图解集合6:LinkedHashMap
初识LinkedHashMap
上两篇文章讲了HashMap和HashMap在多线程下引发的问题,说明了,HashMap是一种非常常见、非常有用的集合,并且在多线程情况下使用不当会有线程安全问题。
大多数情况下,只要不涉及线程安全问题,Map基本都可以使用HashMap,不过HashMap有一个问题,就是迭代HashMap的顺序并不是HashMap放置的顺序,也就是无序。HashMap的这一缺点往往会带来困扰,因为有些场景,我们期待一个有序的Map。
这个时候,LinkedHashMap就闪亮登场了,它虽然增加了时间和空间上的开销,但是通过维护一个运行于所有条目的双向链表,LinkedHashMap保证了元素迭代的顺序。
四个关注点在LinkedHashMap上的答案
| 关 注 点 | 结 论 |
| LinkedHashMap是否允许键值对为空 | Key和Value都允许空 |
| LinkedHashMap是否允许重复数据 | Key重复会覆盖、Value允许重复 |
| LinkedHashMap是否有序 | 有序 |
| LinkedHashMap是否线程安全 | 非线程安全 |
LinkedHashMap基本数据结构
关于LinkedHashMap,先提两点:
1、LinkedHashMap可以认为是HashMap+LinkedList,即它既使用HashMap操作数据结构,又使用LinkedList维护插入元素的先后顺序
2、LinkedHashMap的基本实现思想就是----多态。可以说,理解多态,再去理解LinkedHashMap原理会事半功倍;反之也是,对于LinkedHashMap原理的学习,也可以促进和加深对于多态的理解。
为什么可以这么说,首先看一下,LinkedHashMap的定义:
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V>
extends HashMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
{
...
}
看到,LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类,自然LinkedHashMap也就继承了HashMap中所有非private的方法。再看一下LinkedHashMap中本身的方法:
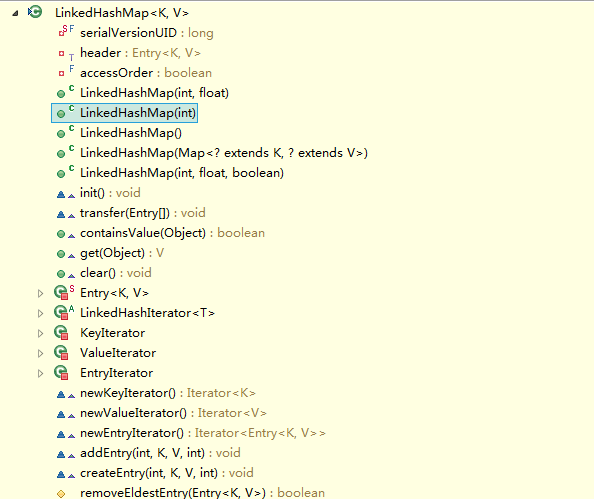
看到LinkedHashMap中并没有什么操作数据结构的方法,也就是说LinkedHashMap操作数据结构(比如put一个数据),和HashMap操作数据的方法完全一样,无非就是细节上有一些的不同罢了。
LinkedHashMap和HashMap的区别在于它们的基本数据结构上,看一下LinkedHashMap的基本数据结构,也就是Entry:
private static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Entry<K,V> {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Entry<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
...
}
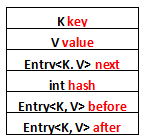
列一下Entry里面有的一些属性吧:
- K key
- V value
- Entry<K, V> next
- int hash
- Entry<K, V> before
- Entry<K, V> after
其中前面四个,也就是红色部分是从HashMap.Entry中继承过来的;后面两个,也就是蓝色部分是LinkedHashMap独有的。不要搞错了next和before、After,next是用于维护HashMap指定table位置上连接的Entry的顺序的,before、After是用于维护Entry插入的先后顺序的。
还是用图表示一下,列一下属性而已:
初始化LinkedHashMap
假如有这么一段代码:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkedHashMap =
new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
linkedHashMap.put("111", "111");
linkedHashMap.put("222", "222");
}
首先是第3行~第4行,new一个LinkedHashMap出来,看一下做了什么:
public LinkedHashMap() {
super();
accessOrder = false;
}
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
}
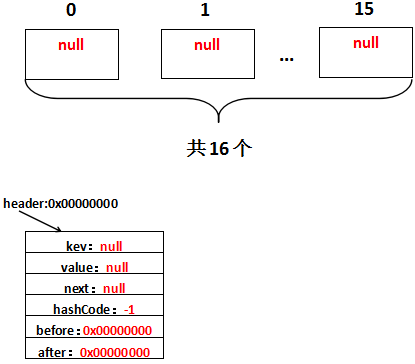
void init() {
header = new Entry<K,V>(-1, null, null, null);
header.before = header.after = header;
}
/**
* The head of the doubly linked list.
