基本的传染病模型:SI、SIS、SIR及其Python代码实现
本文主要参考博客:http://chengjunwang.com/en/2013/08/learn-basic-epidemic-models-with-python/。该博客有一些笔误,并且有些地方表述不准确,推荐大家阅读Albert-Laszlo Barabasi写得书Network Science,大家可以在如下网站直接阅读传染病模型这一章:http://barabasi.com/networksciencebook/chapter/10#contact-networks。Barabasi是一位复杂网络科学领域非常厉害的学者,大家也可以在他的官网上查看作者的一些相关工作。
下面我就直接把SIS模型和SIR模型的代码放上来一起学习一下。我的Python版本是3.6.1,使用的IDE是Anaconda3。Anaconda3这个IDE我个人推荐使用,用起来很方便,而且提供了Jupyther Notebook这个很好的交互工具,大家可以尝试一下,可在官网下载:https://www.continuum.io/downloads/。
在Barabasi写得书中,有两个Hypothesis:1,Compartmentalization; 2, Homogenous Mixing。具体看教材。
默认条件:1, closed population; 2, no births; 3, no deaths; 4, no migrations.
1. SI model
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scipy.integrate as spi
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl beta=1.4247
"""the likelihood that the disease will be transmitted from an infected to a susceptible
individual in a unit time is β"""
gamma=0
#gamma is the recovery rate and in SI model, gamma equals zero
I0=1e-6
#I0 is the initial fraction of infected individuals
ND=70
#ND is the total time step
TS=1.0
INPUT = (1.0-I0, I0) def diff_eqs(INP,t):
'''The main set of equations'''
Y=np.zeros((2))
V = INP
Y[0] = - beta * V[0] * V[1] + gamma * V[1]
Y[1] = beta * V[0] * V[1] - gamma * V[1]
return Y # For odeint t_start = 0.0; t_end = ND; t_inc = TS
t_range = np.arange(t_start, t_end+t_inc, t_inc)
