使用flink Table &Sql api来构建批量和流式应用(2)Table API概述
从flink的官方文档,我们知道flink的编程模型分为四层,sql层是最高层的api,Table api是中间层,DataStream/DataSet Api 是核心,stateful Streaming process层是底层实现。
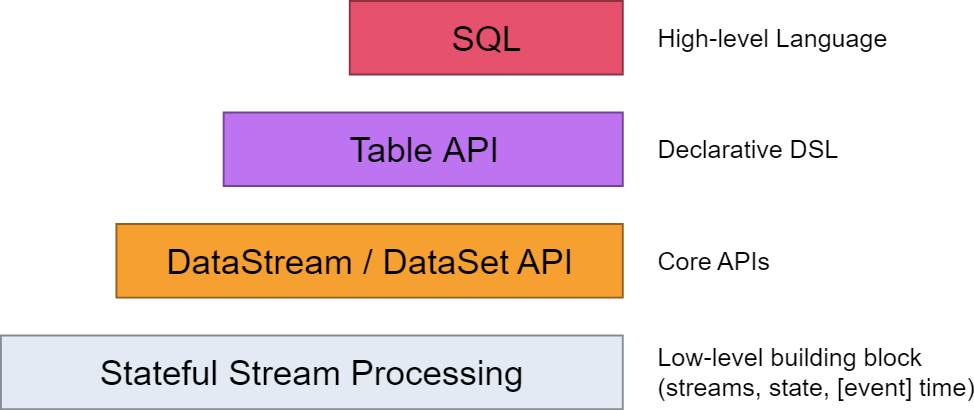
其中,
flink dataset api使用及原理 介绍了DataSet Api
flink DataStream API使用及原理介绍了DataStream Api
flink中的时间戳如何使用?---Watermark使用及原理 介绍了底层实现的基础Watermark
flink window实例分析 介绍了window的概念及使用原理
Flink中的状态与容错 介绍了State的概念及checkpoint,savepoint的容错机制
上篇<使用flink Table &Sql api来构建批量和流式应用(1)Table的基本概念>介绍了Table的基本概念及使用方法
本篇主要看看Table Api有哪些功能?
org.apache.flink.table.api.Table抽象了Table Api的功能
/**
* A Table is the core component of the Table API.
* Similar to how the batch and streaming APIs have DataSet and DataStream,
* the Table API is built around {@link Table}.
*
* <p>Use the methods of {@link Table} to transform data. Use {@code TableEnvironment} to convert a
* {@link Table} back to a {@code DataSet} or {@code DataStream}.
*
* <p>When using Scala a {@link Table} can also be converted using implicit conversions.
*
* <p>Java Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
* BatchTableEnvironment tEnv = BatchTableEnvironment.create(env);
*
* DataSet<Tuple2<String, Integer>> set = ...
* tEnv.registerTable("MyTable", set, "a, b");
*
* Table table = tEnv.scan("MyTable").select(...);
* ...
* Table table2 = ...
* DataSet<MyType> set2 = tEnv.toDataSet(table2, MyType.class);
* }
* </pre>
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* val env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
* val tEnv = BatchTableEnvironment.create(env)
*
* val set: DataSet[(String, Int)] = ...
* val table = set.toTable(tEnv, 'a, 'b)
* ...
* val table2 = ...
* val set2: DataSet[MyType] = table2.toDataSet[MyType]
* }
* </pre>
*
* <p>Operations such as {@code join}, {@code select}, {@code where} and {@code groupBy} either
* take arguments in a Scala DSL or as an expression String. Please refer to the documentation for
* the expression syntax.
