opengl 学习 之 05 lesson
简介
颜色和坐标一眼都是opengl 的属性,不过坐标是作为内建属性之一。
加载纹理
link
http://www.opengl-tutorial.org/uncategorized/2017/06/07/website-update/
UV
When texturing a mesh, you need a way to tell to OpenGL which part of the image has to be used for each triangle. This is done with UV coordinates.
UV坐标是用来对纹理进行适配的,以三角形的方式进行适配。
使用Blender来构建uv坐标
Linear filtering
普通的BMP映射会产生锯齿。使用Linear filtering进行滤波操作。简单来说就是颜色插值
With linear fifiltering, texture() also looks at the other texels around, and mixes the colours according to the distance to each center. This avoids the hard edges seen above.
Anisotropic fifiltering
如果你想要更好的效果,可以使用Anisotropic fifiltering(各向异性滤波)
猜测:应该是选择一个矩形方向,然后按照一定的颜色比例进行调色。
For instance, if the following texture is seen from the side, and a little bit rotated, anisotropic fifiltering will compute the colour contained in the blue rectangle by taking a fifixed number of samples (the “anisotropic level”) along its main direction.
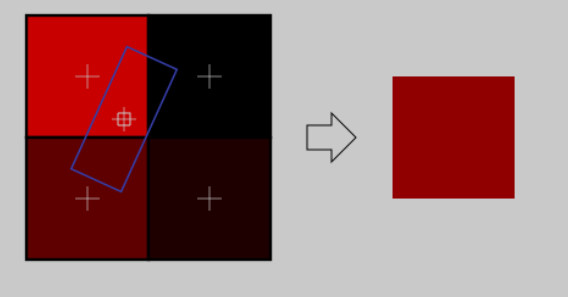
linear and anisotropic filtering都有一个问题, If the texture is seen from far away, mixing only 4 texels won’t be enough(纹理距离足够远的话,仅仅四个像素文进行调色是远远不够的)
Mipmaps
原理很简单就是,缩放一系列纹理,然后在一定距离选择一定的纹理,然后使用linear或者anisotropic filtering
At initialisation time, you scale down your image by 2, successively, until you only have a 1x1 image (which effectively is the average of all the texels in the image)
When you draw a mesh, you select which mipmap is the more appropriate to use given how big the texel should be.
You sample this mipmap with either nearest, linear or anisotropic fifiltering
For additional quality, you can also sample two mipmaps and blend the results
use GLFW to load texture
GLuint loadTGA_glfw(const char * imagepath){
// Create one OpenGL texture
GLuint textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
// "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
// Read the file, call glTexImage2D with the right parameters
glfwLoadTexture2D(imagepath, 0);
// Nice trilinear filtering.
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
// Return the ID of the texture we just created
return textureID;
}
为什么要使用.DDS格式的纹理
如果直接用内存进行和GPU内存的交换会导致性能损失,如果使用DDS然后在传输的过程中进行解压,因为有专门的硬件实现硬解,所以会达到20%的性能提升。
At this point, your image is compressed in a format that is directly compatible with the GPU. Whenever calling texture() in a shader, it will uncompress it on-the-flfly. This can seem slow, but since it takes a LOT less memory, less data needs to be transferred. But memory transfers are expensive; and texture decompression is free (there is dedicated hardware for that). Typically, using texture compression yields a 20% increase in performance. So you save on performance and memory, at the expense of reduced quality.
