Spring Security 4 使用@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize, @Secured, EL实现方法安全
【相关已翻译的本系列其他文章,点击分类里面的spring security 4】
上一篇:Spring
Security 4 整合Hibernate 实现持久化登录验证(带源码)
本文探讨Spring Security 4 基于@PreAuthorize,
@PostAuthorize, @Secured和 Spring EL表达式的方法级的安全。
想要开启Spring方法级安全,你需要在已经添加了@Configuration注解的类上再添加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity注解:
- package com.websystique.springsecurity.configuration;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
- import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
- import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
- import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
- import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
- import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
- @Configuration
- @EnableWebSecurity
- @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
- public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
- @Autowired
- public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
- auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("bill").password("abc123").roles("USER");
- auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("admin").password("root123").roles("ADMIN");
- auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("dba").password("root123").roles("ADMIN","DBA");
- }
- @Override
- protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
- http.authorizeRequests()
- .antMatchers("/", "/home").access("hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') or hasRole('DBA')")
- .and().formLogin().loginPage("/login")
- .usernameParameter("ssoId").passwordParameter("password")
- .and().exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/Access_Denied");
- }
- }
package com.websystique.springsecurity.configuration; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; @Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {@Autowired
public void configureGlobalSecurity(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("bill").password("abc123").roles("USER");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("admin").password("root123").roles("ADMIN");
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().withUser("dba").password("root123").roles("ADMIN","DBA");
} @Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").access("hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') or hasRole('DBA')")
.and().formLogin().loginPage("/login")
.usernameParameter("ssoId").passwordParameter("password")
.and().exceptionHandling().accessDeniedPage("/Access_Denied");
}
}
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 开启Spring
Security 全局方法安全,等价的XML配置如下:
- <beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
- xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
- xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
- xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
- http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-4.0.xsd">
- <http auto-config="true" >
- <intercept-url pattern="/" access="hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')" />
- <intercept-url pattern="/home" access="hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')" />
- <form-login login-page="/login"
- username-parameter="ssoId"
- password-parameter="password"
- authentication-failure-url="/Access_Denied" />
- </http>
- <global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled"/>
- <authentication-manager >
- <authentication-provider>
- <user-service>
- <user name="bill" password="abc123" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
- <user name="admin" password="root123" authorities="ROLE_ADMIN" />
- <user name="dba" password="root123" authorities="ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_DBA" />
- </user-service>
- </authentication-provider>
- </authentication-manager>
- </beans:beans>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-4.0.xsd"><http auto-config="true" >
<intercept-url pattern="/" access="hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')" />
<intercept-url pattern="/home" access="hasRole('USER') or hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')" />
<form-login login-page="/login"
username-parameter="ssoId"
password-parameter="password"
authentication-failure-url="/Access_Denied" />
</http> <global-method-security pre-post-annotations="enabled"/> <authentication-manager >
<authentication-provider>
<user-service>
<user name="bill" password="abc123" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
<user name="admin" password="root123" authorities="ROLE_ADMIN" />
<user name="dba" password="root123" authorities="ROLE_ADMIN,ROLE_DBA" />
</user-service>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
</beans:beans>
注意: @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 可以配置多个参数:
- prePostEnabled :决定Spring Security的前注解是否可用 [@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize,..]
- secureEnabled : 决定是否Spring Security的保障注解 [@Secured] 是否可用
- jsr250Enabled :决定 JSR-250
annotations 注解[@RolesAllowed..] 是否可用.
You can enable more than one type of annotation in the same application, but only one type should be used for any interface or class as the behavior will not be well-defined otherwise. If two annotations are found which apply to a particular method, then only
one of them will be applied.