*/
(1) 查询select
/**
* Performs a selection operation. Similar to a SQL SELECT statement. The field expressions
* can contain complex expressions and aggregations.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.select("key, value.avg + ' The average' as average")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table select(String fields); /**
* Performs a selection operation. Similar to a SQL SELECT statement. The field expressions
* can contain complex expressions and aggregations.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.select('key, 'value.avg + " The average" as 'average)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table select(Expression... fields);
(2) 条件where
/**
* Filters out elements that don't pass the filter predicate. Similar to a SQL WHERE
* clause.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.where("name = 'Fred'")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table where(String predicate); /**
* Filters out elements that don't pass the filter predicate. Similar to a SQL WHERE
* clause.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.where('name === "Fred")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table where(Expression predicate);
(3)过滤Filter
/**
* Filters out elements that don't pass the filter predicate. Similar to a SQL WHERE
* clause.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.filter("name = 'Fred'")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table filter(String predicate); /**
* Filters out elements that don't pass the filter predicate. Similar to a SQL WHERE
* clause.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.filter('name === "Fred")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table filter(Expression predicate);
(4) distinct
/**
* Removes duplicate values and returns only distinct (different) values.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.select("key, value").distinct()
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table distinct();
(5) group by
/**
* Groups the elements on some grouping keys. Use this before a selection with aggregations
* to perform the aggregation on a per-group basis. Similar to a SQL GROUP BY statement.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.groupBy("key").select("key, value.avg")
* }
* </pre>
*/
GroupedTable groupBy(String fields); /**
* Groups the elements on some grouping keys. Use this before a selection with aggregations
* to perform the aggregation on a per-group basis. Similar to a SQL GROUP BY statement.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.groupBy('key).select('key, 'value.avg)
* }
* </pre>
*/
GroupedTable groupBy(Expression... fields);
(6) order by
/**
* Sorts the given {@link Table}. Similar to SQL ORDER BY.
* The resulting Table is sorted globally sorted across all parallel partitions.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.orderBy("name.desc")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table orderBy(String fields); /**
* Sorts the given {@link Table}. Similar to SQL ORDER BY.
* The resulting Table is globally sorted across all parallel partitions.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.orderBy('name.desc)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table orderBy(Expression... fields);
(7) map
/**
* Performs a map operation with an user-defined scalar function or a built-in scalar function.
* The output will be flattened if the output type is a composite type.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* ScalarFunction func = new MyMapFunction();
* tableEnv.registerFunction("func", func);
* tab.map("func(c)");
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table map(String mapFunction); /**
* Performs a map operation with an user-defined scalar function or built-in scalar function.
* The output will be flattened if the output type is a composite type.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* val func = new MyMapFunction()
* tab.map(func('c))
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table map(Expression mapFunction); /**
* Performs a flatMap operation with an user-defined table function or built-in table function.
* The output will be flattened if the output type is a composite type.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* TableFunction func = new MyFlatMapFunction();
* tableEnv.registerFunction("func", func);
* table.flatMap("func(c)");
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table flatMap(String tableFunction); /**
* Performs a flatMap operation with an user-defined table function or built-in table function.
* The output will be flattened if the output type is a composite type.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* val func = new MyFlatMapFunction
* table.flatMap(func('c))
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table flatMap(Expression tableFunction);
(8) aggregate
/**
* Performs a global aggregate operation with an aggregate function. You have to close the
* {@link #aggregate(String)} with a select statement. The output will be flattened if the
* output type is a composite type.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* AggregateFunction aggFunc = new MyAggregateFunction()
* tableEnv.registerFunction("aggFunc", aggFunc);
* table.aggregate("aggFunc(a, b) as (f0, f1, f2)")
* .select("f0, f1")
* }
* </pre>
*/
AggregatedTable aggregate(String aggregateFunction); /**
* Performs a global aggregate operation with an aggregate function. You have to close the
* {@link #aggregate(Expression)} with a select statement. The output will be flattened if the
* output type is a composite type.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* val aggFunc = new MyAggregateFunction
* table.aggregate(aggFunc('a, 'b) as ('f0, 'f1, 'f2))
* .select('f0, 'f1)
* }
* </pre>
*/
AggregatedTable aggregate(Expression aggregateFunction); /**
* Perform a global flatAggregate without groupBy. FlatAggregate takes a TableAggregateFunction
* which returns multiple rows. Use a selection after the flatAggregate.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* TableAggregateFunction tableAggFunc = new MyTableAggregateFunction();
* tableEnv.registerFunction("tableAggFunc", tableAggFunc);
* tab.flatAggregate("tableAggFunc(a, b) as (x, y, z)")
* .select("x, y, z")
* }
* </pre>
*/
FlatAggregateTable flatAggregate(String tableAggregateFunction); /**
* Perform a global flatAggregate without groupBy. FlatAggregate takes a TableAggregateFunction
* which returns multiple rows. Use a selection after the flatAggregate.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* val tableAggFunc = new MyTableAggregateFunction
* tab.flatAggregate(tableAggFunc('a, 'b) as ('x, 'y, 'z))
* .select('x, 'y, 'z)
* }
* </pre>
*/
FlatAggregateTable flatAggregate(Expression tableAggregateFunction);
(9)列的管理
/**
* Adds additional columns. Similar to a SQL SELECT statement. The field expressions
* can contain complex expressions, but can not contain aggregations. It will throw an exception
* if the added fields already exist.
