Mnist手写数字识别 Tensorflow
Mnist手写数字识别 Tensorflow
任务目标
- 了解mnist数据集
- 搭建和测试模型
编辑环境
操作系统:Win10
python版本:3.6
集成开发环境:pycharm
tensorflow版本:1.*
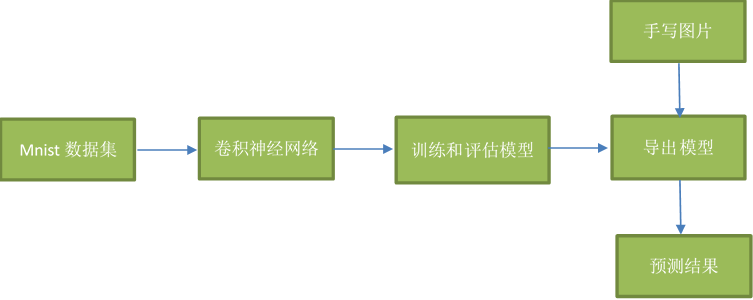
程序流程图
了解mnist数据集
mnist数据集:mnist数据集下载地址
MNIST 数据集来自美国国家标准与技术研究所, National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). 训练集 (training set) 由来自 250 个不同人手写的数字构成, 其中 50% 是高中学生, 50% 来自人口普查局 (the Census Bureau) 的工作人员. 测试集(test set) 也是同样比例的手写数字数据.
图片是以字节的形式进行存储, 我们需要把它们读取到 NumPy array 中, 以便训练和测试算法。
读取mnist数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist_data", one_hot=True)
模型结构
输入层
with tf.variable_scope("data"):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,784],name='x_pred') # 784=28*28*1 宽长为28,单通道图片
y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[None,10]) # 10个类别
第一层卷积
现在我们可以开始实现第一层了。它由一个卷积接一个max pooling完成。卷积在每个5x5的patch中算出32个特征。卷积的权重张量形状是[5, 5, 1, 32],前两个维度是patch的大小,接着是输入的通道数目,最后是输出的通道数目。 而对于每一个输出通道都有一个对应的偏置量。
为了用这一层,我们把x变成一个4d向量,其第2、第3维对应图片的宽、高,最后一维代表图片的颜色通道数(因为是灰度图所以这里的通道数为1,如果是rgb彩色图,则为3)。
我们把x_image和权值向量进行卷积,加上偏置项,然后应用ReLU激活函数,最后进行max pooling。
with tf.variable_scope("conv1"):
w_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,1,32])) # 5*5的卷积核 1个通道的输入图像 32个不同的卷积核,得到32个特征图
b_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[32]))
x_reshape = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) # n张 28*28 的单通道图片
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(x_reshape,w_conv1,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv1) #strides为过滤器步长 padding='SAME' 边缘自动补充
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME") # ksize为池化层过滤器的尺度,strides为过滤器步长 padding="SAME" 考虑边界,如果不够用 用0填充
第二层卷积
为了构建一个更深的网络,我们会把几个类似的层堆叠起来。第二层中,每个5x5的patch会得到64个特征
with tf.variable_scope("conv2"):
w_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,32,64]))
b_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,w_conv2,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv2)
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
密集连接层
现在,图片尺寸减小到7x7,我们加入一个有1024个神经元的全连接层,用于处理整个图片。我们把池化层输出的张量reshape成一些向量,乘上权重矩阵,加上偏置,然后对其使用ReLU。
为了减少过拟合,我们在输出层之前加入dropout。我们用一个placeholder来代表一个神经元的输出在dropout中保持不变的概率。这样我们可以在训练过程中启用dropout,在测试过程中关闭dropout。 TensorFlow的tf.nn.dropout操作除了可以屏蔽神经元的输出外,还会自动处理神经元输出值的scale。所以用dropout的时候可以不用考虑scale。
with tf.variable_scope("fc1"):
w_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*64,1024])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[1024]))
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 在输出层之前加入dropout以减少过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float32",name="keep_prob")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
输出层
&emsp' 最后,我们添加一个softmax层,就像前面的单层softmax regression一样。
with tf.variable_scope("fc2"):
w_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024,10])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[10]))
y_predict = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,w_fc2)+b_fc2
tf.add_to_collection('pred_network', y_predict) # 用于加载模型获取要预测的网络结构
训练和评估模型
为了进行训练和评估,我们使用与之前简单的单层SoftMax神经网络模型几乎相同的一套代码,只是我们会用更加复杂的ADAM优化器来做梯度最速下降,在feed_dict中加入额外的参数keep_prob来控制dropout比例。然后每100次迭代输出一次日志。
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict))
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
# 使用反向传播,利用优化器使损失函数最小化
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
with tf.variable_scope("acc"):
# 检测我们的预测是否真实标签匹配(索引位置一样表示匹配)
# tf.argmax(y_conv,dimension), 返回最大数值的下标 通常和tf.equal()一起使用,计算模型准确度
# dimension=0 按列找 dimension=1 按行找
equal_list = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_true,1),tf.arg_max(y_predict,1))
# 统计测试准确率, 将correct_prediction的布尔值转换为浮点数来代表对、错,并取平均值。
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32))
# tensorboard
# tf.summary.histogram用来显示直方图信息
# tf.summary.scalar用来显示标量信息
# Summary:所有需要在TensorBoard上展示的统计结果
tf.summary.histogram("weight",w_fc2)
tf.summary.histogram("bias",b_fc2)
tf.summary.scalar("loss",loss)
tf.summary.scalar("acc",accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
filewriter = tf.summary.FileWriter("tfboard",graph=sess.graph)
