Conjugate prior relationships
The following diagram summarizes conjugate prior relationships for a number of common sampling distributions.
Arrows point from a sampling distribution to its conjugate prior distribution. The symbol near the arrow indicates which parameter the prior is unknown.
These relationships depends critically on choice of parameterization, some of which are uncommon. This page uses the parameterizations
that make the relationships simplest to state, not necessarily the most common parameterizations. See footnotes below.
Click on a distribution to see its parameterization. Click
on an arrow to see posterior parameters.
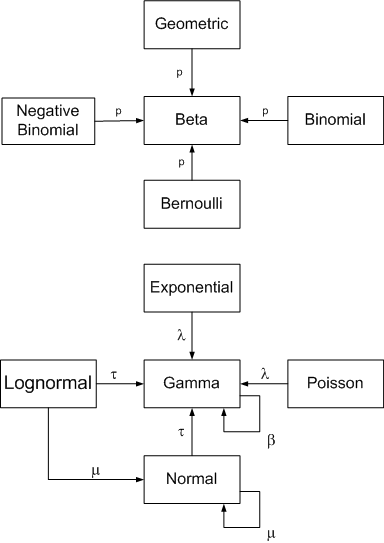
See this page for more
diagrams on this site including diagrams for probability and statistics, analysis, topology, and category theory. Also, please contact me if you’re interested in Bayesian
statistical consulting.
Parameterizations
Let C(n, k)
denote the binomial
coefficient(n, k).
The geometric distribution has only one parameter, p,
and has PMF f(x)
= p (1-p)x.
The binomial distribution with parameters n and p has
PMF f(x)
= C(n, x) px(1-p)n-x.
The negative binomial distribution with parameters r and p has
PMF f(x)
= C(r + x –
1, x)pr(1-p)x.
The Bernoulli distribution has probability of success p.
The beta distribution has PDF f(p)
= Γ(α + β) pα-1(1-p)β-1 /
(Γ(α) Γ(β)).
The exponential distribution parameterized in terms of the rate λ has PDF f(x)
= λ exp(-λ x).
The gamma distribution parameterized in terms of the rate has PDF f(x)
= βα xα-1exp(-β x)
/ Γ(α).
The Poisson distribution has one parameter λ and PMF f(x)
= exp(-λ) λx/ x!.
The normal distribution parameterized in terms of precision τ (τ = 1/σ2)
has PDF f(x)
= (τ/2π)1/2 exp( -τ(x –
μ)2/2 ).
The lognormal distribution parameterized in terms of precision τ has PDF f(x)
= (τ/2π)1/2exp( -τ(log(x)
– μ)2/2 ) / x.
Posterior parameters
For each sampling distribution, assume we have data x1, x2,
…, xn.
If the sampling distribution for x is binomial(m, p)
with m known, and the prior distribution is beta(α,
β), the posterior distribution for p is beta(α
+ Σxi,
β + mn – Σxi).
The Bernoulli is the special case of the binomial with m =
1.
If the sampling distribution for x is negative
binomial(r, p) with r known,
and the prior distribution is beta(α, β), the posterior distribution for p is beta(α
+ nr, β + Σxi).
Thegeometric is the special case of the negative binomial with r =
1.
If the sampling distribution for x is gamma(α,
β) with α known, and the prior distribution on β is gamma(α0,
β0), the posterior distribution
for β is gamma(α0 + n,
β0 + Σxi).
Theexponential is a special case of the gamma with α = 1.
If the sampling distribution for x is Poisson(λ),
and the prior distribution on λ is gamma(α0,
β0), the posterior on λ is gamma(α0 +
Σxi, β0 + n).
If the sampling distribution for x is normal(μ, τ) with τ known, and the prior distribution on μ is normal(μ0,
τ0), the posterior distribution
on μ is normal((μ0 τ0 +
τ Σxi)/(τ0 + nτ),
τ0 + nτ).
If the sampling distribution for x is normal(μ, τ) with μ known, and the prior distribution on τ is gamma(α,
β), the posterior distribution on τ is gamma(α + n/2,
(n-1)S2)
where S2 is
the sample variance.
If the sampling distribution for x is lognormal(μ, τ) with τ known, and the prior distribution on μ is normal(μ0,
τ0), the posterior distribution
on μ is normal((μ0 τ0 +
τ Πxi)/(τ0 + nτ),
τ0 +nτ).
If the sampling distribution for x is lognormal(μ,
τ) with μ known, and the prior distribution on τ is gamma(α, β), the posterior distribution on τ is gamma(α
+ n/2, (n-1)S2)
where S2 is
the sample variance.
References
A
compendium of conjugate priors by Daniel Fink.
See also Wikipedia’s article on conjugate
priors.