在同一个应用程序中,可以启用多个类型的注解,但是只应该设置一个注解对于行为类的接口或者类。如果将2个注解同事应用于某一特定方法,则只有其中一个将被应用。
我们将研究上面提到的前两个注解。
@Secured
此注释是用来定义业务方法的安全配置属性的列表。您可以在需要安全[角色/权限等]的方法上指定 @Secured,并且只有那些角色/权限的用户才可以调用该方法。如果有人不具备要求的角色/权限但试图调用此方法,将会抛出AccessDenied 异常。
@Secured 源于 Spring之前版本.它有一个局限就是不支持Spring EL表达式。可以看看下面的例子:
- package com.websystique.springsecurity.service;
- import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Secured;
- public interface UserService {
- List<User> findAllUsers();
- @Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
- void updateUser(User user);
- @Secured({ "ROLE_DBA", "ROLE_ADMIN" })
- void deleteUser();
- }
package com.websystique.springsecurity.service;
import org.springframework.security.access.annotation.Secured;
public interface UserService {
List<User> findAllUsers();
@Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
void updateUser(User user);
@Secured({ "ROLE_DBA", "ROLE_ADMIN" })
void deleteUser();
}
在上面的例子中,updateUser 方法只能被拥有ADMIN 权限的用户调用。deleteUser 方法只能够被拥有DBA 或者ADMIN 权限的用户调用。
如果有不具有声明的权限的用户调用此方法,将抛出AccessDenied异常。
如果你想指定AND(和)这个条件,我的意思说deleteUser
方法只能被同时拥有ADMIN & DBA 。但是仅仅通过使用 @Secured注解是无法实现的。
但是你可以使用Spring的新的注解@PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize(支持Spring
EL),使得实现上面的功能成为可能,而且无限制。
@PreAuthorize / @PostAuthorize
Spring的 @PreAuthorize/@PostAuthorize 注解更适合方法级的安全,也支持Spring
表达式语言,提供了基于表达式的访问控制。
@PreAuthorize 注解适合进入方法前的权限验证, @PreAuthorize可以将登录用户的roles/permissions参数传到方法中。
@PostAuthorize 注解使用并不多,在方法执行后再进行权限验证。
所以它适合验证带有返回值的权限。Spring EL 提供 返回对象能够在表达式语言中获取返回的对象returnObject。
请参考 Common
Built-In Expressions 获取支持的表达式.
现在言归正常,使用@PreAuthorize / @PostAuthorize注解
- package com.websystique.springsecurity.service;
- import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostAuthorize;
- import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize;
- import com.websystique.springsecurity.model.User;
- public interface UserService {
- List<User> findAllUsers();
- @PostAuthorize ("returnObject.type == authentication.name")
- User findById(int id);
- @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
- void updateUser(User user);
- @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') AND hasRole('DBA')")
- void deleteUser(int id);
- }
package com.websystique.springsecurity.service; import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PostAuthorize;
import org.springframework.security.access.prepost.PreAuthorize; import com.websystique.springsecurity.model.User; public interface UserService {List<User> findAllUsers(); @PostAuthorize ("returnObject.type == authentication.name")
User findById(int id); @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
void updateUser(User user); @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') AND hasRole('DBA')")
void deleteUser(int id);
}
由于 @PreAuthorize可以使用Spring 表达式语言, 使用EL表达式可以轻易的表示任意条件. deleteUser方法 可以被拥有ADMIN & DBA角色的用户调用 .