RES = spi.odeint(diff_eqs,INPUT,t_range)
"""RES is the result of fraction of susceptibles and infectious individuals at each time step respectively"""
print(RES) #Ploting
pl.plot(RES[:,0], '-bs', label='Susceptibles')
pl.plot(RES[:,1], '-ro', label='Infectious')
pl.legend(loc=0)
pl.title('SI epidemic without births or deaths')
pl.xlabel('Time')
pl.ylabel('Susceptibles and Infectious')
pl.savefig('2.5-SI-high.png', dpi=900) # This does increase the resolution.
pl.show()
结果如下图所示
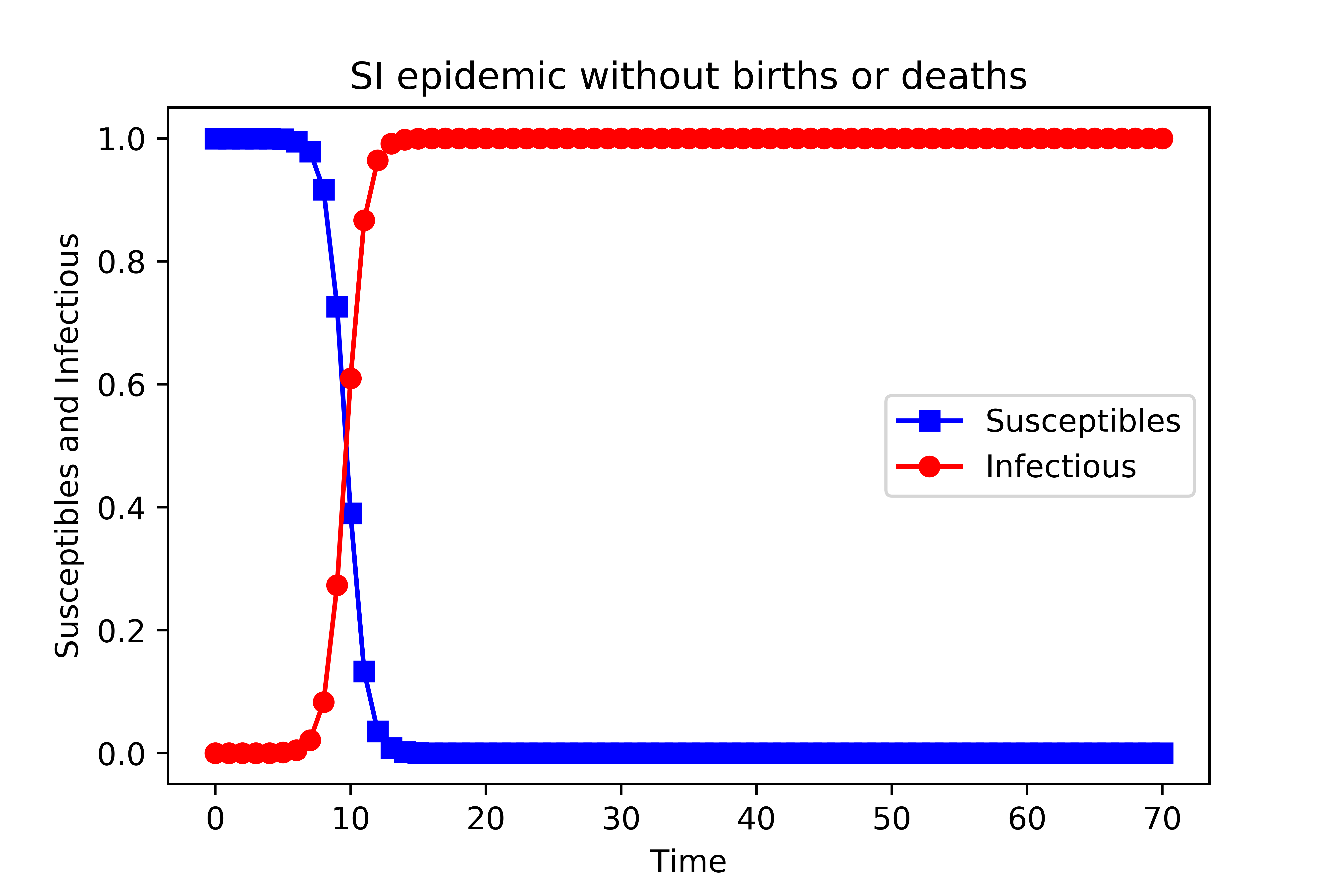
在早期,受感染个体的比例呈指数增长, 最终这个封闭群体中的每个人都会被感染,大概在t=16时,群体中所有个体都被感染了。
2. SIS model
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scipy.integrate as spi
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl beta=1.4247
gamma=0.14286
I0=1e-6
ND=70
TS=1.0
INPUT = (1.0-I0, I0) def diff_eqs(INP,t):
'''The main set of equations'''
Y=np.zeros((2))
V = INP
Y[0] = - beta * V[0] * V[1] + gamma * V[1]
Y[1] = beta * V[0] * V[1] - gamma * V[1]
return Y # For odeint t_start = 0.0; t_end = ND; t_inc = TS
t_range = np.arange(t_start, t_end+t_inc, t_inc)
RES = spi.odeint(diff_eqs,INPUT,t_range) print(RES) #Ploting
pl.plot(RES[:,0], '-bs', label='Susceptibles')
pl.plot(RES[:,1], '-ro', label='Infectious')
pl.legend(loc=0)
pl.title('SIS epidemic without births or deaths')
pl.xlabel('Time')
pl.ylabel('Susceptibles and Infectious')
pl.savefig('2.5-SIS-high.png', dpi=900) # This does increase the resolution.
