写高并发程序时慎用strncpy和sprintf
分享一下最近做程序优化的一点小心得:在写高并发交易代码时要谨慎使用strncpy和sprintf。
下面详细介绍一下这样说的原因及建议实践:
1 慎用strncpy因为它的副作用极大
我们平时使用strncpy防止字符串拷贝时溢出,常常这样写
char buf[] = {};
char str[] = "hello";
strncpy(buf, sizefo(buf), str);
这样写当然没问题,但有些人不知道的是:strncpy一行代码执行时是往buf写了sizeof(buf) = 1024个字节,而不是直观以为的strlen(str) + 1 = 6个字符。
也就是说我们为了复制6个字符却写了1024个字节,多了不少额外消耗。如果这个函数被频繁调用,会导致系统性能出现不少损失。
因为调用strncpy(dest, n, str)时,函数首先将字符从源缓冲区str逐个复制到目标缓冲区dest,直到拷贝了n碰上\0。
紧接着,strncpy函数会往buf填充\0字符直到写满n个字符。
所以我才会说上面的代码strncpy才会写了1024个字节。
可以做一个小实验:
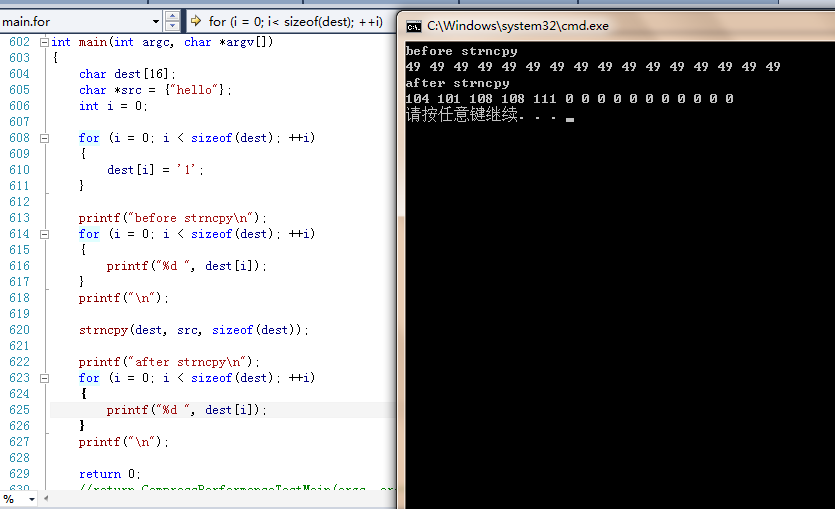
看上面代码及输出结果,我们可以知道在执行strncpy之前dest是用'1'填充的,但在执行strncpy后,前面几个字符变成hello,后面的字符全变成\0;
我个人的解决方法是写一个宏专用于往字符数组拷贝的,与大家分享一下,抛砖引玉。
// 静态断言 从vc拷贝过来(_STATIC_ASSERT) 稍微修改了一下
// 原来是typedef char __static_assert_t[ (expr) ]
// 现在是typedef char __static_assert_t[ (expr) - 1 ]
// 原因是gcc支持0字符数组
//TODO: 这里在win上编译有警告 有待优化 另外在linux宏好像不起作用 原因待查。暂时只有在win编译代码可以用
#ifndef _STATIC_ASSERT_RCC
# ifdef __GNUC__
# define _STATIC_ASSERT_RCC(expr) typedef char __static_assert_t[ (expr) - ]
# else
# define _STATIC_ASSERT_RCC(expr) do { typedef char __static_assert_t[ (expr) ]; } while ()
# endif
#endif //将src复制到字符数组arr 保证不会越界并且末尾肯定会加\0
//_STATIC_ASSERT_RCC这里作用是防止有人传字符串指针进来
#define strncpy2arr(arr, src) do { \
char *dest_ = arr; \
size_t n = strnlen(src, sizeof(arr) - ); \
_STATIC_ASSERT_RCC(sizeof(arr) != sizeof(char *)); \
memcpy(dest_, src, n); \
dest_[n] = '\0'; \
} while () #ifdef WIN32
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char dest[];
char *src = "hello 222";
int i = ; for (i = ; i < sizeof(dest); ++i)
{
dest[i] = '';
} printf("before strncpy\n");
for (i = ; i < sizeof(dest); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", dest[i]);
}
printf("\n"); strncpy2arr(dest, src);
printf("after strncpy\n");
for (i = ; i < sizeof(dest); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", dest[i]);
}
printf("\n"); strncpy(dest, src, sizeof(dest));
printf("after strncpy\n");
for (i = ; i < sizeof(dest); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", dest[i]);
}
printf("\n"); return ; //return CompressPerformanceTestMain(argc, argv);
}
#endif
2 慎用sprintf,因为它的效率比你想象的低
之前我一直没注意到sprintf效率低的问题,直到有一次使用callgrind对程序进行性能分析时,发现有相当大的资源消耗在sprintf上面,我才有所警觉。
为此,我写了一点测试代码,对常用的函数做了一下基准测试,结果如下:
|
测试内容 |
耗时(us) |
|
for循环赋值40亿次 |
13023889 |
|
调用简单函数40亿次 |
16967986 |
|
调用memset函数4亿次 (256个字节) |
6932237 |
|
调用strcpy函数4亿次 (12个字节) |
3239218 |
|
调用memcpy函数4亿次 (12个字节) |
3239201 |
|
调用strcmp函数4亿次 (12个字节) |
2500568 |
|
调用memcmp函数4亿次 (12个字节) |
2668378 |
|
调用strcpy函数4亿次 (74个字节) |
4951085 |
|
调用memcpy函数4亿次 (74个字节) |
4950890 |
|
调用strcmp函数4亿次 (74个字节) |
5551391 |
|
调用memcmp函数4亿次 (74个字节) |
3840448 |
|
