UVa 1103 Ancient Messages(二重深搜)
In order to understand early civilizations, archaeologists often study texts written in ancient languages.One such language, used in Egypt more than 3000 years ago, is based on characters called hieroglyphs.Figure C.1 shows six hieroglyphs and their names. In this problem, you will write a program to recognize these six characters.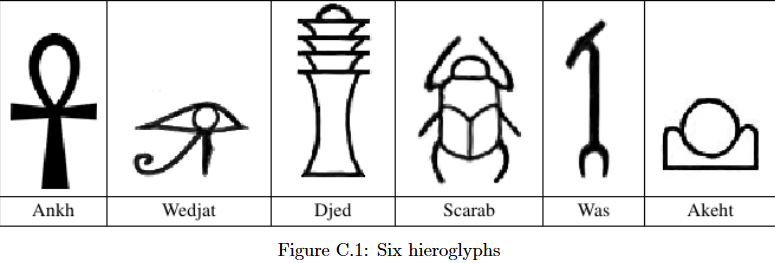
Input
The input consists of several test cases, each of which describes an image containing one or morehieroglyphs chosen from among those shown in Figure C.1. The image is given in the form of a seriesof horizontal scan lines consisting of black pixels (represented by 1) and white pixels (represented by0). In the input data, each scan line is encoded in hexadecimal notation. For example, the sequence ofeight pixels 10011100 (one black pixel, followed by two white pixels, and so on) would be represented inhexadecimal notation as 9c. Only digits and lowercase letters a through f are used in the hexadecimalencoding. The first line of each test case contains two integers, H and W. H (0 < H ≤ 200) is thenumber of scan lines in the image. W (0 < W ≤ 50) is the number of hexadecimal characters in each line. The next H lines contain the hexadecimal characters of the image, working from top to bottom.
Input images conform to the following rules:
• The image contains only hieroglyphs shown in Figure C.1.
• Each image contains at least one valid hieroglyph.
• Each black pixel in the image is part of a valid hieroglyph.
• Each hieroglyph consists of a connected set of black pixels and each black pixel has at least one other black pixel on its top, bottom, left, or right side.
• The hieroglyphs do not touch and no hieroglyph is inside another hieroglyph.
• Two black pixels that touch diagonally will always have a common touching black pixel.
• The hieroglyphs may be distorted but each has a shape that is topologically equivalent to one of the symbols in Figure C.1. (Two figures are topologically equivalent if each can be transformed into the other by stretching without tearing.)
The last test case is followed by a line containing two zeros.
Output
For each test case, display its case number followed by a string containing one character for each
hieroglyph recognized in the image, using the following code:
Ankh: A
Wedjat: J
Djed: D
Scarab: S
Was: W
Akhet: K
In each output string, print the codes in alphabetic order. Follow the format of the sample output.
The sample input contains descriptions of test cases shown in Figures C.2 and C.3. Due to space constraints not all of the sample input can be shown on this page.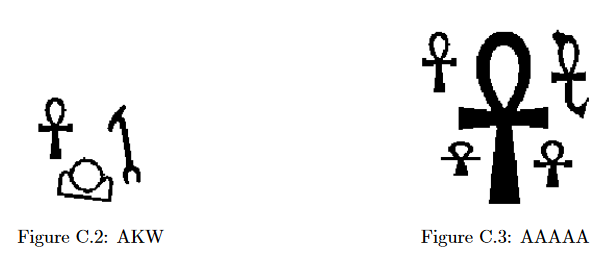
Sample Input
100 25
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
...(50 lines omitted)...
00001fe0000000000007c0000
00003fe0000000000007c0000
...(44 lines omitted)...
0000000000000000000000000
0000000000000000000000000
150 38
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
...(75 lines omitted)...
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
0000000003fffffffffffffffff00000000000
...(69 lines omitted)...
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
000000000000000000000000000000000000
00000000000000000000000000000000000000
0 0
Sample Output
Case 1: AKW
Case 2: AAAAA
题意
给你n行m列十六进制字符(0-f)每个字符等于4个二进制数(1代表黑点,0代表白点),再给你6个图,请按字典序输出所有符号
题解
首先找6个图怎么变都不会变的条件,黑点中间的白洞数量分别为(1,3,5,4,0,2)
问题就在于怎么找符号内的白洞
dfs()用于清除白点0变成2,dfs1()用于找黑点
1.首先根据输入,所有符号不会接触,也就是说,符号外的白点属于多余的白点得去掉
这时候就需要在图的最外一圈填上0,连通所有多余的白点,dfs(0,0)
2.然后根据输入,每个符号都是1个四连块,也就是说,符号是连通的,这样只需要dfs1(黑点)
如果是1,继续搜
如果是0,白洞+1,dfs(这个点)
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
char s[+][*+];
int dx[]={,,,-};
int dy[]={,-,,};
int n,m,cnt;
bool check(int x,int y)//边界
{
if(x>=&&x<=n+&&y>=&&y<=m*+)return true;
return false;
}
int dfs(int x,int y)//清除白点
{ if(s[x][y]=='')return ;
s[x][y]='';
