2016 ICPC Mid-Central USA Region J. Windy Path (贪心)
比赛链接:2016 ICPC Mid-Central USA Region
题目链接:Windy Path
Description
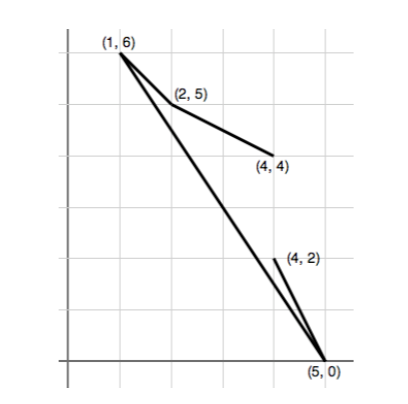
Consider following along the path in the figure above, starting from \((4,4)\) and moving to \((2,5)\). Then the path turns rightward toward \((1,6)\), then sharp left to \((5,0)\) and finally sharp left again to \((4,2)\). If we use ‘\(L\)’ for left and ‘RR’ for right, we see that the sequence of turn directions is given by RLL. Notice that the path does not cross itself: the only intersections of segments are the connection points along the path.
Consider the reverse problem: Given points in an arbitrary order,say \((2,5),(1,6),(4,4),(5,0),(4,2)\),could you find an ordering of the points so the turn directions along the path are given by RLL? Of course to follow the path in the figure,you would start with the third point in the list \((4,4)\),then the first \((2,5)\),second \((1,6)\), fourth \((5,0)\), and fifth \((4,2)\), so the permutation of the points relative to the given initial order would be: \(3\ 1 \ 2 \ 4 \ 5\).
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer \(N\), specifying the number of points such that \(3 \le N \le 50\). The following NN lines each describe a point using two integers \(x_i\) and \(y_i\) such that \(0 \le x_i,y_i \le 1000\). The points are distinct and no three are collinear (i.e., on the same line). The last line contains a string of \(N - 2\) characters, each of which is either ‘\(L\)’ or ‘\(R\)’.
Output
A permutation of\(\{ 1,...,N \}\) that corresponds to a nonintersecting path satisfying the turn conditions. The numbers are to be displayed with separating spaces. (There are always one or more possible solutions, and any one may be used.)
Solution
题意
给定 \(n\) 个点的坐标和一个包含 \(R\) 和 \(L\) 的序列,其中 \(L\) 代表左转,\(R\) 代表右转,求一个访问每个点顺序满足给定的序列。
题解
贪心 构造 计算几何
由于是 special judge,只要想出一种构造方法就可以。本题可以贪心。
- 首先选择最下面最左边的点作为起点,(起点不唯一,比如最左边最下面也可以)。
- 如果第一个字符是 \(R\),第二个点选择最左边的点;反之选择最右边的点。
- 之后每次考察连续两个字符:
- 如果是 \(RL\),选择右边最后一个
- 如果是 \(LR\),选择左边最后一个
- 如果是 \(RR\),选择右边第一个
- 如果是 \(RR\),选择左边第一个
判断点是在向量的左边还是右边可以用 \(ToLeftTest\),查询第一个还是最后一个可以用夹角判断。
/*
思路:
贪心
1. R: 左边第一个
2. L: 右边第一个
3. RL: 右边最后一个
4. LR: 左边最后一个
5. LL: 左边第一个
6. RR: 右边第一个
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Point {
int x, y, index;
} p[100];
int area2(Point p, Point q, Point s) {
return p.x * q.y - p.y * q.x + q.x * s.y - q.y * s.x + s.x * p.y - s.y * p.x;
}
// 判断某个点在向量的左边还是右边
bool toLeftTest(Point p, Point q, Point s) {
return area2(p, q, s) > 0;
}
int cmp(Point p1, Point p2) {
if (p1.y == p2.y)
return p1.x < p2.x;
return p1.y < p2.y;
}
// 求向量 pq 与 向量 ps 之间的夹角
double ang(Point p, Point q, Point s) {
double x1 = q.x - p.x, y1 = q.y - p.y;
double x2 = s.x - p.x, y2 = s.y - p.y;
double ans = (x1 * x2 + y1 * y2) / (sqrt(x1 * x1 + y1 * y1) * sqrt(x2 * x2 + y2 * y2));
return acos(ans);
}
vector<Point> ans; // 存放答案