code that load dds
GLuint loadDDS(const char * imagepath){
unsigned char header[124];
FILE *fp;
/* try to open the file */
fp = fopen(imagepath, "rb");
if (fp == NULL)
return 0;
/* verify the type of file */
char filecode[4];
fread(filecode, 1, 4, fp);
if (strncmp(filecode, "DDS ", 4) != 0) {
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
/* get the surface desc */
fread(&header, 124, 1, fp);
unsigned int height = *(unsigned int*)&(header[8 ]);
unsigned int width = *(unsigned int*)&(header[12]);
unsigned int linearSize = *(unsigned int*)&(header[16]);
unsigned int mipMapCount = *(unsigned int*)&(header[24]);
unsigned int fourCC = *(unsigned int*)&(header[80]);
unsigned char * buffer;
unsigned int bufsize;
/* how big is it going to be including all mipmaps? */
bufsize = mipMapCount > 1 ? linearSize * 2 : linearSize;
buffer = (unsigned char*)malloc(bufsize * sizeof(unsigned char));
fread(buffer, 1, bufsize, fp);
/* close the file pointer */
fclose(fp);
unsigned int components = (fourCC == FOURCC_DXT1) ? 3 : 4;
unsigned int format;
switch(fourCC)
{
case FOURCC_DXT1:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT;
break;
case FOURCC_DXT3:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT3_EXT;
break;
case FOURCC_DXT5:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT5_EXT;
break;
default:
free(buffer);
return 0;
}
// Create one OpenGL texture
GLuint textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
// "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
unsigned int blockSize = (format == GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT) ? 8 : 16;
unsigned int offset = 0;
/* load the mipmaps */
for (unsigned int level = 0; level < mipMapCount && (width || height); ++level)
{
unsigned int size = ((width+3)/4)*((height+3)/4)*blockSize;
glCompressedTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, level, format, width, height,
0, size, buffer + offset);
offset += size;
width /= 2;
height /= 2;
}
free(buffer);
return textureID;
}
TIPS
DXT压缩算法来自于DirectX,他与opengl的v坐标是相反的。需要使用( coord.u, 1.0-coord.v) ,进行UV坐标矫正。
image
DDS:感觉出现cube总出现了裂缝,不知道出了什么问题

BMP
code
// Include standard headers
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Include GLEW
#include <GL/glew.h>
// Include GLFW
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
GLFWwindow* window;
// Include GLM
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
using namespace glm;
#include <common/shader.hpp>
#include <common/texture.hpp>
int main( void )
{
// Initialise GLFW
if( !glfwInit() )
{
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to initialize GLFW\n" );
return -1;
}
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_SAMPLES, 4);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // To make MacOS happy; should not be needed
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
// Open a window and create its OpenGL context
window = glfwCreateWindow( 1024, 768, "Tutorial 05 - Textured Cube", NULL, NULL);
if( window == NULL ){
fprintf( stderr, "Failed to open GLFW window. If you have an Intel GPU, they are not 3.3 compatible. Try the 2.1 version of the tutorials.\n" );
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
// Initialize GLEW
glewExperimental = true; // Needed for core profile
if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLEW\n");
return -1;
}
// Ensure we can capture the escape key being pressed below
glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_STICKY_KEYS, GL_TRUE);
// Dark blue background
glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.0f);
// Enable depth test
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Accept fragment if it closer to the camera than the former one
glDepthFunc(GL_LESS);
GLuint VertexArrayID;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID);
// Create and compile our GLSL program from the shaders
GLuint programID = LoadShaders( "TransformVertexShader.vertexshader", "TextureFragmentShader.fragmentshader" );
// Get a handle for our "MVP" uniform
GLuint MatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "MVP");
// Projection matrix : 45� Field of View, 4:3 ratio, display range : 0.1 unit <-> 100 units
glm::mat4 Projection = glm::perspective(glm::radians(45.0f), 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
// Camera matrix
glm::mat4 View = glm::lookAt(
glm::vec3(4,3,3), // Camera is at (4,3,3), in World Space
glm::vec3(0,0,0), // and looks at the origin
glm::vec3(0,1,0) // Head is up (set to 0,-1,0 to look upside-down)
);
// Model matrix : an identity matrix (model will be at the origin)
glm::mat4 Model = glm::mat4(1.0f);
// Our ModelViewProjection : multiplication of our 3 matrices
glm::mat4 MVP = Projection * View * Model; // Remember, matrix multiplication is the other way around
// Load the texture using any two methods
GLuint Texture = loadBMP_custom("uvtemplate.bmp");
//GLuint Texture = loadDDS("uvtemplate.DDS");
// Get a handle for our "myTextureSampler" uniform
GLuint TextureID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "myTextureSampler");
// Our vertices. Tree consecutive floats give a 3D vertex; Three consecutive vertices give a triangle.