另外,我们增加了带有@PostAuthorize注解的findById()方法。通过@PostAuthorize注解 method(User
object)的返回值在Spring表达式语言中可以通过returnObject 来使用。在例子中我们确保登录用户只能获取他自己的用户对象。
上面就是@Secured, @PreAuthorize, @PostAuthorize 和EL的使用
下面提到的service实现, User 模型& 控制器
- package com.websystique.springsecurity.service;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.List;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
- import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
- import com.websystique.springsecurity.model.User;
- @Service("userService")
- @Transactional
- public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
- static List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
- static{
- users = populateUser();
- }
- public List<User> findAllUsers(){
- return users;
- }
- public User findById(int id){
- for(User u : users){
- if(u.getId()==id){
- return u;
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
- public void updateUser(User user) {
- System.out.println("Only an Admin can Update a User");
- User u = findById(user.getId());
- users.remove(u);
- u.setFirstName(user.getFirstName());
- u.setLastName(user.getLastName());
- u.setType(user.getType());
- users.add(u);
- }
- public void deleteUser(int id){
- User u = findById(id);
- users.remove(u);
- }
- private static List<User> populateUser(){
- List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
- users.add(new User(1,"Sam","Disilva","admin"));
- users.add(new User(2,"Kevin","Brayn","admin"));
- users.add(new User(3,"Nina","Conor","dba"));
- users.add(new User(4,"Tito","Menz","dba"));
- return users;
- }
- }
package com.websystique.springsecurity.service; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import com.websystique.springsecurity.model.User; @Service("userService")
@Transactional
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{static List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>(); static{
users = populateUser();
} public List<User> findAllUsers(){
return users;
} public User findById(int id){
for(User u : users){
if(u.getId()==id){
return u;
}
}
return null;
} public void updateUser(User user) {
System.out.println("Only an Admin can Update a User");
User u = findById(user.getId());
users.remove(u);
u.setFirstName(user.getFirstName());
u.setLastName(user.getLastName());
u.setType(user.getType());
users.add(u);
} public void deleteUser(int id){
User u = findById(id);
users.remove(u);
} private static List<User> populateUser(){
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
users.add(new User(1,"Sam","Disilva","admin"));
users.add(new User(2,"Kevin","Brayn","admin"));
users.add(new User(3,"Nina","Conor","dba"));
users.add(new User(4,"Tito","Menz","dba"));
return users;
}
}
- public class User {
- private int id;
- private String firstName;
- private String lastName;
- private String type;
- //getters/setters
- }
public class User {
private int id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private String type;
//getters/setters
}
- package com.websystique.springsecurity.controller;
- import java.util.List;
- import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
- import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