int vis[100]; // 标记已访问过的点
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
p[i].index = i;
}
sort(p + 1, p + n + 1, cmp);
ans.push_back(p[1]); // 起点
vis[p[1].index] = 1;
double min_ang = 10;
int min_index = 1;
Point tmp, tmp2 = p[1]; // 保存上两个点
string str;
cin >> str;
// 第一个点
if (str[0] == 'R') {
tmp.x = p[1].x - 1;
tmp.y = p[1].y;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
double angle = ang(p[1], p[i], tmp);
if (angle < min_ang) {
min_ang = angle;
min_index = i;
}
}
ans.push_back(p[min_index]);
vis[p[min_index].index] = 1;
} else {
tmp.x = p[1].x + 1;
tmp.y = p[1].y;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
double angle = ang(p[1], p[i], tmp);
if (angle < min_ang) {
min_ang = angle;
min_index = i;
}
}
ans.push_back(p[min_index]);
vis[p[min_index].index] = 1;
}
tmp = p[min_index];
// 之后的点
for (int i = 0; i < str.size() - 1; ++i) {
if (str[i] == 'R' && str[i + 1] == 'L') {
min_ang = 10;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (vis[p[i].index])
continue;
if (toLeftTest(tmp2, tmp, p[i]))
continue;
double angle = ang(tmp, tmp2, p[i]);
if (min_ang > angle) {
min_ang = angle;
min_index = i;
}
}
ans.push_back(p[min_index]);
vis[p[min_index].index] = 1;
tmp2 = tmp;
tmp = p[min_index];
}
else if (str[i] == 'R' && str[i + 1] == 'R') {
min_ang = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (vis[p[i].index])
continue;
if (toLeftTest(tmp2, tmp, p[i]))
continue;
double angle = ang(tmp, tmp2, p[i]);
if (min_ang < angle) {
min_ang = angle;
min_index = i;
}
}
ans.push_back(p[min_index]);
vis[p[min_index].index] = 1;
tmp2 = tmp;
tmp = p[min_index];
} else if (str[i] == 'L' && str[i + 1] == 'R') {
min_ang = 10;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (vis[p[i].index])
continue;
if (!toLeftTest(tmp2, tmp, p[i]))
continue;
double angle = ang(tmp, tmp2, p[i]);
if (min_ang > angle)
{
min_ang = angle;
min_index = i;
}
}
ans.push_back(p[min_index]);
vis[p[min_index].index] = 1;
tmp2 = tmp;
tmp = p[min_index];
} else {
min_ang = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (vis[p[i].index])
continue;
if (!toLeftTest(tmp2, tmp, p[i]))
continue;
double angle = ang(tmp, tmp2, p[i]);
if (min_ang < angle) {
min_ang = angle;
min_index = i;
}
}
ans.push_back(p[min_index]);
vis[p[min_index].index] = 1;
tmp2 = tmp;
tmp = p[min_index];
}
}
// 最后一个点
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (!vis[p[i].index]) {
ans.push_back(p[i]);
break;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); ++i) {
printf("%d", ans[i].index);
printf("%s", i == ans.size() - 1 ? "\n" : " ");
}
return 0;
}
2016 ICPC Mid-Central USA Region J. Windy Path (贪心)的更多相关文章
- 2016 ICPC总结
2016 ICPC总结 九月份开学,开始知识点的补充,刚开始的几周都在刷acmsteps,十月开始进行专题性的学习,首先进行的数据结构,给自己定的计划,十一月前看完数据结构,刚开始的时候看的都是以前的 ...
- HYNB Round 8: 2016 ICPC Amritapuri Regionals
HYNB Round 8: 2016 ICPC Amritapuri Regionals A - Tim and BSTs 做法 经典的树 DP 问题. \(dp[u][i]\) 表示考虑以 u 为根 ...