调用sprintf函数8千万次 (约27个字节) |
21398106 |
|
调用scanf函数8千万次 (约27个字节) |
36158749 |
|
调用fwrite函数8千万次 |
5913579 |
|
调用fprintf函数8千万次 |
24806837 |
|
调用fread函数8千万次 |
3182704 |
|
调用fscanf函数8千万次 |
18739442 |
|
调用WriteLog函数20万次 (15个字节) |
4873746 |
|
调用WriteLog函数20万次 (47个字节) |
4846449 |
|
调用WriteLog函数20万次 (94个字节) |
4950448 |
|
|
1us = 1000ms
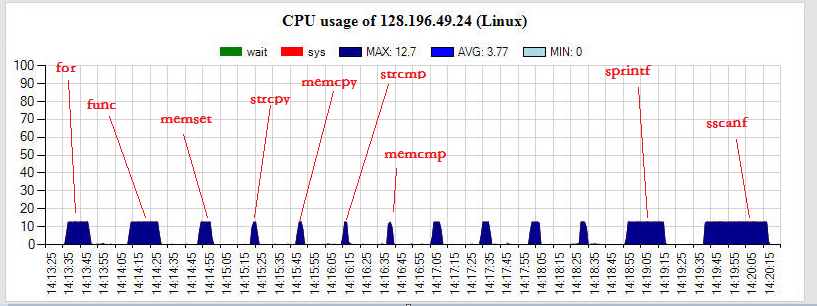
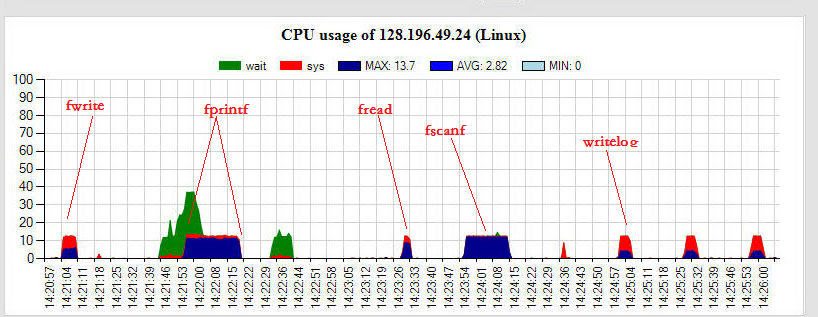
图示:scanf/printf系列函数耗时是其它常见字符串操作函数的10倍以上,甚至比io操作还耗时
测试代码见这里:
#define TEST_LOG_INF NULL, __FILE__, __LINE__
#ifdef WIN32
#define WriteLog lazy_log_output
#define LOG_ERROR NULL, __FILE__, __LINE__
#define LOG_KEY NULL, __FILE__, __LINE__
#define sleep(n) Sleep(100 * n)
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tv, struct timezone *tz)
{
SYSTEMTIME wtm;
GetLocalTime(&wtm);
tv->tv_sec = (long)(wtm.wDayOfWeek * * + wtm.wHour * + wtm.wMinute * + wtm.wSecond);
tv->tv_usec = wtm.wMilliseconds * ;
return ;
}
void InitLog(const char *logname)
{
}
#endif
struct timeval begTimes = {}, endTims = {};
void beginTimer()
{
gettimeofday(&begTimes, NULL);
}
int g_nSleepSec = ;
void stopTimer(char *userdata, const char *file, int fileno, int nSleepFlag)
{
size_t totalTranTimes;
gettimeofday(&endTims, NULL);
totalTranTimes = (size_t)(endTims.tv_sec - begTimes.tv_sec) * + (endTims.tv_usec - begTimes.tv_usec);
#ifdef WIN32
WriteLog(userdata, file, fileno, "== == end == == == totalTranTimes %lu us", (unsigned long) totalTranTimes);
#else
WriteLog(, file, fileno, "== == end == == == totalTranTimes %lu us", (unsigned long) totalTranTimes);
#endif
if (nSleepFlag)
{
WriteLog(LOG_ERROR, "sleep");
sleep(g_nSleepSec);
}
else
{
beginTimer();
}
}
void PerformanceTestLog(char *userdata, const char *file, int fileno, const char *log)
{
stopTimer(userdata, file, fileno, );
#ifdef WIN32
WriteLog(userdata, file, fileno, "== == beg == == == %s", log);
#else
WriteLog(, file, fileno, "== == beg == == == %s", log);
#endif
beginTimer();
}
int func(int argc, char *argv[], char *tmp)
{
tmp[argc] = '';
return ;
}
//基准测试
int BaseTest(unsigned long nTimes)
{
unsigned long i = ;
char tmp[], t1[], t2[], t3[];
int nTmp;
const char *strWriten;
nTimes *= ; //40亿
WriteLog(LOG_KEY, "BaseTest %lu", nTimes);
beginTimer();
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test for");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
i = i;
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test call func");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
func(, NULL, tmp);
}
stopTimer(TEST_LOG_INF, );
nTimes /= ; //4亿
WriteLog(LOG_KEY, "BaseTest %lu", nTimes);
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test memset");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
