基于配置的Spring AOP
前面几篇学习了Spring的依赖注入,这篇开始学习另一个核心功能——面向切面编程AOP。
通过本文,你可以了解到:
1 Spring xml规范
2 通过配置文件实现面向切面编程
3 对比与传统AOP编程
Spring的xml文件
Spring的xml一般起名叫做bean.xml或者xxxapplication.xml这种,然后放在src下通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext进行加载。文件的内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd"> <bean id="audience"class="com.spring.test.aop.Audience"/> <aop:config>
</aop:config>
</beans>
最上面的是xml的编码,这个就不解释了。
下面的<beans>是Spring的配置标签,beans里面几个重要的属性:
xmlns:
是默认的xml文档解析格式,即spring的beans。地址是http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans。
通过设置这个属性,所有在beans里面声明的属性,可以直接通过<>来使用,比如<bean>等等。
xmlns:xsi:
是xml需要遵守的规范,通过URL可以看到,是w3的统一规范,后面通过xsi:schemaLocation来定位所有的解析文件。
xmlns:aop:
这个是重点,是我们这里需要使用到的一些语义规范,与面向切面AOP相关。
xmlns:tx:
Spring中与事务相关的配置内容。
一个XML文件,只能声明一个默认的语义解析的规范。
例如上面的xml中就只有beans一个是默认的,其他的都需要通过特定的标签来使用,比如aop,它自己有很多的属性,如果要使用,前面就必须加上aop:xxx才可以。比如上面的aop:config。
类似的,如果默认的xmlns配置的是aop相关的语义解析规范,那么在xml中就可以直接写config这种标签了。
基于配置的AOP编程过程
首先,如果要在工程中使用AOP需要几个jar包:
1 Aop的核心包,即org.springframework.aop-xxx.jar
2 Spring的联盟包:aopalliance-1.0.jar
3 aspectJ相关的jar包:aspectjrt.jar aspectjweaver.jar
4 如果使用了动态代理,还需要添加cglib相关的jar包:cglib.zip
首先需要一个AOP的切面类,用于定义各种响应事件
package com.spring.test.aop;
public class Audience {
public void takeSeats(){
System.out.println("The audience is taking their seats.");
}
public void turnOffCellPhones(){
System.out.println("The audience is turning off their cellphones");
}
public void applaud(){
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP");
}
public void demandRefund(){
System.out.println("Boo! We want money back");
}
}
然后在bean.xml中编写aop:config的相关内容:
...省略beans的定义内容
<bean id="audience" class="com.spring.test.aop.Audience"/>
<bean id="sax" class="com.spring.test.setter.Saxophone"/>
<bean id="kenny" class="com.spring.test.setter.Instrumentalist">
<property name="song" value="Jingle Bells" />
<property name="age" value="25" />
<property name="instrument" ref="sax"/>
</bean>
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(* com.spring.test.action1.Performer.perform(..))"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="turnOffCellPhones"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applaud"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
这里面的aop:pointcut 就是使用AspectJ来定位的。意思是:当执行com.spring.test.action1.Performer的perform方法时,就会触发该切面的事件响应。
而Performer以及Instrumentalist等等的代码,就在下面简单的都罗列出来了:
配置文件:bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.0.xsd"> <bean id="audience" class="com.spring.test.aop.Audience"/> <bean id="sax" class="com.spring.test.setter.Saxophone"/>
<bean id="kenny" class="com.spring.test.setter.Instrumentalist">
<property name="song" value="Jingle Bells" />
<property name="age" value="25" />
<property name="instrument" ref="sax"/>
