elasticsearch 之 histogram 直方图聚合
1. 简介
直方图聚合是一种基于多桶值聚合,可从文档中提取的数值或数值范围值来进行聚合。它可以对参与聚合的值来动态的生成固定大小的桶。
2. bucket_key如何计算
假设我们有一个值是32,并且桶的大小是5,那么32四舍五入后变成30,因此文档将落入与键30关联的存储桶中。下面的算式可以精确的确定每个文档的归属桶
bucket_key = Math.floor((value - offset) / interval) * interval + offset
offset:的值默认是从0开始。并且offset的值必须在[0, interval)之间。且需要是一个正数。value:值的参与计算的值,比如某个文档中的价格字段等。
3. 有一组数据,如何确定是落入到那个桶中
此处是我自己的一个理解,如果错误欢迎指出。
存在的数据: [3, 8, 15]
offset = 0
interval = 5
那么可能会分成如下几个桶 [0,5) [5,10) [10, 15) [15,+∞)
- 数字3落入的桶 buket_key=
Math.floor((3 - 0) / 5) * 5 + 0 = 0,即落入[0,5)这个桶中 - 数字8落入的桶 buket_key=
Math.floor((8 - 0) / 5) * 5 + 0 = 5,即落入[5,10)这个桶中 - 数字15落入的桶 buket_key=
Math.floor((15 - 0) / 5) * 5 + 0 = 15,即落入[15,+∞)这个桶中
4、需求
我们有一组api响应时间数据,根据这组数据进行histogram聚合统计
4.1 准备mapping
PUT /index_api_response_time
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "long"
},
"api": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"response_time": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
此处的mapping比较简单,就3个字段id,api和response_time。
4.2 准备数据
PUT /index_api_response_time/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"api":"/user/infos","response_time": 3}
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{"api":"/user/add"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"api":"/user/update","response_time": 8}
{"index":{"_id":4}}
{"api":"/user/list","response_time": 15}