memset(tmp, , sizeof(tmp));
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test strcpy");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
strcpy(tmp, "test strcpy");
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test memcpy");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
memcpy(tmp, "test strcpy", sizeof("test strcpy"));
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test strcmp");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
if ( == strcmp(tmp, "test strcpy"))
{
i = i;
}
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test memcmp");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
if ( == memcmp(tmp, "test strcpy", sizeof("test strcpy")))
{
i = i;
}
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test strcpy1");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
strcpy(tmp, "test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpytest strcpy");
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test memcpy1");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
memcpy(tmp, "test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpytest strcpy",
sizeof("test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpytest strcpy"));
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test strcmp1");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
if ( == strcmp(tmp, "test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpytest strcpy"))
{
i = i;
}
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test memcmp1");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
if ( == memcmp(tmp, "test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpytest strcpy",
sizeof("test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpy test strcpytest strcpy")))
{
i = i;
}
}
stopTimer(TEST_LOG_INF, );
nTimes /= ; //8千万
WriteLog(LOG_KEY, "BaseTest %lu", nTimes);
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test sprintf");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
sprintf(tmp, "thiis %s testing %d", "sprintf", i);
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test sscanf");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
sscanf(tmp, "%s %s %s %d", t1, t2, t3, &nTmp);
}
{
FILE *fp;
int nStr;
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "fopen");
fp = fopen("performancetest.txt", "w");
strWriten = "this is testing write\n";
nStr = strlen(strWriten);
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test write file");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
fwrite(strWriten, , nStr, fp);
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "fflush");
fflush(fp);
