基于TensorFlow的服装分类
1、导包
#导入TensorFlow和tf.keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras # Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2、导入Fashion MNIST数据集
#从 TensorFlow中导入和加载Fashion MNIST数据
fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
3、指定名称
#每个图像都会被映射到一个标签。由于数据集不包括类名称,请将它们存储在下方,供稍后绘制图像时使用
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
4、预处理数据
#这些值缩小至 0 到 1 之间,然后将其馈送到神经网络模型
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0
5、浏览数据(可选)
#显示训练集中有 60,000 个图像,每个图像由 28 x 28 的像素表示
print(train_images.shape)
#训练集中有 60,000 个标签
print(len(train_labels))
#每个标签都是一个 0 到 9 之间的整数
print(train_labels)
#测试集中有 10,000 个图像。同样,每个图像都由 28x28 个像素表示
print(test_images.shape)
#测试集包含 10,000 个图像标签
print(len(test_labels))
(60000, 28, 28)
60000
[9 0 0 ... 3 0 5]
(10000, 28, 28)
10000
6、检测图像(可选)
#检查训练集中的第一个图像,您会看到像素值处于 0 到 255 之间
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(train_images[0])
plt.colorbar()
plt.grid(False)
plt.show()

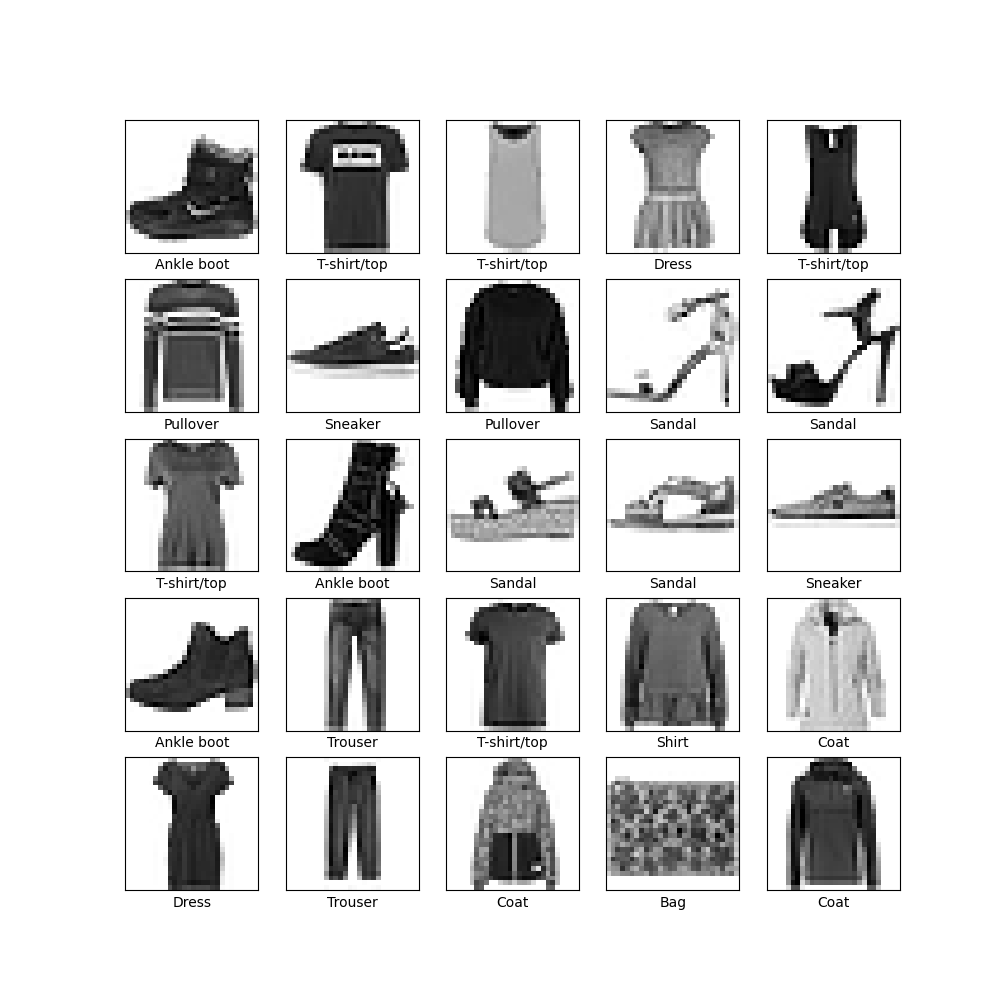
#验证数据的格式是否正确,以及是否已准备好构建和训练网络,显示训练集中的前 25 个图像,并在每个图像下方显示类名称
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5,5,i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]])
plt.show()

7、构建模型