{"index":{"_id":5}}
{"api":"/user/export","response_time": 30}
{"index":{"_id":6}}
{"api":"/user/detail","response_time": 32}
此处先记录 id=2的数据,这个是没有response_time的,后期聚合时额外处理。
5、histogram聚合操作
5.1、根据response_time聚合,间隔为5
5.1.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5
}
}
}
}
5.1.2 java代码
@Test
@DisplayName("根据response_time聚合,间隔为5")
public void test01() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.aggregations("agg_01", agg -> agg.histogram(histogram -> histogram.field("response_time")
.interval(5D))));
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.1.3 运行结果

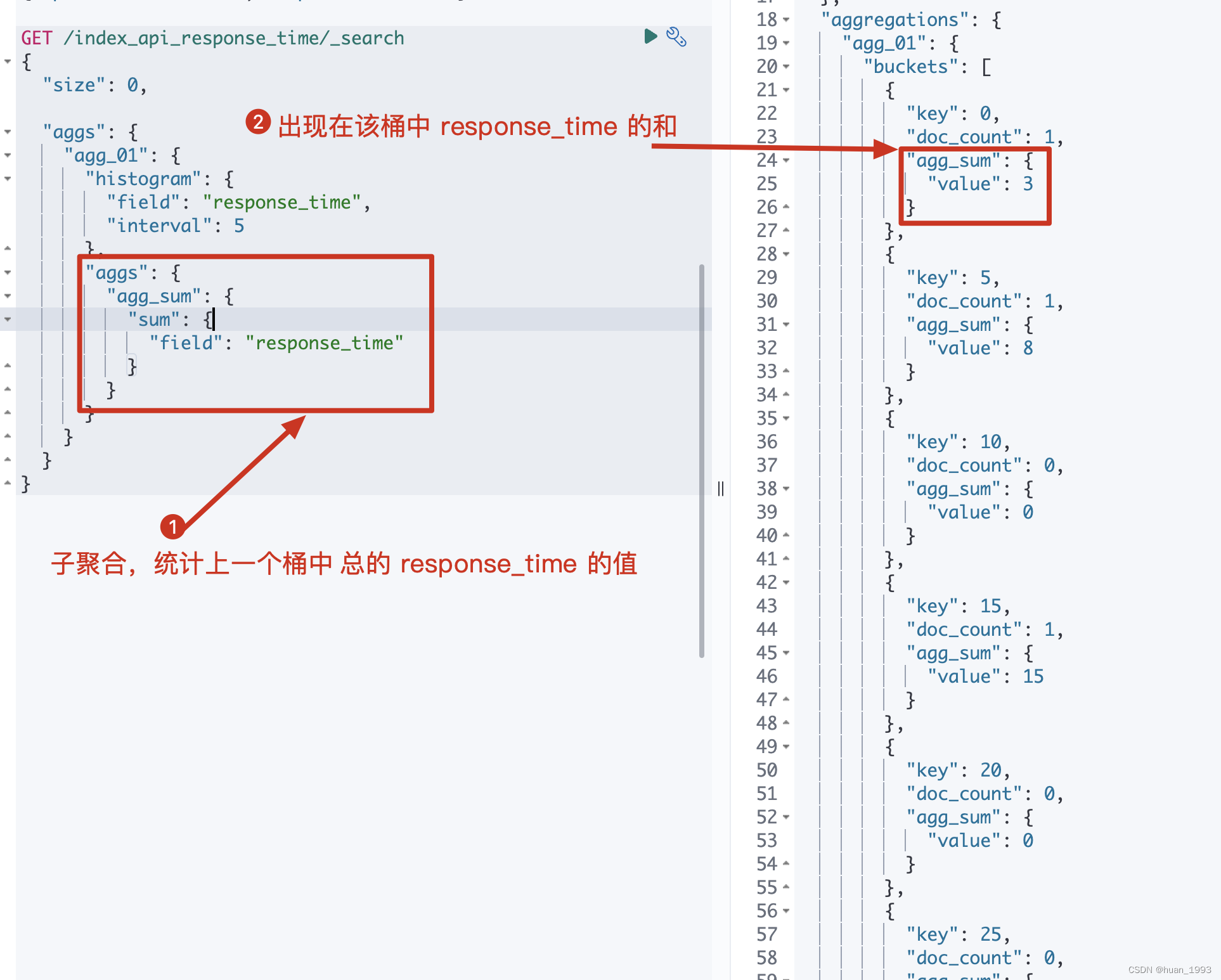
5.2 在5.1基础上聚合出每个桶总的响应时间
此处聚合一下是为了结合已有的数据,看看每个数据是否落入到了相应的桶中
5.2.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5
},
"aggs": {
"agg_sum": {
"sum": {
"field": "response_time"
}
}
}
}
}
}
5.2.2 java代码
@Test
@DisplayName("在test01基础上聚合出每个桶总的响应时间")
public void test02() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D))
.aggregations("agg_sum", aggSum -> aggSum.sum(sum -> sum.field("response_time")))
));
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.2.3 运行结果
5.3 每个桶中必须存在1个文档的结果才返回-min_doc_count
从5.1中的结果我们可以知道,不管桶中是否存在数据,我们都返回了,即返回了很多空桶。 简单理解就是返回的 桶中存在 doc_count=0 的数据,此处我们需要将这个数据不返回
5.3.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"min_doc_count": 1
}
}
}
}
5.3.2 java代码
@Test
