Python—数据结构——链表
数据结构——链表
一.简介
链表是一种物理存储上非连续,数据元素的逻辑顺序通过链表中的指针链接次序,实现的一种线性存储结构。由一系列节点组成的元素集合。每个节点包含两部分,
数据域item和指向下一个节点的指针next。通过节点之间的相互连接,最终串联成一个链表。
链表中的每个节点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域;另一个是存储下一个节点的地址的指针域
双向链表:双链表的每个节点有两个指针:一个指向后一个节点,另一个指向前一个节点。
二.Python实现
♦链表节点
class Node:
def __init__(self, item=None):
self.item = item
self.next = None
♦单向链表
class SingleLinkedList:
"""
单向链表
""" def __init__(self, heda=None):
self._head = heda
self.length = 0
♦添加节点
头插法:从链表的头部(左端)插入

def add_head(self, element):
"""
头插法:从头部插入
:param element: 需要添加进去的元素
:return:
"""
node = Node(element)
if self._head is None:
self._head = node
else:
node.next = self._head
self._head = node
self.length += 1
尾插法:从链表的尾部(右端)插入
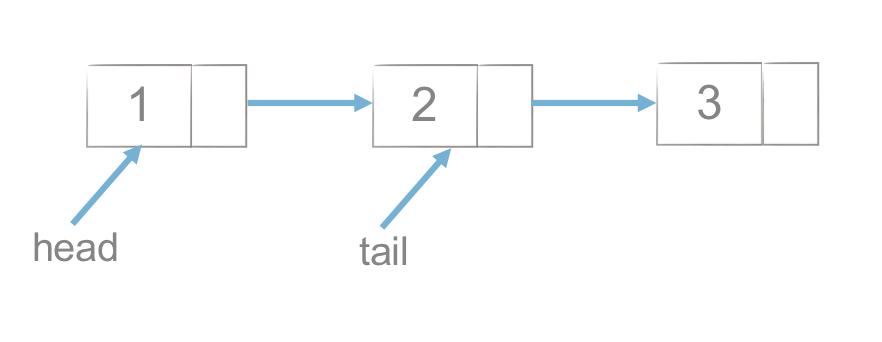
def add_tail(self, element):
"""
尾插法:从尾部添加元素
:param element:需要添加进去的元素
:return:
"""
# 创建一个节点
node = Node(element)
if self._head is None:
self._head = node
else:
cur = self._head
# cur=node,node.next=None
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
return cur.next
self.length += 1
♦插入节点
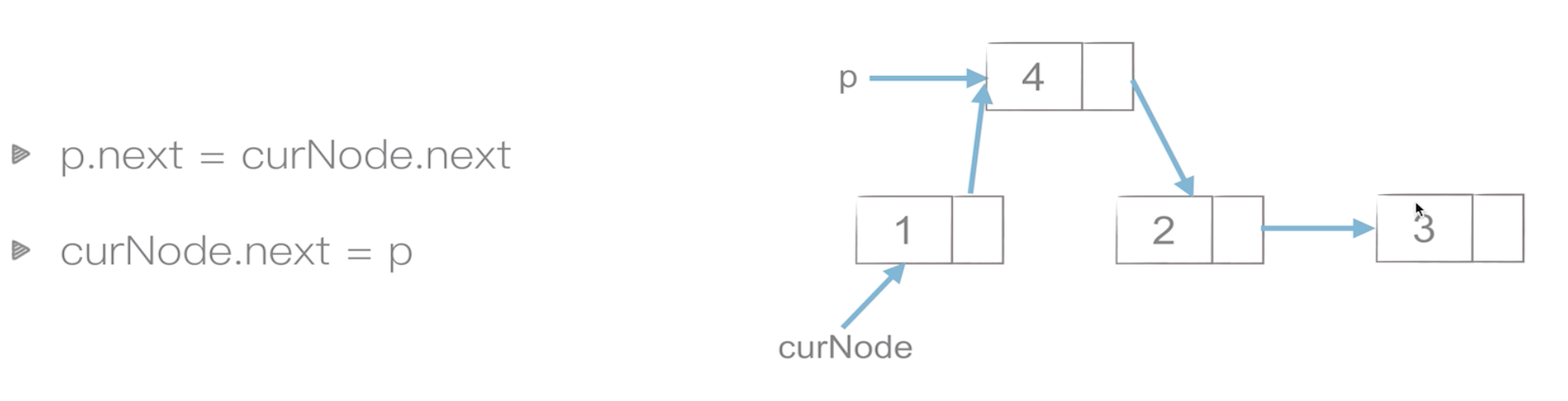
def insert(self, item: Node, index: int):
"""
往链表中指定位置插入值
:param item: 插入的节点
:param index: 插入的位置
:return:
"""
if index < 0 or index > self.length:
print('index out of range')
return
# 构建节点
if isinstance(item, Node):