</bean> <aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(* com.spring.test.action1.Performer.perform(..))"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="turnOffCellPhones"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applaud"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
表演者接口:Performer.java
package com.spring.test.action1;
public interface Performer {
void perform() throws PerformanceException;
}
表演者实现类:Instrumentalist.java
package com.spring.test.setter; import com.spring.test.action1.PerformanceException;
import com.spring.test.action1.Performer; public class Instrumentalist implements Performer{
private String song;
private int age;
private Instrument instrument;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSong() {
return song;
}
public void setSong(String song) {
this.song = song;
}
public Instrument getInstrument() {
return instrument;
}
public void setInstrument(Instrument instrument) {
this.instrument = instrument;
}
public Instrumentalist(){}
public Instrumentalist(String song,int age,Instrument instrument){
this.song = song;
this.age = age;
this.instrument = instrument;
}
public void perform() throws PerformanceException {
System.out.println("Instrumentalist age:"+age);
System.out.print("Playing "+song+":");
instrument.play();
}
}
内部bean接口:Instrument.java
package com.spring.test.setter;
public interface Instrument {
public void play();
}
内部bean实现类:Saxophone.java
package com.spring.test.setter;
public class Saxophone implements Instrument {
public Saxophone(){}
public void play() {
System.out.println("TOOT TOOT TOOT");
}
}
测试主函数:main
package com.spring.test.setter; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.spring.test.action1.PerformanceException; public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws PerformanceException {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); Instrumentalist performer = (Instrumentalist)ctx.getBean("kenny");
performer.perform(); }
}
运行结果:
The audience is taking their seats.
The audience is turning off their cellphones
Instrumentalist age:25
Playing Jingle Bells:TOOT TOOT TOOT
CLAP CLAP CLAP
通过这种声明方式,可以 快速的实现切点与切面的整合,成为下面这种格式的新代码:
class{
try{
audience.takeSeats();
audience.turnOffCellphones();
performance.perform();
audience.applaud();
}catch(Exception){
audience.demandRefund();
}
}
面向切面的好处,要在实际工作中多加领会才可以,常用的场景就是日志的记录了。
与传统的AOP编程相比
前面也做过一个传统的spring aop的实现方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/xing901022/p/4143696.html
不得不说,通过ProxyFactoryBean达到的面向切面的编程,过于复杂,光是那几个功能就要好好理解一番。
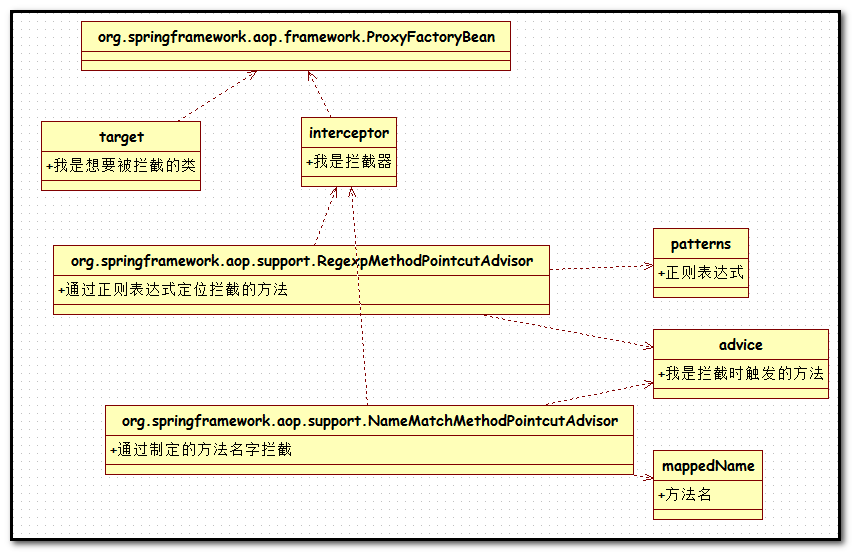
而基于配置的AOP使用就要简单的多,只需要一个切面的程序,然后通过配置文件就可以完全解耦的融入到切点中。
基于配置的Spring AOP的更多相关文章
- 基于注解的Spring AOP的配置和使用
摘要: 基于注解的Spring AOP的配置和使用 AOP是OOP的延续,是Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意思是面向切面编程.可以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现在不 ...