if is_train: # 训练
for i in range(20001):
x_train, y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100==0:
# 评估模型准确度,此阶段不使用Dropout
print("第%d训练,准确率为%f" % (i + 1, sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train, keep_prob: 1.0})))
# # 训练模型,此阶段使用50%的Dropout
sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train,keep_prob: 0.5})
summary = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train, keep_prob: 1})
filewriter.add_summary(summary,i)
saver.save(sess,savemodel)
else: # 测试集预测
count = 0.0
epochs = 300
saver.restore(sess, savemodel)
for i in range(epochs):
x_test, y_test = mnist.train.next_batch(1)
print("第%d张图片,真实值为:%d预测值为:%d" % (i + 1,
tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval(),
tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval()
))
if (tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval() == tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval()):
count = count + 1
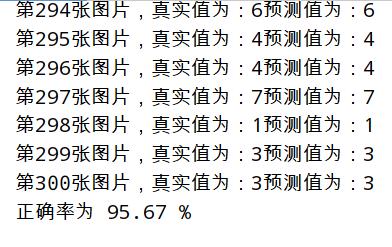
print("正确率为 %.2f " % float(count * 100 / epochs) + "%")
评估结果
传入手写图片,利用模型预测
首先利用opencv包将图片转为单通道(灰度图),调整图像尺寸28*28,并且二值化图像,通过处理最后得到一个(0~1)扁平的图片像素值(一个二维数组)。
手写数字图片
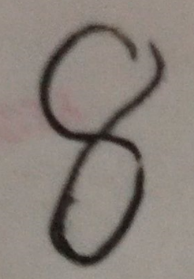
处理手写数字图片
def dealFigureImg(imgPath):
img = cv2.imread(imgPath) # 手写数字图像所在位置
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转换图像为单通道(灰度图)
resize_img = cv2.resize(img, (28, 28)) # 调整图像尺寸为28*28
ret, thresh_img = cv2.threshold(resize_img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化
cv2.imwrite("image/temp.jpg",thresh_img)
im = Image.open('image/temp.jpg')
data = list(im.getdata()) # 得到一个扁平的 图片像素
result = [(255 - x) * 1.0 / 255.0 for x in data] # 像素值范围(0-255),转换为(0-1) ->符合模型训练时传入数据的值
result = np.expand_dims(result, 0) # 扩展维度 ->符合模型训练时传入数据的维度
os.remove('image/temp.jpg')
return result
载入模型进行预测
def predictFigureImg(imgPath):
result = dealFigureImg(imgPath)
with tf.Session() as sess:
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model/mnist_model.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess, "model/mnist_model")
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name('data/x_pred').outputs[0]
keep_prob = graph.get_operation_by_name('fc1/keep_prob').outputs[0]
y = tf.get_collection("pred_network")[0]
predict = np.argmax(sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: result,keep_prob:1.0}))
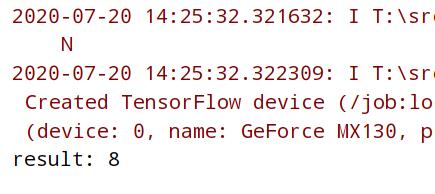
print("result:",predict)
预测结果
完整代码
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# 构造模型
def getMnistModel(savemodel,is_train):
"""
:param savemodel: 模型保存路径
:param is_train: True为训练,False为测试模型
:return:None
"""
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist_data", one_hot=True)
with tf.variable_scope("data"):
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,shape=[None,784],name='x_pred') # 784=28*28*1 宽长为28,单通道图片
y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32,shape=[None,10]) # 10个类别
with tf.variable_scope("conv1"):
w_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,1,32])) # 5*5的卷积核 1个通道的输入图像 32个不同的卷积核,得到32个特征图
b_conv1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[32]))
x_reshape = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) # n张 28*28 的单通道图片
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(x_reshape,w_conv1,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv1) #strides为过滤器步长 padding='SAME' 边缘自动补充
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME") # ksize为池化层过滤器的尺度,strides为过滤器步长 padding="SAME" 考虑边界,如果不够用 用0填充
with tf.variable_scope("conv2"):
w_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,32,64]))
b_conv2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.conv2d(pool1,w_conv2,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv2)
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
with tf.variable_scope("fc1"):
w_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([7*7*64,1024])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[1024]))