node_insert = item
else:
node_insert = Node(item)
if index == 0:
node_insert.next = self._head
self._head = node_insert
else:
# 找到index的前一个节点
pre = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index - 1:
node_insert.next = pre.next
pre.next = node_insert
break
pre = pre.next
self.length += 1
return
♦删除节点

def delete(self, index: int):
"""
删除指定位置的节点
:param index: 节点的位置
:return:
"""
# 判空
if self.is_empty():
print('empty chain')
return
if index < 0 or index > self.length:
print('index out of range')
return if index == 0:
self._head = self._head.next
else:
pre = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index - 1:
pre.next = pre.next.next
break
pre = pre.next
self.length -= 1
return
♦修改节点
def update(self, item, index: int):
"""
修改节点item值
:param item: 修改之后的值
:param index:节点的位置
:return:
"""
# 判空
if self.is_empty():
print('empty chain')
return
if index < 0 or index >= self.length:
print('index out of range')
return node = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index:
node.item = item
return
node = node.next
♦获取节点
def get_item(self, index: int):
"""
获取指定位置的节点item
:param index:指定位置
:return:item
"""
# 判空
if self.is_empty():
print('empty chain')
return
if index < 0 or index >= self.length:
print('index out of range')
return node = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index:
return node.item
node = node.next
♦遍历链表
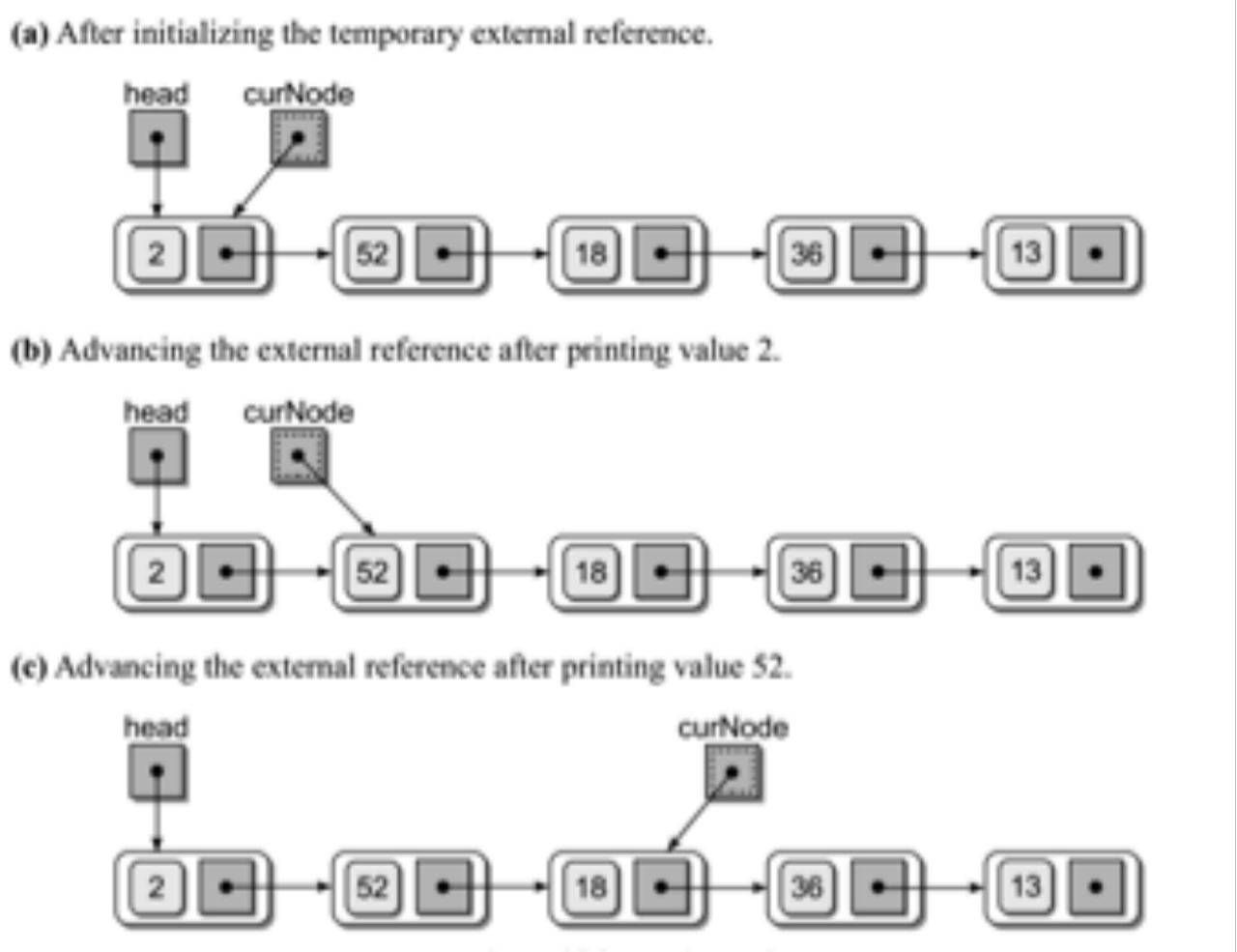
def traversal(self):
"""链表遍历"""
if self._head is None:
return
else:
cur = self._head
while cur:
print(cur.item)
cur = cur.next
♦反转链表
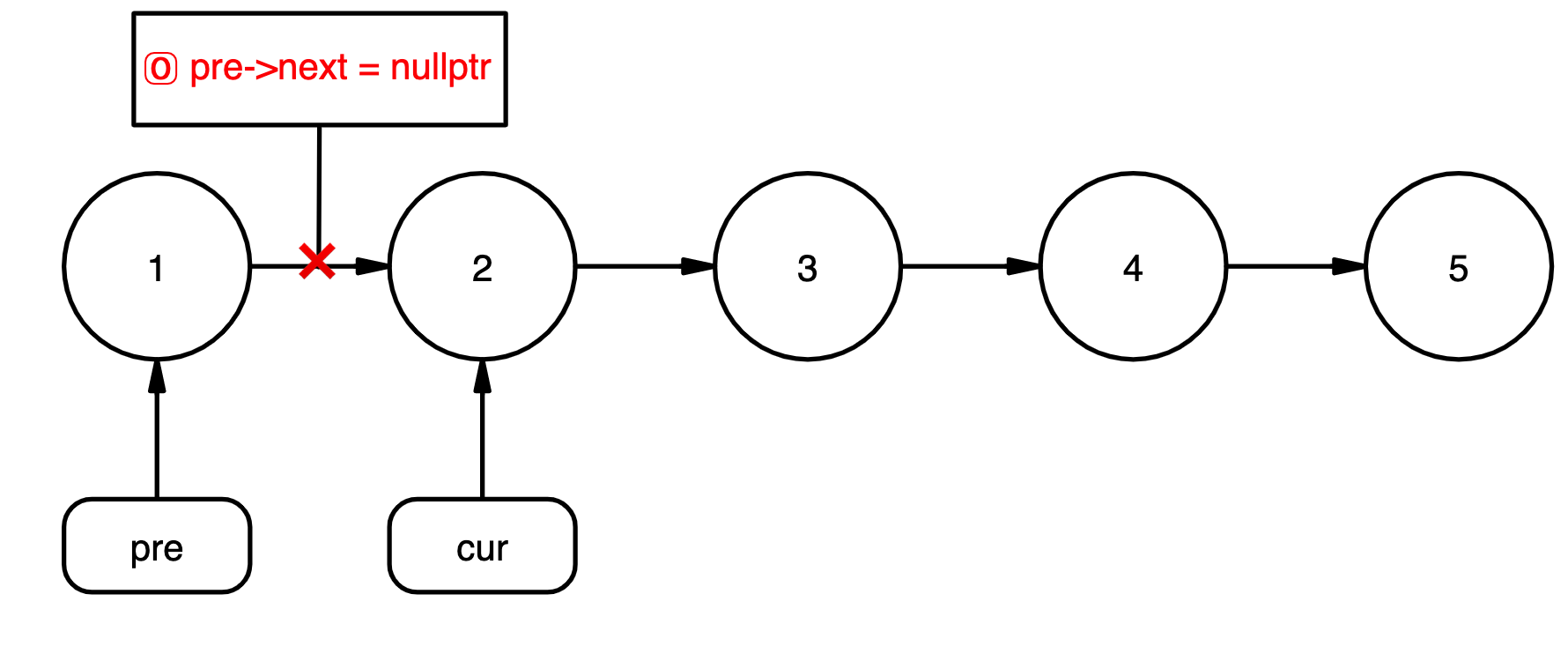





def reverse(self):
"""
单向链表的反转:Input:1>2>3>4>5
Output:5>4>3>2>1
:return:
"""
if self._head is None or self.size() == 1:
return
else:
pre = None
cur = self._head
while cur is not None:
post = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = post
self._head = pre # 逆向后的头节点
self.traversal()
♦双向链表
class Node:
def __init__(self, item=None):
self.item = item
self.next = None
self.prior = None
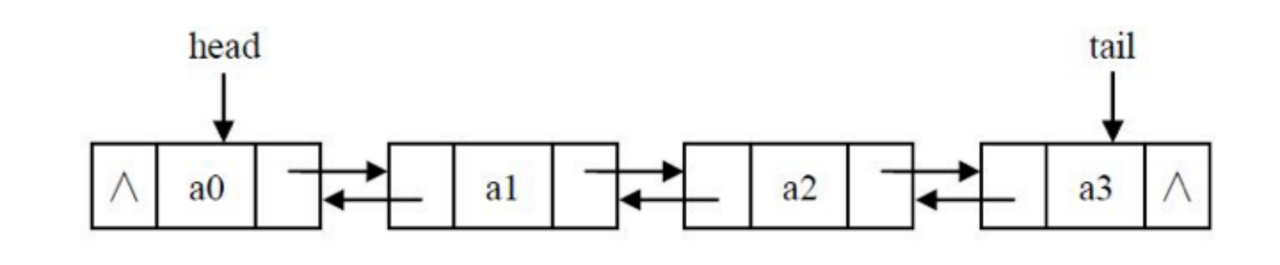
♦双链表节点删除
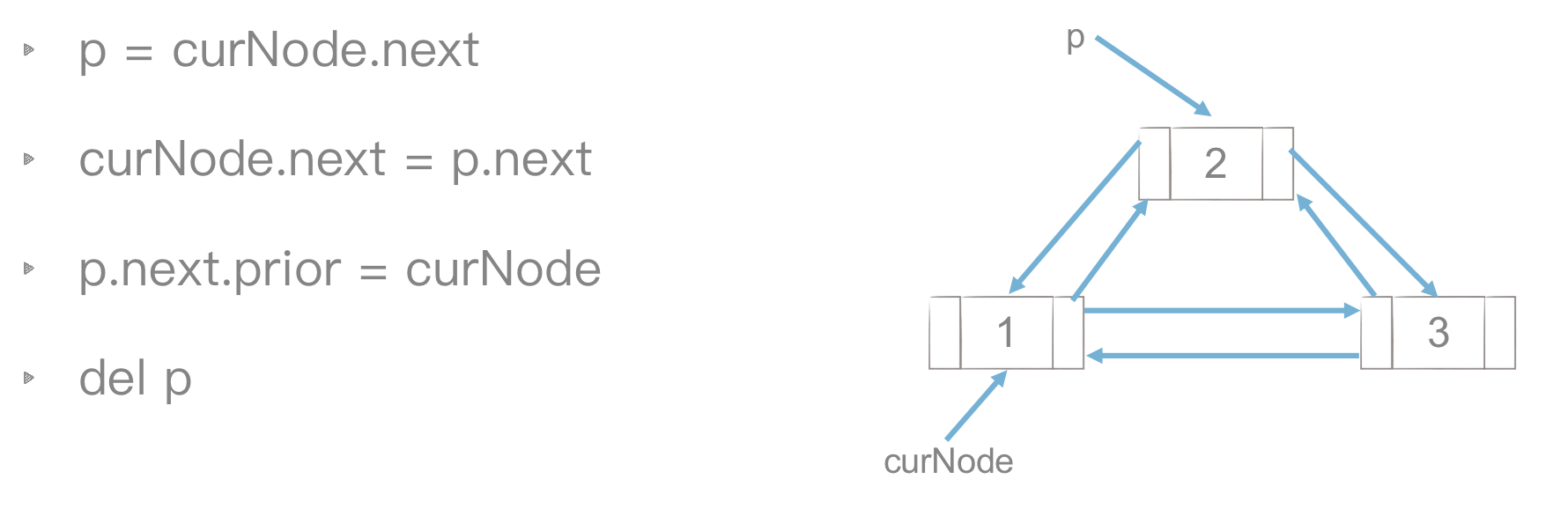
♦双链表节点插入

class Node:
def __init__(self, item=None):
self.item = item
self.next = None
self.prior = None class SingleLinkedList:
"""
单向链表
""" def __init__(self, heda=None):
self._head = heda
self.length = 0 def is_empty(self):
"""判断是否为空"""
return self.length == 0 def add_tail(self, element):
"""
尾插法:从尾部添加元素
:param element:需要添加进去的元素
:return:
"""
# 创建一个节点
node = Node(element)
if self._head is None:
self._head = node
else:
cur = self._head
# cur=node,node.next=None
while cur.next:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