@DisplayName("每个桶中必须存在1个文档的结果才返回-min_doc_count")
public void test03() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.aggregations("agg_01", agg -> agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D).minDocCount(1)
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.3.3 运行结果

5.4 补充空桶数据-extended_bounds
这个是什么意思?假设我们通过 response_time >= 10 进行过滤,并且 interval=5 那么es默认情况下就不会返回 bucket_key =0,5,10的桶,那么如果我想返回那么该如何处理呢?可以通过 extended_bounds 来实现。
使用extended_bounds时,min_doc_count=0时才有意义。 extended_bounds不会过滤桶。

5.4.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"range": {
"response_time": {
"gte": 10
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"min_doc_count": 0,
"extended_bounds": {
"min": 0,
"max": 50
}
}
}
}
}
5.4.2 java代码
@Test
@DisplayName("补充空桶数据-extended_bounds")
public void test04() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg -> agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D).minDocCount(0)
.extendedBounds(bounds -> bounds.min(1D).max(50D))
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.4.3 运行结果

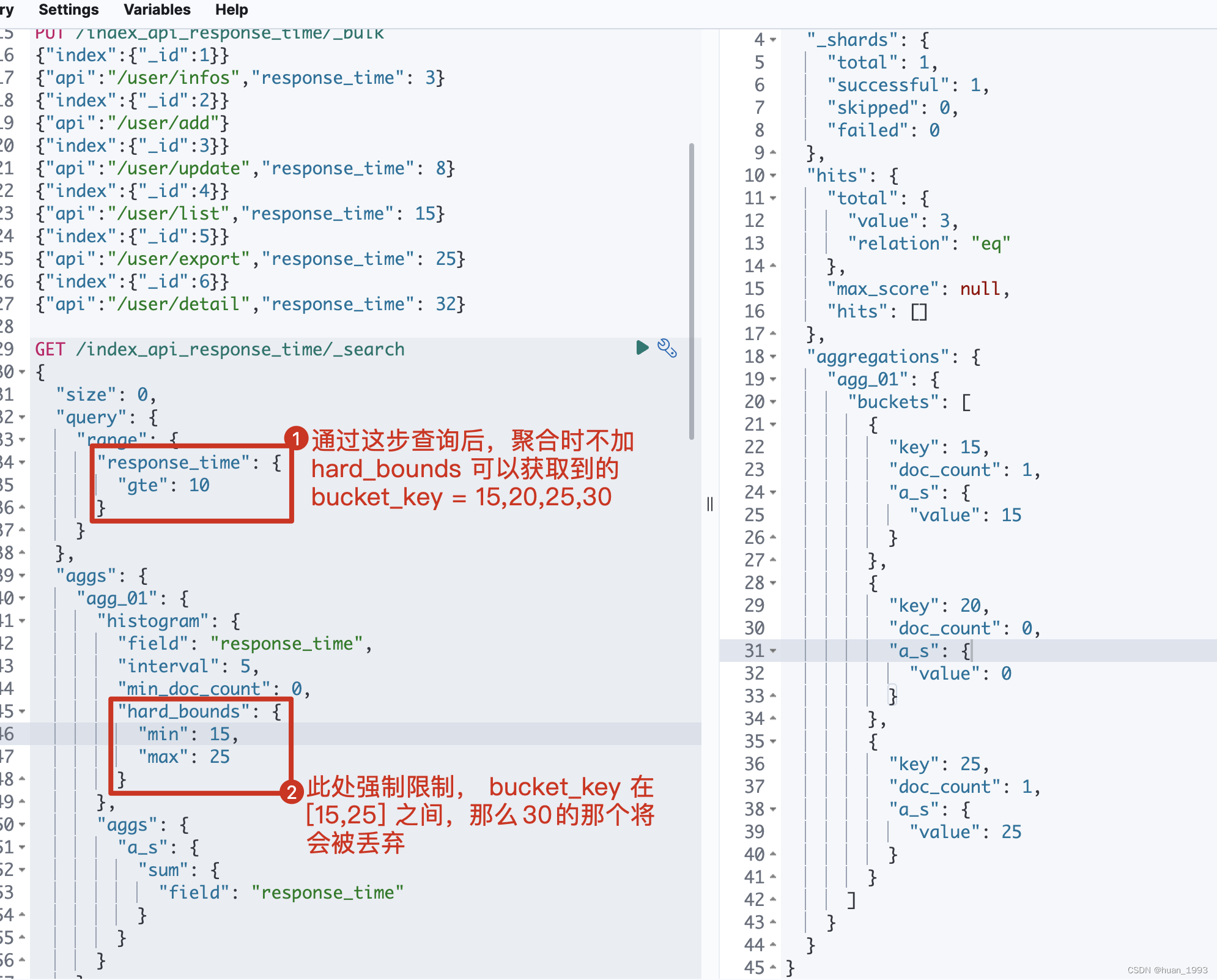
5.5 只展示min-max之间的桶-hard_bounds

此处的数据:
PUT /index_api_response_time/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":1}}
{"api":"/user/infos","response_time": 3}
{"index":{"_id":2}}
{"api":"/user/add"}
{"index":{"_id":3}}
{"api":"/user/update","response_time": 8}
