HDU 6631 line symmetric(枚举)
首先能想到的是至少有一对相邻点或者中间间隔一个点的点对满足轴对称,那么接下来只需要枚举剩下的点对是否满足至多移动一个点可以满足要求。
第一种情况,对于所有点对都满足要求,那么Yes。
第二种情况,有一个点不满足要求,那么显然这种情况只可能是奇数点的时候才出现,那么只需要将这个点移到对称轴上则满足要求,那么Yes。
第三种情况,有两个点不满足要求,然后我们需要枚举这两个点对应的对称点是否满足要求,对于其中一个点的对称点判断他是否和之前所有点重合,以及判断这个点是否在对称轴上。
这样还不够,还需要考虑对于对称轴两边的可能的对应的对称点,他们是不是在对应一侧,如果两个点都不在对应的一侧,说明这两个点自交,则不能满足要求,直接跳过。
多注意细节吧,现场wa到自闭。
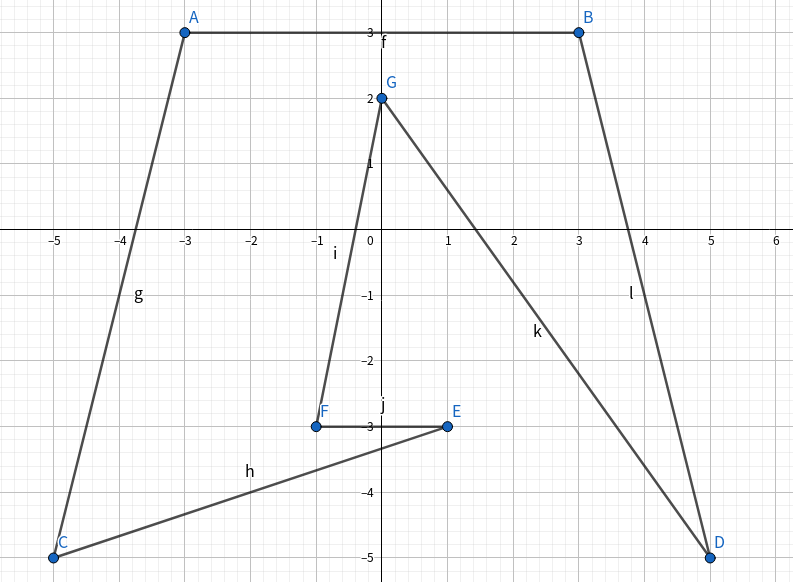
数据:
5
-100 -100
0 0
-100 100
2 -1
100 1
N 7
-3 3
-5 -5
1 -3
-1 -3
0 2
5 -5
3 3
N
附图说明:
// ——By DD_BOND //#include<bits/stdc++.h>
//#include<unordered_map>
//#include<unordered_set>
#include<functional>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
//#include<ext/rope>
#include<iomanip>
#include<climits>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstddef>
#include<cstdio>
#include<memory>
#include<vector>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<deque>
#include<ctime>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set> #define fi first
#define se second
#define MP make_pair
#define pb push_back typedef long long ll; using namespace std; const int MAXN=1e3+;
const double eps=1e-;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f; inline int dcmp(double x){
if(fabs(x)<eps) return ;
return (x>? : -);
} inline double sqr(double x){ return x*x; } struct Point{
double x,y;
Point(){ x=,y=; }
Point(double _x,double _y):x(_x),y(_y){}
void input(){ scanf("%lf%lf",&x,&y); }
bool operator ==(const Point &b)const{
return (dcmp(x-b.x)==&&dcmp(y-b.y)==);
}
Point operator +(const Point &b)const{
return Point(x+b.x,y+b.y);
}
Point operator -(const Point &b)const{
return Point(x-b.x,y-b.y);
}
Point operator *(double a){
return Point(x*a,y*a);
}
Point operator /(double a){
return Point(x/a,y/a);
}
double len2(){ //长度平方
return sqr(x)+sqr(y);
}
Point rotate_left(){ //逆时针旋转90度
return Point(-y,x);
}
}; inline double cross(Point a,Point b){ //叉积
return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;
} inline double dot(Point a,Point b){ //点积
return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;
} struct Line{
Point s,e;
Line(){}
Line(Point _s,Point _e):s(_s),e(_e){} //两点确定直线
}; int relation(Point p,Line l){ //点和向量关系 1:左侧 2:右侧 3:在线上
int c=dcmp(cross(p-l.s,l.e-l.s));
if(c<) return ;
else if(c>) return ;
else return ;
} Point projection(Point p,Line a){ //点在直线上的投影
return a.s+(((a.e-a.s)*dot(a.e-a.s,p-a.s))/(a.e-a.s).len2());
} Point symmetry(Point p,Line a){ //点关于直线的对称点
Point q=projection(p,a);
return Point(*q.x-p.x,*q.y-p.y);
} int vis[MAXN];
vector<Line>st;
Point point[MAXN]; int main(void){
int T; scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
int n,ans=; scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=;i<n;i++) point[i].input();