- import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
- import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
- import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
- import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
- import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.SecurityContextLogoutHandler;
- import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
- import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
- import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
- import com.websystique.springsecurity.model.User;
- import com.websystique.springsecurity.service.UserService;
- @Controller
- public class HelloWorldController {
- @Autowired
- UserService service;
- @RequestMapping(value = { "/", "/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public String listAllUsers(ModelMap model) {
- List<User> users = service.findAllUsers();
- model.addAttribute("users", users);
- return "allusers";
- }
- @RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public String editUser(@PathVariable int id, ModelMap model) {
- User user = service.findById(id);
- model.addAttribute("user", user);
- model.addAttribute("edit", true);
- return "registration";
- }
- @RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.POST)
- public String updateUser(User user, ModelMap model, @PathVariable int id) {
- service.updateUser(user);
- model.addAttribute("success", "User " + user.getFirstName() + " updated successfully");
- return "success";
- }
- @RequestMapping(value = { "/delete-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public String deleteUser(@PathVariable int id) {
- service.deleteUser(id);
- return "redirect:/list";
- }
- @RequestMapping(value = "/Access_Denied", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public String accessDeniedPage(ModelMap model) {
- model.addAttribute("user", getPrincipal());
- return "accessDenied";
- }
- @RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public String loginPage() {
- return "login";
- }
- @RequestMapping(value="/logout", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- public String logoutPage (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
- Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
- if (auth != null){
- new SecurityContextLogoutHandler().logout(request, response, auth);
- }
- return "redirect:/login?logout";
- }
- private String getPrincipal(){
- String userName = null;
- Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
- if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
- userName = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername();
- } else {
- userName = principal.toString();
- }
- return userName;
- }
- }
package com.websystique.springsecurity.controller; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.SecurityContextLogoutHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import com.websystique.springsecurity.model.User;
import com.websystique.springsecurity.service.UserService; @Controller
public class HelloWorldController {@Autowired
UserService service; @RequestMapping(value = { "/", "/list" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String listAllUsers(ModelMap model) { List<User> users = service.findAllUsers();
