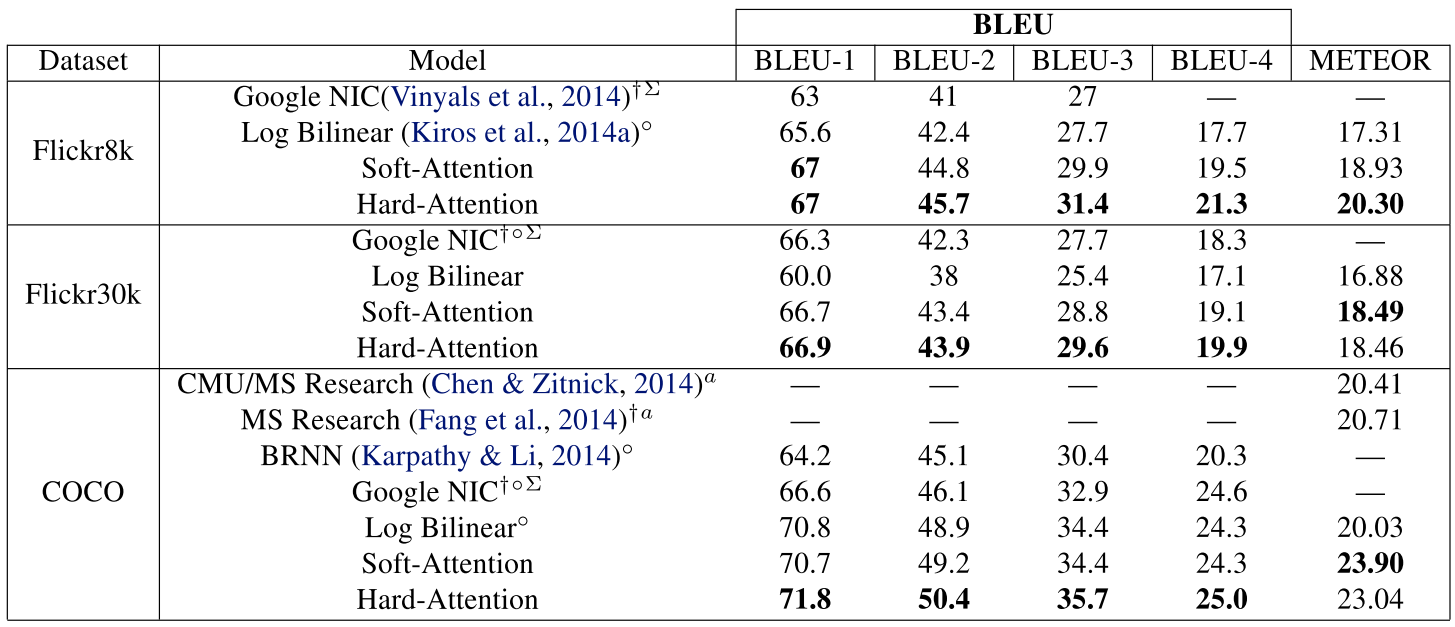
九、实验细节
Training Details:
\1.Both model were trained with stochastic gradient descent using adaptive learning rates. Flickr8k dataset--RMSProp works best, Flickr30k/MSCOCO dataset--Adam algorithm is quite effective.
\2.the encoder (creates the annotations \(a_i\)) -- the Oxford VGGnet pretrained on ImageNet without finetuning, and just use the $14\times14\times512$ feature map of the fourth convolutional layer before max pooling to create the flattened $196\times512$ encoding to the decoder. In addition, with enough data, the encoder could also be trained from scratch (or fine-tune) with the rest of the model.
\3.problem: the implementation requires time proportional to the length of the longest sentence per update, and training on a random group of captions is computationally wasteful.
solution: In preprocessing, building a dictionary to map the length of a sentence to the corresponding subset of captions. During training, randomly sampling a length and retrieve a mini-batch of size 64 of that length.
performance: greatly improved convergence speed with no noticeable diminishment, on the largest dataset(MS COCO) it takes less than 3 days training on an NVIDIA Titan Black GPU.
\4.regularization strategy: dropout, early stopping on BLEU score (it observed a breakdown in correlation between the validation set log-likelihood and BLEU in the later stages of training during the experiments.)
十、验证的问题&效果
Question 1:
single model versus ensemble comparison:
in the results, it just report a single mdel performance.
Question 2:
differences between dataset splits:
Flickr8k -- predefined splits
Flickr30k and COCO -- lack of standardized splits, reported with publicly available splits used in previous work
however, the differences in splits do not make a substantial difference in overall performance.
Question 3:
quantitative effectiveness of attention:
①.obtain state of the art performance on the Flickr8k, Flickr30k and MS COCO.
②.significantly improve the state-of-the-art performance METEOR on MS COCO.
③.it speculates that the improvement connected to some of the regularization techniques and the lower-level representation.
Question 4:
visualizing the attention learned by the model:
add an extra layer of interpretability to the output of the model.