*
* <p>Example:
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.addColumns("a + 1 as a1, concat(b, 'sunny') as b1")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table addColumns(String fields); /**
* Adds additional columns. Similar to a SQL SELECT statement. The field expressions
* can contain complex expressions, but can not contain aggregations. It will throw an exception
* if the added fields already exist.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.addColumns('a + 1 as 'a1, concat('b, "sunny") as 'b1)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table addColumns(Expression... fields); /**
* Adds additional columns. Similar to a SQL SELECT statement. The field expressions
* can contain complex expressions, but can not contain aggregations. Existing fields will be
* replaced if add columns name is the same as the existing column name. Moreover, if the added
* fields have duplicate field name, then the last one is used.
*
* <p>Example:
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.addOrReplaceColumns("a + 1 as a1, concat(b, 'sunny') as b1")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table addOrReplaceColumns(String fields); /**
* Adds additional columns. Similar to a SQL SELECT statement. The field expressions
* can contain complex expressions, but can not contain aggregations. Existing fields will be
* replaced. If the added fields have duplicate field name, then the last one is used.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.addOrReplaceColumns('a + 1 as 'a1, concat('b, "sunny") as 'b1)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table addOrReplaceColumns(Expression... fields); /**
* Renames existing columns. Similar to a field alias statement. The field expressions
* should be alias expressions, and only the existing fields can be renamed.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.renameColumns("a as a1, b as b1")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table renameColumns(String fields); /**
* Renames existing columns. Similar to a field alias statement. The field expressions
* should be alias expressions, and only the existing fields can be renamed.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.renameColumns('a as 'a1, 'b as 'b1)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table renameColumns(Expression... fields); /**
* Drops existing columns. The field expressions should be field reference expressions.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.dropColumns("a, b")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table dropColumns(String fields); /**
* Drops existing columns. The field expressions should be field reference expressions.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.dropColumns('a, 'b)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table dropColumns(Expression... fields);
(10) window操作
/**
* Groups the records of a table by assigning them to windows defined by a time or row interval.
*
* <p>For streaming tables of infinite size, grouping into windows is required to define finite
* groups on which group-based aggregates can be computed.
*
* <p>For batch tables of finite size, windowing essentially provides shortcuts for time-based
* groupBy.
*
* <p><b>Note</b>: Computing windowed aggregates on a streaming table is only a parallel operation
* if additional grouping attributes are added to the {@code groupBy(...)} clause.
* If the {@code groupBy(...)} only references a GroupWindow alias, the streamed table will be
* processed by a single task, i.e., with parallelism 1.
*
* @param groupWindow groupWindow that specifies how elements are grouped.
* @return A windowed table.
*/
GroupWindowedTable window(GroupWindow groupWindow); /**
* Defines over-windows on the records of a table.
*
* <p>An over-window defines for each record an interval of records over which aggregation
* functions can be computed.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* table
* .window(Over partitionBy 'c orderBy 'rowTime preceding 10.seconds as 'ow)
* .select('c, 'b.count over 'ow, 'e.sum over 'ow)
* }
* </pre>
*
* <p><b>Note</b>: Computing over window aggregates on a streaming table is only a parallel
* operation if the window is partitioned. Otherwise, the whole stream will be processed by a
* single task, i.e., with parallelism 1.
*
* <p><b>Note</b>: Over-windows for batch tables are currently not supported.
*
* @param overWindows windows that specify the record interval over which aggregations are
* computed.
* @return An OverWindowedTable to specify the aggregations.
*/
OverWindowedTable window(OverWindow... overWindows);
(11) 表关联
包括Inner join和OuterJoin
/**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary. You can use
* where and select clauses after a join to further specify the behaviour of the join.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} .
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.join(right).where("a = b && c > 3").select("a, b, d")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table join(Table right); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} .
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.join(right, "a = b")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table join(Table right, String joinPredicate); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} .
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.join(right, 'a === 'b).select('a, 'b, 'd)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table join(Table right, Expression joinPredicate); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL left outer join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} and its
* {@code TableConfig} must have null check enabled (default).