return cur.next
self.length += 1 def add_head(self, element):
"""
头插法:从头部插入
:param element: 需要添加进去的元素
:return:
"""
node = Node(element)
if self._head is None:
self._head = node
else:
node.next = self._head
self._head = node
self.length += 1 def size(self): """
获取链表的大小
:return:int
"""
count = 0
if self._head is None:
return count else:
cur = self._head
while cur is not None:
count += 1
cur = cur.next
return count def insert(self, item: Node, index: int):
"""
往链表中指定位置插入值
:param item: 插入的节点
:param index: 插入的位置
:return:
"""
if index < 0 or index > self.length:
print('index out of range')
return
# 构建节点
if isinstance(item, Node):
node_insert = item
else:
node_insert = Node(item)
if index == 0:
node_insert.next = self._head
self._head = node_insert
else:
# 找到index的前一个节点
pre = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index - 1:
node_insert.next = pre.next
pre.next = node_insert
break
pre = pre.next
self.length += 1
return def delete(self, index: int):
"""
删除指定位置的节点
:param index: 节点的位置
:return:
"""
# 判空
if self.is_empty():
print('empty chain')
return
if index < 0 or index > self.length:
print('index out of range')
return if index == 0:
self._head = self._head.next
else:
pre = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index - 1:
pre.next = pre.next.next
break
pre = pre.next
self.length -= 1