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 在输出层之前加入dropout以减少过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float32",name="keep_prob")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
with tf.variable_scope("fc2"):
w_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1024,10])) # 经过两次卷积和池化 28 * 28/(2+2) = 7 * 7
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[10]))
y_predict = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,w_fc2)+b_fc2
tf.add_to_collection('pred_network', y_predict) # 用于加载模型获取要预测的网络结构
with tf.variable_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict))
with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"):
# 使用反向传播,利用优化器使损失函数最小化
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
with tf.variable_scope("acc"):
# 检测我们的预测是否真实标签匹配(索引位置一样表示匹配)
# tf.argmax(y_conv,dimension), 返回最大数值的下标 通常和tf.equal()一起使用,计算模型准确度
# dimension=0 按列找 dimension=1 按行找
equal_list = tf.equal(tf.arg_max(y_true,1),tf.arg_max(y_predict,1))
# 统计测试准确率, 将correct_prediction的布尔值转换为浮点数来代表对、错,并取平均值。
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32))
# tensorboard
# tf.summary.histogram用来显示直方图信息
# tf.summary.scalar用来显示标量信息
# Summary:所有需要在TensorBoard上展示的统计结果
tf.summary.histogram("weight",w_fc2)
tf.summary.histogram("bias",b_fc2)
tf.summary.scalar("loss",loss)
tf.summary.scalar("acc",accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
filewriter = tf.summary.FileWriter("tfboard",graph=sess.graph)
if is_train: # 训练
for i in range(20001):
x_train, y_train = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100==0:
# 评估模型准确度,此阶段不使用Dropout
print("第%d训练,准确率为%f" % (i + 1, sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: x_train, y_true: y_train, keep_prob: 1.0})))
# # 训练模型,此阶段使用50%的Dropout
sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train,keep_prob: 0.5})
summary = sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:x_train,y_true:y_train, keep_prob: 1})
filewriter.add_summary(summary,i)
saver.save(sess,savemodel)
else: # 测试集预测
count = 0.0
epochs = 300
saver.restore(sess, savemodel)
for i in range(epochs):
x_test, y_test = mnist.train.next_batch(1)
print("第%d张图片,真实值为:%d预测值为:%d" % (i + 1,
tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval(),
tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}),
1).eval()
))
if (tf.argmax(sess.run(y_true, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval() == tf.argmax(
sess.run(y_predict, feed_dict={x: x_test, y_true: y_test,keep_prob: 1.0}), 1).eval()):
count = count + 1
print("正确率为 %.2f " % float(count * 100 / epochs) + "%")
# 手写数字图像预测
def dealFigureImg(imgPath):
img = cv2.imread(imgPath) # 手写数字图像所在位置
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转换图像为单通道(灰度图)
resize_img = cv2.resize(img, (28, 28)) # 调整图像尺寸为28*28
ret, thresh_img = cv2.threshold(resize_img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 二值化
cv2.imwrite("image/temp.jpg",thresh_img)
im = Image.open('image/temp.jpg')
data = list(im.getdata()) # 得到一个扁平的 图片像素
result = [(255 - x) * 1.0 / 255.0 for x in data] # 像素值范围(0-255),转换为(0-1) ->符合模型训练时传入数据的值
result = np.expand_dims(result, 0) # 扩展维度 ->符合模型训练时传入数据的维度
os.remove('image/temp.jpg')
return result
def predictFigureImg(imgPath):
result = dealFigureImg(imgPath)
with tf.Session() as sess:
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("model/mnist_model.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess, "model/mnist_model")
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name('data/x_pred').outputs[0]
keep_prob = graph.get_operation_by_name('fc1/keep_prob').outputs[0]
y = tf.get_collection("pred_network")[0]
predict = np.argmax(sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: result,keep_prob:1.0}))
print("result:",predict)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 训练和预测
modelPath = "model/mnist_model"
getMnistModel(modelPath,True) # True 训练 False 预测
# 图片传入模型 进行预测
# imgPath = "image/8.jpg"
# predictFigureImg(imgPath)
Mnist手写数字识别 Tensorflow的更多相关文章
- MNIST手写数字识别 Tensorflow实现
def conv2d(x, W): return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') 1. strides在官方定义中是一 ...
- Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现
Android+TensorFlow+CNN+MNIST 手写数字识别实现 SkySeraph 2018 Email:skyseraph00#163.com 更多精彩请直接访问SkySeraph个人站 ...
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4195577585e6 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写字识别(一)--白话卷积神经网络模型 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识 ...
- Tensorflow之MNIST手写数字识别:分类问题(1)
一.MNIST数据集读取 one hot 独热编码独热编码是一种稀疏向量,其中:一个向量设为1,其他元素均设为0.独热编码常用于表示拥有有限个可能值的字符串或标识符优点: 1.将离散特征的取值扩展 ...
- TensorFlow——MNIST手写数字识别
MNIST手写数字识别 MNIST数据集介绍和下载:http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/ 一.数据集介绍: MNIST是一个入门级的计算机视觉数据集 下载下来的数据集 ...
- 基于TensorFlow的MNIST手写数字识别-初级
一:MNIST数据集 下载地址 MNIST是一个包含很多手写数字图片的数据集,一共4个二进制压缩文件 分别是test set images,test set labels,training se ...
- Tensorflow实现MNIST手写数字识别
之前我们讲了神经网络的起源.单层神经网络.多层神经网络的搭建过程.搭建时要注意到的具体问题.以及解决这些问题的具体方法.本文将通过一个经典的案例:MNIST手写数字识别,以代码的形式来为大家梳理一遍神 ...
- mnist手写数字识别——深度学习入门项目(tensorflow+keras+Sequential模型)
前言 今天记录一下深度学习的另外一个入门项目——<mnist数据集手写数字识别>,这是一个入门必备的学习案例,主要使用了tensorflow下的keras网络结构的Sequential模型 ...
- mnist 手写数字识别
mnist 手写数字识别三大步骤 1.定义分类模型2.训练模型3.评价模型 import tensorflow as tfimport input_datamnist = input_data.rea ...
随机推荐
- 手把手教你基于SqlSugar4编写一个可视化代码生成器(生成实体,以SqlServer为例,文末附源码)
在开发过程中免不了创建实体类,字段少的表可以手动编写,但是字段多还用手动创建的话不免有些浪费时间,假如一张表有100多个字段,手写有些不现实. 这时我们会借助一些工具,如:动软代码生成器.各种ORM框 ...
- Elasticsearch修改分词器以及自定义分词器
Elasticsearch修改分词器以及自定义分词器 参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/shuimofengyang/article/details/88973597
- StringEscapeUtils防止xss攻击详解
StringUtils和StringEscapeUtils这两个实用类. 1.转义防止xss攻击 1.转义可以分为下面的几种情况 第一用户输入特殊字符的时候,在提及的时候不做任何处理保持到数据库,当用 ...
- InfluxDB时序数据库基本知识
InfluxDB是一个由InfluxData开发的开源时序型数据.它由Go写成,着力于高性能地查询与存储时序型数据.InfluxDB被广泛应用于存储系统的监控数据,IoT行业的实时数据等场景. 安装下 ...
- Layer 3.0
https://jeesite.gitee.io/front/layer/3.0/layer.layui.com/index.html
- C++ 半同步半异步的任务队列
代码已发布至 HAsyncTaskQueue
- 11. RobotFramework内置库-Collections
Collections库是RobotFramework用来处理列表和字典的库,详细可参见官方介绍. 官方地址:http://robotframework.org/robotframework/late ...
- python中的多任务--线程
什么是多任务? 简单地说,就是操作系统可以同时运行多个任务. 实现多任务有多种方式,线程.进程.协程. 多任务的概念:并行和并发 并发:指的是任务数多余cpu核数,通过操作系统的各种任务调度算法, 实 ...
- Uni-app登录态管理(vuex)
应用中,保持登录状态是常见需求,本文讲解使用uni-app框架时如何保持用户登录状态. 即:初次进入应用为未登录状态------->登录---------->关闭应用,再次打开------ ...
- web网页动态分享facebook和twitter
介绍 facebook分享 http://www.facebook.com/sharer.php?t=${text}u=encodeURIComponent('静态html') twitter分享 h ...
