『TensorFlow』单&双隐藏层自编码器设计
计算图设计
很简单的实践,
- 多了个隐藏层
- 没有上节的高斯噪声
- 网络写法由上节的面向对象改为了函数式编程,
其他没有特别需要注意的,实现如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' learning_rate = 0.01 # 学习率
training_epochs = 20 # 训练轮数,1轮等于n_samples/batch_size
batch_size = 128 # batch容量
display_step = 1 # 展示间隔
example_to_show = 10 # 展示图像数目 n_hidden_units = 256
n_input_units = 784
n_output_units = n_input_units def WeightsVariable(n_in, n_out, name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_in, n_out]), dtype=tf.float32, name=name_str) def biasesVariable(n_out, name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_out]), dtype=tf.float32, name=name_str) def encoder(x_origin, activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_input_units, n_hidden_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden_units, 'biases')
x_code = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_origin, Weights), biases))
return x_code def decode(x_code, activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden_units, n_output_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_output_units, 'biases')
x_decode = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_code, Weights), biases))
return x_decode with tf.Graph().as_default():
with tf.name_scope('Input'):
X_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input_units])
with tf.name_scope('Encode'):
X_code = encoder(X_input)
with tf.name_scope('decode'):
X_decode = decode(X_code)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(X_input - X_decode, 2))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
Optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate)
train = Optimizer.minimize(loss) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 因为使用了tf.Graph.as_default()上下文环境
# 所以下面的记录必须放在上下文里面,否则记录下来的图是空的(get不到上面的default)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=tf.get_default_graph())
writer.flush()
计算图:
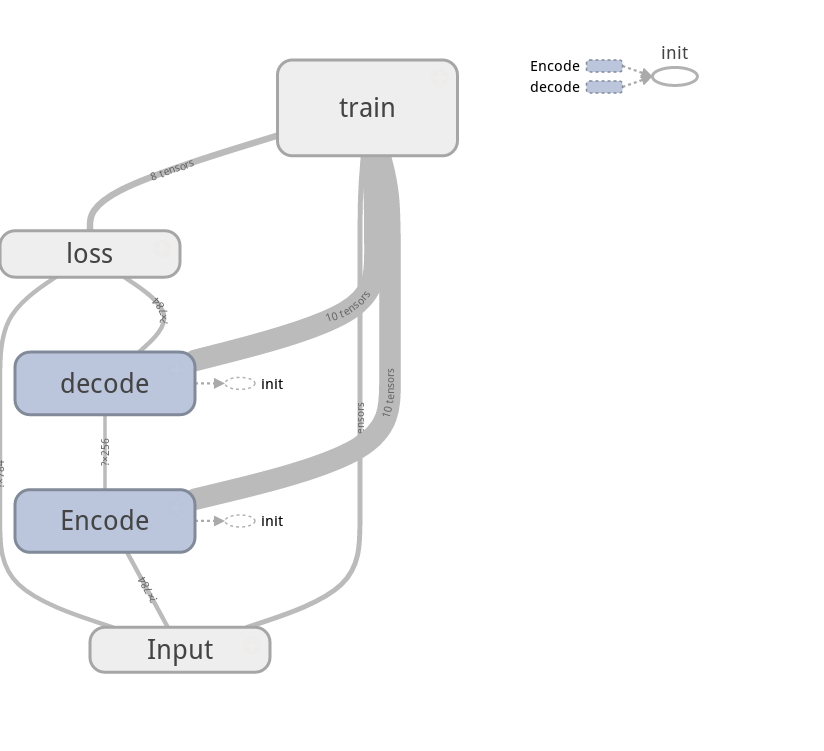
训练程序
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' learning_rate = 0.01 # 学习率
training_epochs = 20 # 训练轮数,1轮等于n_samples/batch_size
batch_size = 128 # batch容量
display_step = 1 # 展示间隔
example_to_show = 10 # 展示图像数目 n_hidden_units = 256
n_input_units = 784
n_output_units = n_input_units def WeightsVariable(n_in, n_out, name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_in, n_out]), dtype=tf.float32, name=name_str) def biasesVariable(n_out, name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_out]), dtype=tf.float32, name=name_str) def encoder(x_origin, activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_input_units, n_hidden_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden_units, 'biases')
x_code = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_origin, Weights), biases))
return x_code def decode(x_code, activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden_units, n_output_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_output_units, 'biases')
x_decode = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_code, Weights), biases))
return x_decode with tf.Graph().as_default():
with tf.name_scope('Input'):
X_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input_units])
with tf.name_scope('Encode'):
X_code = encoder(X_input)
with tf.name_scope('decode'):