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
int xx=x+dx[i];
int yy=y+dy[i];
if(check(xx,yy)&&s[xx][yy]=='')
dfs(xx,yy);
}
return ;
}
int dfs1(int x,int y)//搜索黑点
{
if(s[x][y]=='')return ;
s[x][y]='';
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
int xx=x+dx[i];
int yy=y+dy[i];
if(check(xx,yy))
{
if(s[xx][yy]=='')
dfs1(xx,yy);
if(s[xx][yy]=='')
cnt++,dfs(xx,yy);
}
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
int o=;
char ch;
map<char,string> ma;
ma['']="";ma['']="";ma['']="";ma['']="";ma['']="";
ma['']="";ma['']="";ma['']="";ma['']="";ma['']="";
ma['a']="";ma['b']="";ma['c']="";ma['d']="";ma['e']="";
ma['f']="";
map<int,char> mb;
mb[]='W';mb[]='A';mb[]='K';mb[]='J';mb[]='S';mb[]='D';
while(scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)!=EOF,n||m)
{
getchar();
memset(s,'',sizeof(s));//填0
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<m;j++)
{
scanf("%c",&ch);
s[i][j*+]=ma[ch][];
s[i][j*+]=ma[ch][];
s[i][j*+]=ma[ch][];
s[i][j*+]=ma[ch][];
}
getchar();
}
dfs(,);
vector<char> vec;
for(int i=;i<=n+;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<=m*+;j++)
{
if(s[i][j]=='')
{
cnt=;
dfs1(i,j);
vec.push_back(mb[cnt]);
}
}
}
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
printf("Case %d: ",o++);
for(int i=;i<vec.size();i++)
printf("%c",vec[i]);
printf("\n");
}
return ;
}
UVa 1103 Ancient Messages(二重深搜)的更多相关文章
- Uva 1103 Ancient Messages
大致思路是DFS: 1. 每个图案所包含的白色连通块数量不一: Ankh : 1 ; Wedjat : 3 ; Djed : 5 ; Scarab : 4 ; Was : 0 ; Ak ...
- UVA 10160 Servicing Stations(深搜 + 剪枝)
Problem D: Servicing stations A company offers personal computers for sale in N towns (3 <= N < ...
- UVA 165 Stamps (DFS深搜回溯)
Stamps The government of Nova Mareterrania requires that various legal documents have stamps attac ...
- 图-用DFS求连通块- UVa 1103和用BFS求最短路-UVa816。
这道题目甚长, 代码也是甚长, 但是思路却不是太难.然而有好多代码实现的细节, 确是十分的巧妙. 对代码阅读能力, 代码理解能力, 代码实现能力, 代码实现技巧, DFS方法都大有裨益, 敬请有兴趣者 ...
- K - Ancient Messages(dfs求联通块)
K - Ancient Messages Time Limit:3000MS Memory Limit:0KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Subm ...
- hdu 1010 Tempter of the Bone(深搜+奇偶剪枝)
Tempter of the Bone Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Othe ...
- HDU--杭电--1195--Open the Lock--深搜--都用双向广搜,弱爆了,看题了没?语文没过关吧?暴力深搜难道我会害羞?
这个题我看了,都是推荐的神马双向广搜,难道这个深搜你们都木有发现?还是特意留个机会给我装逼? Open the Lock Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) ...
- 利用深搜和宽搜两种算法解决TreeView控件加载文件的问题。
利用TreeView控件加载文件,必须遍历处所有的文件和文件夹. 深搜算法用到了递归. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using Sy ...
- 2016弱校联盟十一专场10.3---Similarity of Subtrees(深搜+hash、映射)
题目链接 https://acm.bnu.edu.cn/v3/problem_show.php?pid=52310 problem description Define the depth of a ...
随机推荐
- JVM的 GC机制和内存管理
GC机制:java垃圾回收机制,垃圾收集器线程(Garbage Collection Thread)在 JVM 处于空闲循环式,会自动回收无用的内存块. 垃圾收集算法:1.引用计数 2.根搜索 3 ...
- sqoop连接SqlServer2012示例
sqoop import --connect 'jdbc:sqlserver://192.168.xx.xx:1433;username=sa;password=xxxx;database=WindE ...
- ARP工作过程、ARP欺骗的原理和现象、如何防范ARP欺骗
地址解析协议(Address Resolution Protocol,ARP)是在仅知道主机的IP地址时确定其物理地址的一种协议. 下面假设在一个局域网内,主机A要向主机B发送IP数据报. ARP ...
- search() 方法解析
search()方法支持正则表达式的String对象的方法. 好,我们直接来贴代码,看效果,从实践理解透析方法的知识点和实际运用. var str="Visit W3School!" ...
- Spring3.0学习1.1(模拟spring)
层次划分 面向抽象编程 带来极大的灵活性 IOC(DI) 依赖注入 控制反转: 正式使用spring IOC 控制反转 不用自己写实现 由容器完成 建议使用appicatiioncontext ...
- 学习QT——GUI的基础用法(2)
1.listWidget列表 在构造函数里面添加: ; i<; i++) { ui->listWidget->addItem(QString::number(i)+"ite ...
- pandas 常用清洗数据(二)
1. df.head() Here we import pandas using the alias 'pd', then we read in our data. df.head - shows u ...
- EF CodeFirst学习笔记003--如何创建表
参考: http://www.cnblogs.com/Wayou/archive/2012/09/20/EF_CodeFirst.html webconfig中修改: <connectionSt ...
- 766. Toeplitz Matrix
A matrix is Toeplitz if every diagonal from top-left to bottom-right has the same element. Now given ...
- 【C++】c++11多线程初探
相关头文件c++11 新标准中引入了四个头文件来支持多线程编程,他们分别是<atomic> ,<thread>,<mutex>,<condition_vari ...
