Codeforces 438D The Child and Sequence - 线段树
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
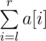 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 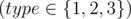 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
8 5
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
49 15 23 1 9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
题目大意 维护一个数列,有3种操作,分别是区间求和,区间取模和单点修改。
显然线段树(请不要问我为什么。。。学长的Tag打在那儿的)
区间求和和单点修改都是线段树的拿手好戏,但是对于区间取模似乎不是那么好做。考虑可以区间批量更新sum吗?显然不行。
但是考虑到这里只有单点修改,而且对一个大于模数的数取模,它的值至多为它原来的值的一半。
所以区间记录一个最大值剪枝,每次区间取模先判断是否有必要进行递归取模,如果有,就暴力递归下去,在底层修改。
Code
/**
* Codeforces
* Problem#438D
* Accepted
* Time: 436ms
* Memory: 8740k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#ifndef WIN32
#define Auto "%lld"
#else
#define Auto "%I64d"
#endif
using namespace std; typedef class SegTreeNode {
public:
int maxv;
long long sum;
SegTreeNode *l, *r; SegTreeNode():maxv(), sum(), l(NULL), r(NULL) { } inline void pushUp() {
maxv = max(l->maxv, r->maxv);
sum = l->sum + r->sum;
}
}SegTreeNode; typedef class SegTree {
public:
SegTreeNode* root; SegTree():root(NULL) { }
SegTree(int n, int* a) {
build(root, , n, a);
} void build(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int* a) {
node = new SegTreeNode();
if(l == r) {
node->sum = node->maxv = a[l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
build(node->l, l, mid, a);
build(node->r, mid + , r, a);
node->pushUp();
} void update(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int idx, int val) {
if(l == r) {
node->maxv = node->sum = val;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if(idx <= mid) update(node->l, l, mid, idx, val);
else update(node->r, mid + , r, idx, val);
node->pushUp();
} void update(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int moder) {
if(l == r) {
node->maxv = (node->sum %= moder);
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if(qr <= mid && node->l->maxv >= moder) update(node->l, l, mid, ql, qr, moder);
else if(ql > mid && node->r->maxv >= moder) update(node->r, mid + , r, ql, qr, moder);
else if(qr > mid && ql <= mid) {
if(node->l->maxv >= moder)
update(node->l, l, mid, ql, mid, moder);
if(node->r->maxv >= moder)
update(node->r, mid + , r, mid + , qr, moder);
}
node->pushUp();
} long long query(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int ql, int qr) {
if(l == ql && r == qr) {
return node->sum;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if(qr <= mid) return query(node->l, l, mid, ql, qr);
if(ql > mid) return query(node->r, mid + , r, ql, qr);
return query(node->l, l, mid, ql, mid) + query(node->r, mid + , r, mid + , qr);
}
}SegTree; int n, m;
int* arr;
SegTree st;
inline void init() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
arr = new int[(n + )];
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", arr + i);
st = SegTree(n, arr);
} inline void solve() {
int opt, a, b, c;
while(m--) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &opt, &a, &b);
if(opt == ) {
printf(Auto"\n", st.query(st.root, , n, a, b));
} else if(opt == ) {
scanf("%d", &c);
st.update(st.root, , n, a, b, c);
} else {
st.update(st.root, , n, a, b);
}
}
} int main() {
init();
solve();
return ;
}
Codeforces 438D The Child and Sequence - 线段树的更多相关文章
- CodeForces 438D The Child and Sequence (线段树 暴力)
传送门 题目大意: 给你一个序列,要求在序列上维护三个操作: 1)区间求和 2)区间取模 3)单点修改 这里的操作二很讨厌,取模必须模到叶子节点上,否则跑出来肯定是错的.没有操作二就是线段树水题了. ...
- CF(438D) The Child and Sequence(线段树)
题意:对数列有三种操作: Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of . Modulo operation l, r, x. ...
- 2018.07.23 codeforces 438D. The Child and Sequence(线段树)
传送门 线段树维护区间取模,单点修改,区间求和. 这题老套路了,对一个数来说,每次取模至少让它减少一半,这样每次单点修改对时间复杂度的贡献就是一个log" role="presen ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树 区间取摸
D. The Child and Sequence Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树 区间求和+点修改+区间取模
D. The Child and Sequence At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his h ...
- 题解——CodeForces 438D The Child and Sequence
题面 D. The Child and Sequence time limit per test 4 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input ...
- cf250D. The Child and Sequence(线段树 均摊复杂度)
题意 题目链接 单点修改,区间mod,区间和 Sol 如果x > mod ,那么 x % mod < x / 2 证明: 即得易见平凡, 仿照上例显然, 留作习题答案略, 读者自证不难. ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence (线段树)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/438/D 给你n个数,m个操作,1操作是查询l到r之间的和,2操作是将l到r之间大于等于x的数xor于x, ...
- Codeforces 438D The Child and Sequence
题意:给定一个n个数的序列,完成以下3个操作: 1.给定区间求和 2.给定区间对x取模 3.单点修改 对一个数取模,这个数至少折半.于是我们记一个最大值max,如果x>max则不做处理. #in ...
随机推荐
- (已解决)Eclipse报错:Could not find XXX.apk. 没有Android项目命名. There is no android project named
可能是你把当前项目设置为library项目了,按以下步骤切换回普通项目: 选择 Project->Properties 在左边的列表中,选择 Android 取消钩中"Is Libra ...
- cocos2d-x JS 获取当前系统时间(解决屏幕双击点击事件)
记录一下,好开心,感觉今天自己又学到东西了,对于屏幕双击事件本来还毫无头绪的,今天得以解决总算没白费加班,其实原理很简单:就是在点击事件里做一个判断,这个判断就是需要获取当前系统的时间的毫秒差,第一次 ...
- c++基础:之封装
原创: 零灵柒 C/C++的编程教室 2月4日 什么是类 C++是什么?C++设计之初就是class with c,所以简单点说,C++就是带类的C,那么什么是类? 类,简单点说就是类型,在 ...
- LeetCode35.搜索插入位置
给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引.如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置. 你可以假设数组中无重复元素. 示例 1: 输入: [1,3,5,6], 5 输 ...
- ef entity转json引起的Self referencing loop
问题简介:前段时间做项目时,将取到的entity往Redis cache里存放时报多重引用的错误. Self referencing loop detected for property 'Check ...
- Vue系列之 => 结合ajax完成列表增删查
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 从js中提取数据
<script language="JavaScript" type="text/javascript+gk-onload"> SKART = (S ...
- MVC 翻頁的那些坑
思绪良久,最后还是决定记录一下遇到的坑,毕竟被 ‘折磨’ 了三天,关于分页,这个话题,我一开始时拒绝的,因为真正接触项目的时候,才发现每个框架都会封装一套自己的分页,毕竟相同风格的项目是不常见的,而在 ...
- Java8 异步编排类CompletableFuture
为了防止无良网站的爬虫抓取文章,特此标识,转载请注明文章出处.LaplaceDemon/ShiJiaqi. https://www.cnblogs.com/shijiaqi1066/p/8758206 ...
- web3.js编译Solidity,发布,调用全部流程(手把手教程)
web3.js编译Solidity,发布,调用全部流程(手把手教程) 下面教程是打算在尽量牵涉可能少的以太坊的相关工具,主要使用web3.js这个以太坊提供的工具包,来完成合约的编译,发布,合约方法调 ...