{"index":{"_id":4}}
{"api":"/user/list","response_time": 15}
{"index":{"_id":5}}
{"api":"/user/export","response_time": 25}
{"index":{"_id":6}}
{"api":"/user/detail","response_time": 32}
5.5.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"range": {
"response_time": {
"gte": 10
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"min_doc_count": 0,
"hard_bounds": {
"min": 15,
"max": 25
}
},
"aggs": {
"a_s": {
"sum": {
"field": "response_time"
}
}
}
}
}
}
5.5.2 java代码
@Test
@DisplayName("只展示min-max之间的桶-hard_bounds")
public void test05() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D).minDocCount(0)
.hardBounds(bounds -> bounds.min(1D).max(50D))
)
.aggregations("a_s", sumAgg -> sumAgg.sum(sum -> sum.field("response_time")))
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.5.3 运行结果
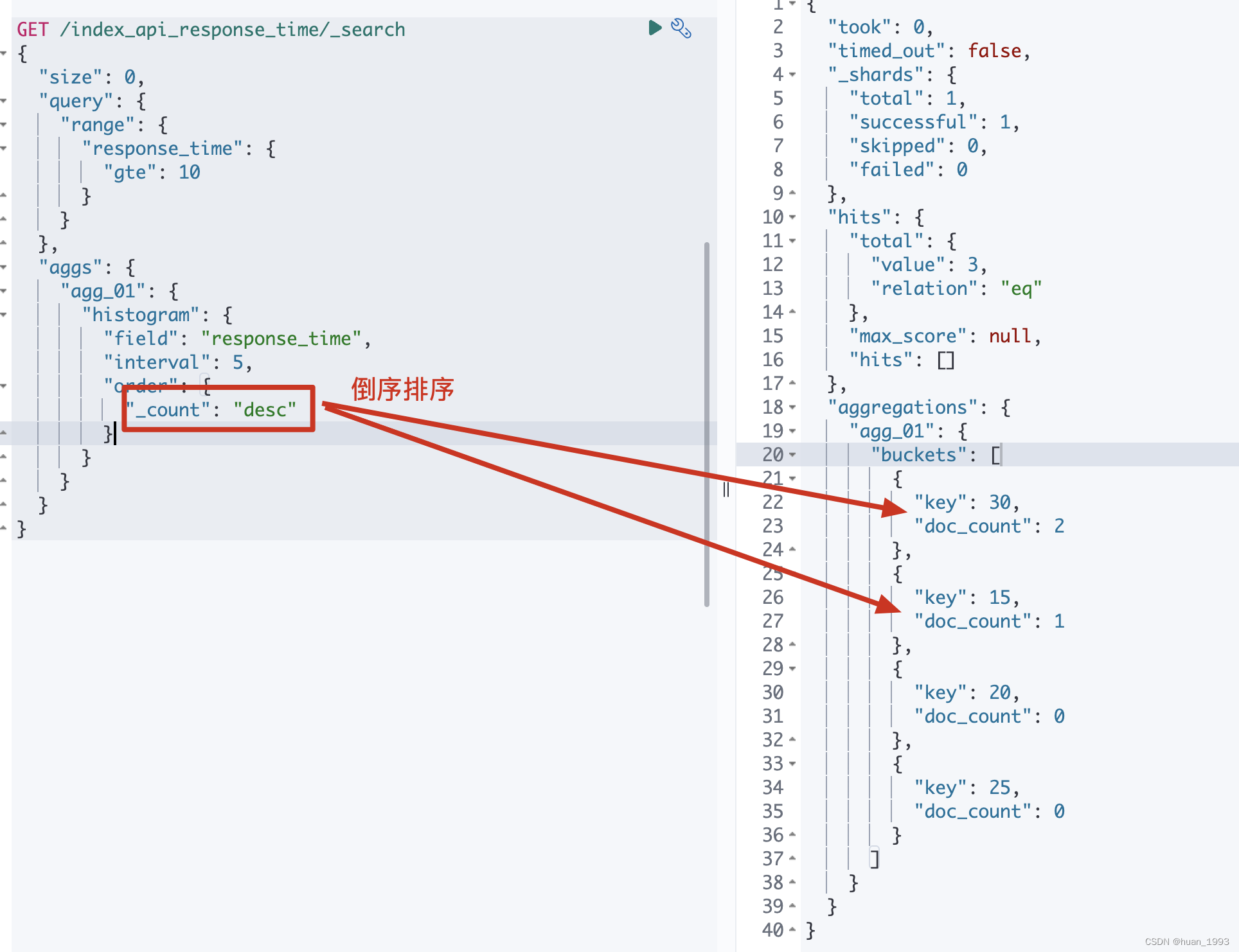
5.6 排序-order
By default the returned buckets are sorted by their key ascending, though the order behaviour can be controlled using the order setting. Supports the same order functionality as the Terms Aggregation.
5.6.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"range": {
"response_time": {
"gte": 10
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"order": {
"_count": "desc"
}
}
}
}
}
5.6.2 java代码
@Test
@DisplayName("排序order")
public void test06() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D)