for(int i=;i<n&&!ans;i++){
int s=i,t=(i+)%n;
Point mid=(point[s]+point[t])/,vec=(point[s]-point[t]).rotate_left();
Line line(mid,mid+vec);
int num=,error=;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
while(!vis[s]&&!vis[t]){
vis[s]=,vis[t]=;
Point p1=(point[s]+point[t])/,dir=(point[s]-point[t]).rotate_left();
Point p2=p1+dir;
if(dcmp(cross(point[i]-mid,vec))*dcmp(cross(point[s]-mid,vec))<&&dcmp(cross(point[(i+)%n]-mid,vec))*dcmp(cross(point[t]-mid,vec))<) error=;
if(relation(p1,line)==&&relation(p2,line)==){
if(s!=t) num+=;
else num++;
}
s=(s-+n)%n,t=(t+)%n;
}
if(error) continue;
if(num+>=n) ans=;
else if(num+==n){
s=i,t=(i+)%n;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
while(!vis[s]&&!vis[t]){
vis[s]=,vis[t]=;
Point p1=(point[s]+point[t])/,vec=(point[s]-point[t]).rotate_left();
Point p2=p1+vec;
if(relation(p1,line)!=||relation(p2,line)!=){
if(relation(point[s],line)!=&&relation(point[t],line)!=){
int f1=,f2=;
Point s1=symmetry(point[s],line),s2=symmetry(point[t],line);
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
if(point[j]==s1)
f1=;
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
if(point[j]==s2)
f2=;
if(!f2||!f1) ans=;
}
break;
}
s=(s-+n)%n,t=(t+)%n;
}
}
}
for(int i=;i<n&&!ans;i++){
int s=(i-+n)%n,t=(i+)%n;
Point mid=(point[s]+point[t])/,vec=(point[s]-point[t]).rotate_left();
Line line(mid,mid+vec);
int num=,error=; s=t=i;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
while(!vis[s]&&!vis[t]){
vis[s]=,vis[t]=;
Point p1=(point[s]+point[t])/,dir=(point[s]-point[t]).rotate_left();
Point p2=p1+dir;
if(dcmp(cross(point[(i-+n)%n]-mid,vec))*dcmp(cross(point[s]-mid,vec))<&&dcmp(cross(point[(i+)%n]-mid,vec))*dcmp(cross(point[t]-mid,vec))<) error=;
if(relation(p1,line)==&&relation(p2,line)==){
if(s!=t) num+=;
else num++;
}
s=(s-+n)%n,t=(t+)%n;
}
if(error) continue;
if(num+>=n) ans=;
else if(num+==n){
s=t=i;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
while(!vis[s]&&!vis[t]){
vis[s]=,vis[t]=;
Point p1=(point[s]+point[t])/,vec=(point[s]-point[t]).rotate_left();
Point p2=p1+vec;
if(relation(p1,line)!=||relation(p2,line)!=){
if(relation(point[s],line)!=&&relation(point[t],line)!=){
int f1=,f2=;
Point s1=symmetry(point[s],line),s2=symmetry(point[t],line);
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
if(point[j]==s1)
f1=;
for(int j=;j<n;j++)
if(point[j]==s2)
f2=;
if(!f2||!f1) ans=;
}
break;
}
s=(s-+n)%n,t=(t+)%n;
}
}
}
if(ans) puts("Y");
else puts("N");
}
return ;
}
HDU 6631 line symmetric(枚举)的更多相关文章
- HDU 6631 line symmetric 计算几何
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6631 题意:共\(T\)组数据,每组数据给出\(n\)个点的坐标,这\(n\)个点按顺序给出,相邻的点 ...