X_decode = decode(X_code)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(X_input - X_decode, 2))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
Optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate)
train = Optimizer.minimize(loss) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 因为使用了tf.Graph.as_default()上下文环境
# 所以下面的记录必须放在上下文里面,否则记录下来的图是空的(get不到上面的default)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=tf.get_default_graph())
writer.flush() mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('../Mnist_data/', one_hot=True) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, Loss = sess.run([train, loss], feed_dict={X_input: batch_xs})
Loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={X_input: batch_xs})
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print('Epoch: %04d' % (epoch + 1), 'loss= ', '{:.9f}'.format(Loss))
writer.close()
print('训练完毕!') '''比较输入和输出的图像'''
# 输出图像获取
reconstructions = sess.run(X_decode, feed_dict={X_input: mnist.test.images[:example_to_show]})
# 画布建立
f, a = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(10, 2))
for i in range(example_to_show):
a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(mnist.test.images[i], (28, 28)))
a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(reconstructions[i], (28, 28)))
f.show() # 渲染图像
plt.draw() # 刷新图像
# plt.waitforbuttonpress()
debug一上午的收获:接受sess.run输出的变量名不要和tensor节点的变量名重复,会出错的... ...好低级的错误。mmdz
比较图像一部分之前没做过,介绍了matplotlib.pyplot的花式用法,
原来plt.subplots()是会返回 画布句柄 & 子图集合 句柄的,子图集合句柄可以像数组一样调用子图
pyplot是有show()和draw()两个方法的,show是展示出画布,draw会刷新原图,可以交互的修改画布
waitforbuttonpress()监听键盘按键如果用户按的是键盘,返回True,如果是其他(如鼠标单击),则返回False
另,发现用surface写程序其实还挺带感... ...
输出图像如下:
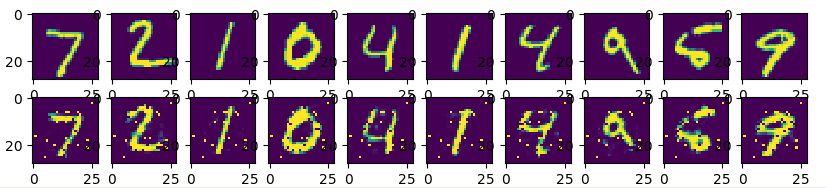
双隐藏层版本
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' batch_size = 128 # batch容量
display_step = 1 # 展示间隔
learning_rate = 0.01 # 学习率
training_epochs = 20 # 训练轮数,1轮等于n_samples/batch_size
example_to_show = 10 # 展示图像数目 n_hidden1_units = 256 # 第一隐藏层
n_hidden2_units = 128 # 第二隐藏层
n_input_units = 784
n_output_units = n_input_units def WeightsVariable(n_in, n_out, name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_in, n_out]), dtype=tf.float32, name=name_str) def biasesVariable(n_out, name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_out]), dtype=tf.float32, name=name_str) def encoder(x_origin, activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer1'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_input_units, n_hidden1_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden1_units, 'biases')
x_code1 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_origin, Weights), biases))
with tf.name_scope('Layer2'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden1_units, n_hidden2_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden2_units, 'biases')
x_code2 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_code1, Weights), biases))
return x_code2 def decode(x_code, activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer1'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden2_units, n_hidden1_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden1_units, 'biases')
x_decode1 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_code, Weights), biases))
with tf.name_scope('Layer2'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden1_units, n_output_units, 'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_output_units, 'biases')
