MySQL索引与Index Condition Pushdown(employees示例)
实验
先从一个简单的实验开始直观认识ICP的作用。
安装数据库
首先需要安装一个支持ICP的MariaDB或MySQL数据库。我使用的是MariaDB 5.5.34,如果是使用MySQL则需要5.6版本以上。
Mac环境下可以通过brew安装:
- brew install mairadb
其它环境下的安装请参考MariaDB官网关于下载安装的文档。
导入示例数据
与前文一样,我们使用Employees Sample Database,作为示例数据库。完整示例数据库的下载地址为:https://launchpad.net/test-db/employees-db-1/1.0.6/+download/employees_db-full-1.0.6.tar.bz2。
将下载的压缩包解压后,会看到一系列的文件,其中employees.sql就是导入数据的命令文件。执行
- mysql -h[host] -u[user] -p < employees.sql
就可以完成建库、建表和load数据等一系列操作。此时数据库中会多一个叫做employees的数据库。库中的表如下:
- MariaDB [employees]> SHOW TABLES;
- +---------------------+
- | Tables_in_employees |
- +---------------------+
- | departments |
- | dept_emp |
- | dept_manager |
- | employees |
- | salaries |
- | titles |
- +---------------------+
- 6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
我们将使用employees表做实验。
建立联合索引
employees表包含雇员的基本信息,表结构如下:
- MariaDB [employees]> DESC employees.employees;
- +------------+---------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
- | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
- +------------+---------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
- | emp_no | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
- | birth_date | date | NO | | NULL | |
- | first_name | varchar(14) | NO | | NULL | |
- | last_name | varchar(16) | NO | | NULL | |
- | gender | enum('M','F') | NO | | NULL | |
- | hire_date | date | NO | | NULL | |
- +------------+---------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
- 6 rows in set (0.01 sec)
这个表默认只有一个主索引,因为ICP只能作用于二级索引,所以我们建立一个二级索引:
- ALTER TABLE employees.employees ADD INDEX first_name_last_name (first_name, last_name);
这样就建立了一个first_name和last_name的联合索引。
查询
为了明确看到查询性能,我们启用profiling并关闭query cache:
- SET profiling = 1;
- SET query_cache_type = 0;
- SET GLOBAL query_cache_size = 0;
然后我们看下面这个查询:
- MariaDB [employees]> SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man';
- +--------+------------+------------+-----------+--------+------------+
- | emp_no | birth_date | first_name | last_name | gender | hire_date |
- +--------+------------+------------+-----------+--------+------------+
- | 254642 | 1959-01-17 | Mary | Botman | M | 1989-11-24 |
- | 471495 | 1960-09-24 | Mary | Dymetman | M | 1988-06-09 |
- | 211941 | 1962-08-11 | Mary | Hofman | M | 1993-12-30 |
- | 217707 | 1962-09-05 | Mary | Lichtman | F | 1987-11-20 |
- | 486361 | 1957-10-15 | Mary | Oberman | M | 1988-09-06 |
- | 457469 | 1959-07-15 | Mary | Weedman | M | 1996-11-21 |
- +--------+------------+------------+-----------+--------+------------+
根据MySQL索引的前缀匹配原则,两者对索引的使用是一致的,即只有first_name采用索引,last_name由于使用了模糊前缀,没法使用索引进行匹配。我将查询联系执行三次,结果如下:
- +----------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
- | Query_ID | Duration | Query |
- +----------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
- | 38 | 0.00084400 | SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man' |
- | 39 | 0.00071800 | SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man' |
- | 40 | 0.00089600 | SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man' |
- +----------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
然后我们关闭ICP:
- SET optimizer_switch='index_condition_pushdown=off';
在运行三次相同的查询,结果如下:
- +----------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
- | Query_ID | Duration | Query |
- +----------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
- | 42 | 0.00264400 | SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man' |
- | 43 | 0.01418900 | SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man' |
- | 44 | 0.00234200 | SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man' |
- +----------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------+
有意思的事情发生了,关闭ICP后,同样的查询,耗时是之前的三倍以上。下面我们用explain看看两者有什么区别:
- MariaDB [employees]> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man';
- +------+-------------+-----------+------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+
- | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
- +------+-------------+-----------+------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+
- | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | ref | first_name_last_name | first_name_last_name | 44 | const | 224 | Using index condition |
- +------+-------------+-----------+------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+------+-----------------------+
- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
- MariaDB [employees]> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man';
- +------+-------------+-----------+------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+
- | id | select_type | table | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | Extra |
- +------+-------------+-----------+------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+
- | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | ref | first_name_last_name | first_name_last_name | 44 | const | 224 | Using where |
- +------+-------------+-----------+------+----------------------+----------------------+---------+-------+------+-------------+
- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
前者是开启ICP,后者是关闭ICP。可以看到区别在于Extra,开启ICP时,用的是Using index condition;关闭ICP时,是Using where。
其中Using index condition就是ICP提高查询性能的关键。下一节说明ICP提高查询性能的原理。
root@localhost:3306.sock [employees]> EXPLAIN format=json SELECT * FROM employees
-> WHERE first_name='Mary' AND last_name LIKE '%man'\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
EXPLAIN: {
"query_block": {
"select_id": 1,
"cost_info": {
"query_cost": "268.80"
},
"table": {
"table_name": "employees",
"access_type": "ref",
"possible_keys": [
"first_name_last_name"
],
"key": "first_name_last_name",
"used_key_parts": [
"first_name"
],
"key_length": "58",
"ref": [
"const"
],
"rows_examined_per_scan": 224,
"rows_produced_per_join": 24,
"filtered": "11.11",
"index_condition": "(employees.employees.last_name like '%man')",
"cost_info": {
"read_cost": "224.00",
"eval_cost": "4.98",
"prefix_cost": "268.80",
"data_read_per_join": "3K"
},
"used_columns": [
"emp_no",
"birth_date",
"first_name",
"last_name",
"gender",
"hire_date"
]
}
}
}
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
原理
ICP的原理简单说来就是将可以利用索引筛选的where条件在存储引擎一侧进行筛选,而不是将所有index access的结果取出放在server端进行where筛选。
以上面的查询为例,在没有ICP时,首先通过索引前缀从存储引擎中读出224条first_name为Mary的记录,然后在server段用where筛选last_name的like条件;而启用ICP后,由于last_name的like筛选可以通过索引字段进行,那么存储引擎内部通过索引与where条件的对比来筛选掉不符合where条件的记录,这个过程不需要读出整条记录,同时只返回给server筛选后的6条记录,因此提高了查询性能。
下面通过图两种查询的原理详细解释。
关闭ICP
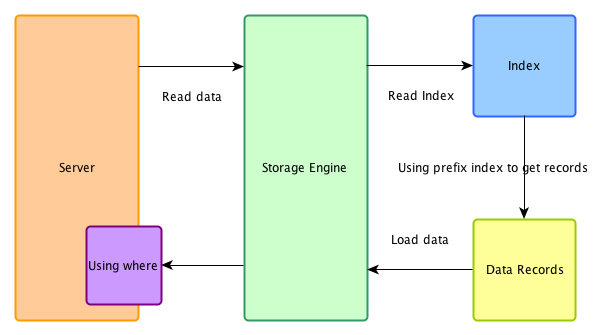
在不支持ICP的系统下,索引仅仅作为data access使用。
开启ICP
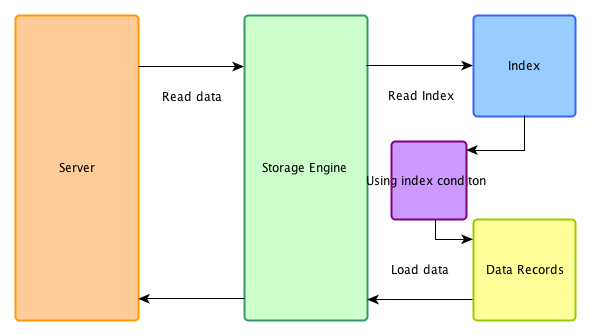
在ICP优化开启时,在存储引擎端首先用索引过滤可以过滤的where条件,然后再用索引做data access,被index condition过滤掉的数据不必读取,也不会返回server端。
注意事项
有几个关于ICP的事情要注意:
- ICP只能用于二级索引,不能用于主索引。
- 也不是全部where条件都可以用ICP筛选,如果某where条件的字段不在索引中,当然还是要读取整条记录做筛选,在这种情况下,仍然要到server端做where筛选。
- ICP的加速效果取决于在存储引擎内通过ICP筛选掉的数据的比例。
ICP的使用限制
1 当sql需要全表访问时,ICP的优化策略可用于range, ref, eq_ref, ref_or_null 类型的访问数据方法 。
2 支持InnoDB和MyISAM表。
3 ICP只能用于二级索引,不能用于主索引。
4 并非全部where条件都可以用ICP筛选。
如果where条件的字段不在索引列中,还是要读取整表的记录到server端做where过滤。
5 ICP的加速效果取决于在存储引擎内通过ICP筛选掉的数据的比例。
6 5.6 版本的不支持分表的ICP 功能,5.7 版本的开始支持。
7 当sql 使用覆盖索引时,不支持ICP 优化方法。
参考
[1] https://mariadb.com/kb/en/index-condition-pushdown/
[2] http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/index-condition-pushdown-optimization.html
MySQL索引与Index Condition Pushdown(employees示例)的更多相关文章
- MySQL索引与Index Condition Pushdown
实际上,这个页面所讲述的是在MariaDB 5.3.3(MySQL是在5.6)开始引入的一种叫做Index Condition Pushdown(以下简称ICP)的查询优化方式.由于本身不是一个层面的 ...