①.the only time the feature maps decrease in size are due to the max pooling layers, because the 19-layer OxfordNet uses stacks of 3x3 filters.
②.The input image is resized so that the shortest side is 256-dimensional with preserved aspect ratio, and input the center-cropped 224x224 image to the convolutional network, then with four max pooling layers, it gets an output dimension of the top convolutional layer of 14x14.
③.upsample the weights by a factor of $2^4=16$ and apply a Gaussian filter to emulate the large receptive field size to visulize the attention weights for the soft model.


论文:Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention-阅读总结的更多相关文章
- 论文笔记:Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention
Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention 2018-08-10 10:15:06 Pap ...
- [Paper Reading] Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03044.pdf 代码链接:https://github.com/kelvinxu/arctic-captions & htt ...
- Paper Reading - Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention ( ICML 2015 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03044.pdf Main Points: Encoder-Decoder Framework: Enco ...
- 论文:Show and Tell: A Neural Image Caption Generator-阅读总结
Show and Tell: A Neural Image Caption Generator-阅读总结 笔记不能简单的抄写文中的内容,得有自己的思考和理解. 一.基本信息 标题 作者 作者单位 发表 ...
- Paper Reading - Show and Tell: A Neural Image Caption Generator ( CVPR 2015 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1411.4555 Main Points: A generative model ( NIC, GoogLeNet ...
- 论文解读《Bilinear Graph Neural Network with Neighbor Interactions》
论文信息 论文标题:Bilinear Graph Neural Network with Neighbor Interactions论文作者:Hongmin Zhu, Fuli Feng, Xiang ...
- 从Image Caption Generation理解深度学习
0. 前面的话 建丁让我写一篇深度学习相关小文章,目标读者是国内的开发者.刚接到这个任务时我是颇为忐忑的,写文章要讲究厚积薄发,如果“水之积也不厚”,“则其负大舟也无力”.因为我自知水平很有限,又不是 ...
- 论文笔记之: Recurrent Models of Visual Attention
Recurrent Models of Visual Attention Google DeepMind 模拟人类看东西的方式,我们并非将目光放在整张图像上,尽管有时候会从总体上对目标进行把握,但是也 ...
- Paper Reading - Mind’s Eye: A Recurrent Visual Representation for Image Caption Generation ( CVPR 2015 )
Link of the Paper: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7298856/ A Correlative Paper: Learning a Rec ...
随机推荐
- C语言编译过程以及Windows中的gcc编译程序(通过cmd、记事本)
C语言的编译过程 1)预处理:宏定义展开.头文件展开.条件编译等,同时将代码中的注释删除,这里并不会检查语法 2)编译:检查语法,将预处理后的文件编译生成汇编文件 3)汇编:将汇编文件生成目标文件(二 ...
- Jmeter(二十一) - 从入门到精通 - JMeter断言 - 上篇(详解教程)
1.简介 最近由于宏哥在搭建自己的个人博客可能更新的有点慢.断言组件用来对服务器的响应数据做验证,常用的断言是响应断言,其支持正则表达式.虽然我们的通过响应断言能够完成绝大多数的结果验证工作,但是JM ...
- 封装react antd的upload上传组件
上传文件也是我们在实际开发中常遇到的功能,比如上传产品图片以供更好地宣传我们的产品,上传excel文档以便于更好地展示更多的产品信息,上传zip文件以便于更好地收集一些资料信息等等.至于为何要把上传组 ...
- Testflight无法接入App Store connect,对TF上架的应用会造成什么影响吗?
感觉进入8月份以来,苹果也进入了多事之秋.不仅是App Store被下架,testflight也频频出问题,很多人反馈出现了Testflight无法接入App Store connect的问题,我们之 ...
- 多线程的指令重排问题:as-if-serial语义,happens-before语义;volatile关键字,volatile和synchronized的区别
一.指令重排问题 你写的代码有可能,根本没有按照你期望的顺序执行,因为编译器和 CPU 会尝试指令重排来让代码运行更高效,这就是指令重排. 1.1 虚拟机层面 我们都知道CPU执行指令的时候,访问内存 ...
- 大数据理论篇HDFS的基石——Google File System
Google File System 但凡是要开始讲大数据的,都绕不开最初的Google三驾马车:Google File System(GFS), MapReduce,BigTable. 为这一切的基 ...
- linux 强制重启!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/wipy/p/4261472.html 有时候,linux 由于硬盘或者其它原因, 某个进程挂住了,怎么也杀不死, 输入 reboot 命令也 ...
- HM16.0之帧间预测——xCheckRDCostInter()函数
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/nb_vol_1/article/category/6179825/1? 1.源代码: #if AMP_MRG Void TEncCu::xCheck ...
- VMDNAMD命令规则(转载)
输出体系的整个带电量:measure sumweights $all weight charge 给PDB文件设置周期边界条件:pbc set {54 54 24 } -all 将此晶胞内原子脱除周期 ...
- Answers for Q1 and Q2
A1: 1. enetity-data model mapping: 2. database design 2.1 sql create table A_manufacturer_info(manu ...