// A cube has 6 faces with 2 triangles each, so this makes 6*2=12 triangles, and 12*3 vertices
static const GLfloat g_vertex_buffer_data[] = {
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f
};
// Two UV coordinatesfor each vertex. They were created with Blender.
static const GLfloat g_uv_buffer_data[] = {
0.000059f, 1.0f-0.000004f,
0.000103f, 1.0f-0.336048f,
0.335973f, 1.0f-0.335903f,
1.000023f, 1.0f-0.000013f,
0.667979f, 1.0f-0.335851f,
0.999958f, 1.0f-0.336064f,
0.667979f, 1.0f-0.335851f,
0.336024f, 1.0f-0.671877f,
0.667969f, 1.0f-0.671889f,
1.000023f, 1.0f-0.000013f,
0.668104f, 1.0f-0.000013f,
0.667979f, 1.0f-0.335851f,
0.000059f, 1.0f-0.000004f,
0.335973f, 1.0f-0.335903f,
0.336098f, 1.0f-0.000071f,
0.667979f, 1.0f-0.335851f,
0.335973f, 1.0f-0.335903f,
0.336024f, 1.0f-0.671877f,
1.000004f, 1.0f-0.671847f,
0.999958f, 1.0f-0.336064f,
0.667979f, 1.0f-0.335851f,
0.668104f, 1.0f-0.000013f,
0.335973f, 1.0f-0.335903f,
0.667979f, 1.0f-0.335851f,
0.335973f, 1.0f-0.335903f,
0.668104f, 1.0f-0.000013f,
0.336098f, 1.0f-0.000071f,
0.000103f, 1.0f-0.336048f,
0.000004f, 1.0f-0.671870f,
0.336024f, 1.0f-0.671877f,
0.000103f, 1.0f-0.336048f,
0.336024f, 1.0f-0.671877f,
0.335973f, 1.0f-0.335903f,
0.667969f, 1.0f-0.671889f,
1.000004f, 1.0f-0.671847f,
0.667979f, 1.0f-0.335851f
};
GLuint vertexbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(g_vertex_buffer_data), g_vertex_buffer_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
GLuint uvbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &uvbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(g_uv_buffer_data), g_uv_buffer_data, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
do{
// Clear the screen
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Use our shader
glUseProgram(programID);
// Send our transformation to the currently bound shader,
// in the "MVP" uniform
glUniformMatrix4fv(MatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &MVP[0][0]);
// Bind our texture in Texture Unit 0
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, Texture);
// Set our "myTextureSampler" sampler to use Texture Unit 0
glUniform1i(TextureID, 0);
// 1rst attribute buffer : vertices
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
0, // attribute. No particular reason for 0, but must match the layout in the shader.
3, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
);
// 2nd attribute buffer : UVs
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
1, // attribute. No particular reason for 1, but must match the layout in the shader.
2, // size : U+V => 2
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
);
// Draw the triangle !