pl.show()
运行之后得到结果如下图:
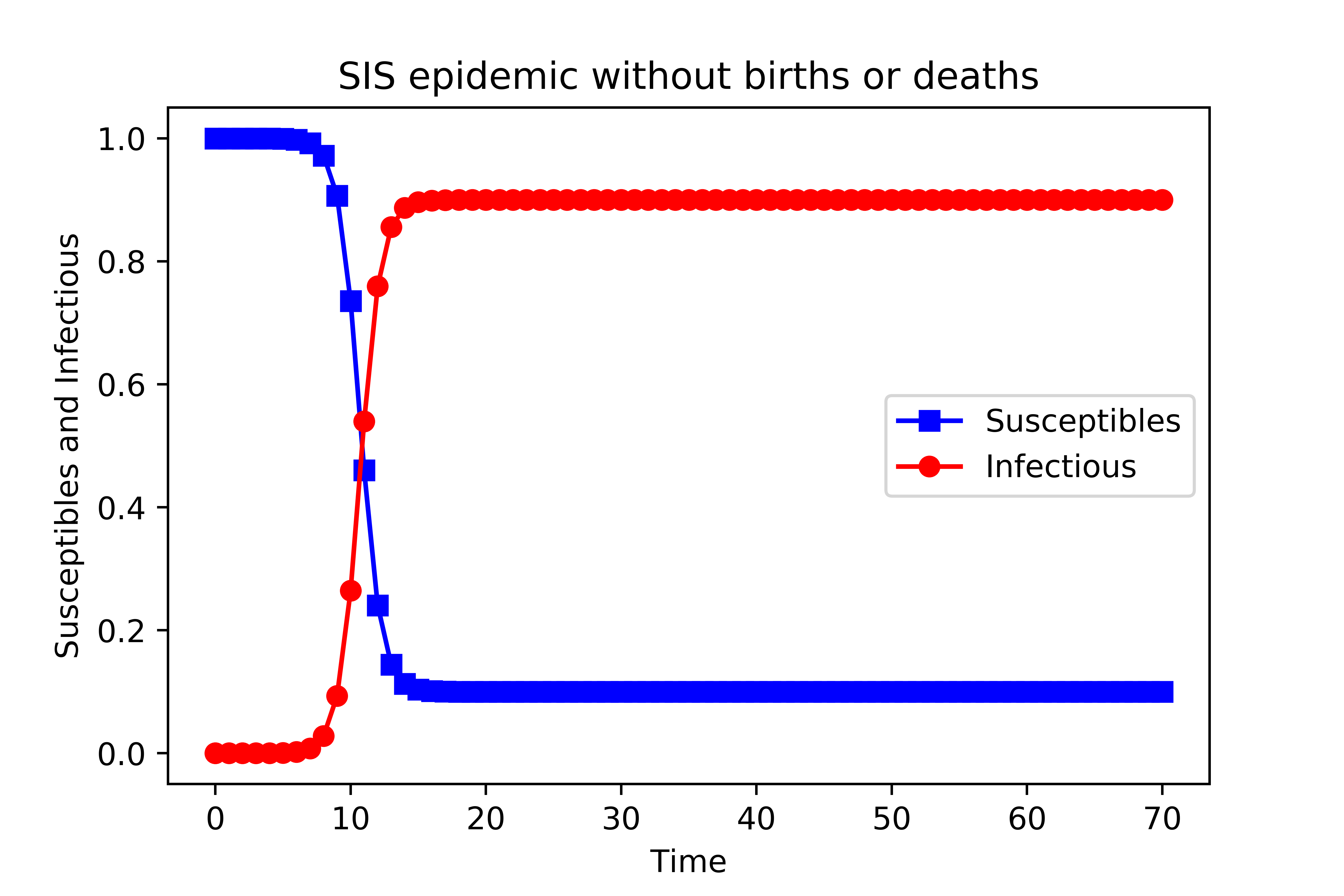
由于个体被感染后可以恢复,所以在一个大的时间步,上图是t=17,系统达到一个稳态,其中感染个体的比例是恒定的。因此,在稳定状态下,只有有限部分的个体被感染,此时并不意味着感染消失了,而是此时在任意一个时间点,被感染的个体数量和恢复的个体数量达到一个动态平衡,双方比例保持不变。请注意,对于较大的恢复率gamma,感染个体的数量呈指数下降,最终疾病消失,即此时康复的速度高于感染的速度,故根据恢复率gamma的大小,最终可能有两种可能的结果。
3. SIR model
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import scipy.integrate as spi
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl beta=1.4247
gamma=0.14286
TS=1.0
ND=70.0
S0=1-1e-6
I0=1e-6
INPUT = (S0, I0, 0.0) def diff_eqs(INP,t):
'''The main set of equations'''
Y=np.zeros((3))
V = INP
Y[0] = - beta * V[0] * V[1]
Y[1] = beta * V[0] * V[1] - gamma * V[1]
Y[2] = gamma * V[1]
return Y # For odeint t_start = 0.0; t_end = ND; t_inc = TS
t_range = np.arange(t_start, t_end+t_inc, t_inc)
