Java 树结构的基础部分(二)
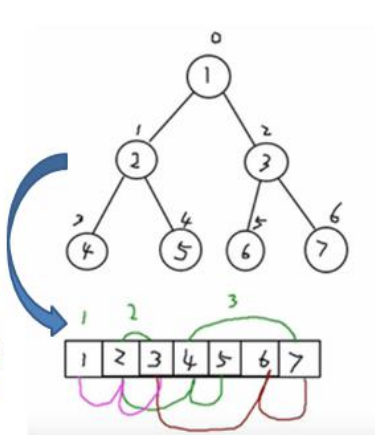
package com.lin.tree_0308;
public class ArrBinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
ArrBinaryTree arrBinaryTree = new ArrBinaryTree(arr);
System.out.println("前序遍历:");
arrBinaryTree.preOrder();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
arrBinaryTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("后序遍历:");
arrBinaryTree.postOrder();
}
}
class ArrBinaryTree{
private int[] arr;
public ArrBinaryTree(int[] arr) {
super();
this.arr = arr;
}
// 重载
public void preOrder() {
this.preOrder(0);
}
public void infixOrder() {
this.infixOrder(0);
}
public void postOrder() {
this.postOrder(0);
}
/**
*
* @Description:
* @author LinZM
* @date 2021-3-8 19:14:45
* @version V1.8
* @param index 数组下标
*/
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder(int index) {
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空!");
}
// 输出当前数据
System.out.print(arr[index] + " ");
// 向左递归
if( ( index * 2 + 1 ) < arr.length ) {
preOrder( index * 2 + 1 );
}
// 向右递归
if( ( index * 2 +2 ) < arr.length ) {
preOrder( index * 2 + 2 );
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder(int index) {
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空!");
}
// 向左递归
if( ( index * 2 + 1 ) < arr.length) {
infixOrder( index * 2 + 1);
}
// 输出当前数据
System.out.print(arr[index] + " ");
// 向右递归
if( ( index * 2 + 2 ) < arr.length) {
infixOrder(index*2 + 2);
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder(int index) {
if(arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空!");
}
// 向左递归
if( ( index * 2 + 1) < arr.length ) {
postOrder(index * 2 + 1);
}
// 向右递归
if( ( index * 2 + 2 ) < arr.length) {
postOrder(index * 2 + 2);
}
// 输出当前数据
System.out.print(arr[index] + " ");
}
}

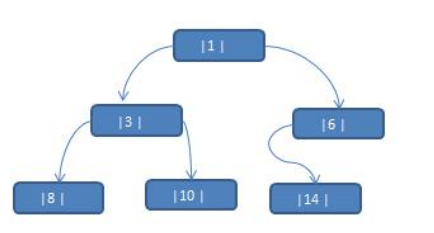
package com.lin.tree_0308;
public class ThreadeBinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TNode tNode1 = new TNode(1, "Tom");
TNode tNode2 = new TNode(3, "Jack");
TNode tNode3 = new TNode(6, "Smith");
TNode tNode4 = new TNode(8, "Marry");
TNode tNode5 = new TNode(10, "Linda");
TNode tNode6 = new TNode(14, "King");
tNode1.setLeft(tNode2);
tNode1.setRight(tNode3);
tNode2.setLeft(tNode4);
tNode2.setRight(tNode5);
tNode3.setLeft(tNode6);
TBinaryTree tBinaryTree = new TBinaryTree();
tBinaryTree.setRoot(tNode1);
tBinaryTree.threadedInfixNodes(tNode1);// 10test
TNode left = tNode5.getLeft();
TNode right = tNode5.getRight();
System.out.println(left);
System.out.println(right);
// // 中序遍历线索化二叉树
// System.out.println("中序遍历线索化二叉树:");
// tBinaryTree.threadedInfixList();
}
}
class TBinaryTree{
private TNode root;
// 前驱节点的指针,总是保留前一个节点
private TNode pre;
public void setRoot(TNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
public void threadedPreNodes(TNode node) {
if(node == null) {
System.out.println("空!!!");
return;
}
// 1 线索当前节点
// 先处理节点的前驱节点
if (node.getLeft() == null) {
// 让当前节点的左指针指向前驱节点
node.setLeft(pre);
// 修改当前节点的左指针的类型
node.setLeftType(1);
}
// 处理后继节点
if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {
pre.setRight(node);
pre.setRigthType(1);
}
// 每处理一个节点后,让当前节点是下一个节点前驱节点
pre = node;
threadedPreNodes(node.getLeft());
threadedPreNodes(node.getRight());
}
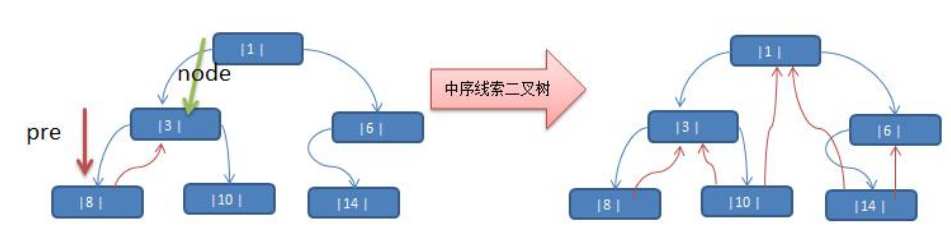
// 二叉树中序线索化
/**
*
* @Description:
* @author LinZM
* @date 2021-3-8 22:14:51
* @version V1.8
* @param node 线索化节点
*/
public void threadedInfixNodes(TNode node) {
if(node == null) {
return;
}
// 1 先线索化左子树
threadedInfixNodes(node.getLeft());
// 2 线索化当前节点
// 先处理节点的前驱节点
// 节点8->节点3,一开始8为node,后面3为node
if(node.getLeft() == null ) {
// 让当前节点的左指针指向前驱节点
node.setLeft(pre);
// 修改当前节点的左指针的类型
node.setLeftType(1);
}
// 处理后继节点
if(pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {
pre.setRight(node);
pre.setRigthType(1);
}
// 每处理一个节点后,让当前节点是下一个节点前驱节点
// pre = 8
pre = node;
// 3 线索化右子树
threadedInfixNodes(node.getRight());
}
// 中序遍历线索二叉树