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 12*3); // 12*3 indices starting at 0 -> 12 triangles
glDisableVertexAttribArray(0);
glDisableVertexAttribArray(1);
// Swap buffers
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
} // Check if the ESC key was pressed or the window was closed
while( glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE ) != GLFW_PRESS &&
glfwWindowShouldClose(window) == 0 );
// Cleanup VBO and shader
glDeleteBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &uvbuffer);
glDeleteProgram(programID);
glDeleteTextures(1, &Texture);
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
// Close OpenGL window and terminate GLFW
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
#ifndef TEXTURE_HPP
#define TEXTURE_HPP
// Load a .BMP file using our custom loader
GLuint loadBMP_custom(const char * imagepath);
//// Since GLFW 3, glfwLoadTexture2D() has been removed. You have to use another texture loading library,
//// or do it yourself (just like loadBMP_custom and loadDDS)
//// Load a .TGA file using GLFW's own loader
//GLuint loadTGA_glfw(const char * imagepath);
// Load a .DDS file using GLFW's own loader
GLuint loadDDS(const char * imagepath);
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <GL/glew.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
GLuint loadBMP_custom(const char * imagepath){
printf("Reading image %s\n", imagepath);
// Data read from the header of the BMP file
unsigned char header[54];
unsigned int dataPos;
unsigned int imageSize;
unsigned int width, height;
// Actual RGB data
unsigned char * data;
// Open the file
FILE * file = fopen(imagepath,"rb");
if (!file){
printf("%s could not be opened. Are you in the right directory ? Don't forget to read the FAQ !\n", imagepath);
getchar();
return 0;
}
// Read the header, i.e. the 54 first bytes
// If less than 54 bytes are read, problem
if ( fread(header, 1, 54, file)!=54 ){
printf("Not a correct BMP file\n");
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
// A BMP files always begins with "BM"
if ( header[0]!='B' || header[1]!='M' ){
printf("Not a correct BMP file\n");
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
// Make sure this is a 24bpp file
if ( *(int*)&(header[0x1E])!=0 ) {printf("Not a correct BMP file\n"); fclose(file); return 0;}
if ( *(int*)&(header[0x1C])!=24 ) {printf("Not a correct BMP file\n"); fclose(file); return 0;}
// Read the information about the image
dataPos = *(int*)&(header[0x0A]);
imageSize = *(int*)&(header[0x22]);
width = *(int*)&(header[0x12]);
height = *(int*)&(header[0x16]);
// Some BMP files are misformatted, guess missing information
if (imageSize==0) imageSize=width*height*3; // 3 : one byte for each Red, Green and Blue component
if (dataPos==0) dataPos=54; // The BMP header is done that way
// Create a buffer
data = new unsigned char [imageSize];
// Read the actual data from the file into the buffer
fread(data,1,imageSize,file);
// Everything is in memory now, the file can be closed.
fclose (file);
// Create one OpenGL texture
GLuint textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
// "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
// Give the image to OpenGL
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0,GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_BGR, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data);
// OpenGL has now copied the data. Free our own version
delete [] data;
// Poor filtering, or ...
//glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
//glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
// ... nice trilinear filtering ...
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
// ... which requires mipmaps. Generate them automatically.
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
// Return the ID of the texture we just created
return textureID;
}
// Since GLFW 3, glfwLoadTexture2D() has been removed. You have to use another texture loading library,
// or do it yourself (just like loadBMP_custom and loadDDS)
//GLuint loadTGA_glfw(const char * imagepath){
//
// // Create one OpenGL texture
// GLuint textureID;
// glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
//
// // "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
// glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
//
// // Read the file, call glTexImage2D with the right parameters
// glfwLoadTexture2D(imagepath, 0);
//
// // Nice trilinear filtering.