RES = spi.odeint(diff_eqs,INPUT,t_range) print(RES) #Ploting
pl.plot(RES[:,0], '-bs', label='Susceptibles') # I change -g to g-- # RES[:,0], '-g',
pl.plot(RES[:,2], '-g^', label='Recovereds') # RES[:,2], '-k',
pl.plot(RES[:,1], '-ro', label='Infectious')
pl.legend(loc=0)
pl.title('SIR epidemic without births or deaths')
pl.xlabel('Time')
pl.ylabel('Susceptibles, Recovereds, and Infectious')
pl.savefig('2.1-SIR-high.png', dpi=900) # This does, too
pl.show()
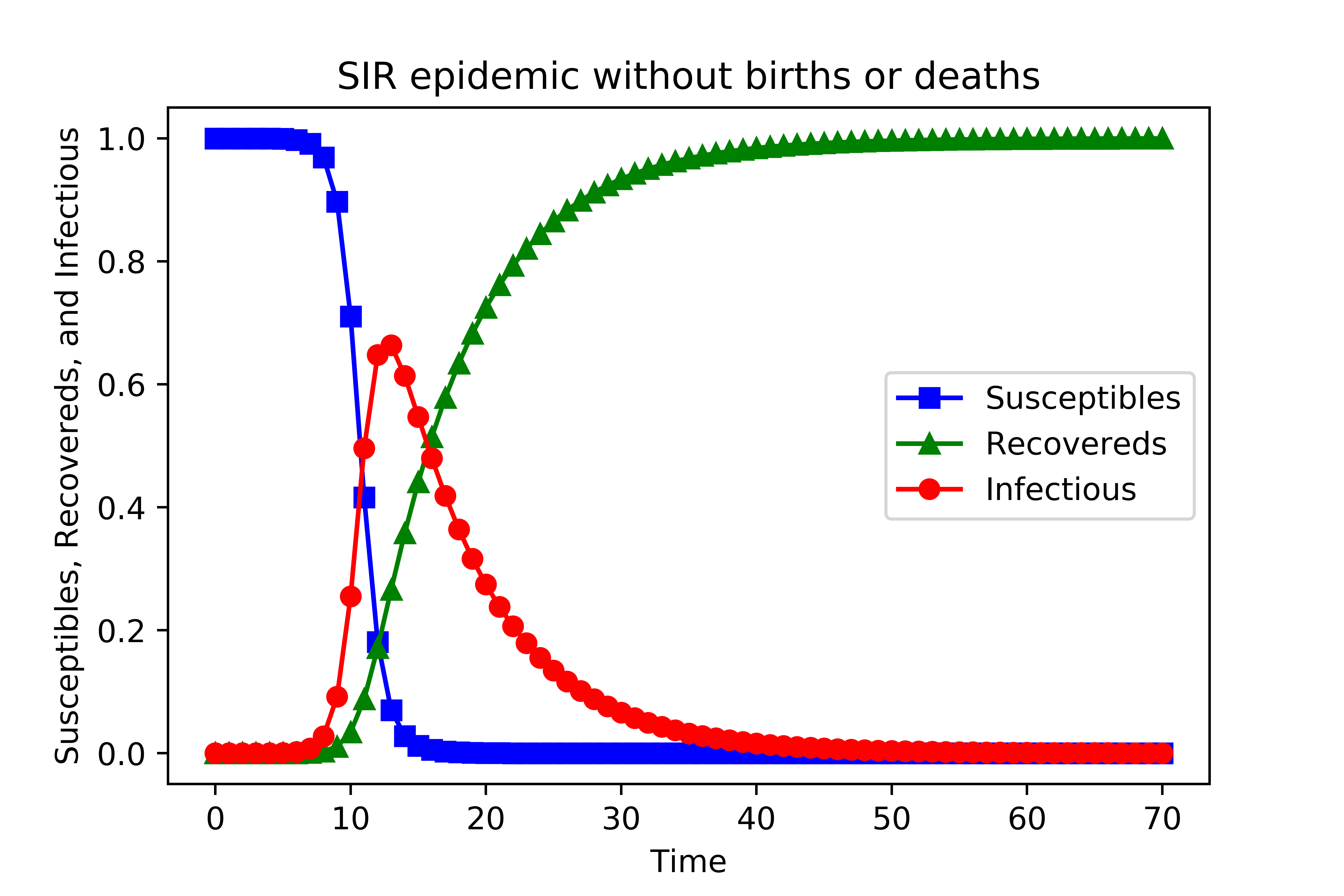
所得结果如下图:
基本的传染病模型:SI、SIS、SIR及其Python代码实现的更多相关文章
- 传染病传播模型(SIS)Matlab代码
function spreadingability=sir(A,beta,mu) for i=1:length(A) for N=1:50%随机次数 InitialState=zeros(length ...
- matlab练习程序(传染病模型)
最近新型冠状病毒疫情越来越严重了,待在家中没法出去,学习一下经典传染病模型. 这里总结了五个模型,分别是SI模型,SIS模型,SIR模型,SIRS模型,SEIR模型. 这几种模型的特点先介绍一下. 首 ...