x_decode2 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_decode1, Weights), biases))
return x_decode2 with tf.Graph().as_default():
with tf.name_scope('Input'):
X_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_input_units])
with tf.name_scope('Encode'):
X_code = encoder(X_input)
with tf.name_scope('decode'):
X_decode = decode(X_code)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(X_input - X_decode, 2))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
Optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate)
train = Optimizer.minimize(loss) init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 因为使用了tf.Graph.as_default()上下文环境
# 所以下面的记录必须放在上下文里面,否则记录下来的图是空的(get不到上面的default)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=tf.get_default_graph())
writer.flush() mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('../Mnist_data/', one_hot=True) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_, Loss = sess.run([train, loss], feed_dict={X_input: batch_xs})
Loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={X_input: batch_xs})
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print('Epoch: %04d' % (epoch + 1), 'loss= ', '{:.9f}'.format(Loss))
writer.close()
print('训练完毕!') '''比较输入和输出的图像'''
# 输出图像获取
reconstructions = sess.run(X_decode, feed_dict={X_input: mnist.test.images[:example_to_show]})
# 画布建立
f, a = plt.subplots(2, 10, figsize=(10, 2))
for i in range(example_to_show):
a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(mnist.test.images[i], (28, 28)))
a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(reconstructions[i], (28, 28)))
f.show() # 渲染图像
plt.draw() # 刷新图像
# plt.waitforbuttonpress()
输出图像如下:
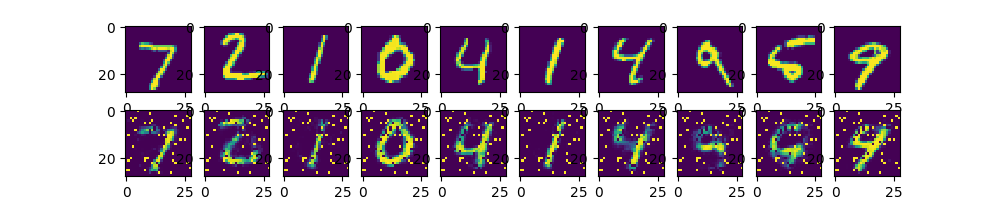
由于压缩到128个节点损失信息过多,所以结果不如之前单层的好。
有意思的是我们把256的那层改成128(也就是双128)后,结果反而比上面的要好:
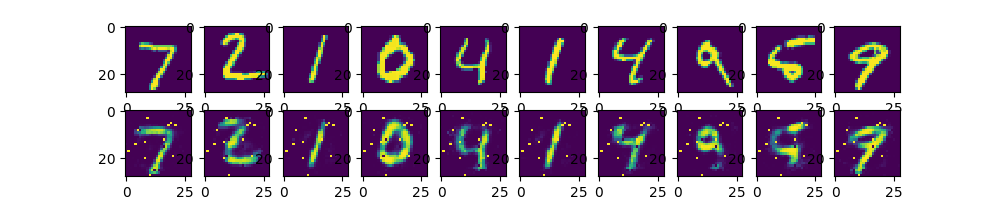
但是仍然比不上单隐藏层,数据比较简单时候复杂网络效果可能不那么好(loss值我没有截取,但实际上是这样,虽然不同网络loss直接比较没什么意义),当然,也有可能是复杂网络没收敛的结果。
可视化双隐藏层自编码器
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import os os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2' batch_size = 128 # batch容量
display_step = 1 # 展示间隔
learning_rate = 0.01 # 学习率
training_epochs = 20 # 训练轮数,1轮等于n_samples/batch_size
example_to_show = 10 # 展示图像数目 n_hidden1_units = 256 # 第一隐藏层
n_hidden2_units = 128 # 第二隐藏层
n_input_units = 784
n_output_units = n_input_units def variable_summaries(var): #<---
"""
可视化变量全部相关参数
:param var:
:return:
"""
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.histogram('mean', mean)
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev) # 注意,这是标量
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var) def WeightsVariable(n_in,n_out,name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_in,n_out]),dtype=tf.float32,name=name_str) def biasesVariable(n_out,name_str):
return tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_out]),dtype=tf.float32,name=name_str) def encoder(x_origin,activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer1'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_input_units,n_hidden1_units,'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden1_units,'biases')
x_code1 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_origin,Weights),biases))
variable_summaries(Weights) #<---
variable_summaries(biases) #<---
