压测工具Locuse的使用
我是听朋友提起的"蝗虫"(Locust),然而她不想用python,我就拿来试一试~
http的 各种压测工具也已经太多了,所以主要是试试locust在当前比较流行的rpc协议上的效果
目的 -- 调研locust应用于grpc协议
服务 -- grpc的helloworld
一 环境准备
1 需要python环境,我使用的是python2.7
2 安装locust
pip install locustio
pip install pyzmq // 分布式运行多个起压locust时使用
pip install gevent==1.1 // 据说是因为升级后的gevent不能很好的支持python2系列?
locust -h // 查看可用参数
二 被测服务编写
1 windows的web界面测试
① python代码,写好保存在为test_001.py
from locust import HttpLocust,TaskSet,task
import subprocess
import json class UserBehavior(TaskSet):
def on_start(self):
pass @task()
def list_header(self):
r = self.client.get("/") class WebUserLocust(HttpLocust):
weight =
task_set = UserBehavior
host = "http://www.baidu.com"
min_wait =
max_wait =
② 在命令行执行
locust -f E:\Work\PyCharmTest\locusttest\test_001.py
③ 打开浏览器,输入网址:localhost:8089 (locust 的默认监听端口为8089)
在显示页面输入模拟用户数和每个用户的req/s,点击 start swarming 即可开始 
④ 需要手动结束,在页面点击stop或者在命令行ctrl+c退出locust启动命令,即可查看结果如下:
显示总请求数、失败请求数、请求的耗时分布、qps、传输字节数等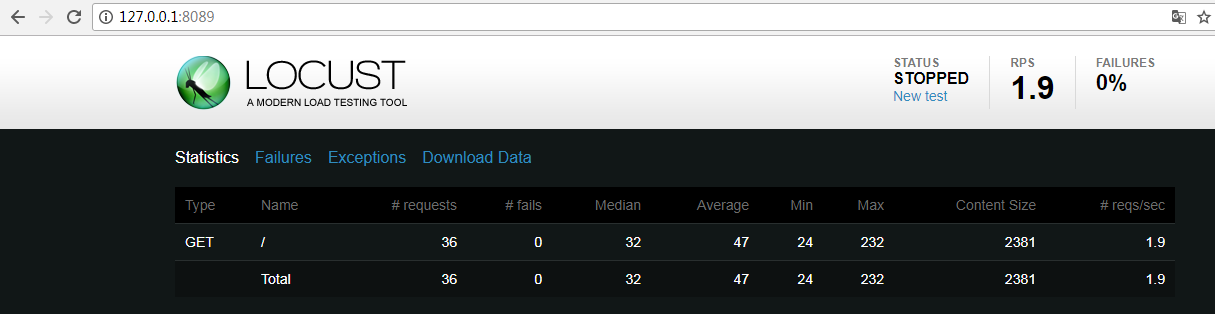
2 linux运行
① python代码 -- 此处写的proto文件,helloworld
syntax = "proto3";
option java_package = "io.grpc.examples";
package helloworld; // The greeter service definition.
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
} // The request meesage containing the user'name.
message HelloRequest {
string name = ;
} // The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = ;
}
② 转成python
执行如下命令,生成helloworld_pb2.py和helloworld_pb2_grpc两个文件
protoc --python_out=. helloworld.proto
③ 启动helloworld的server(该部分随意,根据实际设置)
该部分用的python的server,启动端口设置为50052
import sys
import grpc
import time
sys.path.append("..") from concurrent import futures
from helloworld.helloworld import helloworld_pb2, helloworld_pb2_grpc _ONE_DAY_IN_SECONDS = * *
_HOST = 'localhost'
_PORT = ''
class Greeter(helloworld_pb2_grpc.GreeterServicer):
def SayHello(self, request, context):
str = request.name
return helloworld_pb2.HelloReply(message='hello, '+str) def serve():
grpcServer = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=))
helloworld_pb2_grpc.add_GreeterServicer_to_server(Greeter(), grpcServer)
grpcServer.add_insecure_port(_HOST + ':' + _PORT)
grpcServer.start() try:
while True:
time.sleep(_ONE_DAY_IN_SECONDS)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
grpcServer.stop() if __name__ == '__main__':
serve()
④ 编写locust文件,对端口50052的服务进行压测,locust文件如下:
我抄的,从这儿:http://codegist.net/code/grpc%20locust/
#!/usr/bin/env python 2.7
# -*- coding:utf- -*- import os,sys, argparse
sys.path.append("..")
import grpc
import json
import requests
import time
import random
import string from helloworld.helloworld import helloworld_pb2, helloworld_pb2_grpc
from locust import Locust, TaskSet, task, events
from locust.stats import RequestStats
from locust.events import EventHook def parse_arguments():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(prog='locust')
parser.add_argument('--hatch_rate')
parser.add_argument('--master', action='store_true')
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
opts = vars(args)
return args.host, int(args.clients), int(args.hatch_rate) #HOST, MAX_USERS_NUMBER, USERS_PRE_SECOND = parse_arguments()
HOST, MAX_USERS_NUMBER, USERS_PRE_SECOND = '127.0.0.1:50052', ,
# 分布式,需要启多台压测时,有一个master,其余为slave
slaves_connect = []
slave_report = EventHook()
ALL_SLAVES_CONNECTED = True
SLAVES_NUMBER =
def on_my_event(client_id, data):
global ALL_SLAVES_CONNECTED
if not ALL_SLAVES_CONNECTED:
slaves_connect.append(client_id)
if len(slaves_connect) == SLAVES_NUMBER:
print "All Slaves Connected"
ALL_SLAVES_CONNECTED = True
# print events.slave_report._handlers
header = {'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
import resource rsrc = resource.RLIMIT_NOFILE
soft, hard = resource.getrlimit(rsrc)
print 'RLIMIT_NOFILE soft limit starts as : ', soft soft, hard = resource.getrlimit(rsrc)
print 'RLIMIT_NOFILE soft limit change to: ', soft events.slave_report += on_my_event class GrpcLocust(Locust):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(GrpcLocust, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs) class ApiUser(GrpcLocust):
min_wait =
max_wait =
stop_timeout = class task_set(TaskSet):
def getEnviron(self, key, default):
if key in os.environ:
return os.environ[key]
else:
return default def getToken(self):
consumer_key = self.getEnviron('SELDON_OAUTH_KEY', 'oauthkey')
consumer_secret = self.getEnviron('SELDON_OAUTH_SECRET', 'oauthsecret')
params = {} params["consumer_key"] = consumer_key
params["consumer_secret"] = consumer_secret url = self.oauth_endpoint + "/token"
r = requests.get(url, params=params)
if r.status_code == requests.codes.ok:
j = json.loads(r.text)
# print j
return j["access_token"]
else:
print "failed call to get token"
return None def on_start(self):
# print "on start"
# self.oauth_endpoint = self.getEnviron('SELDON_OAUTH_ENDPOINT', "http://127.0.0.1:50053")
# self.token = self.getToken()
self.grpc_endpoint = self.getEnviron('SELDON_GRPC_ENDPOINT', "127.0.0.1:50052")
self.data_size = int(self.getEnviron('SELDON_DEFAULT_DATA_SIZE', "")) @task
def get_prediction(self):
conn = grpc.insecure_channel(self.grpc_endpoint)
client = helloworld_pb2_grpc.GreeterStub(conn)
start_time = time.time()
name = string.join(random.sample(['a','b','c','d','e','f','g'], )).replace(" ","")
request = helloworld_pb2.HelloRequest(name=name)
try:
reply = client.SayHello(request)
except Exception,e:
total_time = int((time.time() - start_time) * )
events.request_failure.fire(request_type="grpc", name=HOST, response_time=total_time, exception=e)
else:
total_time = int((time.time() - start_time) * )
events.request_success.fire(request_type="grpc", name=HOST, response_time=total_time, response_length=)
⑤ 启动locust,查看结果
locust --help可以看到命令的使用帮助。注意 -c -n -r 参数的使用需要配合 --no-web

三 问题及解决
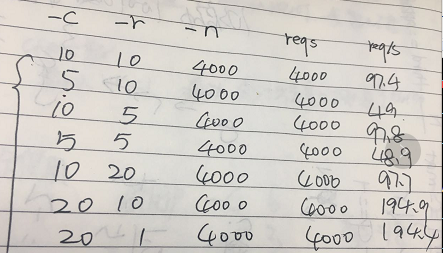
问题倒是有,但是我没解决,我不知道这个起压的req怎么设置的
原本以为 -c 模拟用户数 -r 每个用户发出的秒请求数 --- 那么服务每秒承受的压力就应该为-c * -r
但是我跑出来的结果确实这样的,特别像是-c * 10 ,大脸懵逼了
压测工具Locuse的使用的更多相关文章
- Http压测工具wrk使用指南
用过了很多压测工具,却一直没找到中意的那款.最近试了wrk感觉不错,写下这份使用指南给自己备忘用,如果能帮到你,那也很好. 安装 wrk支持大多数类UNIX系统,不支持windows.需要操作系统支持 ...
- web压测工具http_load原理分析
一.前言 http_load是一款测试web服务器性能的开源工具,从下面的网址可以下载到最新版本的http_load: http://www.acme.com/software/http_load/ ...
- [软件测试]网站压测工具Webbench源码分析
一.我与webbench二三事 Webbench是一个在linux下使用的非常简单的网站压测工具.它使用fork()模拟多个客户端同时访问我们设定的URL,测试网站在压力下工作的性能.Webbench ...
- Http压测工具wrk使用指南【转】
用过了很多压测工具,却一直没找到中意的那款.最近试了wrk感觉不错,写下这份使用指南给自己备忘用,如果能帮到你,那也很好. 安装 wrk支持大多数类UNIX系统,不支持windows.需要操作系统支持 ...
- python服务端多进程压测工具
本文描述一个python实现的多进程压测工具,这个压测工具的特点如下: 多进程 在大多数情况下,压测一般适用于IO密集型场景(如访问接口并等待返回),在这种场景下多线程多进程的区分并不明显(详情请参见 ...
- 内存压测工具Memtester
在做压力测试时,发现一个内存压测工具Memtester,可以随意设置内存占用大小,非常方便 下载地址:http://pyropus.ca/software/memtester/old-versions ...
- Http 压测工具 wrk 基本使用
Http 压测工具 wrk 基本使用 Intro wrk 是一款现代HTTP基准测试工具,能够在单个多核CPU上运行时产生显着负载.它将多线程设计与可扩展事件通知系统(如epoll和kqueue)结合 ...
- 压测工具使用(vegeta)
一.压测工具vegeta 1.介绍 Vegeta 是一个用 Go 语言编写的多功能的 HTTP 负载测试工具,它提供了命令行工具和一个开发库. 官方地址:https://github.com/tsen ...
- 003_ab http压测工具
一. ab -r -k -c 20000 -n 25000000 https://www.uuwatch.me/abtest #ab压测工具单机最大并发为20000,可以在多台机器上执行以增大并发 y ...
随机推荐
- OPEN(SAP) UI5 学习入门系列之一:扫盲与热身(下)
1 UI5代码结构 上一次我们一起用了20秒的时间完成一个UI5版的Hello World.应用打开后有一个按钮,按钮的文字是Hello World,点击这个按钮之后,按钮会慢慢的消失掉(Fade o ...
- js之验证码倒计时功能
<!DOCTYPE html> <html > <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" conten ...
- CentOS 7.0 yum安装Apache、PHP和MySQL
centos7默认将mariadb视作mysql. p.s.因为mysql被oracle收购后,原作者担心mysql闭源,所以又写了一个mariadb,这个数据库可以理解为mysql的分支. 卸载ma ...
- open和close函数
1.open函数的使用 调用open函数可以打开或创建一个文件 #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <sy ...
- ORACLE 12C RMAN 功能增强
在ORACLE 12C中对rman的功能有了不少增强,在以前的文章中写过RMAN RECOVER TABLE功能,这里另外补充rman增强的两个小功能(sql语句和数据文件分割)数据库版本 SQL&g ...
- Qt学习之秒表的实现(StopWatch) (转)
秒表对于我来说并不陌生,在之前自己学习单片机时,实现过秒表和数字钟:基本思路:开启单片机带的定时器,并设置它没10ms溢出一次,分别用三个变量hour,minute,secong记录秒表的时分秒,然后 ...
- centos 限制只能访问某个目录的php文件
vi /etc/php.ini #编辑 open_basedir = .:/tmp/ #在380行 设置表示允许访问当前目录(即PHP脚本文件所在之目录)和/tmp/目录,可以防止php木马跨站,如果 ...
- STM32的启动过程分析
对于stm32的启动过程一直心存疑惑.今天找了很多资料,进行了一个大致的分析. 1.cortex M3的复位过程(来自官方资料) 上述开机启动流程比较详细,内容较为全面,但部分步骤可以省略(红字可省略 ...
- cocos2d-js 3.0 ios平台编译打包
原帖在http://www.cocoachina.com/bbs/read.php?tid=209356 整理到github的https://github.com/faint2death/cocos2 ...
- 了解IHttpModule接口事件执行顺便 获取Session
本文转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/eflylab/archive/2008/05/29/1209767.html 最近公司一个项目让人SQL注入了-为了临时先解决这个问题,使攻 ...
