LeetCode 218. The Skyline Problem 天际线问题(C++/Java)
题目:
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Now suppose you are given the locations and height of all the buildings as shown on a cityscape photo (Figure A), write a program to output the skyline formed by these buildings collectively (Figure B).


The geometric information of each building is represented by a triplet of integers [Li, Ri, Hi], where Li and Ri are the x coordinates of the left and right edge of the ith building, respectively, and Hi is its height. It is guaranteed that 0 ≤ Li, Ri ≤ INT_MAX, 0 < Hi ≤ INT_MAX, and Ri - Li > 0. You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
For instance, the dimensions of all buildings in Figure A are recorded as: [ [2 9 10], [3 7 15], [5 12 12], [15 20 10], [19 24 8] ] .
The output is a list of "key points" (red dots in Figure B) in the format of [ [x1,y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3], ... ] that uniquely defines a skyline. A key point is the left endpoint of a horizontal line segment. Note that the last key point, where the rightmost building ends, is merely used to mark the termination of the skyline, and always has zero height. Also, the ground in between any two adjacent buildings should be considered part of the skyline contour.
For instance, the skyline in Figure B should be represented as:[ [2 10], [3 15], [7 12], [12 0], [15 10], [20 8], [24, 0] ].
Notes:
- The number of buildings in any input list is guaranteed to be in the range
[0, 10000]. - The input list is already sorted in ascending order by the left x position
Li. - The output list must be sorted by the x position.
- There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance,
[...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...]is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
分析:
给定一组描述建筑物的三元组[Li, Ri, Hi],其中 Li 和 Ri 分别是第 i 座建筑物左右边缘的 x 坐标,Hi 是其高度。最后求出一组坐标来表示天际线。
利用扫描线法,想象一条垂直的线从左至右扫描所有的建筑,根据图例我们不难发现,扫描到建筑的左边时,也就是有新的建筑出现,如果这个建筑的高度等于当前扫描的所有建筑的最高高度时,当前的这个坐标和高度应该加入到结果中,如果扫描到建筑的右边时,也就是有一个建筑离开了,此时扫描的建筑的最高高度发生了改变,则要把离开后的最高高度和当前坐标加入到结果中。
以上图为例,当扫描到红色建筑[3,15]时,此时我们应该保存扫描的高度集合,最大值恰好是15也就是红色建筑的高度,我们把[3,15]加入到天际线中。
当扫描到x=7时,也就是红色建筑[7,15]离开时,最高的高度由15变成了12,所以我们把[7,12]加入到天际线中。
那么为了模拟扫描建筑,实际上我们将表示建筑的线进行排序,然后再依次遍历即可。同时这里还有一个小技巧,例如红色建筑的两条线分别是[3, 15]和[7,15](x坐标,高度)我们把离开扫描线的建筑的边的高度记为负值,用来区分是进入还是离去,也就是[3, 15]和[7,-15],同时还要对所有的建筑按x的值进行升序排序,不过对于x相等的情况,我们来看一下特例:

也就是前一个建筑的右边和后一个建筑的左边在同一条线上,那么边的排序应该是如上图所示,也就是当x相同时,比较高度,高度大的排在前面。如果这里想不太清楚的同学,可以根据边的排序将两个建筑稍微重合一点或者分离一点,就能清楚的发现,高度长的边应该排在前面,只有这样才能正确求得天际线。
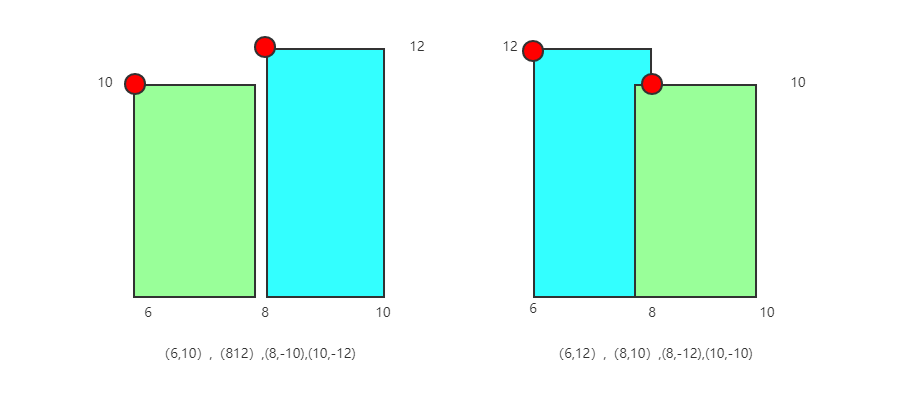
此外还有几种特殊情况我们来看一下:
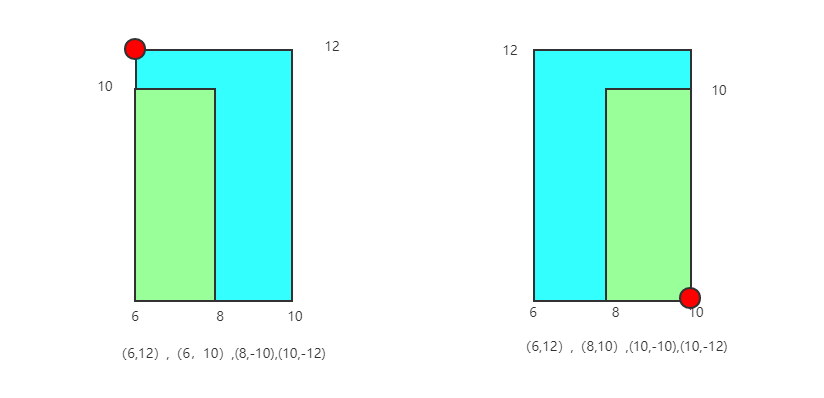
这两种情况则是建筑左边横坐标相同,或者右边横坐标相同,此时排序的规则依旧是横坐标相同,按照高度的值!!降序排序,因为我们将离开的边编码为负数,所以在扫描到建筑离开的时候我们希望建筑高度低的排在前面,那么反映到编码上就是高度的值排序即可。以左边为例,如果将6,10排到6,12前面,显然不对,因为根据我们的规则,6,10也成为了天际线,但实际上只需要记录6,12即可。右边的图同理。
在存储高度时,我们使用树结构存储,可以保证删除操作在O(logn)内完成。
小技巧:存储高度集合中先加入0,当扫描建筑后没有建筑时,可以直接得到答案,而不用进行特殊处理。
程序:
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> getSkyline(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
vector<pair<int, int>> lines;
vector<vector<int>> res;
multiset<int, greater<int>> h;
for(auto &a:buildings){
lines.push_back({a[], a[]});
lines.push_back({a[], -a[]});
}
sort(lines.begin(), lines.end(), cmp());
h.insert();
for(auto iter = lines.begin(); iter != lines.end(); ++iter){
int x = (*iter).first;
int height = (*iter).second;
int maxHeight = *h.begin();
if(height > ){
if(height > maxHeight){
res.push_back({x, height});
}
h.insert(height);
}else{
height = -height;
h.erase(h.find(height));
if(maxHeight != *h.begin()){
res.push_back({x, *h.begin()});
}
}
}
return res;
}
struct cmp {
bool operator() (const pair<int, int>& A, const pair<int, int>& B) {
if (A.first < B.first) {
return true;
} else if (A.first == B.first) {
return A.second > B.second;
} else {
return false;
}
}
};
};
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
List<Pair<Integer, Integer>> lines = new ArrayList<>();
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> h = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int[] a:buildings){
lines.add(new Pair(a[0], a[2]));
lines.add(new Pair(a[1], -a[2]));
}
Collections.sort(lines, new Comparator<Pair<Integer, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Pair<Integer, Integer> o1, Pair<Integer, Integer> o2) {
int x1 = o1.getKey();
int y1 = o1.getValue();
int x2 = o2.getKey();
int y2 = o2.getValue();
if(x1 != x2)
return x1 - x2;
else{
return y2 - y1;
}
}
});
h.put(0, 1);
for(Pair p:lines){
int x = (int)p.getKey();
int height = (int)p.getValue();
int maxHeight = h.firstKey();
if(height > 0){
if(height > maxHeight){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(x, height)));
}
h.put(height, h.getOrDefault(height, 0)+1);
}else{
height = -height;
Integer v = h.get(height);
if(v == 1){
h.remove(height);
}else{
h.put(height, v-1);
}
if(maxHeight != h.firstKey()){
res.add(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(x, h.firstKey())));
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
LeetCode 218. The Skyline Problem 天际线问题(C++/Java)的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 218. The Skyline Problem 天际线问题
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city whe ...