#该网络的第一层 tf.keras.layers.Flatten 将图像格式从二维数组(28 x 28 像素)转换成一维数组(28 x 28 = 784 像素)。将该层视为图像中未堆叠的像素行并将其排列起来。该层没有要学习的参数,它只会重新格式化数据。 展平像素后,网络会包括两个 tf.keras.layers.Dense 层的序列。它们是密集连接或全连接神经层。第一个 Dense 层有 128 个节点(或神经元)。第二个(也是最后一个)层会返回一个长度为 10 的 logits 数组。每个节点都包含一个得分,用来表示当前图像属于 10 个类中的哪一类。
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(10)
])
8、编译模型
#损失函数 - 用于测量模型在训练期间的准确率。您会希望最小化此函数,以便将模型“引导”到正确的方向上。
#优化器 - 决定模型如何根据其看到的数据和自身的损失函数进行更新。
#指标 - 用于监控训练和测试步骤。以下示例使用了准确率,即被正确分类的图像的比率
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
9、训练模型
训练神经网络模型需要执行以下步骤:
- 将训练数据馈送给模型。在本例中,训练数据位于
train_images和train_labels数组中。 - 模型学习将图像和标签关联起来。
- 要求模型对测试集(在本例中为
test_images数组)进行预测。 - 验证预测是否与
test_labels数组中的标签相匹配。
向模型馈送数据
#调用 model.fit 方法,这样命名是因为该方法会将模型与训练数据进行“拟合”
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10)
Epoch 1/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.4970 - accuracy: 0.8263
Epoch 2/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3764 - accuracy: 0.8646
Epoch 3/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3386 - accuracy: 0.8768
Epoch 4/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.3131 - accuracy: 0.8852
Epoch 5/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2979 - accuracy: 0.8905
Epoch 6/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2817 - accuracy: 0.8946
Epoch 7/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2701 - accuracy: 0.8997