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
// glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
// glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
//
// // Return the ID of the texture we just created
// return textureID;
//}
#define FOURCC_DXT1 0x31545844 // Equivalent to "DXT1" in ASCII
#define FOURCC_DXT3 0x33545844 // Equivalent to "DXT3" in ASCII
#define FOURCC_DXT5 0x35545844 // Equivalent to "DXT5" in ASCII
GLuint loadDDS(const char * imagepath){
unsigned char header[124];
FILE *fp;
/* try to open the file */
fp = fopen(imagepath, "rb");
if (fp == NULL){
printf("%s could not be opened. Are you in the right directory ? Don't forget to read the FAQ !\n", imagepath); getchar();
return 0;
}
/* verify the type of file */
char filecode[4];
fread(filecode, 1, 4, fp);
if (strncmp(filecode, "DDS ", 4) != 0) {
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
/* get the surface desc */
fread(&header, 124, 1, fp);
unsigned int height = *(unsigned int*)&(header[8 ]);
unsigned int width = *(unsigned int*)&(header[12]);
unsigned int linearSize = *(unsigned int*)&(header[16]);
unsigned int mipMapCount = *(unsigned int*)&(header[24]);
unsigned int fourCC = *(unsigned int*)&(header[80]);
unsigned char * buffer;
unsigned int bufsize;
/* how big is it going to be including all mipmaps? */
bufsize = mipMapCount > 1 ? linearSize * 2 : linearSize;
buffer = (unsigned char*)malloc(bufsize * sizeof(unsigned char));
fread(buffer, 1, bufsize, fp);
/* close the file pointer */
fclose(fp);
unsigned int components = (fourCC == FOURCC_DXT1) ? 3 : 4;
unsigned int format;
switch(fourCC)
{
case FOURCC_DXT1:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT;
break;
case FOURCC_DXT3:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT3_EXT;
break;
case FOURCC_DXT5:
format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT5_EXT;
break;
default:
free(buffer);
return 0;
}
// Create one OpenGL texture
GLuint textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);
// "Bind" the newly created texture : all future texture functions will modify this texture
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
glPixelStorei(GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT,1);
unsigned int blockSize = (format == GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT) ? 8 : 16;
unsigned int offset = 0;
/* load the mipmaps */
for (unsigned int level = 0; level < mipMapCount && (width || height); ++level)
{
unsigned int size = ((width+3)/4)*((height+3)/4)*blockSize;
glCompressedTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, level, format, width, height,
0, size, buffer + offset);
offset += size;
width /= 2;
height /= 2;
// Deal with Non-Power-Of-Two textures. This code is not included in the webpage to reduce clutter.
if(width < 1) width = 1;
if(height < 1) height = 1;
}
free(buffer);
return textureID;
}
#version 330 core
// Input vertex data, different for all executions of this shader.
layout(location = 0) in vec3 vertexPosition_modelspace;
layout(location = 1) in vec2 vertexUV;
// Output data ; will be interpolated for each fragment.
out vec2 UV;
// Values that stay constant for the whole mesh.
uniform mat4 MVP;
void main(){
// Output position of the vertex, in clip space : MVP * position
gl_Position = MVP * vec4(vertexPosition_modelspace,1);
// UV of the vertex. No special space for this one.
UV = vertexUV;
}
#version 330 core
// Interpolated values from the vertex shaders
in vec2 UV;
// Ouput data
out vec3 color;
// Values that stay constant for the whole mesh.
uniform sampler2D myTextureSampler;
void main(){
// Output color = color of the texture at the specified UV
color = texture( myTextureSampler, UV ).rgb;
}
opengl 学习 之 05 lesson的更多相关文章
- OpenGL学习之windows下安装opengl的glut库
OpenGL学习之windows下安装opengl的glut库 GLUT不是OpenGL所必须的,但它会给我们的学习带来一定的方便,推荐安装. Windows环境下的GLUT下载地址:(大小约为15 ...
- OpenGL学习笔记3——缓冲区对象
在GL中特别提出了缓冲区对象这一概念,是针对提高绘图效率的一个手段.由于GL的架构是基于客户——服务器模型建立的,因此默认所有的绘图数据均是存储在本地客户端,通过GL内核渲染处理以后再将数据发往GPU ...
- OpenGL学习进程(12)第九课:矩阵乘法实现3D变换
本节是OpenGL学习的第九个课时,下面将详细介绍OpenGL的多种3D变换和如何操作矩阵堆栈. (1)3D变换: OpenGL中绘制3D世界的空间变换包括:模型变换.视图变换.投影变换和视口 ...
- OpenGL学习进程(11)第八课:颜色绘制的详解
本节是OpenGL学习的第八个课时,下面将详细介绍OpenGL的颜色模式,颜色混合以及抗锯齿. (1)颜色模式: OpenGL支持两种颜色模式:一种是RGBA,一种是颜色索引模式. R ...
- OpenGL学习笔记:拾取与选择
转自:OpenGL学习笔记:拾取与选择 在开发OpenGL程序时,一个重要的问题就是互动,假设一个场景里面有很多元素,当用鼠标点击不同元素时,期待作出不同的反应,那么在OpenGL里面,是怎么知道我当 ...