model.addAttribute("users", users);
return "allusers";
} @RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String editUser(@PathVariable int id, ModelMap model) {
User user = service.findById(id);
model.addAttribute("user", user);
model.addAttribute("edit", true);
return "registration";
} @RequestMapping(value = { "/edit-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String updateUser(User user, ModelMap model, @PathVariable int id) {
service.updateUser(user);
model.addAttribute("success", "User " + user.getFirstName() + " updated successfully");
return "success";
} @RequestMapping(value = { "/delete-user-{id}" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable int id) {
service.deleteUser(id);
return "redirect:/list";
} @RequestMapping(value = "/Access_Denied", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String accessDeniedPage(ModelMap model) {
model.addAttribute("user", getPrincipal());
return "accessDenied";
} @RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String loginPage() {
return "login";
} @RequestMapping(value="/logout", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String logoutPage (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
Authentication auth = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
if (auth != null){
new SecurityContextLogoutHandler().logout(request, response, auth);
}
return "redirect:/login?logout";
} private String getPrincipal(){
String userName = null;
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal(); if (principal instanceof UserDetails) {
userName = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername();
} else {
userName = principal.toString();
}
return userName;
}
}
项目代码将在文章最后提供。
不部署 & 运行
下载本文末尾的项目代码 在一个 Servlet 3.0 容器中发布本应用. 在这里我使用的是tomcat
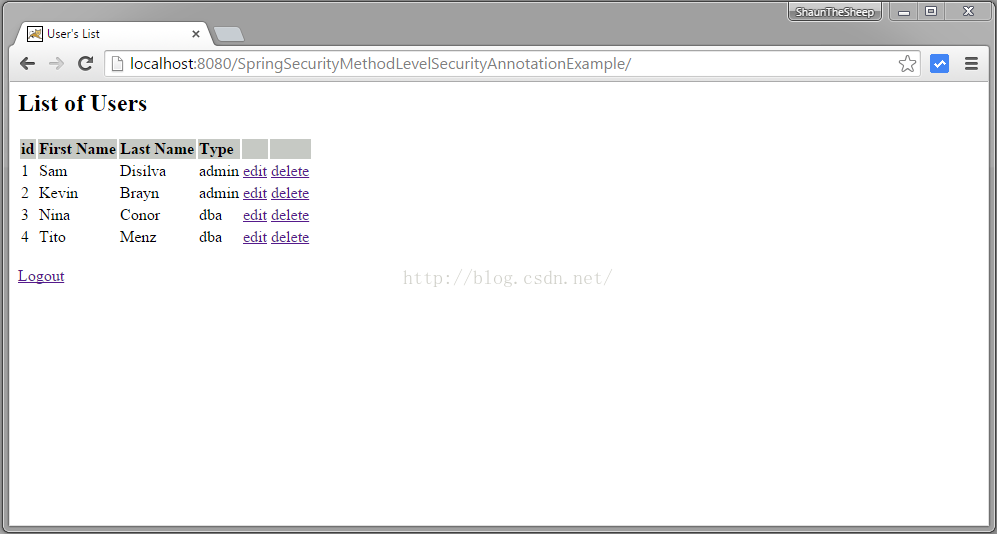
打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:8080/SpringSecurityMethodLevelSecurityAnnotationExample/, 将被转到登录界面. 填入 USER 权限的证书。
提交表单,能够看到用户列表
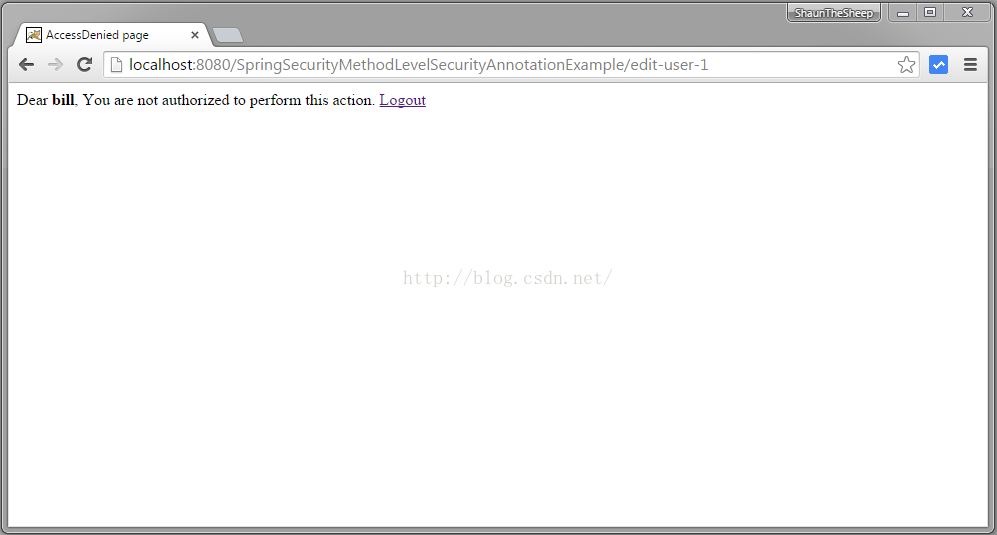
尝试删除用户,就会转到 访问拒绝页面因为USER 角色没有删除权限。
用ADMIN角色的账户登录
提交表单将看到用户列表页面
编辑第一行 带有“admin”权限的用户
回到用户列表界面
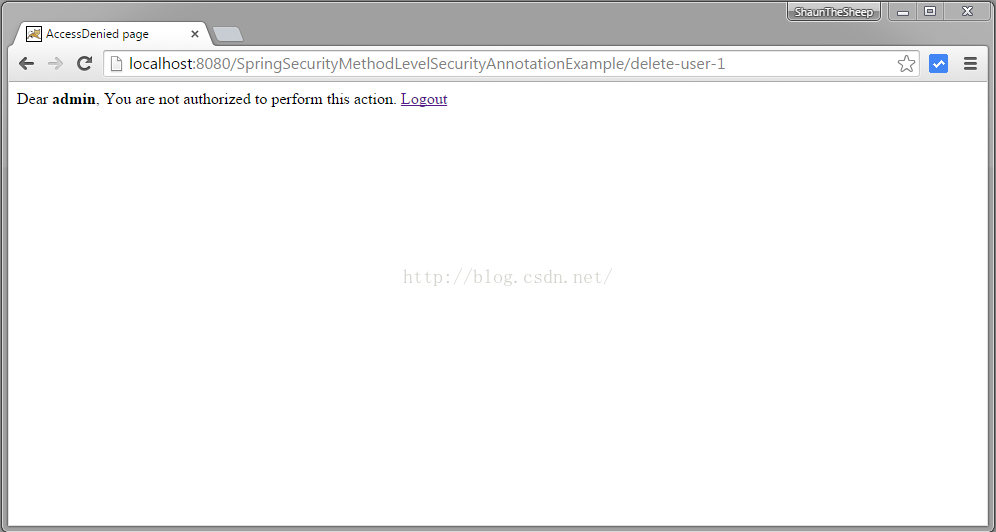
编辑一个带有dba角色的账户
访问拒绝的原因是带有@PostAuthorize
注解的findById 方法,带有Spring EL表单式限制只有dba角色的用户才可以调用。
只能够删除dba角色的账户,删除其他账户都会出现访问拒绝页面。
退出然后用拥有DBA角色的账户登录
[dba,root123],点击第一个用户的删除链接。这个用户将被成功删除掉。
项目源码下载地址:http://websystique.com/?smd_process_download=1&download_id=1475
Spring Security 4 使用@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize, @Secured, EL实现方法安全的更多相关文章
- Security注解:@PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize, @Secured, EL实现方法安全
说明 (1)JDK版本:1.8(2)Spring Boot 2.0.6(3)Spring Security 5.0.9(4)Spring Data JPA 2.0.11.RELEASE(5)hibe ...
- Spring Security 4 Method security using @PreAuthorize,@PostAuthorize, @Secured, EL--转
原文地址:http://websystique.com/spring-security/spring-security-4-method-security-using-preauthorize-pos ...
- 255.Spring Boot+Spring Security:使用md5加密
说明 (1)JDK版本:1.8 (2)Spring Boot 2.0.6 (3)Spring Security 5.0.9 (4)Spring Data JPA 2.0.11.RELEASE (5)h ...
- 256.Spring Boot+Spring Security: MD5是加密算法吗?