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.leftOuterJoin(right).select("a, b, d")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table leftOuterJoin(Table right); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL left outer join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} and its
* {@code TableConfig} must have null check enabled (default).
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.leftOuterJoin(right, "a = b").select("a, b, d")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table leftOuterJoin(Table right, String joinPredicate); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL left outer join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} and its
* {@code TableConfig} must have null check enabled (default).
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.leftOuterJoin(right, 'a === 'b).select('a, 'b, 'd)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table leftOuterJoin(Table right, Expression joinPredicate); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL right outer join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} and its
* {@code TableConfig} must have null check enabled (default).
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.rightOuterJoin(right, "a = b").select("a, b, d")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table rightOuterJoin(Table right, String joinPredicate); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL right outer join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} and its
* {@code TableConfig} must have null check enabled (default).
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.rightOuterJoin(right, 'a === 'b).select('a, 'b, 'd)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table rightOuterJoin(Table right, Expression joinPredicate); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL full outer join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} and its
* {@code TableConfig} must have null check enabled (default).
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.fullOuterJoin(right, "a = b").select("a, b, d")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table fullOuterJoin(Table right, String joinPredicate); /**
* Joins two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL full outer join. The fields of the two joined
* operations must not overlap, use {@code as} to rename fields if necessary.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment} and its
* {@code TableConfig} must have null check enabled (default).
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.fullOuterJoin(right, 'a === 'b).select('a, 'b, 'd)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table fullOuterJoin(Table right, Expression joinPredicate); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL inner join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of the
* table is joined with all rows produced by the table function.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction<String> {
* public void eval(String str) {
* str.split("#").forEach(this::collect);
* }
* }
*
* TableFunction<String> split = new MySplitUDTF();
* tableEnv.registerFunction("split", split);
* table.joinLateral("split(c) as (s)").select("a, b, c, s");
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table joinLateral(String tableFunctionCall); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL inner join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of the
* table is joined with all rows produced by the table function.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction[String] {
* def eval(str: String): Unit = {
* str.split("#").foreach(collect)
* }
* }
*
* val split = new MySplitUDTF()
* table.joinLateral(split('c) as ('s)).select('a, 'b, 'c, 's)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table joinLateral(Expression tableFunctionCall); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL inner join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of the
* table is joined with all rows produced by the table function.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction<String> {
* public void eval(String str) {
* str.split("#").forEach(this::collect);
* }
* }
*
* TableFunction<String> split = new MySplitUDTF();
* tableEnv.registerFunction("split", split);
* table.joinLateral("split(c) as (s)", "a = s").select("a, b, c, s");
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table joinLateral(String tableFunctionCall, String joinPredicate); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL inner join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of the
* table is joined with all rows produced by the table function.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction[String] {
* def eval(str: String): Unit = {
* str.split("#").foreach(collect)
* }
* }
*
* val split = new MySplitUDTF()
* table.joinLateral(split('c) as ('s), 'a === 's).select('a, 'b, 'c, 's)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table joinLateral(Expression tableFunctionCall, Expression joinPredicate); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL left outer join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of
* the table is joined with all rows produced by the table function. If the table function does
* not produce any row, the outer row is padded with nulls.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction<String> {
* public void eval(String str) {
* str.split("#").forEach(this::collect);
* }
* }
*
* TableFunction<String> split = new MySplitUDTF();
* tableEnv.registerFunction("split", split);
* table.leftOuterJoinLateral("split(c) as (s)").select("a, b, c, s");
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table leftOuterJoinLateral(String tableFunctionCall); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL left outer join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of
* the table is joined with all rows produced by the table function. If the table function does
* not produce any row, the outer row is padded with nulls.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction[String] {
* def eval(str: String): Unit = {
* str.split("#").foreach(collect)
* }
* }
*
* val split = new MySplitUDTF()
* table.leftOuterJoinLateral(split('c) as ('s)).select('a, 'b, 'c, 's)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table leftOuterJoinLateral(Expression tableFunctionCall); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL left outer join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of
* the table is joined with all rows produced by the table function. If the table function does
* not produce any row, the outer row is padded with nulls.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction<String> {
* public void eval(String str) {
* str.split("#").forEach(this::collect);
* }
* }
*
* TableFunction<String> split = new MySplitUDTF();
* tableEnv.registerFunction("split", split);
* table.leftOuterJoinLateral("split(c) as (s)", "a = s").select("a, b, c, s");
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table leftOuterJoinLateral(String tableFunctionCall, String joinPredicate); /**
* Joins this {@link Table} with an user-defined {@link TableFunction}. This join is similar to
* a SQL left outer join with ON TRUE predicate but works with a table function. Each row of
* the table is joined with all rows produced by the table function. If the table function does
* not produce any row, the outer row is padded with nulls.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* class MySplitUDTF extends TableFunction[String] {
* def eval(str: String): Unit = {
* str.split("#").foreach(collect)
* }
* }
*
* val split = new MySplitUDTF()
* table.leftOuterJoinLateral(split('c) as ('s), 'a === 's).select('a, 'b, 'c, 's)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table leftOuterJoinLateral(Expression tableFunctionCall, Expression joinPredicate);
(12) 集合操作
/**
* Minus of two {@link Table}s with duplicate records removed.