- OpenGL学习之路(一)
1 引子 虽然是计算机科班出身,但从小对几何方面的东西就不太感冒,空间想象能力也较差,所以从本科到研究生,基本没接触过<计算机图形学>.为什么说基本没学过呢?因为好奇(尤其是惊叹于三维游戏 ...
- OpenGL学习之路(三)
1 引子 这些天公司一次次的软件发布节点忙的博主不可开交,另外还有其它的一些事也占用了很多时间.现在坐在电脑前,在很安静的环境下,与大家分享自己的OpenGL学习笔记和理解心得,感到格外舒服.这让我回 ...
- OpenGL学习之路(四)
1 引子 上次读书笔记主要是学习了应用三维坐标变换矩阵对二维的图形进行变换,并附带介绍了GLSL语言的编译.链接相关的知识,之后介绍了GLSL中变量的修饰符,着重介绍了uniform修饰符,来向着色器 ...
- OpenGL学习之路(五)
1 引子 不知不觉我们已经进入到读书笔记(五)了,我们先对前四次读书笔记做一个总结.前四次读书笔记主要是学习了如何使用OpenGL来绘制几何图形(包括二维几何体和三维几何体),并学习了平移.旋转.缩放 ...
- 机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————05.Logistic回归
机器学习实战(Machine Learning in Action)学习笔记————05.Logistic回归 关键字:Logistic回归.python.源码解析.测试作者:米仓山下时间:2018- ...
随机推荐
- 聊聊@Autowired与@Resource的区别
1. 前言 从事过很多家公司,见过很多项目,发现@Autowired和@Resource的使用都是一样的乱, 一个项目中有使用@Autowired的,有使用@Resource的, 甚至有的类中一会儿使 ...
- AD 侦查-MSRPC Over SMB
本文通过 Google 翻译 AD Recon – MSRPC Over SMB (135/139/445) 这篇文章所产生,本人仅是对机器翻译中部分表达别扭的字词进行了校正及个别注释补充. 导航 0 ...
- Java--利用打印流(PrintStream)输出信息
package demo; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; /** ...
- P10856 【MX-X2-T5】「Cfz Round 4」Xor-Forces题解
题意: 给定一个长度为 \(n=2^k\) 的数组 \(a\),下标从 \(0\) 开始,维护 \(m\) 次操作: 给定 \(x\),设数列 \(a'\) 满足 \(a'_i=a_{i\oplus ...
- 把iview的table做成更适合展现大量数据的样式(字体变小、去除多余的padding等)
<style> .ivu-table { font-size: 12px !important; } .ivu-table-header thead tr th { padding: 0p ...
- 基于.NetCore开发 StarBlog 番外篇 (4) 文章一键发布工具Publisher大升级,AI功能增强与界面优化
前言 自从上次开发了 StarBlogPublisher 这个文章创作神器之后 我的博客+公众号文章工作流效率提升了不少 不过这软件还有一些功能欠缺和我不满意的地方 这次就在这个下暴雨的周末,把这个软 ...
- VNCTF-Misc
VNCTF-Misc VN_Lang 直接IDApro打开,shift+F12检索字符串 Echo Flowers echo_flowers.ovf文件,可以使用vmware挂载 有个imToken, ...
- B1061 判断题 (15 分)
描述 判断题的评判很简单,本题就要求你写个简单的程序帮助老师判题并统计学生们判断题的得分. 输入格式: 输入在第一行给出两个不超过 100 的正整数 N 和 M,分别是学生人数和判断题数量.第二行给出 ...
- codeup之打印日期
Description 给出年分m和一年中的第n天,算出第n天是几月几号. Input 输入包括两个整数y(1<=y<=3000),n(1<=n<=366). Output 可 ...
- MySQL的表空间释放
概述 最近为了对 MySQL 数据库磁盘占用瘦身,对一张近100GB表的历史数据进行了 delete 删除,删除了约2/3的数据,删除后发现该表占用的空间并未减少.通过下面语句查看该表的磁盘占用情况: ...