.order(NamedValue.of("_count", SortOrder.Desc))
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.6.3 运行结果
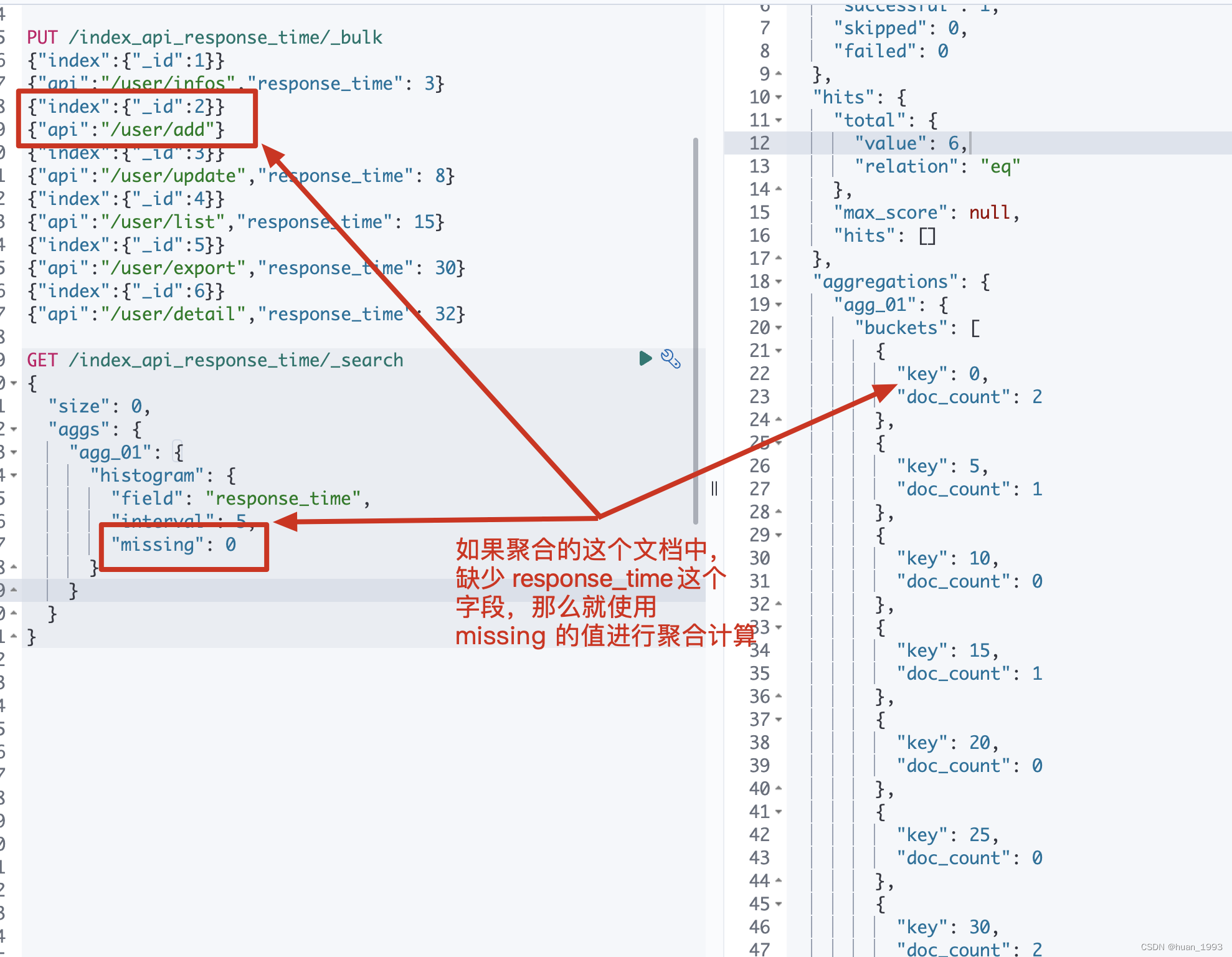
5.7 文档中缺失聚合字段时如何处理-missing

5.7.1 dsl
GET /index_api_response_time/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"agg_01": {
"histogram": {
"field": "response_time",
"interval": 5,
"missing": 0
}
}
}
}
5.7.2 java代码
@Test
@DisplayName("文档中缺失聚合字段时如何处理-missing")
public void test07() throws IOException {
SearchRequest request = SearchRequest.of(search ->
search
.index("index_api_response_time")
.size(0)
.query(query-> query.range(range -> range.field("response_time").gte(JsonData.of(10))))
.aggregations("agg_01", agg ->
agg.histogram(
histogram -> histogram.field("response_time").interval(5D) .missing(0D)
)
)
);
System.out.println("request: " + request);
SearchResponse<String> response = client.search(request, String.class);
System.out.println("response: " + response);
}
5.7.3 运行结果
6、完整代码
7、参考文档
elasticsearch 之 histogram 直方图聚合的更多相关文章
- Elasticsearch聚合 之 Histogram 直方图聚合
Elasticsearch支持最直方图聚合,它在数字字段自动创建桶,并会扫描全部文档,把文档放入相应的桶中.这个数字字段既可以是文档中的某个字段,也可以通过脚本创建得出的. 桶的筛选规则 举个例子,有 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (37) - 信息聚合系列之内存与延时
ElasticSearch 2 (37) - 信息聚合系列之内存与延时 摘要 控制内存使用与延时 版本 elasticsearch版本: elasticsearch-2.x 内容 Fielddata ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (34) - 信息聚合系列之多值排序
