Seaborn时间线图和热图
lineplot()
绘制与时间相关性的线图。
sns.lineplot(
x=None,
y=None,
hue=None,
size=None,
style=None,
data=None,
palette=None,
hue_order=None,
hue_norm=None,
sizes=None,
size_order=None,
size_norm=None,
dashes=True,
markers=None,
style_order=None,
units=None,
estimator='mean',
ci=95,
n_boot=1000,
sort=True,
err_style='band',
err_kws=None,
legend='brief',
ax=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Draw a line plot with possibility of several semantic groupings.
The relationship between ``x`` and ``y`` can be shown for different subsets
of the data using the ``hue``, ``size``, and ``style`` parameters. These
parameters control what visual semantics are used to identify the different
subsets. It is possible to show up to three dimensions independently by
using all three semantic types, but this style of plot can be hard to
interpret and is often ineffective. Using redundant semantics (i.e. both
``hue`` and ``style`` for the same variable) can be helpful for making
graphics more accessible.
See the :ref:`tutorial <relational_tutorial>` for more information.
By default, the plot aggregates over multiple ``y`` values at each value of
``x`` and shows an estimate of the central tendency and a confidence
interval for that estimate.
Parameters
----------
x, y : names of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Input data variables; must be numeric. Can pass data directly or
reference columns in ``data``.
hue : name of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Grouping variable that will produce lines with different colors.
Can be either categorical or numeric, although color mapping will
behave differently in latter case.
size : name of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Grouping variable that will produce lines with different widths.
Can be either categorical or numeric, although size mapping will
behave differently in latter case.
style : name of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Grouping variable that will produce lines with different dashes
and/or markers. Can have a numeric dtype but will always be treated
as categorical.
data : DataFrame
Tidy ("long-form") dataframe where each column is a variable and each
row is an observation.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
hue_order : list, optional
Specified order for the appearance of the ``hue`` variable levels,
otherwise they are determined from the data. Not relevant when the
``hue`` variable is numeric.
hue_norm : tuple or Normalize object, optional
Normalization in data units for colormap applied to the ``hue``
variable when it is numeric. Not relevant if it is categorical.
sizes : list, dict, or tuple, optional
An object that determines how sizes are chosen when ``size`` is used.
It can always be a list of size values or a dict mapping levels of the
``size`` variable to sizes. When ``size`` is numeric, it can also be
a tuple specifying the minimum and maximum size to use such that other
values are normalized within this range.
size_order : list, optional
Specified order for appearance of the ``size`` variable levels,
otherwise they are determined from the data. Not relevant when the
``size`` variable is numeric.
size_norm : tuple or Normalize object, optional
Normalization in data units for scaling plot objects when the
``size`` variable is numeric.
dashes : boolean, list, or dictionary, optional
Object determining how to draw the lines for different levels of the
``style`` variable. Setting to ``True`` will use default dash codes, or
you can pass a list of dash codes or a dictionary mapping levels of the
``style`` variable to dash codes. Setting to ``False`` will use solid
lines for all subsets. Dashes are specified as in matplotlib: a tuple
of ``(segment, gap)`` lengths, or an empty string to draw a solid line.
markers : boolean, list, or dictionary, optional
Object determining how to draw the markers for different levels of the
``style`` variable. Setting to ``True`` will use default markers, or
you can pass a list of markers or a dictionary mapping levels of the
``style`` variable to markers. Setting to ``False`` will draw
marker-less lines. Markers are specified as in matplotlib.
style_order : list, optional
Specified order for appearance of the ``style`` variable levels
otherwise they are determined from the data. Not relevant when the
``style`` variable is numeric.
units : {long_form_var}
Grouping variable identifying sampling units. When used, a separate
line will be drawn for each unit with appropriate semantics, but no
legend entry will be added. Useful for showing distribution of
experimental replicates when exact identities are not needed.
estimator : name of pandas method or callable or None, optional
Method for aggregating across multiple observations of the ``y``
variable at the same ``x`` level. If ``None``, all observations will
be drawn.
ci : int or "sd" or None, optional
Size of the confidence interval to draw when aggregating with an
estimator. "sd" means to draw the standard deviation of the data.