with tf.name_scope('Layer2'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden1_units,n_hidden2_units,'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden2_units,'biases')
x_code2 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_code1,Weights),biases))
variable_summaries(Weights) #<---
variable_summaries(biases) #<---
return x_code2 def decode(x_code,activate_func=tf.nn.sigmoid):
with tf.name_scope('Layer1'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden2_units,n_hidden1_units,'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_hidden1_units,'biases')
x_decode1 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_code,Weights),biases))
variable_summaries(Weights) #<---
variable_summaries(biases) #<---
with tf.name_scope('Layer2'):
Weights = WeightsVariable(n_hidden1_units,n_output_units,'Weights')
biases = biasesVariable(n_output_units,'biases')
x_decode2 = activate_func(tf.add(tf.matmul(x_decode1,Weights),biases))
variable_summaries(Weights) #<---
variable_summaries(biases) #<---
return x_decode2 with tf.Graph().as_default():
with tf.name_scope('Input'):
X_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,n_input_units])
with tf.name_scope('Encode'):
X_code = encoder(X_input)
with tf.name_scope('decode'):
X_decode = decode(X_code)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(X_input - X_decode,2))
with tf.name_scope('train'):
Optimizer = tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate)
train = Optimizer.minimize(loss) # 标量汇总
with tf.name_scope('LossSummary'):
tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)
tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate',learning_rate) # 图像展示
with tf.name_scope('ImageSummary'):
image_original = tf.reshape(X_input,[-1, 28, 28, 1])
image_reconstruction = tf.reshape(X_decode, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
tf.summary.image('image_original', image_original, 9)
tf.summary.image('image_recinstruction', image_reconstruction, 9) # 汇总
merged_summary = tf.summary.merge_all() init = tf.global_variables_initializer() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir='logs', graph=tf.get_default_graph())
writer.flush() mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('../Mnist_data/', one_hot=True) with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
total_batch = int(mnist.train.num_examples / batch_size)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_,Loss = sess.run([train,loss],feed_dict={X_input: batch_xs})
Loss = sess.run(loss,feed_dict={X_input: batch_xs})
if epoch % display_step == 0:
print('Epoch: %04d' % (epoch + 1),'loss= ','{:.9f}'.format(Loss))
summary_str = sess.run(merged_summary,feed_dict={X_input: batch_xs}) #<---
writer.add_summary(summary_str,epoch) #<---
writer.flush() #<---
writer.close()
print('训练完毕!')
几个有意思的发现,
使用之前的图像输出方式时,win下matplotlib.pyplot的绘画框会立即退出,所以要使用 plt.waitforbuttonpress() 命令。
win下使用plt绘画色彩和linux不一样,效果如下:
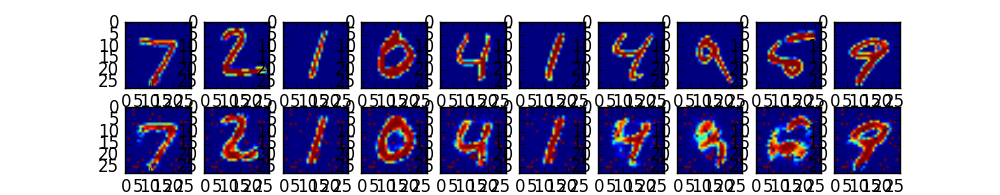
输出图如下:

对比图像如下(截自tensorboard):

『TensorFlow』单&双隐藏层自编码器设计的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 神经网络——TENSORFLOW 双隐藏层自编码器设计处理MNIST手写数字数据集并使用TENSORBORD描绘神经网络数据2
import os import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data os.envi ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_降噪自编码器
『TensorFlow』降噪自编码器设计 之前学习过的代码,又敲了一遍,新的收获也还是有的,因为这次注释写的比较详尽,所以再次记录一下,具体的相关知识查阅之前写的文章即可(见上面链接). # Aut ...