Conjugate prior relationships的更多相关文章
- 共轭先验(conjugate prior)
共轭是贝叶斯理论中的一个概念,一般共轭要说是一个先验分布与似然函数共轭: 那么就从贝叶斯理论中的先验概率,后验概率以及似然函数说起: 在概率论中有一个条件概率公式,有两个变量第一个是A,第二个是B , ...
- The Joys of Conjugate Priors
The Joys of Conjugate Priors (Warning: this post is a bit technical.) Suppose you are a Bayesian rea ...
- 转:Conjugate prior-共轭先验的解释
Conjugate prior-共轭先验的解释 原文:http://blog.csdn.net/polly_yang/article/details/8250161 一 问题来源: 看PRML第 ...
- Gibbs sampling
In statistics and in statistical physics, Gibbs sampling or a Gibbs sampler is aMarkov chain Monte C ...
- Wishart distribution
Introduction In statistics, the Wishart distribution is generalization to multiple dimensions of the ...
- [综] Latent Dirichlet Allocation(LDA)主题模型算法
多项分布 http://szjc.math168.com/book/ebookdetail.aspx?cateid=1&§ionid=983 二项分布和多项分布 http:// ...
- PRML读书笔记——2 Probability Distributions
2.1. Binary Variables 1. Bernoulli distribution, p(x = 1|µ) = µ 2.Binomial distribution + 3.beta dis ...
- 关于Beta分布、二项分布与Dirichlet分布、多项分布的关系
在机器学习领域中,概率模型是一个常用的利器.用它来对问题进行建模,有几点好处:1)当给定参数分布的假设空间后,可以通过很严格的数学推导,得到模型的似然分布,这样模型可以有很好的概率解释:2)可以利用现 ...
- [zz] 混合高斯模型 Gaussian Mixture Model
聚类(1)——混合高斯模型 Gaussian Mixture Model http://blog.csdn.net/jwh_bupt/article/details/7663885 聚类系列: 聚类( ...
随机推荐
- Sql语句里的递归查询
Sql语句里的递归查询 SqlServer2005和Oracle 两个版本 以前使用Oracle,觉得它的递归查询很好用,就研究了一下SqlServer,发现它也支持在Sql里递归查询举例说明:Sql ...
- 测试驱动开发实践 - Test-Driven Development(转)
一.前言 不知道大家有没听过“测试先行的开发”这一说法,作为一种开发实践,在过去进行开发时,一般是先开发用户界面或者是类,然后再在此基础上编写测试. 但在TDD中,首先是进行测试用例的编写,然后再进行 ...
- 构建高转化率的着陆页-PS+HTML+网络营销
课程简介 本课程是全网独家专业的着陆页课程,课程完整的再现了整个着陆页实战案例的开发过程,包括:策划.设计和实现.上线后的推广.优化及提高转化率的技巧等,本套课程能帮助您迅速掌握着陆页的能力,迅速洞察 ...
- ViewConfiguration.getScaledTouchSlop () 用法
getScaledTouchSlop是一个距离,表示滑动的时候,手的移动要大于这个距离才开始移动控件.如果小于这个距离就不触发移动控件,如viewpager就是用这个距离来判断用户是否翻页 ViewC ...
- ios 定位 航向检测
// ViewController.m // CoreLocation框架的基本使用—定位 // 注意 点: 1.设置地位可用 2. 设置允许本程序定位(对弹出的框,允许即可) 3. 为模拟器 设置位 ...
- 怎样写 OpenStack Neutron 的 Extension (一)
前两篇文章讨论了怎么写一个 Neutron 的插件.但是最基本的插件只包括 Network, Port,和 Subnet 三种资源.如果需要引入新的资源,比如一个二层的 gateway 的话,就需要在 ...
- 360wifi 在 windows server 2008 / 2003 的使用方法
1. 安装驱动 在地址栏输入:Control Panel\System and Security\Administrative Tools , 然后找到Server Manager 打开 Server ...
- C#中的yield return与Unity中的Coroutine(协程)(下)
Unity中的Coroutine(协程) 估计熟悉Unity的人看过或者用过StartCoroutine() 假设我们在场景中有一个UGUI组件, Image: 将以下代码绑定到Image using ...
- js遍历json数据
先看看json返回的数据结构: 我需要遍历取出bookreno 与 title 加载到页面容器中去 首先我要取到 recommendedBookList 字典结构数据,然后遍历反射到相应对象 ...
- 10.C#匿名函数的变量捕获(五章5.5)
首先感谢园友的指定,后续的文章一定会多码多想,出来的文章才有说服力.那今天接上篇我们来聊一聊匿名函数,对于匿名函数,我们知道使用delegate关键字,那我们来需要知道匿名函数在变量是的处理方式,先说 ...