Setting to ``None`` will skip bootstrapping.
n_boot : int, optional
Number of bootstraps to use for computing the confidence interval.
sort : boolean, optional
If True, the data will be sorted by the x and y variables, otherwise
lines will connect points in the order they appear in the dataset.
err_style : "band" or "bars", optional
Whether to draw the confidence intervals with translucent error bands
or discrete error bars.
err_band : dict of keyword arguments
Additional paramters to control the aesthetics of the error bars. The
kwargs are passed either to ``ax.fill_between`` or ``ax.errorbar``,
depending on the ``err_style``.
legend : "brief", "full", or False, optional
How to draw the legend. If "brief", numeric ``hue`` and ``size``
variables will be represented with a sample of evenly spaced values.
If "full", every group will get an entry in the legend. If ``False``,
no legend data is added and no legend is drawn.
ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes object to draw the plot onto, otherwise uses the current Axes.
kwargs : key, value mappings
Other keyword arguments are passed down to ``plt.plot`` at draw time.
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
Returns the Axes object with the plot drawn onto it.
See Also
--------
scatterplot : Show the relationship between two variables without
emphasizing continuity of the ``x`` variable.
pointplot : Show the relationship between two variables when one is
categorical.
#设置风格
sns.set_style('whitegrid')
#导入数据
fmri = sns.load_dataset("fmri" , data_home='seaborn-data')
fmri
#时间线图
ax = sns.lineplot(data=fmri, x="timepoint", y="signal")
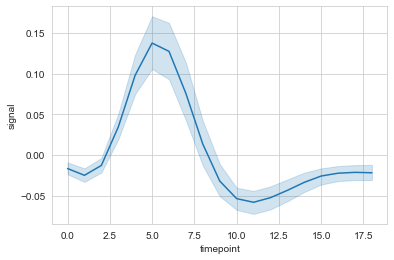
#hue设置分类
ax = sns.lineplot(data=fmri, x="timepoint", y="signal", hue="region")

#style使用线性进行再分类
ax = sns.lineplot(data=fmri, x="timepoint", y="signal", hue="region", style="event")
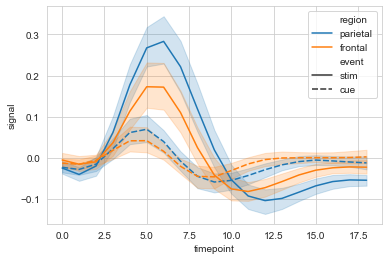
#markers设置是否显示散点,dashses设置是否显示虚线
sx = sns.lineplot(data=fmri, x="timepoint", y="signal",
hue="region", style="event",
markers=True, dashes=False
)
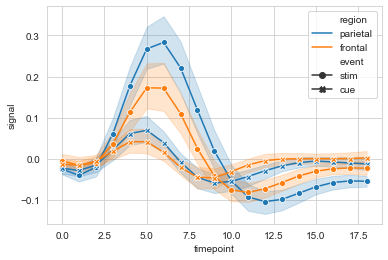
#err_style设置误差线类型,默认band; ci设置置信区间,默认95%
ax = sns.lineplot(data=fmri, x="timepoint", y="signal",
hue="region", style="event",
err_style='bars', ci=68
)
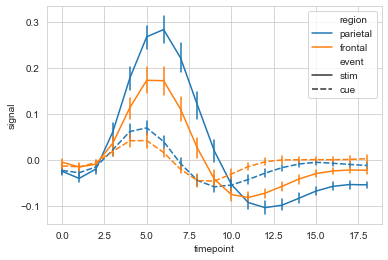
#选取部分数据,多条线显示
ax = sns.lineplot(data=fmri.query("region=='frontal'"),
x="timepoint", y='signal',
hue='event', units='subject',
estimator=None,lw=1
)
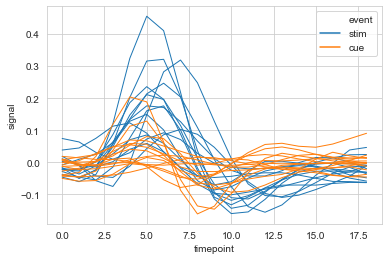
relplot()
用于分列绘制时间相关线图,relplot() = lineplot() + FaceGrid
sns.relplot(
x=None,
y=None,
hue=None,
size=None,
style=None,
data=None,
row=None,
col=None,
col_wrap=None,
row_order=None,
col_order=None,
palette=None,
hue_order=None,
hue_norm=None,
sizes=None,
size_order=None,
size_norm=None,
markers=None,
dashes=None,
style_order=None,
legend='brief',
kind='scatter',
height=5,
aspect=1,
facet_kws=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Figure-level interface for drawing relational plots onto a FacetGrid.