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 神经网络——TENSORFLOW 单隐藏层自编码器设计处理MNIST手写数字数据集并使用TensorBord描绘神经网络数据
import os import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow ...
- 『TensorFlow』专题汇总
TensorFlow:官方文档 TensorFlow:项目地址 本篇列出文章对于全零新手不太合适,可以尝试TensorFlow入门系列博客,搭配其他资料进行学习. Keras使用tf.Session训 ...
- 『TensorFlow』模型保存和载入方法汇总
『TensorFlow』第七弹_保存&载入会话_霸王回马 一.TensorFlow常规模型加载方法 保存模型 tf.train.Saver()类,.save(sess, ckpt文件目录)方法 ...
- 『TensorFlow』SSD源码学习_其一:论文及开源项目文档介绍
一.论文介绍 读论文系列:Object Detection ECCV2016 SSD 一句话概括:SSD就是关于类别的多尺度RPN网络 基本思路: 基础网络后接多层feature map 多层feat ...
- 『TensorFlow』DCGAN生成动漫人物头像_下
『TensorFlow』以GAN为例的神经网络类范式 『cs231n』通过代码理解gan网络&tensorflow共享变量机制_上 『TensorFlow』通过代码理解gan网络_中 一.计算 ...
- 『TensorFlow』滑动平均
滑动平均会为目标变量维护一个影子变量,影子变量不影响原变量的更新维护,但是在测试或者实际预测过程中(非训练时),使用影子变量代替原变量. 1.滑动平均求解对象初始化 ema = tf.train.Ex ...
- 『TensorFlow』流程控制
『PyTorch』第六弹_最小二乘法对比PyTorch和TensorFlow TensorFlow 控制流程操作 TensorFlow 提供了几个操作和类,您可以使用它们来控制操作的执行并向图中添加条 ...
随机推荐
- linux之more和less的基本使用
more 基本介绍 more 是我们最常用的工具之一,最常用的就是显示输出的内容,然后根据窗口的大小进行分页显示,然后还能提示文件的百分比.more命令从前向后读取文件,因此在启动时就加载整个文件. ...
- python练习题-day10
1.继续整理函数相关知识点,写博客. 2.写函数,接收n个数字,求这些参数数字的和.(动态传参) def fun(*args): sum=0 for i in args: sum+=i return ...
- IP-v4&IP-v6
IPv6与IPv4区别: 1:IPv6的地址空间更大.IPv4中规定IP地址长度为32,即有2^32-1个地址: 而IPv6中IP地址的长度为128,即有2^128-1个地址. 2.IPv6的路由表更 ...
- airflow中的两个参数
'trigger_rule':'all_done','retry_delay':timedelta(),
- angular中的MVC思想
MVC是一种使用 MVC(Model View Controller 模型-视图-控制器)设计模式,该模型的理念也被许多框架所吸纳.在学习angular的过程中,我在网上查找关于angular MVC ...
- 微信小程序 地图地址解析
1.微信小程序提供了几个方式,引入地图, wx.getLocation(OBJECT) 获取当前的地理位置.速度.当用户离开小程序后,此接口无法调用:当用户点击“显示在聊天顶部”时,此接口可继续调用 ...
- mysql 事务锁超时时间 innodb_lock_wait_timeout
mysql 事务锁超时时间 innodb_lock_wait_timeout: # 查询全局等待事务锁超时时间 SHOW GLOBAL VARIABLES LIKE 'innodb_lock_wait ...
- cron笔记
以前以为添加计划任务就是crontab -e来添加,知道今天偶然发现了/etc/cron.d目录,才发现事情没有那么简单.. crontab -e命令编辑的文件是保存在/var/spool/cron/ ...
- JNI与底层调用
交叉编译 在一个平台下,编译出另一个平台能够执行的二进制的代码 平台:windows,mac os,linux 处理器:x86,arm,mips 交叉编译的原理 源代码->编译->链接-& ...
- python中多继承C3算法研究
在python的面向对象继承问题中,单继承简单易懂,全部接受传承类的属性,并可添加自带属性, 但是,在多继承情况下,会遇到多个被继承者的顺序问题,以及多次继承后查找前几次继承者需求属性时,可能不易发现 ...