Epoch 8/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2584 - accuracy: 0.9039
Epoch 9/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 1ms/step - loss: 0.2494 - accuracy: 0.9071
Epoch 10/10
1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.2416 - accuracy: 0.9094
评估准确率
#比较模型在测试集上的表现
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2) print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc)
Test accuracy: 0.8792999982833862
10、进行预测
#进行预测
probability_model = tf.keras.Sequential([model,
tf.keras.layers.Softmax()])
predictions = probability_model.predict(test_images)
#测试第一个预测结果
print(predictions[0])
#找出置信度最大的标签
print(np.argmax(predictions[0]))
#检查测试标签
print(test_labels[0])
[1.4007558e-08 6.0697776e-09 6.0778667e-08 3.8483901e-08 1.5276806e-08
2.0785581e-03 2.9759491e-07 5.4935408e-03 5.0426343e-07 9.9242699e-01]
9
9
11、绘制图表
def plot_image(i, predictions_array, true_label, img):
predictions_array, true_label, img = predictions_array, true_label[i], img[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([]) plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary) predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
if predicted_label == true_label:
color = 'blue'
else:
color = 'red' plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label],
100*np.max(predictions_array),
class_names[true_label]),
color=color) def plot_value_array(i, predictions_array, true_label):
predictions_array, true_label = predictions_array, true_label[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks(range(10))
plt.yticks([])
thisplot = plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array, color="#777777")
plt.ylim([0, 1])
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array) thisplot[predicted_label].set_color('red')
thisplot[true_label].set_color('blue')
12、验证预测结果
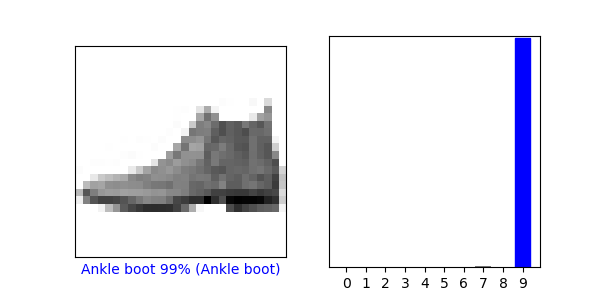
#对图像进行检测
#看看第 0 个图像、预测结果和预测数组。正确的预测标签为蓝色,错误的预测标签为红色。数字表示预测标签的百分比(总计为 100)。
i = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
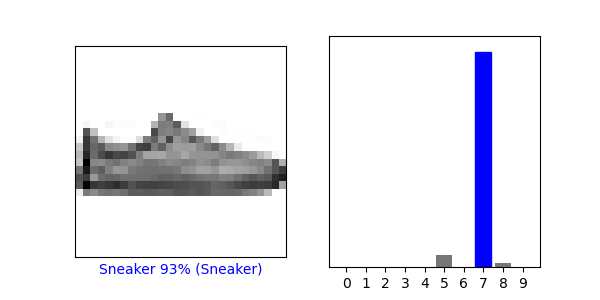
#看第12个图像
i = 12
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
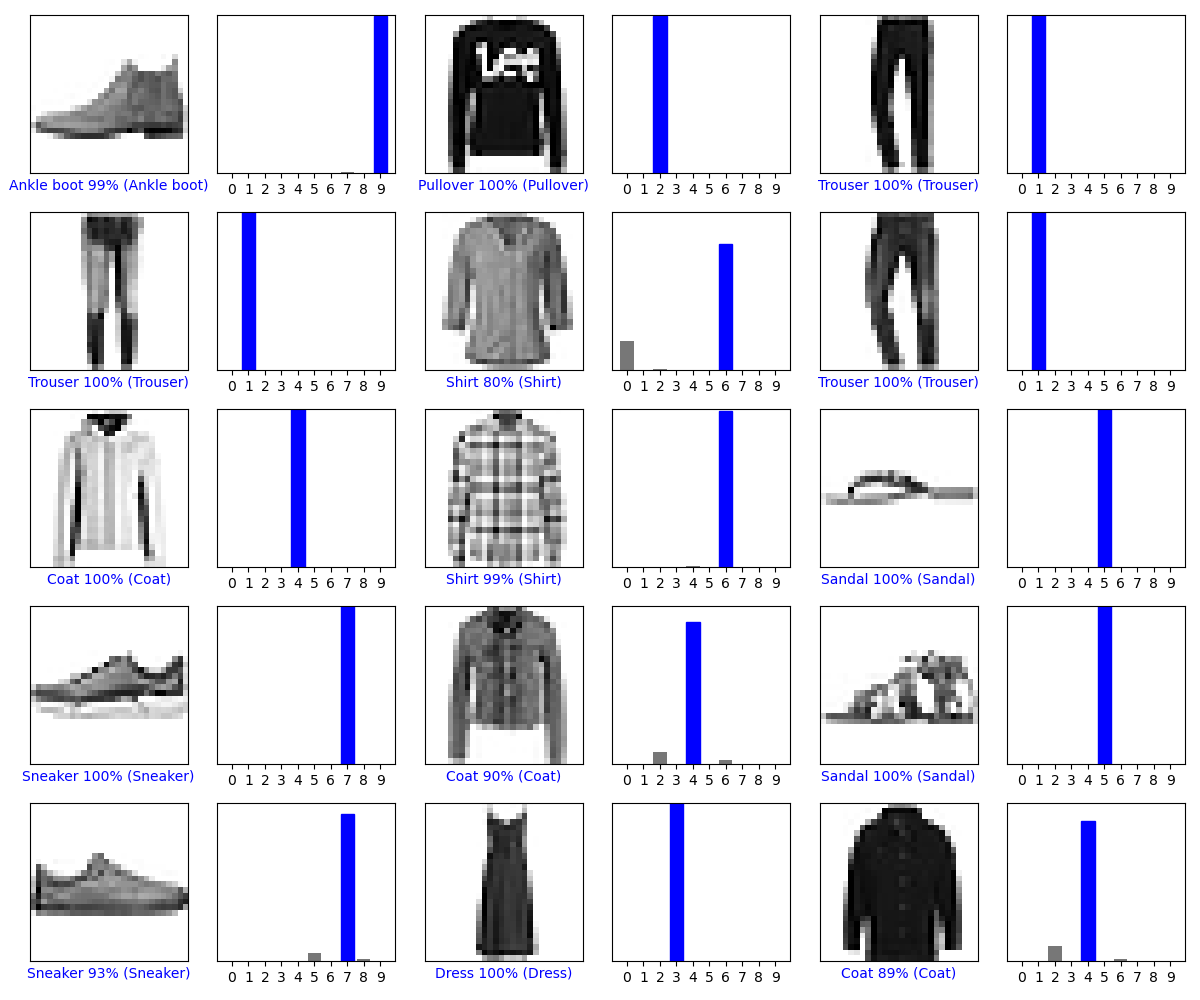
#用模型预测绘制几张图像
# Plot the first X test images, their predicted labels, and the true labels.
# Color correct predictions in blue and incorrect predictions in red.
num_rows = 5
num_cols = 3
num_images = num_rows*num_cols
plt.figure(figsize=(2*2*num_cols, 2*num_rows))
for i in range(num_images):
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

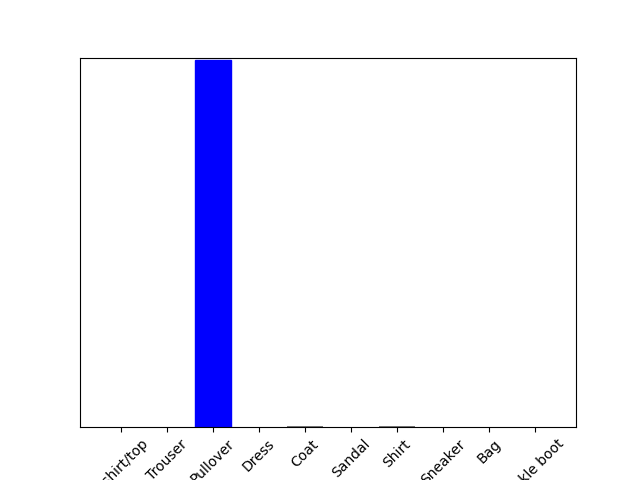
13、使用训练的模型
使用训练好的模型对单张图片进行预测
#使用训练好的模型对单个图像进行预测
# Grab an image from the test dataset.
img = test_images[1]
print(img.shape)
(28, 28)
#将其添加到列表中
# Add the image to a batch where it's the only member.
img = (np.expand_dims(img,0)) print(img.shape)
(1, 28, 28)
#预测这个图像的正确标签
predictions_single = probability_model.predict(img) print(predictions_single)
[[1.0675135e-05 2.4023437e-12 9.9772269e-01 1.3299730e-09 1.2968916e-03
8.7469149e-14 9.6970733e-04 5.4669354e-19 2.4514609e-11 1.8405429e-12]]
plot_value_array(1, predictions_single[0], test_labels)
_ = plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45)
#在批次中获取对我们(唯一)图像的预测
print(np.argmax(predictions_single[0]))
2
14、源代码
# -*- coding = utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/3/16
# @Author : pistachio
# @File : imagesort1.py
# @Software : PyCharm #导入TensorFlow和tf.keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras # Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #从 TensorFlow中导入和加载Fashion MNIST数据
fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data() #每个图像都会被映射到一个标签。由于数据集不包括类名称,请将它们存储在下方,供稍后绘制图像时使用
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot'] #这些值缩小至 0 到 1 之间,然后将其馈送到神经网络模型
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0 #浏览数据
print(train_images.shape)
print(len(train_labels))
print(train_labels)
print(test_images.shape)
print(len(test_labels)) plt.figure()
plt.imshow(train_images[0])
plt.colorbar()
plt.grid(False)
plt.show()
#为了验证数据的格式是否正确,以及您是否已准备好构建和训练网络,让我们显示训练集中的前 25 个图像,并在每个图像下方显示类名称
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5, 5, i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]])
plt.show() #训练模型
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(10)
]) model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10) test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2) print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc) #进行预测
probability_model = tf.keras.Sequential([model,
tf.keras.layers.Softmax()])
predictions = probability_model.predict(test_images)
#测试第一个预测结果
print(predictions[0])
#找出置信度最大的标签
print(np.argmax(predictions[0]))
#检查测试标签
print(test_labels[0]) #将其绘制成图表,看看模型对于全部 10 个类的预测
def plot_image(i, predictions_array, true_label, img):
predictions_array, true_label, img = predictions_array, true_label[i], img[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([]) plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary) predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
if predicted_label == true_label:
color = 'blue'
else:
color = 'red' plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label],
100*np.max(predictions_array),
class_names[true_label]),
color=color) def plot_value_array(i, predictions_array, true_label):
predictions_array, true_label = predictions_array, true_label[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks(range(10))
plt.yticks([])
thisplot = plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array, color="#777777")
plt.ylim([0, 1])
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array) thisplot[predicted_label].set_color('red')
thisplot[true_label].set_color('blue') #对图像进行检测
#看看第 0 个图像、预测结果和预测数组。正确的预测标签为蓝色,错误的预测标签为红色。数字表示预测标签的百分比(总计为 100)。
i = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
#看第12个图像
i = 12
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
#用模型预测绘制几张图像
# Plot the first X test images, their predicted labels, and the true labels.
# Color correct predictions in blue and incorrect predictions in red.
num_rows = 5
num_cols = 3
num_images = num_rows*num_cols
plt.figure(figsize=(2*2*num_cols, 2*num_rows))
for i in range(num_images):
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(num_rows, 2*num_cols, 2*i+2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show() #使用训练好的模型对单个图像进行预测
# Grab an image from the test dataset.
img = test_images[1]
print(img.shape) #将其添加到列表中
# Add the image to a batch where it's the only member.
img = (np.expand_dims(img,0))
print(img.shape) #预测这个图像的正确标签
predictions_single = probability_model.predict(img) print(predictions_single) plot_value_array(1, predictions_single[0], test_labels)
_ = plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45)
plt.show()
print(np.argmax(predictions_single[0]))
基于TensorFlow的服装分类的更多相关文章
- 基于tensorflow的文本分类总结(数据集是复旦中文语料)
代码已上传到github:https://github.com/taishan1994/tensorflow-text-classification 往期精彩: 利用TfidfVectorizer进行 ...
- 基于tensorflow的逻辑分类
#!/usr/local/bin/python3 ##ljj [2] ##logic classify model import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib. ...
- 使用Python基于TensorFlow的CIFAR-10分类训练
TensorFlow Models GitHub:https://github.com/tensorflow/models Document:https://github.com/jikexueyua ...
- Chinese-Text-Classification,用卷积神经网络基于 Tensorflow 实现的中文文本分类。
用卷积神经网络基于 Tensorflow 实现的中文文本分类 项目地址: https://github.com/fendouai/Chinese-Text-Classification 欢迎提问:ht ...
- tensorflow实现基于LSTM的文本分类方法
tensorflow实现基于LSTM的文本分类方法 作者:u010223750 引言 学习一段时间的tensor flow之后,想找个项目试试手,然后想起了之前在看Theano教程中的一个文本分类的实 ...