This function provides access to several different axes-level functions
that show the relationship between two variables with semantic mappings
of subsets. The ``kind`` parameter selects the underlying axes-level
function to use:
- :func:`scatterplot` (with ``kind="scatter"``; the default)
- :func:`lineplot` (with ``kind="line"``)
Extra keyword arguments are passed to the underlying function, so you
should refer to the documentation for each to see kind-specific options.
The relationship between ``x`` and ``y`` can be shown for different subsets
of the data using the ``hue``, ``size``, and ``style`` parameters. These
parameters control what visual semantics are used to identify the different
subsets. It is possible to show up to three dimensions independently by
using all three semantic types, but this style of plot can be hard to
interpret and is often ineffective. Using redundant semantics (i.e. both
``hue`` and ``style`` for the same variable) can be helpful for making
graphics more accessible.
See the :ref:`tutorial <relational_tutorial>` for more information.
After plotting, the :class:`FacetGrid` with the plot is returned and can
be used directly to tweak supporting plot details or add other layers.
Note that, unlike when using the underlying plotting functions directly,
data must be passed in a long-form DataFrame with variables specified by
passing strings to ``x``, ``y``, and other parameters.
Parameters
----------
x, y : names of variables in ``data``
Input data variables; must be numeric.
hue : name in ``data``, optional
Grouping variable that will produce elements with different colors.
Can be either categorical or numeric, although color mapping will
behave differently in latter case.
size : name in ``data``, optional
Grouping variable that will produce elements with different sizes.
Can be either categorical or numeric, although size mapping will
behave differently in latter case.
style : name in ``data``, optional
Grouping variable that will produce elements with different styles.
Can have a numeric dtype but will always be treated as categorical.
data : DataFrame
Tidy ("long-form") dataframe where each column is a variable and each
row is an observation.
row, col : names of variables in ``data``, optional
Categorical variables that will determine the faceting of the grid.
col_wrap : int, optional
"Wrap" the column variable at this width, so that the column facets
span multiple rows. Incompatible with a ``row`` facet.
row_order, col_order : lists of strings, optional
Order to organize the rows and/or columns of the grid in, otherwise the
orders are inferred from the data objects.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
hue_order : list, optional
Specified order for the appearance of the ``hue`` variable levels,
otherwise they are determined from the data. Not relevant when the
``hue`` variable is numeric.
hue_norm : tuple or Normalize object, optional
Normalization in data units for colormap applied to the ``hue``
variable when it is numeric. Not relevant if it is categorical.
sizes : list, dict, or tuple, optional
An object that determines how sizes are chosen when ``size`` is used.
It can always be a list of size values or a dict mapping levels of the
``size`` variable to sizes. When ``size`` is numeric, it can also be
a tuple specifying the minimum and maximum size to use such that other
values are normalized within this range.
size_order : list, optional
Specified order for appearance of the ``size`` variable levels,
otherwise they are determined from the data. Not relevant when the
``size`` variable is numeric.
size_norm : tuple or Normalize object, optional
Normalization in data units for scaling plot objects when the
``size`` variable is numeric.
legend : "brief", "full", or False, optional
How to draw the legend. If "brief", numeric ``hue`` and ``size``
variables will be represented with a sample of evenly spaced values.