return def update(self, item, index: int):
"""
修改节点item值
:param item: 修改之后的值
:param index:节点的位置
:return:
"""
# 判空
if self.is_empty():
print('empty chain')
return
if index < 0 or index >= self.length:
print('index out of range')
return node = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index:
node.item = item
return
node = node.next def get_item(self, index: int):
"""
获取指定位置的节点item
:param index:指定位置
:return:item
"""
# 判空
if self.is_empty():
print('empty chain')
return
if index < 0 or index >= self.length:
print('index out of range')
return node = self._head
for i in range(self.length):
if i == index:
return node.item
node = node.next def traversal(self):
"""链表遍历"""
if self._head is None:
return
else:
cur = self._head
while cur:
print(cur.item)
cur = cur.next def reverse(self):
"""
单向链表的反转:Input:1>2>3>4>5
Output:5>4>3>2>1
思路:先将head.next断开,即指向断开的元素pre(none);再将pre赋值head,将head赋值head.next;最后将head赋值pre
:return:
"""
if self._head is None or self.size() == 1:
return
else:
pre = None
cur = self._head
while cur is not None:
post = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = post
self._head = pre # 逆向后的头节点
self.traversal()
LinkedList
Python—数据结构——链表的更多相关文章
- Python 数据结构 链表
什么是时间复杂度 时间频度:一个算法执行所耗费的时间,从理论上是不能算出来的,必须上机运行测试才知道.但是我们不可能也没有必要对每一个算法都进行上机测试,只需要知道那个算法花费的时间多,那个算法花费得 ...