*/
private transient Entry<K,V> header;
这里出现了第一个多态:init()方法。尽管init()方法定义在HashMap中,但是由于:
1、LinkedHashMap重写了init方法
2、实例化出来的是LinkedHashMap
因此实际调用的init方法是LinkedHashMap重写的init方法。假设header的地址是0x00000000,那么初始化完毕,实际上是这样的:
LinkedHashMap添加元素
继续看LinkedHashMap添加元素,也就是put("111","111")做了什么,首先当然是调用HashMap的put方法:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
第17行又是一个多态,因为LinkedHashMap重写了addEntry方法,因此addEntry调用的是LinkedHashMap重写了的方法:
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
// Remove eldest entry if instructed, else grow capacity if appropriate
Entry<K,V> eldest = header.after;
if (removeEldestEntry(eldest)) {
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
} else {
if (size >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
}
因为LinkedHashMap由于其本身维护了插入的先后顺序,因此LinkedHashMap可以用来做缓存,第5行~第7行是用来支持FIFO算法的,这里暂时不用去关心它。看一下createEntry方法:
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMap.Entry<K,V> old = table[bucketIndex];
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<K,V>(hash, key, value, old);
table[bucketIndex] = e;
e.addBefore(header);
size++;
}
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
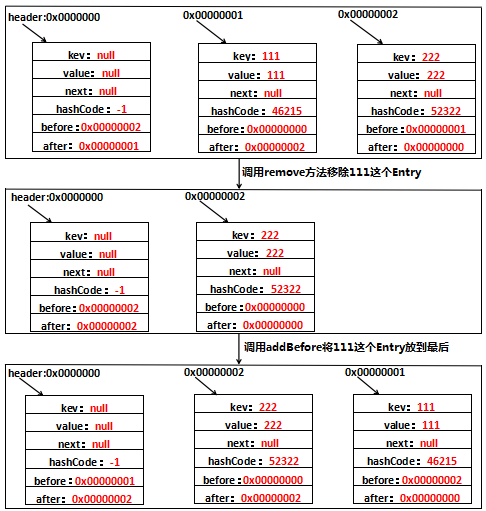
第2行~第4行的代码和HashMap没有什么不同,新添加的元素放在table[i]上,差别在于LinkedHashMap还做了addBefore操作,这四行代码的意思就是让新的Entry和原链表生成一个双向链表。假设字符串111放在位置table[1]上,生成的Entry地址为0x00000001,那么用图表示是这样的:

如果熟悉LinkedList的源码应该不难理解,还是解释一下,注意下existingEntry表示的是header:
1、after=existingEntry,即新增的Entry的after=header地址,即after=0x00000000
2、before=existingEntry.before,即新增的Entry的before是header的before的地址,header的before此时是0x00000000,因此新增的Entry的before=0x00000000
3、before.after=this,新增的Entry的before此时为0x00000000即header,header的after=this,即header的after=0x00000001
4、after.before=this,新增的Entry的after此时为0x00000000即header,header的before=this,即header的before=0x00000001
这样,header与新增的Entry的一个双向链表就形成了。再看,新增了字符串222之后是什么样的,假设新增的Entry的地址为0x00000002,生成到table[2]上,用图表示是这样的:

就不细解释了,只要before、after清除地知道代表的是哪个Entry的就不会有什么问题。
总得来看,再说明一遍,LinkedHashMap的实现就是HashMap+LinkedList的实现方式,以HashMap维护数据结构,以LinkList的方式维护数据插入顺序。
利用LinkedHashMap实现LRU算法缓存
前面讲了LinkedHashMap添加元素,删除、修改元素就不说了,比较简单,和HashMap+LinkedList的删除、修改元素大同小异,下面讲一个新的内容。
LinkedHashMap可以用来作缓存,比方说LRUCache,看一下这个类的代码,很简单,就十几行而已:
public class LRUCache extends LinkedHashMap
{
public LRUCache(int maxSize)
{
super(maxSize, 0.75F, true);
maxElements = maxSize;
} protected boolean removeEldestEntry(java.util.Map.Entry eldest)
{
return size() > maxElements;
} private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected int maxElements;
}
顾名思义,LRUCache就是基于LRU算法的Cache(缓存),这个类继承自LinkedHashMap,而类中看到没有什么特别的方法,这说明LRUCache实现缓存LRU功能都是源自LinkedHashMap的。LinkedHashMap可以实现LRU算法的缓存基于两点:
1、LinkedList首先它是一个Map,Map是基于K-V的,和缓存一致
2、LinkedList提供了一个boolean值可以让用户指定是否实现LRU