If "full", every group will get an entry in the legend. If ``False``,
no legend data is added and no legend is drawn.
kind : string, optional
Kind of plot to draw, corresponding to a seaborn relational plot.
Options are {``scatter`` and ``line``}.
height : scalar, optional
Height (in inches) of each facet. See also: ``aspect``.
aspect : scalar, optional
Aspect ratio of each facet, so that ``aspect * height`` gives the width
of each facet in inches.
facet_kws : dict, optional
Dictionary of other keyword arguments to pass to :class:`FacetGrid`.
kwargs : key, value pairings
Other keyword arguments are passed through to the underlying plotting
function.
Returns
-------
g : :class:`FacetGrid`
Returns the :class:`FacetGrid` object with the plot on it for further
tweaking.
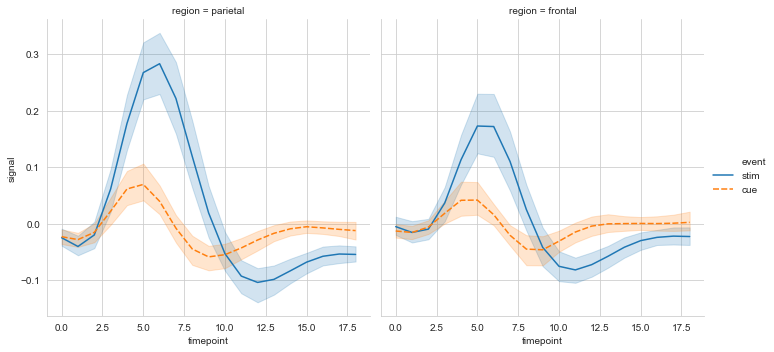
#col设置分栏绘制
ax = sns.relplot(data=fmri, x='timepoint', y='signal',
col='region', hue='event', style='event',
kind='line'
)
heatmap()
用于绘制热点图。
sns.heatmap(
data,
vmin=None,
vmax=None,
cmap=None,
center=None,
robust=False,
annot=None,
fmt='.2g',
annot_kws=None,
linewidths=0,
linecolor='white',
cbar=True,
cbar_kws=None,
cbar_ax=None,
square=False,
xticklabels='auto',
yticklabels='auto',
mask=None,
ax=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Plot rectangular data as a color-encoded matrix.
This is an Axes-level function and will draw the heatmap into the
currently-active Axes if none is provided to the ``ax`` argument. Part of
this Axes space will be taken and used to plot a colormap, unless ``cbar``
is False or a separate Axes is provided to ``cbar_ax``.
Parameters
----------
data : rectangular dataset
2D dataset that can be coerced into an ndarray. If a Pandas DataFrame
is provided, the index/column information will be used to label the
columns and rows.
vmin, vmax : floats, optional
Values to anchor the colormap, otherwise they are inferred from the
data and other keyword arguments.
cmap : matplotlib colormap name or object, or list of colors, optional
The mapping from data values to color space. If not provided, the
default will depend on whether ``center`` is set.
center : float, optional
The value at which to center the colormap when plotting divergant data.
Using this parameter will change the default ``cmap`` if none is
specified.
robust : bool, optional
If True and ``vmin`` or ``vmax`` are absent, the colormap range is
computed with robust quantiles instead of the extreme values.
annot : bool or rectangular dataset, optional
If True, write the data value in each cell. If an array-like with the
same shape as ``data``, then use this to annotate the heatmap instead
of the raw data.
fmt : string, optional
String formatting code to use when adding annotations.
annot_kws : dict of key, value mappings, optional
Keyword arguments for ``ax.text`` when ``annot`` is True.
linewidths : float, optional
Width of the lines that will divide each cell.
linecolor : color, optional
Color of the lines that will divide each cell.
cbar : boolean, optional
Whether to draw a colorbar.
cbar_kws : dict of key, value mappings, optional
Keyword arguments for `fig.colorbar`.
cbar_ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes in which to draw the colorbar, otherwise take space from the
main Axes.
square : boolean, optional
If True, set the Axes aspect to "equal" so each cell will be
square-shaped.
xticklabels, yticklabels : "auto", bool, list-like, or int, optional
If True, plot the column names of the dataframe. If False, don't plot
the column names. If list-like, plot these alternate labels as the
xticklabels. If an integer, use the column names but plot only every
n label. If "auto", try to densely plot non-overlapping labels.
mask : boolean array or DataFrame, optional
If passed, data will not be shown in cells where ``mask`` is True.