说明 (1)JDK版本:1.8 (2)Spring Boot 2.0.6 (3)Spring Security 5.0.9 (4)Spring Data JPA 2.0.11.RELEASE (5)h ...
- spring security 在controller层 方法级别使用注解 @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ROLE_xxx')")设置权限拦截 ,无权限则返回403
1.前言 以前学习的时候使用权限的拦截,一般都是对路径进行拦截 ,要么用拦截器设置拦截信息,要么是在配置文件内设置拦截信息, spring security 支持使用注解的形式 ,写在方法和接口上拦截 ...
- Spring Security:Authorization 授权(二)
Authorization 授权 在更简单的应用程序中,身份验证可能就足够了:用户进行身份验证后,便可以访问应用程序的每个部分. 但是大多数应用程序都有权限(或角色)的概念.想象一下:有权访问你的面向 ...
- Spring Security(16)——基于表达式的权限控制
目录 1.1 通过表达式控制URL权限 1.2 通过表达式控制方法权限 1.2.1 使用@PreAuthorize和@PostAuthorize进行访问控制 1.2.2 ...
- spring security注解(1)
Chapter 15. 基于表达式的权限控制 Spring Security 3.0介绍了使用Spring EL表达式的能力,作为一种验证机制 添加简单的配置属性的使用和访问决策投票,就像以前一样. ...
- Spring Security方法级别授权使用介绍
1.简介 简而言之,Spring Security支持方法级别的授权语义. 通常,我们可以通过限制哪些角色能够执行特定方法来保护我们的服务层 - 并使用专用的方法级安全测试支持对其进行测试. 在本文中 ...
随机推荐
- Google自带截图工具的使用
转载自:http://chromecj.com/utilities/2017-12/859.html
- [转]web计时机制——performance对象
页面性能一直都是Web开发人员比较关注的领域.但在实际应用中,度量页面性能的指标,是javascript的Date对象.Web Timing API改变了这个局面,让开发人员通过javascript就 ...
- Hibernate_添加联系人练习
分析: 联系人与客户是多对一,一个客户(公司)有多个联系人,在多的这一方,即LinkMan, 1.LinkMan.java中除自身属性外,还需要 2.在hbm.xml文件中,加上 意思是建立一个外键用 ...
- HDU3887 Counting Offspring [2017年6月计划 树上问题03]
Counting Offspring Time Limit: 15000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Othe ...
- Leetcode686.Repeated String Match重复叠加字符串匹配
给定两个字符串 A 和 B, 寻找重复叠加字符串A的最小次数,使得字符串B成为叠加后的字符串A的子串,如果不存在则返回 -1. 举个例子,A = "abcd",B = " ...
- SQLyog12.0.9下载、安装和破解
原文转载连接:https://blog.csdn.net/lihua5419/article/details/73881837/ sqlyog百度云链接(永久有效):http://pan.baidu. ...
- 当移动数据分析需求遇到Quick BI
我叫洞幺,是一名大型婚恋网站“我在这等你”的资深老员工,虽然在公司五六年,还在一线搬砖.“我在这等你”成立15年,目前积累注册用户高达2亿多,在我们网站成功牵手的用户达2千多万.目前我们的公司在CEO ...
- linux安装软件报错: Can't locate ExtUtils/Embed.pm in @INC...
安装snmp服务, 中间报错: Can't locate ExtUtils/Embed.pm in @INC (@INC contains: /usr/local/lib64/perl5 /usr/l ...
- golang中特殊的标识符
你会发现在 Go 代码中的几乎所有东西都有一个名称或标识符.另外,Go 语言也是区分大小写的,这与 C 家族中的其它语言相同.有效的标识符必须以字符(可以使用任何 UTF-8 编码的字符或 _)开头, ...
- SPSS统计分析过程包括描述性统计、均值比较、一般线性模型、相关分析、回归分析、对数线性模型、聚类分析、数据简化、生存分析、时间序列分析、多重响应等几大类
https://www.zhihu.com/topic/19582125/top-answershttps://wenku.baidu.com/search?word=spss&ie=utf- ...