那么,首先我们了解一下什么是LRU:LRU即Least Recently Used,最近最少使用,也就是说,当缓存满了,会优先淘汰那些最近最不常访问的数据。比方说数据a,1天前访问了;数据b,2天前访问了,缓存满了,优先会淘汰数据b。
我们看一下LinkedList带boolean型参数的构造方法:
public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor,
boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}
就是这个accessOrder,它表示:
(1)false,所有的Entry按照插入的顺序排列
(2)true,所有的Entry按照访问的顺序排列
第二点的意思就是,如果有1 2 3这3个Entry,那么访问了1,就把1移到尾部去,即2 3 1。每次访问都把访问的那个数据移到双向队列的尾部去,那么每次要淘汰数据的时候,双向队列最头的那个数据不就是最不常访问的那个数据了吗?换句话说,双向链表最头的那个数据就是要淘汰的数据。
"访问",这个词有两层意思:
1、根据Key拿到Value,也就是get方法
2、修改Key对应的Value,也就是put方法
首先看一下get方法,它在LinkedHashMap中被重写:
public V get(Object key) {
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
e.recordAccess(this);
return e.value;
}
然后是put方法,沿用父类HashMap的:
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
修改数据也就是第6行~第14行的代码。看到两端代码都有一个共同点:都调用了recordAccess方法,且这个方法是Entry中的方法,也就是说每次的recordAccess操作的都是某一个固定的Entry。
recordAccess,顾名思义,记录访问,也就是说你这次访问了双向链表,我就把你记录下来,怎么记录?把你访问的Entry移到尾部去。这个方法在HashMap中是一个空方法,就是用来给子类记录访问用的,看一下LinkedHashMap中的实现:
void recordAccess(HashMap<K,V> m) {
LinkedHashMap<K,V> lm = (LinkedHashMap<K,V>)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
private void remove() {
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}
private void addBefore(Entry<K,V> existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
看到每次recordAccess的时候做了两件事情:
1、把待移动的Entry的前后Entry相连
2、把待移动的Entry移动到尾部
当然,这一切都是基于accessOrder=true的情况下。最后用一张图表示一下整个recordAccess的过程吧:
代码演示LinkedHashMap按照访问顺序排序的效果
最后代码演示一下LinkedList按照访问顺序排序的效果,验证一下上一部分LinkedHashMap的LRU功能:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkedHashMap =
new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(16, 0.75f, true);
linkedHashMap.put("111", "111");
linkedHashMap.put("222", "222");
linkedHashMap.put("333", "333");
linkedHashMap.put("444", "444");
loopLinkedHashMap(linkedHashMap);
linkedHashMap.get("111");
loopLinkedHashMap(linkedHashMap);
linkedHashMap.put("222", "2222");
loopLinkedHashMap(linkedHashMap);
} public static void loopLinkedHashMap(LinkedHashMap<String, String> linkedHashMap)
{
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> set = inkedHashMap.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> iterator = set.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext())
{
System.out.print(iterator.next() + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
注意这里的构造方法要用三个参数那个且最后的要传入true,这样才表示按照访问顺序排序。看一下代码运行结果:
111=111 222=222 333=333 444=444
222=222 333=333 444=444 111=111
333=333 444=444 111=111 222=2222
代码运行结果证明了两点:
1、LinkedList是有序的
2、每次访问一个元素(get或put),被访问的元素都被提到最后面去了
图解集合6:LinkedHashMap的更多相关文章
- Java基础知识强化之集合框架笔记58:Map集合之LinkedHashMap类的概述
1. LinkedHashMap类的概述 LinkedHashMap:Map接口的哈希表(保证唯一性) 和 链接(保证有序性)列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序. 2. 代码示例: package cn. ...