- HDU 3400 Line belt (三分再三分)
HDU 3400 Line belt (三分再三分) ACM 题目地址: pid=3400" target="_blank" style="color:rgb ...
- HDU 5778 abs (枚举)
abs 题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5778 Description Given a number x, ask positive ...
- 三分套三分 --- HDU 3400 Line belt
Line belt Problem's Link: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3400 Mean: 给出两条平行的线段AB, CD,然后一 ...
- HDU 3835 R(N)(枚举)
题目链接 Problem Description We know that some positive integer x can be expressed as x=A^2+B^2(A,B are ...
- HDU 4709 Herding (枚举)
Herding Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Sub ...
- HDU 4462Scaring the Birds(枚举所有状态)
Scaring the Birds Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others ...
- 2015多校第6场 HDU 5358 First One 枚举,双指针
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5358 题意:如题. 解法:观察式子发现,由于log函数的存在,使得这个函数的值域<=34,然后我 ...
- HDU 4431 Mahjong(枚举+模拟)(2012 Asia Tianjin Regional Contest)
Problem Description Japanese Mahjong is a four-player game. The game needs four people to sit around ...
随机推荐
- ubuntu16.04 配置tomcat开机启动
使用脚本方式设置开机启动 1.将tomcat目录下/bin中的catalina.sh拷贝到/etc/init.d下: cp /usr/local/java/apache-tomcat-/bin/cat ...
- 基于flask的可视化动漫分析网站【python入门必学】
课程设计项目名称:基于flask的可视化动漫分析网站,如果你在学习Python的过程中,往往因为没有好的教程或者没人指导从而导致自己容易放弃,为此我建了个Python交流.裙 :一久武其而而流一思(数 ...
- [CF434D Div1] Tree
问题描述 给定一颗 n 个点的树,树边带权,试求一个排列 P,使下式的值最大 \[ \sum_{i=1}^{n-1}maxflow(P_i,P_{i+1}) \] 其中 maxflow(s, t) 表 ...
- vue组件学习(一)
1, vue中的 is 的用法,有时候我们需要把一个组件绑定到指定的标签下,比如把tr组件放到table下,直接这样写是不行的, <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang ...
- js 获取滚动位置,滚动到指定位置,平滑滚动
1.获取当前滚动条位置信息 var top = dom.scrollTop; // 获取y轴上的滚动位置 var left = dom.scrollLeft; // 获取x轴上的滚动位置 2.滚动到指 ...
- mysql LEFT JOIN关键字 语法
mysql LEFT JOIN关键字 语法 作用:LEFT JOIN 关键字会从左表 (table_name1) 那里返回所有的行,即使在右表 (table_name2) 中没有匹配的行. 大理石构件 ...
- POJ 2385 Apple Catching ( 经典DP )
题意 : 有两颗苹果树,在 1~T 的时间内会有两颗中的其中一颗落下一颗苹果,一头奶牛想要获取最多的苹果,但是它能够在树间转移的次数为 W 且奶牛一开始是在第一颗树下,请编程算出最多的奶牛获得的苹果数 ...
- github 的 fork 取消功能
进入该 fork 目录后 找到 Settings 点击后拉到底 找到含有 Delete 字样的按钮点击 弹出的对话框输入你删除的这个项目名 后删除 链接
- 实用工具/API
实用工具/API PNG图片无损压缩 在线给图片加水印 随机密码生成 随机头像生成 微博一键清理工具 CSS压缩 在线工具 免费虚拟主机 技术摘要 https://github.com/biezhi/ ...
- Xcode Server持续集成
这是一篇2017-11-12 年我还在 ezbuy 的一篇文章,时间过去很早了,最近在整理笔记的时候发现了, 同步过来,文章内容现在是否有效不确定,应该大差不差,读者仅做参考 最后更新 2017-11 ...