- [LeetCode] 281. The Skyline Problem 天际线问题
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city whe ...
- [LeetCode#218] The Skyline Problem
Problem: A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that ...
- Java for LeetCode 218 The Skyline Problem【HARD】
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city whe ...
- [LeetCode] The Skyline Problem 天际线问题
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city whe ...
- 218. The Skyline Problem (LeetCode)
天际线问题,参考自: 百草园 天际线为当前线段的最高高度,所以用最大堆处理,当遍历到线段右端点时需要删除该线段的高度,priority_queue不提供删除的操作,要用unordered_map来标记 ...
- 218. The Skyline Problem
题目: A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city ...
- 218. The Skyline Problem *HARD* -- 矩形重叠
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city whe ...
- [LeetCode] The Skyline Problem
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city whe ...
随机推荐
- Qt5学习(1)
1. In Qt, if you want to apply styles to the main window itself, you must apply it to its central ...
- Freemarker 的基础使用 (二)
freemarker 的基础使用二 ftl 文件 <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" cont ...
- JVM之GC算法的实现(垃圾回收器)
上一节:<JVM之GC算法> 知道GC算法的理论基础,我们来看看具体的实现.只有落地的理论,才是真理. 一.JVM垃圾回收器的结构 JVM虚拟机规范对垃圾收集器应该如何实现没有规定,因为没 ...
- Docker入门之快速安装和卸载使用Centos7
一.检查内核版本 注意:Docker要求操作系统必须是64位,如果使用的Centos内核版本为3.10以上 执行命令:uname -r 二.安装依赖软件包 执行命令:yum install -y y ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 80 D E
A了三题,rk1000左右应该可以上分啦,开
- Vue中的nextTick()浅析
引言 在开发过程中,我们经常遇到这样的问题:我明明已经更新了数据,为什么当我获取某个节点的数据时,却还是更新前的数据? 一,浅析 为什么会这样呢?带着这个疑问先往下看. 先看一个小的例子: <d ...
- kubernetes concepts (一)
Concepts The Concepts section helps you learn about the parts of the Kubernetes system and the abstr ...
- maven版本对应的jdk
今天配置项目环境发现jdk1.6与maven-3.39不能匹配 查询jdk与maven的版本对应关系 关系网址:http://maven.apache.org/docs/history.html Ma ...
- 为BlueLake主题增加自定义icon图标
一.前言 hexo 的 Bluelake 主题是我一直在用的,简单大方,很喜欢.但最近有了添加自定义 icon 图标的需求,比如,添加 "地址"."扫一扫".& ...
- [bzoj3926] [loj2137] [Zjoi2015] 诸神眷顾的幻想乡
Description 幽香是全幻想乡里最受人欢迎的萌妹子,这天,是幽香的2600岁生日,无数幽香的粉丝到了幽香家门前的太阳花田上来为幽香庆祝生日. 粉丝们非常热情,自发组织表演了一系列节目给幽香看. ...