Cells with missing values are automatically masked.
ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes in which to draw the plot, otherwise use the currently-active
Axes.
kwargs : other keyword arguments
All other keyword arguments are passed to ``ax.pcolormesh``.
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
Axes object with the heatmap.
See also
--------
clustermap : Plot a matrix using hierachical clustering to arrange the
rows and columns.
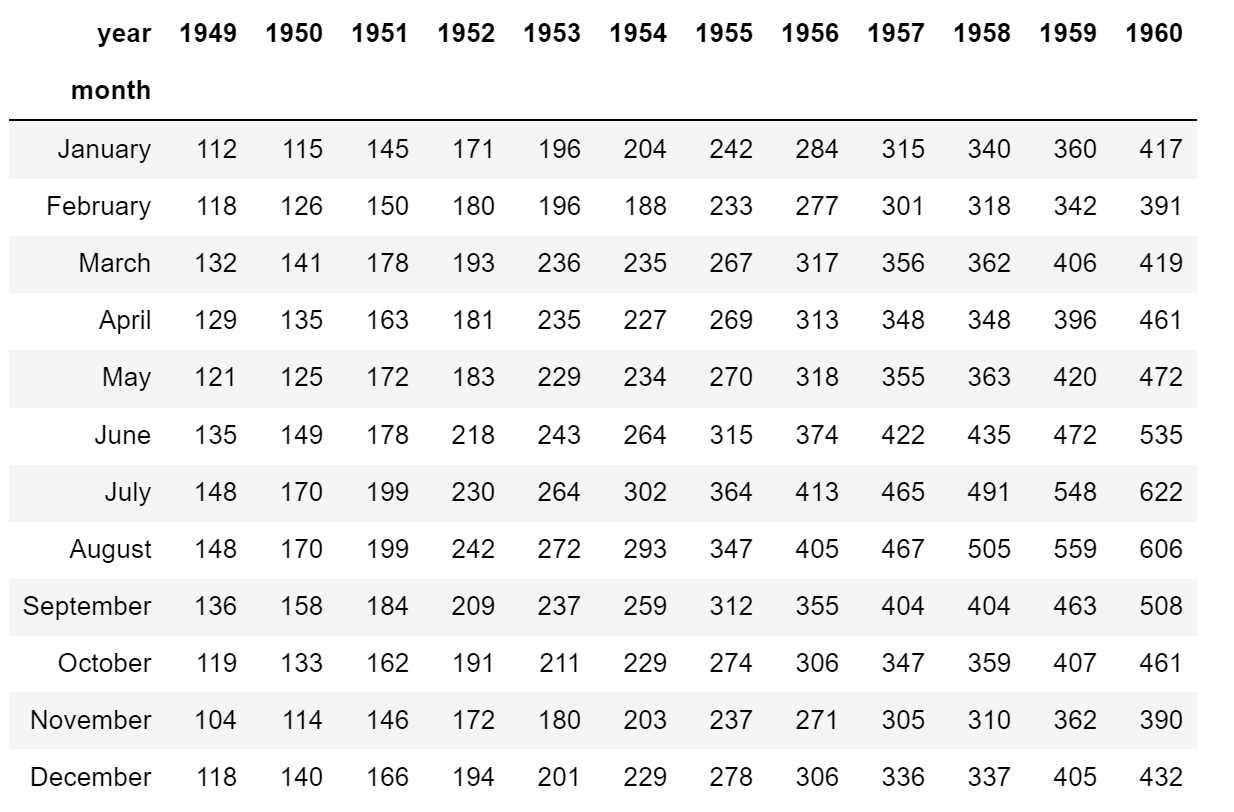
# 导入数据
flights = sns.load_dataset('flights', data_home='seaborn-data')
flights = flights.pivot('month', 'year', 'passengers')
flights
#简易热图
ax = sns.heatmap(flights)
#linewidths设置线宽
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, linewidth=.5)
#annot设置是否显示数据,fmt设置数据显示的格式