- Spring Aop(七)——基于XML配置的Spring Aop
转发:https://www.iteye.com/blog/elim-2396043 7 基于XML配置的Spring AOP 基于XML配置的Spring AOP需要引入AOP配置的Schema,然 ...
- 基于注解的Spring AOP示例
基于注解的Spring AOP示例 目录 在XML配置文件中开启 @AspectJ 支持 声明切面及切入点 声明通知 测试 结语 在XML配置文件中开启 @AspectJ 支持 要使用Spring的A ...
- 基于注解的Spring AOP的配置和使用--转载
AOP是OOP的延续,是Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意思是面向切面编程.可以通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态统一添加功能的一种技术. ...
- 基于Aspectj表达式配置的Spring AOP
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming, 面向切面编程):是一种新的方法论, 是对传统OOP(Object-Oriented Programming, 面向对象编程)的补充. ...
- 基于配置的Spring MVC3
网上查找的spring mvc3大部分都是基于注射的方式,总感觉注射有点怪怪.不利于后期扩展和项目管理,于是特意写下这篇基于xml配置的Spring MVC3.以供大家參考. 怎么建立web项目和下载 ...
- 基于 Annotation 的 Spring AOP 权限验证方法的实现
1. 配置 applicationContext 在 Spring 中支持 AOP 的配置非常的简单,只需要在 Spring 配置文件 applicationContext.xml 中添加: < ...
- 基于注解的Spring AOP拦截含有泛型的DAO
出错场景 1.抽象类BaseDao public abstract class BaseDao<T> { public BaseDao() { entityClass = (Class&l ...
- 基于XML配置的spring aop增强配置和使用
在我的另一篇文章中(http://www.cnblogs.com/anivia/p/5687346.html),通过一个例子介绍了基于注解配置spring增强的方式,那么这篇文章,只是简单的说明,如何 ...
随机推荐
- scrapy模块之分页处理,post请求,cookies处理,请求传参
一.scrapy分页处理 1.分页处理 如上篇博客,初步使用了scrapy框架了,但是只能爬取一页,或者手动的把要爬取的网址手动添加到start_url中,太麻烦接下来介绍该如何去处理分页,手动发起分 ...
- js的apply和call
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 二维vector容器读取txt坐标
template <class vector> struct HeadLocation{ vector x; vector y; }; vector<HeadLocation< ...
- Android四层架构
Andrid系统的体系结构设计为多层结构,这种结构在给用户提供安全保护的同时还保持了开放平台的灵活性.如下图所示: Google官方提供的Android系统的四层架构图 从上到下进行简单介绍: 一 ...
- Fragment、Activity比较——Android碎片介绍
Fragment是Android honeycomb 3.0新增的概念,Fragment名为碎片不过却和Activity十分相似,下面介绍下Android Fragment的作用和用法.Fragmen ...
- 记自己的hexo个人博客
https://othercoding.github.io/
- [转]ASP.NET Web API系列教程(目录)
本文转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/r01cn/archive/2012/11/11/2765432.html 注:微软随ASP.NET MVC 4一起还发布了一个框架,叫做ASP ...
- 微信小程序支付c#后台实现
今天为大家带来比较简单的支付后台处理 首先下载官方的c#模板(WxPayAPI),将模板(WxPayAPI)添加到服务器上,然后在WxPayAPI项目目录中添加两个“一般处理程序” (改名为GetOp ...
- 关于supersocker的数据传输中遇到的问题
最近在学socket,在使用socket时数据的传输与接口都是byte,所以文本与文件的传输只要对传过来的byte处理好就可以. 但是在supersocket上,我却花费了很长的时间.原因如下: 1. ...
- 一、IP地址
IP地址 1)网络地址 IP地址由网络号(包括子网号)和主机号组成,网络地址的主机号为全0,网络地址代表着整个网络. 2)广播地址 广播地址通常称为直接广播地址,是为了区分受限广播地址. 广播地址与网 ...