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test fprintf file");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
//太过简单的fprintf好像会被自动优化成fwrite,即使没开优化选项
//例如 fprintf(fp, "%s", "strWriten");
fprintf(fp, "%s %d\n", "strWriten", i);
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "fclose");
fclose(fp);
}
{
FILE *fp;
int nStr;
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "fopen 1");
fp = fopen("performancetest.txt", "r");
nStr = strlen(strWriten);
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test read file");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
fread(tmp, , nStr, fp);
tmp[nStr] = '\0';
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "test fscanf file");
tmp[] = t1[] = '\0';
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
fscanf(fp, "%s %s", tmp, t1);
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "fclose");
fclose(fp);
}
fclose(fopen("performancetest.txt", "w"));
nTimes /= ; //20万
WriteLog(LOG_KEY, "BaseTest %lu", nTimes);
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "WriteLog 1");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
WriteLog(LOG_ERROR, "this is loging");
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "WriteLog 2");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
WriteLog(LOG_ERROR, "this is loging this is loging this is loging");
}
PerformanceTestLog(TEST_LOG_INF, "WriteLog 3");
for (i = ; i < nTimes; ++i)
{
WriteLog(LOG_ERROR, "this is loging this is loging this is loging this is loging this is loging this is loging");
}
stopTimer(TEST_LOG_INF, );
return ;
}
从基准测试结果可以知道,sprintf系列函数效率是比较低的,是我们常见的字符串操作函数的1/10以下。
我个人的解决方案是sprintf该用还是用,但有些情况不是特别必要用的情况,用自己写一些小函数代替。例如下面这个宏是用来代替sprintf(buf, "%02d", i)的
//sprintf比较慢 这里需要写一些简单的字符串组装函数
//这个是代替%02d的(但不会添加\0结尾)顾名思义,传入的值需要保证0 <= vallue < 100
//再次提醒注意,这里为了方便调用,不会添加\0! 不会添加\0! 不会添加\0!
#define itoaLt100Ge0(value, buff_output) do \
{\
int value_ = (int)(value);\
char *buff_output_ = (buff_output);\
if ((value_) >= ) { int nDigit_ = value_ / ; buff_output_[] = '' + nDigit_; buff_output_[] = '' + (value_ - nDigit_ * ); }\
else { buff_output_[] = ''; buff_output_[] = '' + (value_); } \
} while ()
总结一下就是:高并发交易需要慎用strncpy和sprintf,因为不恰当使用它们可能会成为程序性能瓶颈。
如果大家有啥想法,欢迎分享,我是黄词辉,一个程序员 ^_^
写高并发程序时慎用strncpy和sprintf的更多相关文章
- 【Java并发基础】利用面向对象的思想写好并发程序
前言 下面简单总结学习Java并发的笔记,关于如何利用面向对象思想写好并发程序的建议.面向对象的思想和并发编程属于两个领域,但是在Java中这两个领域却可以融合到一起.在Java语言中,面向对象编程的 ...
- java高并发程序设计模式-并发级别:阻塞、无障碍、无锁、无等待【转载】
一般认为并发可以分为阻塞与非阻塞,对于非阻塞可以进一步细分为无障碍.无锁.无等待,下面就对这几个并发级别,作一些简单的介绍. 1.阻塞 阻塞是指一个线程进入临界区后,其它线程就必须在临界区外等待,待进 ...
- javascript小记一则:今天在写VS2005——.NET程序时,写的一个JS图片示例案例
源码如下,如遇调试问题,可以找我解决: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" &quo ...