public void threadedInfixList() {
// 定义一个变量,存储当前遍历的节点,从root开始
TNode node = root;
if(node == null) {
System.out.println("空树!");
return;
}
while(node != null) {
// 循环找到leftType == 1 的节点,第一个找到就是8节点
// 后面随着遍历而变化,因为当leftType == 1,说明该节点是按照线索化处理后的有效节点
while(node.getLeftType() == 0) {
node = node.getLeft();
}
// 找到8节点
System.out.println(node);
// 如果当前节点的右指针指向的是后继节点,就一直输出
while(node.getRigthType() == 1) {
node = node.getRight();
System.out.println(node);
}
// 如果不是后继节点,则替换这个遍历的节点
node = node.getRight();
}
}
// 删除节点
public void delNode(int no) {
if (root != null) {
// 如果只有一个root
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空树!");
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空!");
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空!");
}
}
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空!");
}
}
// 前序查找
public TNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if(root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 中序查找
public TNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
// 后序查找
public TNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
class TNode{
private String name;
private int no;
private TNode left;
private TNode right;
// leftType == 0 为左子树, 如果为1则表示指向前驱节点
// rightType == 0 为右子树, 如果为1则表示指向后继节点
private int leftType;
private int rigthType;
public int getLeftType() {
return leftType;
}
public void setLeftType(int leftType) {
this.leftType = leftType;
}
public int getRigthType() {
return rigthType;
}
public void setRigthType(int rigthType) {
this.rigthType = rigthType;
}
public TNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public TNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(TNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public TNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(TNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "TNode [name=" + name + ", no=" + no + "]";
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); // 输出父节点
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
// 中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this); // 输出父节点
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
System.out.println(this); // 输出父节点
}
// 前序查找
public TNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("1");
// 比较当前节点是不是
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 1 判断当前节点的左节点是否为空,如果不为空,则递归前序查找
// 2 如果左递归前序查找,找到节点,则返回
TNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {// 说明左子树找到了
return resNode;
}
// 1 左递归如果没有找到,则继续判断
// 2 当前节点的右节点是否为空,如果不为空,则继续向右递归前序查找
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
// 这时候不管有没有找到都要返回resNode
return resNode;
}
// 中序查找
public TNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
TNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("1");
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
// 后序查找
public TNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
TNode resNode = null;
if(this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
if(this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if(resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("1");
if(this.no == no) {
return this;
}
// 如果都没有找到
return resNode;
}
/**
*
* @Description:1 因为我们的二叉树是单向,所以我们是判断当前节点的子节点是否需要删除节点,而不是直接去判断当前节点是否需要删除节点。<br>
* 2 如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,并且左子节点就是要删除节点,就将this.left = null;并且就返回(结束递归删除) <br>
* 3 如果当前节点的右子节点不为空,并且右子节点就是要删除节点,就将this.right = null;并且就返回(结束递归删除) <br>
* 4 如果第2和第3都没有删除节点,那么我们就需要向左子树进行递归删除<br>
* 5 如果第4补也没有删除节点,则向右子树进行递归删除<br>
* @author LinZM
* @date 2021-3-8 15:17:32
* @version V1.8
*/
public void delNode(int no) {
if(this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
if(this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
}
仅供参考,有错误还请指出!
有什么想法,评论区留言,互相指教指教。
觉得不错的可以点一下右边的推荐哟
Java 树结构的基础部分(二)的更多相关文章
- JVM 内部原理(七)— Java 字节码基础之二
JVM 内部原理(七)- Java 字节码基础之二 介绍 版本:Java SE 7 为什么需要了解 Java 字节码? 无论你是一名 Java 开发者.架构师.CxO 还是智能手机的普通用户,Java ...