* Similar to a SQL EXCEPT clause. Minus returns records from the left table that do not
* exist in the right table. Duplicate records in the left table are returned
* exactly once, i.e., duplicates are removed. Both tables must have identical field types.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment}.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.minus(right)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table minus(Table right); /**
* Minus of two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL EXCEPT ALL.
* Similar to a SQL EXCEPT ALL clause. MinusAll returns the records that do not exist in
* the right table. A record that is present n times in the left table and m times
* in the right table is returned (n - m) times, i.e., as many duplicates as are present
* in the right table are removed. Both tables must have identical field types.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment}.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.minusAll(right)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table minusAll(Table right); /**
* Unions two {@link Table}s with duplicate records removed.
* Similar to a SQL UNION. The fields of the two union operations must fully overlap.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment}.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.union(right)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table union(Table right); /**
* Unions two {@link Table}s. Similar to a SQL UNION ALL. The fields of the two union
* operations must fully overlap.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment}.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.unionAll(right)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table unionAll(Table right); /**
* Intersects two {@link Table}s with duplicate records removed. Intersect returns records that
* exist in both tables. If a record is present in one or both tables more than once, it is
* returned just once, i.e., the resulting table has no duplicate records. Similar to a
* SQL INTERSECT. The fields of the two intersect operations must fully overlap.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment}.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.intersect(right)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table intersect(Table right); /**
* Intersects two {@link Table}s. IntersectAll returns records that exist in both tables.
* If a record is present in both tables more than once, it is returned as many times as it
* is present in both tables, i.e., the resulting table might have duplicate records. Similar
* to an SQL INTERSECT ALL. The fields of the two intersect operations must fully overlap.
*
* <p>Note: Both tables must be bound to the same {@code TableEnvironment}.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* left.intersectAll(right)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table intersectAll(Table right);
(13) 创建临时表
/**
* Creates {@link TemporalTableFunction} backed up by this table as a history table.
* Temporal Tables represent a concept of a table that changes over time and for which
* Flink keeps track of those changes. {@link TemporalTableFunction} provides a way how to
* access those data.
*
* <p>For more information please check Flink's documentation on Temporal Tables.
*
* <p>Currently {@link TemporalTableFunction}s are only supported in streaming.
*
* @param timeAttribute Must points to a time attribute. Provides a way to compare which
* records are a newer or older version.
* @param primaryKey Defines the primary key. With primary key it is possible to update
* a row or to delete it.
* @return {@link TemporalTableFunction} which is an instance of {@link TableFunction}.
* It takes one single argument, the {@code timeAttribute}, for which it returns
* matching version of the {@link Table}, from which {@link TemporalTableFunction}
* was created.
*/
TemporalTableFunction createTemporalTableFunction(String timeAttribute, String primaryKey); /**
* Creates {@link TemporalTableFunction} backed up by this table as a history table.
* Temporal Tables represent a concept of a table that changes over time and for which
* Flink keeps track of those changes. {@link TemporalTableFunction} provides a way how to
* access those data.
*
* <p>For more information please check Flink's documentation on Temporal Tables.
*
* <p>Currently {@link TemporalTableFunction}s are only supported in streaming.
*
* @param timeAttribute Must points to a time indicator. Provides a way to compare which
* records are a newer or older version.
* @param primaryKey Defines the primary key. With primary key it is possible to update
* a row or to delete it.
* @return {@link TemporalTableFunction} which is an instance of {@link TableFunction}.