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, annot=True, fmt='d')
#解决上下两行显示不全
ax = ax.set_ylim(len(flights)+0.1, -0.1)

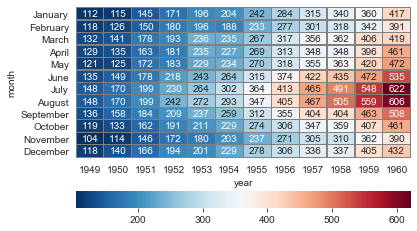
#cmap设置调色板,linewidths设置方格间隔, linecolor设置间隔线颜色, cbar_kws设置颜色条参数
ax = sns.heatmap(flights, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='RdBu_r',
linewidths=0.3, linecolor='grey',
cbar_kws={'orientation': 'horizontal'}
)
ax = ax.set_ylim(len(flights)+0.1, -0.1)
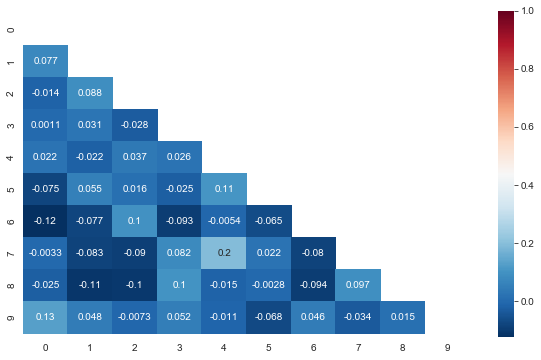
三角热力图
#布尔矩阵热图,若为矩阵内为True,则热力图相应的位置的数据将会被屏蔽掉(常用在绘制相关系数矩阵图)
data_new = np.random.randn(200, 10)
pd.DataFrame(data_new)
#相关系数矩阵(对称矩阵)
corr = np.corrcoef(data_new, rowvar=False)
pd.DataFrame(corr)
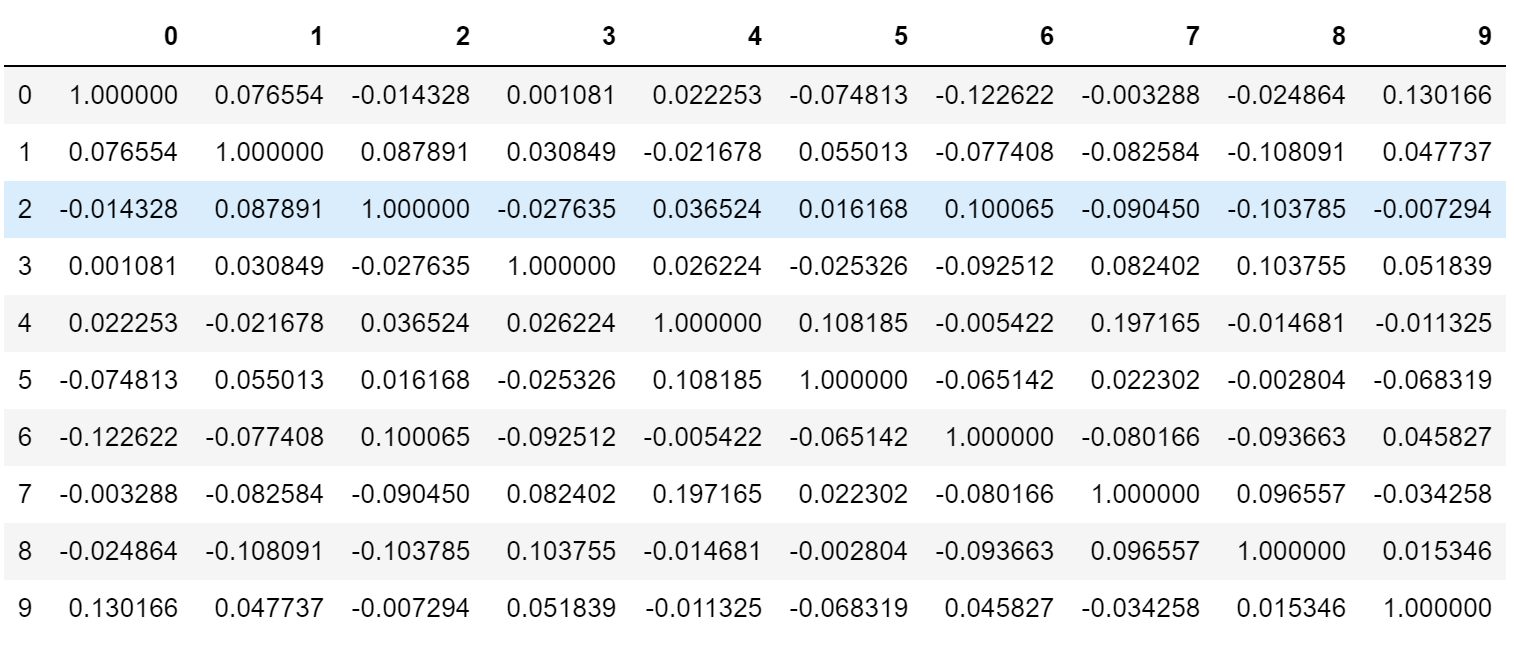
#以corr的形状生成一个零矩阵
mask = np.zeros_like(corr)
mask
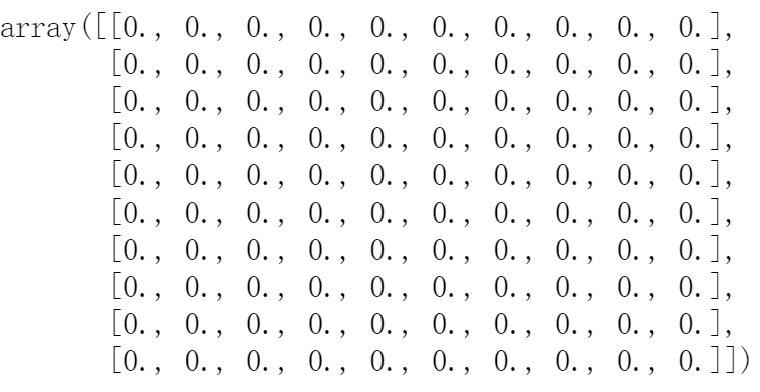
#设置mask对角线以上为True
mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True
mask

#绘制对称矩阵数据的热图
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
ax = sns.heatmap(corr, mask=mask, annot=True, cmap='RdBu_r')
ax.set_ylim(len(corr)+0.1, -0.1)
Seaborn时间线图和热图的更多相关文章
- python matplotlib绘图大全(散点图、柱状图、饼图、极坐标图、热量图、三维图以及热图)
//2019.7.14晚matplotlib七种常见图像输出编程大全 七种图形汇总输出如下: import numpy as np #导入数据结构nmupy模块import matplotlib.py ...
- seaborn线性关系数据可视化:时间线图|热图|结构化图表可视化
一.线性关系数据可视化lmplot( ) 表示对所统计的数据做散点图,并拟合一个一元线性回归关系. lmplot(x, y, data, hue=None, col=None, row=None, p ...
- 基于HTML5实现3D热图Heatmap应用
Heatmap热图通过众多数据点信息,汇聚成直观可视化颜色效果,热图已广泛被应用于气象预报.医疗成像.机房温度监控等行业,甚至应用于竞技体育领域的数据分析. http://www.hightopo.c ...
- 基于HTML5实现的Heatmap热图3D应用
Heatmap热图通过众多数据点信息,汇聚成直观可视化颜色效果,热图已广泛被应用于气象预报.医疗成像.机房温度监控等行业,甚至应用于竞技体育领域的数据分析. 已有众多文章分享了生成Heatmap热图原 ...