- OpenResty + Lua访问Redis,实现高并发访问时的毫秒级响应打回
一.lua中redis的配置依赖: 1.OpenResty的lua访问redis的插件:https://github.com/openresty/lua-resty-redis 二.下载后,导入对应的 ...
- 分布式大数据高并发的web开发框架
一.引言 通常我们认为静态网页html的网站速度是最快的,但是自从有了动态网页之后,很多交互数据都从数据库查询而来,数据也是经常变化的,除了一些新闻资讯类的网站,使用html静态化来提高访问速度是不太 ...
- Golang适合高并发场景的原因分析
http://blog.csdn.NET/ghj1976/article/details/27996095 典型的两个现实案例: 我们先看两个用Go做消息推送的案例实际处理能力. 360消息推送的数据 ...
- 高并发系统保护~ing
由于公司业务发展,需要考虑一些高并发系统保护的问题,整理记录一下. 当发现你的系统出现访问卡顿,服务器各种性能指标接近100%(如果一个初创型企业系统正常运行情况下出现这个问题,那么应该恭喜你,你懂得 ...
- 朱晔的互联网架构实践心得S2E6:浅谈高并发架构设计的16招
朱晔的互联网架构实践心得S2E6:浅谈高并发架构设计的16招 概览 标题中的高并发架构设计是指设计一套比较合适的架构来应对请求.并发量很大的系统,使系统的稳定性.响应时间符合预期并且能在极端的情况下自 ...
- 15套java互联网架构师、高并发、集群、负载均衡、高可用、数据库设计、缓存、性能优化、大型分布式 项目实战视频教程
* { font-family: "Microsoft YaHei" !important } h1 { color: #FF0 } 15套java架构师.集群.高可用.高可扩 展 ...
随机推荐
- September 14th 2017 Week 37th Thursday
Don't let the past steal your present. 别让过去悄悄偷走了我们的当下. We take what we can get and make the best of ...
- 我的Java之旅——之后的学习计划
在写完第一个Java程序之后,对于一些最最基本的东西有了大致的了解,对于之后的学习,我做了简单的计划. 7月17号:补充一些基本内容. 7月18.19号: 1. Java的一些常用类,包括 :Nu ...
- 【Alpha】事后诸葛亮
一. 项目的预期计划 / 项目的现实进展 详见Alpha冲刺博客第一篇 二. 完成项目过程中的体会 详见Alpha冲刺博客第十二篇 三. 团队成员的分工及在Alpha阶段的工作量比例 成员 职务 博客 ...
- Matlab面向对象编程基础
DeepLab是一款基于Matlab面向对象编程的深度学习工具箱,所以了解Matlab面向对象编程的特点是必要的.笔者在做Matlab面向对象编程的时候发现无论是互联网上还是书店里卖的各式Matlab ...
- 扯不清楚的virtual和abstract
定义Person类: class Person { public void Say() { Console.WriteLine("I am a person"); } } 现在,我 ...
- HBase学习之路 (十)HBase表的设计原则
建表高级属性 下面几个 shell 命令在 hbase 操作中可以起到很大的作用,且主要体现在建表的过程中,看 下面几个 create 属性 1. BLOOMFILTER 默认是 NONE 是否使用布 ...
- C# 通过word模板动态生成Word
object oMissing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value; Word._Application oWord = new Word.Application(); ...
- datagrid 完整dom结构
<!-- datagrid的最外层容器,可以使用$(target).datagrid('getPanel')或者$.data(target,'datagrid').panel得到这个DOM对象, ...
- PAT乙级1027
1027 打印沙漏 (20 分) 本题要求你写个程序把给定的符号打印成沙漏的形状.例如给定17个“*”,要求按下列格式打印 ***** *** * *** ***** 所谓“沙漏形状”,是指每行输 ...
- Struts2 的ActionContext 详解
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/shaohz2014/p/3962779.html ActionContext是Action的上下文,Struts2自动在其中保存了一些在Actio ...