- MySQL索引与Index Condition Pushdown(二)
实验 先从一个简单的实验开始直观认识ICP的作用. 安装数据库 首先需要安装一个支持ICP的MariaDB或MySQL数据库.我使用的是MariaDB 5.5.34,如果是使用MySQL则需要5.6版 ...
- 浅析MySQL中的Index Condition Pushdown (ICP 索引条件下推)和Multi-Range Read(MRR 索引多范围查找)查询优化
本文出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/wy123/p/7374078.html(保留出处并非什么原创作品权利,本人拙作还远远达不到,仅仅是为了链接到原文,因为后续对可能存在的一些错误 ...
- MySQL 查询优化之 Index Condition Pushdown
MySQL 查询优化之 Index Condition Pushdown Index Condition Pushdown限制条件 Index Condition Pushdown工作原理 ICP的开 ...
- MySQL ICP(Index Condition Pushdown)特性
一.SQL的where条件提取规则 在ICP(Index Condition Pushdown,索引条件下推)特性之前,必须先搞明白根据何登成大神总结出一套放置于所有SQL语句而皆准的where查询条 ...
- 【mysql】关于Index Condition Pushdown特性
ICP简介 Index Condition Pushdown (ICP) is an optimization for the case where MySQL retrieves rows from ...
- MySQL 5.6 Index Condition Pushdown
ICP(index condition pushdown)是mysql利用索引(二级索引)元组和筛字段在索引中的where条件从表中提取数据记录的一种优化操作.ICP的思想是:存储引擎在访问索引的时候 ...
- MySQL 中Index Condition Pushdown (ICP 索引条件下推)和Multi-Range Read(MRR 索引多范围查找)查询优化
一.ICP优化原理 Index Condition Pushdown (ICP),也称为索引条件下推,体现在执行计划的上是会出现Using index condition(Extra列,当然Extra ...
- MySQL 优化之 ICP (index condition pushdown:索引条件下推)
ICP技术是在MySQL5.6中引入的一种索引优化技术.它能减少在使用 二级索引 过滤where条件时的回表次数 和 减少MySQL server层和引擎层的交互次数.在索引组织表中,使用二级索引进行 ...
随机推荐
- Vue + Element UI 实现权限管理系统 前端篇(一):搭建开发环境
技术基础 开发之前,请先熟悉下面的4个文档 vue.js2.0中文, 优秀的JS框架 vue-router, vue.js 配套路由 vuex,vue.js 应用状态管理库 Element,饿了么提供 ...
- Linux-(ping,traceroute,ss)
ping命令 1.命令格式: ping [参数] [主机名或IP地址] 2.命令功能: ping命令用于:确定网络和各外部主机的状态:跟踪和隔离硬件和软件问题:测试.评估和管理网络.如果主机正在运行并 ...
- ABP框架源码中的Linq扩展方法
文件目录:aspnetboilerplate-dev\aspnetboilerplate-dev\src\Abp\Collections\Extensions\EnumerableExtensions ...
- 复刻smartbits的国产网络测试工具minismb-如何测试协议限速
复刻smartbits的网络性能测试工具MiniSMB,是一款专门用于测试智能路由器,网络交换机的性能和稳定性的软硬件相结合的工具.可以通过此工具测试任何ip网络设备的端口吞吐率,带宽,并发连接数和最 ...
- goconfig - INI 解析器
goconfig简介 goconfig是一个由Go语言开发的针对windows下常见的ini格式的配置文件解析器.该解析器在涵盖了所有ini文件操作的基础之上,又针对Go语言实际开发过程中遇到的一些需 ...
- 让 markdown 生成带目录的 html 文件
安装 npm install -g i5ting_toc 用法 进入 markdown 文件所在的文件夹 举个栗子: 你的sample.md文件放在桌面上 cd /Users/dora/Desktop ...
- MVC实现删除数据库记录
本次MVC练习,我们想实现对数据库的记录进行删除.在网页的记录列表上,点击删除,将带到另外一个详细页面,显示详细的信息,让用户对删除的信息进行确认,再点击删除动作.不管怎样,得先在数据库创建一个删除的 ...
- Eclipse中导入外部jar包步骤
昨天,学习了Jar包的打包过程,现在打算记录一下,如何在Eclipse中导入外部Jar包. 第一步:在项目中鼠标右键>>New>>点击Folder. 第二步:在弹出窗口将Fol ...
- Killing Monsters(hdu4970)
Killing Monsters Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Others)T ...
- Android-多线程AsyncTask
http://www.cnblogs.com/plokmju/p/android_AsyncTask.html AsyncTask,异步任务,可以简单进行异步操作,并把执行结果发布到UI主线程.Asy ...