- java接口自动化基础知识(二)
二.HttpClient+testNG实现对接口的测试及校验 在上面第一篇中已经实现了基础配置和测试用例数据准备,本篇文章将以登录举例进行测试执行. 这是之前login接口的代码 @Test(grou ...
- JAVA之Mybatis基础入门二 -- 新增、更新、删除
上一节说了Mybatis的框架搭建和简单查询,这次我们来说一说用Mybatis进行基本的增删改操作: 一. 插入一条数据 1.首先编写USER.XML(表的xml)使用insert元素,元素写在map ...
- Java面试题-基础篇二(干货)
11.是否可以从一个static方法内部发出对非static方法的调用? 不可以.因为非static方法是要与对象关联在一起的,必须创建一个对象后,才可以在该对象上进行方法调用,而static方法调用 ...
- 第2章 Java并行程序基础(二)
2.3 volatile 与 Java 内存模型(JMM) volatile对于保证操作的原子性是由非常大的帮助的(可见性).但是需要注意的是,volatile并不能代替锁,它也无法保证一些复合操作的 ...
- Java 树结构的基础部分(一)
二叉树 1.1 为什么需要树这种数据结构 1) 数组存储方式的分析 优点:通过下标方式访问元素,速度快.对于有序数组,还可使用二分查找提高检索速度. 缺点:如果要检索具体某个值,或者插入值(按一定顺序 ...
- Java语言基础(二) Java关键字
Java语言基础(二) Java关键字 Java关键字比较多,我就不列举出来了,只记录一些常用的小知识点: ①Java的关键字只有小写. ②then.sizeof都不是Java的关键字,熟悉C++的程 ...
- Java语言基础(二)
Java语言基础(二) 一.变量续 (1).变量有明确的类型 (2).变量必须有声明,初始化以后才能使用 (3).变量有作用域,离开作用域后自动回收 变量作用域在块内有效 (4).在同一定义域中变量不 ...
- java 基础知识二 基本类型与运算符
java 基础知识二 基本类型与运算符 1.标识符 定义:为类.方法.变量起的名称 由大小写字母.数字.下划线(_)和美元符号($)组成,同时不能以数字开头 2.关键字 java语言保留特殊含义或者 ...
随机推荐
- 详解Go语言I/O多路复用netpoller模型
转载请声明出处哦~,本篇文章发布于luozhiyun的博客:https://www.luozhiyun.com 本文使用的go的源码15.7 可以从 Go 源码目录结构和对应代码文件了解 Go 在不同 ...
- Open3d之交互式可视化
本篇教程介绍了Open3D的可视化窗口的交互功能. # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import copy import numpy as np import open3d as o3d ...
- Zabbix 监控网站
官网教学步骤 配置 Web 监控 创建 Web 场景 配置 Web 场景 配置 Web 监控步骤 一共划分为 5 个步骤: 监测访问登录页面 模拟登录功能 # sid 变量的值 regex:name= ...
- Kubernetes安装EFK教程(非存储持久化方式部署)
1.简介 这里所指的EFK是指:ElasticSearch,Fluentd,Kibana ElasticSearch Elasticsearch是一个基于Apache Lucene的开源搜索和数据分析 ...
- Dapr是如何简化微服务的开发和部署
基于微服务设计模式的现代应用程序面临着一系列挑战.微服务需要有一个强大的服务发现机制来实现动态连接.它们需要松散耦合,实现自主性和独立缩放.微服务需要支持多种语言,其中每个服务都是以最合适的语言.框架 ...
- hdu5693D++游戏 区间DP-暴力递归
主要的收获是..如何优化你递推式里面不必要的决策 之前的代码 这个代码在HDU超时了,这就对了..这个复杂度爆炸.. 但是这个思路非常地耿直..那就是只需要暴力枚举删两个和删三个的情况,于是就非常耿直 ...
- CS144学习(2)TCP协议实现
Lab1-4 分别是完成一个流重组器,TCP接收端,TCP发送端,TCP连接四个部分,将四个部分组合在一起就是一个完整的TCP端了.之后经过包装就可以进行TCP的接收和发送了. 代码全部在github ...
- how to copy to clipboard using windows cmd
how to copy to clipboard using windows cmd Windows clipboard command line https://www.labnol.org/sof ...
- taro error
taro error index.json 中没有申明 "component: true" 或其他异常 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35629609/arti ...
- NGK八大板块:为何郊区市场近来火爆?-VALAITIS, PETER ANTHONY分析
PAUL ADAMS ARCHITECT LTD董事长VALAITIS, PETER ANTHONY称受大环境影响很多纽约人都选择离开纽约市中心,搬往附近郊区,因此附近地区楼市开始不断升温. 根据房地 ...