* It takes one single argument, the {@code timeAttribute}, for which it returns
* matching version of the {@link Table}, from which {@link TemporalTableFunction}
* was created.
*/
TemporalTableFunction createTemporalTableFunction(Expression timeAttribute, Expression primaryKey);
(14) 重命名
/**
* Renames the fields of the expression result. Use this to disambiguate fields before
* joining to operations.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.as("a, b")
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table as(String fields); /**
* Renames the fields of the expression result. Use this to disambiguate fields before
* joining to operations.
*
* <p>Scala Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.as('a, 'b)
* }
* </pre>
*/
Table as(Expression... fields); /**
* Filters out elements that don't pass the filter predicate. Similar to a SQL WHERE
* clause.
*
* <p>Example:
*
* <pre>
* {@code
* tab.filter("name = 'Fred'")
* }
* </pre>
*/
(15)插入数据表
/**
* Writes the {@link Table} to a {@link TableSink} that was registered under the specified path.
* For the path resolution algorithm see {@link TableEnvironment#useDatabase(String)}.
*
* <p>A batch {@link Table} can only be written to a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.BatchTableSink}, a streaming {@link Table} requires a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.AppendStreamTableSink}, a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.RetractStreamTableSink}, or an
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.UpsertStreamTableSink}.
*
* @param tablePath The first part of the path of the registered {@link TableSink} to which the {@link Table} is
* written. This is to ensure at least the name of the {@link TableSink} is provided.
* @param tablePathContinued The remaining part of the path of the registered {@link TableSink} to which the
* {@link Table} is written.
*/
void insertInto(String tablePath, String... tablePathContinued); /**
* Writes the {@link Table} to a {@link TableSink} that was registered under the specified name
* in the initial default catalog.
*
* <p>A batch {@link Table} can only be written to a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.BatchTableSink}, a streaming {@link Table} requires a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.AppendStreamTableSink}, a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.RetractStreamTableSink}, or an
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.UpsertStreamTableSink}.
*
* @param tableName The name of the {@link TableSink} to which the {@link Table} is written.
* @param conf The {@link QueryConfig} to use.
* @deprecated use {@link #insertInto(QueryConfig, String, String...)}
*/
@Deprecated
void insertInto(String tableName, QueryConfig conf); /**
* Writes the {@link Table} to a {@link TableSink} that was registered under the specified path.
* For the path resolution algorithm see {@link TableEnvironment#useDatabase(String)}.
*
* <p>A batch {@link Table} can only be written to a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.BatchTableSink}, a streaming {@link Table} requires a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.AppendStreamTableSink}, a
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.RetractStreamTableSink}, or an
* {@code org.apache.flink.table.sinks.UpsertStreamTableSink}.
*
* @param conf The {@link QueryConfig} to use.
* @param tablePath The first part of the path of the registered {@link TableSink} to which the {@link Table} is
* written. This is to ensure at least the name of the {@link TableSink} is provided.
* @param tablePathContinued The remaining part of the path of the registered {@link TableSink} to which the
* {@link Table} is written.
*/
void insertInto(QueryConfig conf, String tablePath, String... tablePathContinued);
总结:
本篇抓住Table api的核心类Table来发现其拥有的功能,并提供了使用用例。Flink Table Api 主要包括了查询select,条件where,过滤filter,排序order by,分组group by,去重distinct,表关联join,重命名as等常规sql操作,也提供了flink自身特性的操作:
窗口操作window,表聚合操作,map操作,aggregate操作。
使用flink Table &Sql api来构建批量和流式应用(2)Table API概述的更多相关文章
- 使用flink Table &Sql api来构建批量和流式应用(1)Table的基本概念
从flink的官方文档,我们知道flink的编程模型分为四层,sql层是最高层的api,Table api是中间层,DataStream/DataSet Api 是核心,stateful Stream ...
- 使用flink Table &Sql api来构建批量和流式应用(3)Flink Sql 使用
从flink的官方文档,我们知道flink的编程模型分为四层,sql层是最高层的api,Table api是中间层,DataStream/DataSet Api 是核心,stateful Stream ...
- Java 8 集合之流式(Streams)操作, Streams API 详解
因为当时公司的业务需要对集合进行各种各样的业务逻辑操作,为了提高性能,就用到了这个东西,因为以往我们以前用集合都是需要去遍历(串行),所以效率和性能都不是特别的好,而Streams就可以使用并行的方式 ...