- ICPC North Central NA Contest 2018
目录 ICPC North Central NA Contest 2018 1. 题目分析 2. 题解 A.Pokegene B.Maximum Subarrays C.Rational Ratio ...
- ICPC Mid-Central USA Region 2019 题解
队友牛逼!带我超神!蒟蒻的我还是一点一点的整理题吧... Dragon Ball I 这个题算是比较裸的题目吧....学过图论的大概都知道应该怎么做.题目要求找到七个龙珠的最小距离.很明显就是7个龙珠 ...
- 2016 ICPC青岛站---k题 Finding Hotels(K-D树)
题目链接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5992 Problem Description There are N hotels all over ...
- HDU 5884 Sort -2016 ICPC 青岛赛区网络赛
题目链接 #include <iostream> #include <math.h> #include <stdio.h> #include<algorith ...
- 2013 ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Changsha Online J Candies
AC了,但是不知道为什么,但是恶心的不得了~最近写代码,思路都非常清晰,但是代码各种bug~T.T~说说思路吧:二分~330ms~ 小队友fribbi的思路是离线250msAC~ 预处理solve函数 ...
- ICPC 2018 南京网络赛 J Magical Girl Haze(多层图最短路)
传送门:https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/A1958 题意:n个点m条边的路,你有k次机会将某条路上的边权变为0,问你最短路径长度 题解:最短路变形,我们需要在常规的最短路上多 ...
- 2016 ICPC大连站---F题 Detachment
题意:输入一个x,将x拆分成一些小的数(这些数不能相同,即x=a1+a2+...... ai!=aj when i!=j),然后这些数相乘得到一个成积(s=a1*a2*......),求最大的乘积 ...
随机推荐
- c#网络通信框架networkcomms内核解析之六 处理接收到的二进制数据
本文基于networkcomms2.3.1开源版本 gplv3协议 在networkcomms通信系统中,服务器端收到某连接上的数据后,数据会暂时存放在"数据包创建器"(Pack ...
- 推荐两款远程管理Linux工具(基于Windows系统)
推荐两款远程管理Linux工具(基于Windows系统) 1.Xshell 百度百科:Xshell 是一个强大的安全终端模拟软件,它支持SSH1, SSH2, 以及Microsoft Windows ...
- Python常用模块系列
1.时间模块 import time,datetime # print(time.time()) #时间戳 # print(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X") ...
- Java对象相等比较(Equals)
以下代码显示如何实现equals()和hashCode()方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 ...
- Kotlin 和 Flutter 对于开发者究竟意味着什么?
更多阿里P7架构进阶学习视频:阿里P7Android架构进阶学习视频回放近些年来,编程语言流行度的变化其实不大,在 TIOBE 编程语言排行榜上,Java.C.C++ 固若金山,也就只有 Python ...
- Failed! Error: Unknown error 1130
如有需要可以加我Q群[308742428]大家一起讨论技术,有偿服务. 后面会不定时为大家更新文章,敬请期待. 喜欢的朋友可以关注下. 在使用navicat远程连接mysql报了一个错误信息 Fail ...
- mid
""" Cross Site Request Forgery Middleware. This module provides a middleware that imp ...
- IIS ASP.NET MVC 上传文件到NAS目录
项目要求,网站用户上传的文件,存储到服务器挂接的NAS磁盘里,死活也写不进去,一直提示 System.IO.IOException: 指定的服务器无法运行请求的操作 阿里的客服也问过了, 一群只知道发 ...
- Java中super关键字的位置
1.子类的构造函数如果要引用super的话,必须把super放在函数的首行. 例如: class Base { Base() { System.out.println("Base&qu ...
- Install ncurses (ncurses-devel) and try again
apt install libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev
