android笔记:Service
服务:在后台运行,没有界面的组件。
服务生命周期如下:
两种启动方式:
1、startService(): onCreate()-->onStartCommand()-->onDestroy().
2、bindService(): onCreate()-->onBind()-->onUnbind()-->onDestroy().
一、定义一个服务,得做到以下:
1.继承Service,重写onBind()、onCreate()、onStartCommand()和 onDestroy();
2.在AndroidManifest里面注册才能生效.
二、启动服务:
Intent startIntent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
startService(startIntent);
三、停止服务:
Intent stopIntent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
stopService(stopIntent);
四、绑定服务:
1.onBind()方法返回Binder对象;
2.创建了ServiceConnection 的匿名类,重写onServiceConnected()方法和 onServiceDisconnected()方法;
3.用bindService()方法将 Activity 和 Service 进行绑定。
bindService()方法接收三个参数,第一个参数就是 Intent 对象,第二个参数是ServiceConnection 的实例,第三个
参数则是一个标志位,可以传入 BIND_AUTO_CREATE 表示在活动和服务进行绑定后自动创建服务。
示例如下:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
bindService(bindIntent, connection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
五、解绑服务:
unbindService(connection);
六、使用IntentService
优点:
1.异步,可以在子线程处理耗时操作
2.执行完毕自动停止
代码示例如下:
MainActivity.java
package com.example.servicedemo; import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button startService;
private Button stopService;
private Button bindService;
private Button unbindService;
private MyService.DownloadBinder downloadBinder;
private Button startIntentService;
private boolean mIsBound =false;
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
downloadBinder=(MyService.DownloadBinder)service;
downloadBinder.startDownload();
downloadBinder.getProgress();
} @Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
startService=(Button)findViewById(R.id.start);
stopService=(Button)findViewById(R.id.stop);
bindService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind_service);
unbindService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind_service);
startIntentService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_intent_service);
startIntentService.setOnClickListener(this);
startService.setOnClickListener(this);
stopService.setOnClickListener(this);
bindService.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindService.setOnClickListener(this);
} @Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
switch(v.getId()) {
case R.id.start:
Intent startIntent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
startService(startIntent);
break;
case R.id.stop:
Intent stopIntent=new Intent(this,MyService.class);
stopService(stopIntent);
break;
case R.id.bind_service:
Intent bindIntent = new Intent(this, MyService.class);
bindService(bindIntent,connection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);//绑定服务
mIsBound = true;
break;
case R.id.unbind_service:
if(mIsBound) {
unbindService(connection); //解绑服务
Log.d("MainActivity","UnbindService");
mIsBound=false;
}
break;
case R.id.start_intent_service:
Log.d("MainActivity","Thread id is "+Thread.currentThread().getId());
Intent intentService=new Intent(this,MyIntentService.class);
startService(intentService);
break;
default:
break;
}
} @Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
MyService.java:
package com.example.servicedemo; import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log; public class MyService extends Service{
private DownloadBinder mBinder = new DownloadBinder();
//继承Binder的内部类,一个方法开始下载,另一个方法获取进度
class DownloadBinder extends Binder {
public void startDownload() {
Log.d("MyService", "startDownload executed");
}
public int getProgress() {
Log.d("MyService", "getProgress executed");
return 0;
}
} @Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return mBinder;
} public void onCreate(){
super.onCreate();
Log.d("MyService","onCreate executed");
} public int onStartCommand(Intent intent,int flags,int startId){
Log.d("MyService","onStartCommand executed");
return super.onStartCommand(intent,flags,startId); } public void onDestroy(){
Log.d("MyService","onDestroy executed");
super.onDestroy();
} }
MyIntentService.java:
package com.example.servicedemo; import android.app.IntentService;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.util.Log; public class MyIntentService extends IntentService{ public MyIntentService() {
super("MyIntentService");
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
} @Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.d("MyIntentService", "Thread id is " + Thread.currentThread().
getId());
} public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.d("MyIntentService", "onDestroy executed");
}
}
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" > <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/start"
android:text="start service" /> <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/stop"
android:text="stop service"
android:layout_below="@id/start"
/> <Button
android:id="@+id/bind_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Bind Service"
android:layout_below="@id/stop" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbind_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Unbind Service"
android:layout_below="@id/bind_service" /> <Button
android:id="@+id/start_intent_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Start IntentService"
android:layout_below="@id/unbind_service" /> </RelativeLayout>
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.servicedemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" /> <application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.servicedemo.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name=".MyService"
></service>
<service android:name=".MyIntentService"></service>
</application> </manifest>
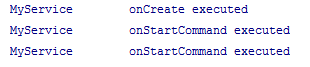
运行效果如下所示:
start Service:

多次start Service:
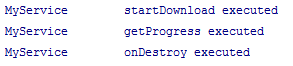
Bind Service:
start IntentService:

android笔记:Service的更多相关文章
- Android笔记二十七.Service组件入门(一).什么是Service?
转载请表明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/u012637501(嵌入式_小J的天空) 一.Service 1.Service简单介绍 Service为Android四大组件之中 ...
- Android 学习笔记 Service服务与远程通信...(AIDL)
PS:这一章节看的我有几分迷茫,不是很容易理解...不过还好总算是明白了一大半了...基本的迷惑是解决了... 学习内容: 1.跨应用启动服务... 2.跨应用绑定服务... 3.跨应用实现通信... ...
- Android 学习笔记 Service
PS:前几篇的内容光是上代码了,也没有细细的讲解..感觉这样写很不好..因此还是多一些讲解吧... 学习内容: 1.了解Service... 2.Service的启动与停止.. 3.绑定与取消绑定Se ...
- Android笔记三十四.Service综合实例二
综合实例2:client訪问远程Service服务 实现:通过一个button来获取远程Service的状态,并显示在两个文本框中. 思路:如果A应用须要与B应用进行通信,调用B应用中的getName ...
- Android笔记(五十九)Android总结:四大组件——Service篇
什么是服务? 服务(service)是Android中实现程序后台运行的解决方案,适用于去执行那些不需要和用户交互并且还需要长期运行的任务.服务的运行不依赖于任何用户界面. 服务运行在主线程中,所以在 ...
- Android笔记(十七) Android中的Service
定义和用途 Service是Android的四大组件之一,一直在后台运行,没有用户界面.Service组件通常用于为其他组件提供后台服务或者监控其他组件的运行状态,例如播放音乐.记录地理位置,监听用户 ...
- android服务Service(上)- IntentService
Android学习笔记(五一):服务Service(上)- IntentService 对于需要长期运行,例如播放音乐.长期和服务器的连接,即使已不是屏幕当前的activity仍需要运行的情况,采用服 ...
- Android:Service
Android Service: http://www.apkbus.com/android-15649-1-1.html android service 的各种用法(IPC.AIDL): http: ...
- android 远程Service以及AIDL的跨进程通信
在Android中,Service是运行在主线程中的,如果在Service中处理一些耗时的操作,就会导致程序出现ANR. 但如果将本地的Service转换成一个远程的Service,就不会出现这样的问 ...
随机推荐
- MyEclipse中复制web项目,部署之后访问报错
- R语言学习——列表
1.列表 列表是一种泛化的向量,其并没有要求所有元素都是同一类型,其元素甚至可为任意类型. 列表格式自由,为统计的计算结果的返回提供了极便利的方法. 2.列表的创建 可以用list()函数创建列表. ...
- 管理oracle 11g RAC 常用命令
1).检查集群状态: [grid@rac02 ~]$ crsctl check cluster CRS-4537: Cluster Ready Services is online CRS-4529: ...
- Spark分析之DAGScheduler
DAGScheduler概述:是一个面向Stage层面的调度器: 主要入参有: dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, ...
- django中视图处理请求方式(FBV、CBV)
FBV FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求. 在之前django的学习中,我们一直使用的是这种方式,所以不再赘述. CBV CBV(class base v ...
- Tomcat组成与工作原理
laosijikaichele 关注 0.2 2018.06.02 10:44 字数 5175 阅读 2798评论 0喜欢 8 原文:https://juejin.im/post/58eb5fdda ...
- tomcat原理分析与简单实现
tomcat原理分析与简单实现 https://blog.csdn.net/u014795347/article/details/52328221 2016年08月26日 14:48:18 卫卫羊习习 ...
- js-传送file
这是选择文件的标签 <input type="file" class="add-image-input"> 这是js实现传输文件 var addIm ...
- 文件的编辑命令-echo/cat
touch test.yaml echo "line1 line2" >> test.yaml cat test.yaml line1 line2 # 创建test.y ...
- android提权
Android的内核就是Linux,所以Android获取root其实和Linux获取root权限是一回事儿. 你 想在Linux下获取root权限的时候就是执行sudo或者su,接下来系统会提示你输 ...