ElasticSearch 2 (34) - 信息聚合系列之多值排序 摘要 多值桶(terms.histogram 和 date_histogram)动态生成很多桶,Elasticsearch 是如何 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (31) - 信息聚合系列之时间处理
ElasticSearch 2 (31) - 信息聚合系列之时间处理 摘要 如果说搜索是 Elasticsearch 里最受欢迎的功能,那么按时间创建直方图一定排在第二位.为什么需要使用时间直方图? ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (30) - 信息聚合系列之条形图
ElasticSearch 2 (30) - 信息聚合系列之条形图 摘要 版本 elasticsearch版本: elasticsearch-2.x 内容 聚合还有一个令人激动的特性就是能够十分容易地 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (38) - 信息聚合系列之结束与思考
ElasticSearch 2 (38) - 信息聚合系列之结束与思考 摘要 版本 elasticsearch版本: elasticsearch-2.x 内容 本小节涵盖了许多基本理论以及很多深入的技 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (36) - 信息聚合系列之显著项
ElasticSearch 2 (36) - 信息聚合系列之显著项 摘要 significant_terms(SigTerms)聚合与其他聚合都不相同.目前为止我们看到的所有聚合在本质上都是简单的数学 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (35) - 信息聚合系列之近似聚合
ElasticSearch 2 (35) - 信息聚合系列之近似聚合 摘要 如果所有的数据都在一台机器上,那么生活会容易许多,CS201 课商教的经典算法就足够应付这些问题.但如果所有的数据都在一台机 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (33) - 信息聚合系列之聚合过滤
ElasticSearch 2 (33) - 信息聚合系列之聚合过滤 摘要 聚合范围限定还有一个自然的扩展就是过滤.因为聚合是在查询结果范围内操作的,任何可以适用于查询的过滤器也可以应用在聚合上. 版 ...
- ElasticSearch 2 (32) - 信息聚合系列之范围限定
ElasticSearch 2 (32) - 信息聚合系列之范围限定 摘要 到目前为止我们看到的所有聚合的例子都省略了搜索请求,完整的请求就是聚合本身. 聚合与搜索请求同时执行,但是我们需要理解一个新 ...
随机推荐