- python数据结构链表之单向链表
单向链表 单向链表也叫单链表,是链表中最简单的一种形式,它的每个节点包含两个域,一个信息域(元素域)和一个链接域.这个链接指向链表中的下一个节点,而最后一个节点的链接域则指向一个空值. 表元素域ele ...
- Python数据结构--链表
class Node(): def __init__(self, dataval=None): self.dataval = dataval self.nextval = None class SLi ...
- Python数据结构——链表的实现
链表由一系列不必在内存中相连的结构构成,这些对象按线性顺序排序.每个结构含有表元素和指向后继元素的指针.最后一个单元的指针指向NULL.为了方便链表的删除与插入操作,可以为链表添加一个表头. 删除操作 ...
- python数据结构与算法——链表
具体的数据结构可以参考下面的这两篇博客: python 数据结构之单链表的实现: http://www.cnblogs.com/yupeng/p/3413763.html python 数据结构之双向 ...
- Python数据结构之单链表
Python数据结构之单链表 单链表有后继结点,无前继结点. 以下实现: 创建单链表 打印单链表 获取单链表的长度 判断单链表是否为空 在单链表后插入数据 获取单链表指定位置的数据 获取单链表指定元素 ...
- python数据结构之链表(一)
数据结构是计算机科学必须掌握的一门学问,之前很多的教材都是用C语言实现链表,因为c有指针,可以很方便的控制内存,很方便就实现链表,其他的语言,则没那么方便,有很多都是用模拟链表,不过这次,我不是用模拟 ...
- python数据结构与算法
最近忙着准备各种笔试的东西,主要看什么数据结构啊,算法啦,balahbalah啊,以前一直就没看过这些,就挑了本简单的<啊哈算法>入门,不过里面的数据结构和算法都是用C语言写的,而自己对p ...
- 算法之python创建链表实现cache
算法之python创建链表实现cache 本节内容 问题由来 解决思路 实现代码 总结 1. 问题由来 问题起因于朋友的一次面试题,面试公司直接给出两道题,要求四十八小时之内做出来,语言不限,做出来之 ...
随机推荐
- java.neo的ByteBuffer与Netty 的ByteBuf
JDK的ByteBuffer的缺点: 1.final byte[] hb;这是JDKde ByteBuffer对象中用于存储数据的对象声明;可以看到,其字节数组是被声明为final的,也就是长度是固定 ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然java开发常用类库学习笔记:同步与死锁
class MyThread implements Runnable{ private int ticket = 5 ; // 假设一共有5张票 public void run(){ for(int ...
- python --- 日志模块 logging
1.日志的使用 import logging class CommonLog(object): def _common_log(self,level,message): # 设定收集器,再设定收集的级 ...
- 配置anaconda 的仓库镜像
conda config --add channels https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/ conda config -- ...
- 74.Python中ORM聚合函数详解:Max,Min
Max和Min:获取指定对象的最大值和最小值. 1. 比如:想要获取Author表中的最大的年龄和最小的年龄.示例代码如下: from django.http import HttpResponse ...
- 九十二、SAP中ALV事件之六,复制一个标准工具栏到自己的程序
一.我们来到SE41,点击复制状态按钮 二.点击复制状态后,弹出一个框框,上面是模板内容,下面是我们自己的程序 三.我们根据上一篇的标准模板内容,填好相应的模板和我们的程序的内容 三.点击复制按钮 五 ...
- 五十一、SAP中使程序结构化,模块化
一.我们创建3个引用单元,这3个单元里面分别存放定义相关,执行相关和子程序相关的内容 二.将程序中的各部分都拆分到INCLUDE文件中,DEF文件内容如下 三.INC文件内容 四.MAIN文件中写程序 ...
- Scanner类的next()方法和nextLine()方法的区别(简)
1. 空白符:回车.空格.tab等 2. next()方法读取到空白符就结束 3. nextLine()方法读取到回车结束,也就是 "\r"
- 本地的jar包导入到maven仓库
需要引入本地jar,然后百度跟着教程实现了,做个记录加深印象.https://www.cnblogs.com/lixuwu/p/5855031.html 1首先找到要传入maven的jar包(放在一个 ...
- 通过Navicat Premium 实现Oracle的连接和基本操作
一.Oracle的连接 以下为Navicat Premium连接Oracle数据库的教程 一.需要准备的软件(下载适合自己系统的软件) 1.Navicat premium 官方下载地址:http:// ...