- 隐马尔科夫模型,第三种问题解法,维比特算法(biterbi) algorithm python代码
上篇介绍了隐马尔科夫模型 本文给出关于问题3解决方法,并给出一个例子的python代码 回顾上文,问题3是什么, 下面给出,维比特算法(biterbi) algorithm 下面通过一个具体例子,来说 ...
- 转:关于Latent Dirichlet Allocation及Hierarchical LDA模型的必读文章和相关代码
关于Latent Dirichlet Allocation及Hierarchical LDA模型的必读文章和相关代码 转: http://andyliuxs.iteye.com/blog/105174 ...
- TensorFlow 训练好模型参数的保存和恢复代码
TensorFlow 训练好模型参数的保存和恢复代码,之前就在想模型不应该每次要个结果都要重新训练一遍吧,应该训练一次就可以一直使用吧. TensorFlow 提供了 Saver 类,可以进行保存和恢 ...
- 传染病模型(SIR模型)
- 网络传播模型Python代码实现
SI模型 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import smallworld as sw #邻接矩阵 a = sw.a # 感染率 ...
- 混合高斯模型:opencv中MOG2的代码结构梳理
/* 头文件:OurGaussmix2.h */ #include "opencv2/core/core.hpp" #include <list> #include&q ...
- 做量化模型Matlab、R、Python、F#和C++到底选择哪一个?
MATLAB是matrix&laboratory两个词的组合,意为矩阵工厂(矩阵实验室).是由美国mathworks公司发布的主要面对科学计算.可视化以及交互式程序设计的高科技计算环境.它将数 ...
随机推荐
- Http状态码大全(来自菜鸟教程)
HTTP协议(HyperText Transfer Protocol,超文本传输协议)是因特网上应用最为广泛的一种网络传输协议,所有的WWW文件都必须遵守这个标准. HTTP是一个基于TCP/IP通信 ...
- SQL语句集锦
-语 句 功 能 --数据操作 SELECT --从数据库表中检索数据行和列 INSERT --向数据库表添加新数据行 ...
- 一个想法照进现实-《IT连》创业项目:直觉型面试招聘的漏洞
前言: 创业转眼又过去了一个月,是时候抽时间写写文向大伙继续汇报进度了. 还记得上一篇创业文章,我还在说:创业时该不该用新手程序员. 嗯,然后,然后,报应就来了:所以这篇要写写自己在新人招聘上出现的问 ...
- 微信小程序多张图片上传
微信小程序上传图片每次只能上传一张,所有很多朋友就会问想要多张图片上传怎么办? 首先,我们来看一看wx.chooseImage(object)和wx.uploadFile(OBJECT)这两个个api ...
- 【锋利的jQuery】中全局事件ajaxStart、ajaxStop不执行
最近一直都在研究[锋利的jQuery],确实是一本好书,受益匪浅.但由于技术发展及版本更新等原因,里面还是有些坑需要踩的. 比如:第六章七节中提到的全局事件ajaxStart.ajaxStop照着案例 ...
- [原创] 利用前端+php批量生成html文件,传入新文本,输出新的html文件
本人因为要想自己写个小说网站练练手,在其中遇到的一些问题,将其解决方法总结出来,例如: 1:小说网站存储了大量的小说,每个小说主页都很相似,url不同,不是使用的history属性改写的,所以如果人工 ...
- log4j 在项目中的详细配置
1.添加log4j 包 2.首先在src目录下添加log4j.properties文件 log4j.rootLogger=debug, stdout, R log4j.appender.stdout= ...
- 关于Javascript循环体变量声明与初始化的效率问题
针对循环体变量声明与初始化的效率问题,将执行的简单测试代码如下: function test(n) { console.time('Internally initialized'); for (var ...
- TIOBE:全球编程语言最新排名(Kotlin排名进入前50名)
作为coder,大家当然关心自己所使用语言的应用趋势.要是几年后所用语言变得默默无闻,那岂不是之前的知识储备与经验积累都会大打折扣.TIOBE排行榜是根据互联网上有经验的程序员.课程和第三方厂商的数量 ...
- windbg工具安装配置及dump抓取
安装与配置windbg 安装与配置windbg的symbol(符号) 第一步 下载WinDBG, 第二步 双击下载的文件安装windbg.安装时注意记住安装到那里了. 第三步 windbg访问符号需要 ...