- Java从入门到放弃18---Map集合/HashMap/LinkedHashMap/TreeMap/集合嵌套/Collections工具类常用方法
Java从入门到放弃18—Map集合/HashMap/LinkedHashMap/TreeMap/集合嵌套/Collections工具类常用方法01 Map集合Map集合处理键值映射关系的数据为了方便 ...
- Java集合之LinkedHashMap
一.初识LinkedHashMap 上篇文章讲了HashMap.HashMap是一种非常常见.非常有用的集合,但在多线程情况下使用不当会有线程安全问题. 大多数情况下,只要不涉及线程安全问题,Map基 ...
- 图解集合4:HashMap
初识HashMap 之前的List,讲了ArrayList.LinkedList,最后讲到了CopyOnWriteArrayList,就前两者而言,反映的是两种思想: (1)ArrayList以数组形 ...
- Map集合、HashMap集合、LinkedHashMap集合、Hashtable集合、Collections工具类和模拟斗地主洗牌和发牌
1.Map集合概述和特点 * A:Map接口概述 * 查看API可以知道: * 将键映射到值的对象 * 一个映射不能包含重复的键 * 每个键最多 ...
- JDK(六)JDK1.8源码分析【集合】LinkedHashMap
本文转载自joemsu,原文连接 [JDK1.8]JDK1.8集合源码阅读——LinkedHashMap LinkedHashMap的数据结构 可以从上图中看到,LinkedHashMap数据结构相比 ...
- Java8集合框架——LinkedHashMap源码分析
本文的结构如下: 一.LinkedHashMap 的 Javadoc 文档注释和简要说明 二.LinkedHashMap 的内部实现:一些扩展属性和构造函数 三.LinkedHashMap 的 put ...
- 图解集合5:不正确地使用HashMap引发死循环及元素丢失
问题引出 前一篇文章讲解了HashMap的实现原理,讲到了HashMap不是线程安全的.那么HashMap在多线程环境下又会有什么问题呢? 几个月前,公司项目的一个模块在线上运行的时候出现了死循环,死 ...
- 图解集合3:CopyOnWriteArrayList
初识CopyOnWriteArrayList 第一次见到CopyOnWriteArrayList,是在研究JDBC的时候,每一个数据库的Driver都是维护在一个CopyOnWriteArrayLis ...
随机推荐
- 10201启动时候报ORA-27125
[ora10g@oracle ~]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.1.0 - Production on Thu Feb 26 18:46 ...
- KeyedPriorityQueue
// <copyright file="KeyedPriorityQueue.cs" company="Microsoft">Copyright ( ...
- Eclipse启动时发生An internal error occurred during: "Initializing Java Tooling".错误的解决方法
问题描述: Eclipse启动时发生An internal error occurred during: "Initializing JavaTooling".错误的解决方法 解决 ...
- iOS 利用Charles抓包
1.安装 Mac下好用的HTTP/HTTPS抓包工具Charles,到官网http://www.charlesproxy.com/可下载到最新版本(若不支持rMBP可拖到Retinizer中把文字变清 ...
- 基于redis的点赞功能设计
前言 点赞其实是一个很有意思的功能.基本的设计思路有大致两种, 一种自然是用mysql等 数据库直接落地存储, 另外一种就是利用点赞的业务特征来扔到redis(或memcache)中, 然后离线刷回m ...
- iMetro
body { background:#FFFFFF url("http://images.cnblogs.com/cnblogs_com/mookmark/745172/o_8.jpg&qu ...
- Vim 插入递增列
<C-a> ++1 <C-x> --1 安装Plugin 'terryma/vim-multiple-cursors'后 <C-v> 选所有数字 <C ...
- BZOJ4597: [Shoi2016]随机序列
Description 你的面前有N个数排成一行.分别为A1, A2, … , An.你打算在每相邻的两个 Ai和 Ai+1 间都插入一个加号或者 减号或者乘号.那么一共有 3^(n-1) 种可能的表 ...
- Logback_日志使用详解(转)
概述 Logback建立于三个主要类之上:日志记录器(Logger),输出端(Appender)和日志格式化器(Layout).这三种组件协同工作,使开发者可以按照消息类型和级别来记录消息,还可以在程 ...
- sublime 安装 插件
从菜单 View - Show Console 或者 ctrl + ~ 快捷键,调出 console.将以下 Python 代码粘贴进去并 enter 执行,不出意外即完成安装.以下提供 ST3 和 ...