- Flink 另外一个分布式流式和批量数据处理的开源平台
Apache Flink是一个分布式流式和批量数据处理的开源平台. Flink的核心是一个流式数据流动引擎,它为数据流上面的分布式计算提供数据分发.通讯.容错.Flink包括几个使用 Flink引擎创 ...
- Flink table&Sql中使用Calcite
Apache Calcite是什么东东 Apache Calcite面向Hadoop新的sql引擎,它提供了标准的SQL语言.多种查询优化和连接各种数据源的能力.除此之外,Calcite还提供了OLA ...
- Demo:基于 Flink SQL 构建流式应用
Flink 1.10.0 于近期刚发布,释放了许多令人激动的新特性.尤其是 Flink SQL 模块,发展速度非常快,因此本文特意从实践的角度出发,带领大家一起探索使用 Flink SQL 如何快速构 ...
- kafka传数据到Flink存储到mysql之Flink使用SQL语句聚合数据流(设置时间窗口,EventTime)
网上没什么资料,就分享下:) 简单模式:kafka传数据到Flink存储到mysql 可以参考网站: 利用Flink stream从kafka中写数据到mysql maven依赖情况: <pro ...
- Flink Batch SQL 1.10 实践
Flink作为流批统一的计算框架,在1.10中完成了大量batch相关的增强与改进.1.10可以说是第一个成熟的生产可用的Flink Batch SQL版本,它一扫之前Dataset的羸弱,从功能和性 ...
- Flink系列之1.10版流式SQL应用
随着Flink 1.10的发布,对SQL的支持也非常强大.Flink 还提供了 MySql, Hive,ES, Kafka等连接器Connector,所以使用起来非常方便. 接下来咱们针对构建流式SQ ...
随机推荐
- Windows 10开发基础——网络编程
主要内容: HttpClient类 Socket通信 WCF通信 HttpClient类 在UWP中可以用来进行网络通信的HttpClient类有两个,System.Net.Http.Htt ...
- python 动态调用模块&类&方法
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/bluefrog/archive/2012/05/11/2496439.html 一直想知道python里有没有类似php中的 $classnam ...
- Qt-vs-addin失效的问题
Qt-vs-addin的小问题 使用Visual Studio进行Qt开发的时候,需要安装一个插件.然而有时候这个插件的一些工具却莫名其妙的失效: 其中qt5appwrapper.exe用于编辑Qt工 ...
- 通过异步程序调用(APC)实现的定时功能
定时器是一个在特定时间或者规则间隔被激发的内核对象.结合定时器的异步程序调用可以允许回调函数在任何定时器被激发的时候执行.本文的例子代码显示了如何实现. 使用本定时器时,你需要把常量_WIN32_WI ...
- 毕设(一)C#的百度api调用
这个学期就要毕业了,选了一个无人机地面站软件设计的题目,这几天也开始着手做, 首先做了一个百度地图的调用,这里因为是上位机的开发,所有就不介绍Javascript的 调用方法,核心是用到一个类Http ...
- Bokeh 0.9.0dev 发布,交互式可视化库
快速使用Romanysoft LAB的技术实现 HTML 开发Mac OS App,并销售到苹果应用商店中. <HTML开发Mac OS App 视频教程> 土豆网同步更新:http: ...
- Westciv Tools主要为CSS3提供了渐变gradients、盒子阴影box-shadow、变形transform和文字描边四种在线生成效果的工具
Westciv Tools主要为CSS3提供了渐变gradients.盒子阴影box-shadow.变形transform和文字描边四种在线生成效果的工具 1.Westciv Tools 彩蛋爆料直击 ...
- 认识Docker
以下是个人学习过程中所记,仅作为学习经历和备忘,有问题不负责,但可以交流和探讨. 1 什么是Docker? 在Docker的官网,Docker的设计师们对Docker的定义是: Docke ...
- 使用Arcgis Api for Javascript 调用 本地Portal发布的WebMap
1.环境搭建 安装Arcgis Portal 10.4,Server 10.4,DataStore ,WebAdaptor for IIS,搭建arcgis api for javascript 4. ...
- Webapi实现websocket实时通讯
应用场景:前端页面发起一个websocket请求与后端进行实时通讯.后端监听某端口获取数据,将监听到的数据加工处理,通过websocket发送到前端. 这里只提供后台的处理方案仅供参考. 1.后端监听 ...