- GreatSQL vs MySQL性能测试来了,速围观~
GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源. GreatSQL是MySQL的国产分支版本,使用上与MySQL一致. 1.结论先行 无论ibp(innodb_buffer ...
- c#中容易被忽视的foreach
有句俗语:百姓日用而不知.我们c#程序员很喜欢,也非常习惯地用foreach.今天呢,我就带大家一起探索foreach,走,开始我们的旅程. 一.for语句用的好好的,为什么要提供一个foreach? ...
- 我眼中的大数据(三)——MapReduce
这次来聊聊Hadoop中使用广泛的分布式计算方案--MapReduce.MapReduce是一种编程模型,还是一个分布式计算框架. MapReduce作为一种编程模型功能强大,使用简单.运算内容不 ...
- Django 聚合分组F与Q查询及choices
一.聚合查询 需要导入模块:from django.db.models import Max, Min, Sum, Count, Avg 关键语法:aggregate(聚合结果别名 = 聚合函数(参数 ...
- 4.第三篇 PKI基础概念、cfssl工具介绍及kubernetes中证书
文章转载自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzI1MDgwNzQ1MQ==&mid=2247483787&idx=1&sn=08dd3404 ...
- 银河麒麟安装node,mysql,forever环境
这就是国产银河系统的界面,测试版本是麒麟V10 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1_-ICBkgSZPKvmcdy1nVxVg 提取码: xhep 一.传输文件 cd /hom ...
- 分布式ID详解(5种分布式ID生成方案)
分布式架构会涉及到分布式全局唯一ID的生成,今天我就来详解分布式全局唯一ID,以及分布式全局唯一ID的实现方案@mikechen 什么是分布式系统唯一ID 在复杂分布式系统中,往往需要对大量的数据和消 ...
- day04-MySQL常用函数01
5.MySQL常用函数 5.1合计/统计函数 5.1.1合计函数-count count 返回行的总数 Select count(*)|count (列名) from table_name [WHER ...
- HDU2586 How far away ? (树链剖分求LCA)
用树链剖分求LCA的模板: 1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 using namespace std; 4 const ...
- Java学生管理系统(详解)
相信大部分人都有接触过这个 Java 小项目--学生管理系统,下面会分享我在做这个项目时的一些方法以及程序代码供大家参考(最后附上完整的项目代码). 首本人只是个初学Java的小白,可能项目中有许多地 ...