- 基于matplotlib的数据可视化 - 热图imshow
热图: Display an image on the axes. 可以用来比较两个矩阵的相似程度 mp.imshow(z, cmap=颜色映射,origin=垂直轴向) imshow( X, cma ...
- 扩增子图表解读3热图:差异菌、OTU及功能
热图是使用颜色来展示数值矩阵的图形.通常还会结合行.列的聚类分析,以表达实验数据多方面的结果. 热图在生物学领域应用广泛,尤其在高通量测序的结果展示中很流行,如样品-基因表达,样品-OTU相对丰度矩 ...
- Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:3. 线性关系数据| 时间线图表| 热图
1. 线性关系数据可视化 lmplot( ) import numpy as np import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import ...
- HeatMap(热图)的原理和实现
先来看两张图: (1)10年世界杯决赛,冠军西班牙队中门将.后卫.中场及前锋的跑位热图 通过热图,我们可以很清楚的看出四个球员在比赛中跑动位置的差异. (2)历史地震震源位置的热图 也可以很清楚的看出 ...
- R语言学习 - 热图简化
绘制热图除了使用ggplot2,还可以有其它的包或函数,比如pheatmap::pheatmap (pheatmap包中的pheatmap函数).gplots::heatmap.2等. 相比于gg ...
- R语言学习 - 热图绘制heatmap
生成测试数据 绘图首先需要数据.通过生成一堆的向量,转换为矩阵,得到想要的数据. data <- c(1:6, 6:1, 6:1, 1:6, (6:1)/10, (1:6)/10, (1:6)/ ...
随机推荐
- 【Azure 云服务】当Windows系统发布新的安全漏洞后,如何查看Azure云服务(Cloud Service)的实例是否也更新了安全补丁呢?
问题描述 当Windows发布新的安全漏洞后,会根据安全漏洞的级别分类来确定是紧急打补丁升级,还是每一月的补丁日( 每月第二周的星期二)来统一推送补丁. 比如最近的一个安全漏洞(9月13号发布) C ...
- C++ mySQL数据库连接池(windows平台)
C++ MySQL数据库连接池 新手学了C++多线程,看了些资料练手写了C++数据库连接池小项目,自己的源码地址 关键技术点 MySQL数据库编程.单例模式.queue队列容器.C++11多线程编程. ...
- C++ //string字符串拼接
1 //string字符串拼接 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 8 ...
- acme.sh 免费泛解析证书生成
环境准备 本篇文章使用的 ACME 客户端是基于 Docker 容器使用的,所以需要准备 Docker 运行环境.本文使用的是 CentOS 7.x 与 Docker CE - 19.03.13,且已 ...
- open cv java 可以 对图片进行分析,得到数据。考试答题卡 2B铅笔涂黑嘎达 识别
open cv java 可以 对图片进行分析,得到数据.考试答题卡 2B铅笔涂黑嘎达 识别
- Prometheus组件构成及介绍
Prometheus是一个开源的监控和告警工具包,其常用的组件主要包括以下几个部分: Prometheus Server 功能:Prometheus Server是Prometheus的核心组件,负责 ...
- windows10 使用gcc编译生成可执行文件exe实例解析
一 操作步骤 1.生成可执行程序 cd xxx # 先进入源程序所在的目录 gcc hello.cpp # 一次性编译,windows系统生成a.exe文件,Linux系统生成a.out文件 gcc ...
- 开源K线图辅助线编辑工具模块
基本就像使用photoshop一样,同一DC上应用叠加图像. 辅助线模块,提供浮动工具条,以及两层Layer,附加在DC上,交互处理DC对应窗口区域的鼠标事件,时间轴价格轴与x轴y轴坐标转换. XW全 ...
- java生产者消费者模式代码示例
package test; import java.util.LinkedList; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args ...
- 从 Linux 内核角度探秘 JDK MappedByteBuffer
本文涉及到的内核源码版本为: 5.4 ,JVM 源码为:OpenJDK17,RocketMQ 源码版本为:5.1.1 在之前的文章<一步一图带你深入剖析 JDK NIO ByteBuffer 在 ...