- 一文详解如何用 TensorFlow 实现基于 LSTM 的文本分类(附源码)
雷锋网按:本文作者陆池,原文载于作者个人博客,雷锋网已获授权. 引言 学习一段时间的tensor flow之后,想找个项目试试手,然后想起了之前在看Theano教程中的一个文本分类的实例,这个星期就用 ...
- 基于 TensorFlow 在手机端实现文档检测
作者:冯牮 前言 本文不是神经网络或机器学习的入门教学,而是通过一个真实的产品案例,展示了在手机客户端上运行一个神经网络的关键技术点 在卷积神经网络适用的领域里,已经出现了一些很经典的图像分类网络,比 ...
- 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识别(二)--入门篇
http://www.jianshu.com/p/4195577585e6 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写字识别(一)--白话卷积神经网络模型 基于tensorflow的MNIST手写数字识 ...
- 【小白学PyTorch】15 TF2实现一个简单的服装分类任务
[新闻]:机器学习炼丹术的粉丝的人工智能交流群已经建立,目前有目标检测.医学图像.时间序列等多个目标为技术学习的分群和水群唠嗑的总群,欢迎大家加炼丹兄为好友,加入炼丹协会.微信:cyx64501661 ...
随机推荐
- 【maven】mvn不是内部命令 也不是可运行的程序
按解压.配置环境变量,重启cmd,还是出现这个问题 使用java -version确定是不是安装了jdk.因为maven是java开发,需要依赖jdk 将系统变量中Path的%MAVEM_HOME%\ ...
- C# 泛型Generic
泛型(Generic),是将不确定的类型预先定义下来的一种C#高级语法,我们在使用一个类,接口或者方法前,不知道用户将来传什么类型,或者我们写的类,接口或方法相同的代码可以服务不同的类型,就可以定义为 ...
- Windows反调试技术(下)
OD的DBGHELP模块 检测DBGHELP模块,此模块是用来加载调试符号的,所以一般加载此模块的进程的进程就是调试器.绕过方法也很简单,将DBGHELP.DLL改名. #include <Wi ...
- mysql枚举和集合
create table consumer( id int, name char(16), sex enum('male','female','other'), level enum('vip1',' ...
- 实战-加密grub防止黑客通过单用户系统破解root密码
基于Centos8进行grub加密 加密grub 实战场景:给grub加密,不让别人通过grub进入单用户. 使用grub2-mkpasswd-pbkdf2创建密文 [root@localhost ~ ...
- Ansible_常用文件模块使用详解
一.Ansibel常用文件模块使用详解 1.file模块 1️⃣:file模块常用的参数列表: path 被管理文件的路径 state状态常用参数: absent 删除 ...
- 国产龙芯3A3000处理器评测:与英特尔差距明显
国产龙芯3A3000处理器评测:与英特尔差距明显 国产龙芯3A3000处理器评测:与英特尔差距明显 新浪财经APP缩小字体放大字体收藏微博微信分享579 新酷产品第一时间免费试玩,还有众多优质达人分享 ...
- Docker存储(4)
一.docker存储资源类型 用户在使用 Docker 的过程中,势必需要查看容器内应用产生的数据,或者需要将容器内数据进行备份,甚至多个容器之间进行数据共享,这必然会涉及到容器的数据管理 (1)Da ...
- IDEA 2019.2.4 破解安装教程
将下载的 IDEA 压缩包解压,找到 idealIU-2019.2.4.exe 安装文件,然后双击进行安装 安装完后不要运行,打开解压包中破解补丁与激活码文件夹,找到 jetbrains-agent. ...
- 彻底弄懂HTTP缓存机制及原理【转载】
前言 Http 缓存机制作为 web 性能优化的重要手段,对于从事 Web 开发的同学们来说,应该是知识体系库中的一个基础环节,同时对于有志成为前端架构师的同学来说是必备的知识技能.但是对于很多前端同 ...
