[Java Basics3] XML, Unit testing
| What's the difference between DOM and SAX? | DOM creates tree-like representation of the XML document in memory, SAX is event-based. |
| What's the difference between XSD and DTD? | XSD is in XML, DTD is not. XSD is much more comprehensive than DTD |
| You're given an XML file, and you're supposed to retrieve the value of a specific element in the file. How do you do that? | Open-ended question. See how the candidate uses various types of parsers (DOM, SAX, etc) and see if he explores the usage of XPath. |
| You're supposed to unit test Java class that accesses a database, in a machine that doesn't have database server installed, and no external connectivity at all. What's your approach? |
Open-ended question. See if the answer tackles the problem effectively. See if he/she suggests mocking as an option |
| How do you ensure your unit tests have covered all paths / possibilities? |
Use code coverage tool like Cobertura, Emma, etc |
| How do you unit-test a private method? | - Use Reflection, set accessible property of that method to true - Call an accessible method that calls the private method and observe the effect caused by calling the private method |
XML Message Verification in B-Puma:
1, First get the XML message from cache component, using the ConsumerTemplate.receiverBody(uri, TIMEOUT, Node.class); and cast to Element.
2, Pass the obtained Element to OrderVerifier constructor which builds a XPathVerifyDelegate(Node):
private static XPath xpath = XPathFactory.newInstance().newXPath();
String actual = xpath.evaluate(key, node); //key is like @limitPrice, the path of the data
在这里,Node是从camel consumerTemplate里直接收到的,如果你的XML在一个file里而且你想用XPath读,你需要首先读进一个DOM object里:
DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();DocumentBuilder builder = null;try { builder = builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }try { Document document = builder.parse(newFileInputStream("c:\\employees.xml"));} catch (SAXException e) { e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}//read an xml node using xpathString expression = "/Employees/Employee[@emplid='3333']/email";Node node = (Node) xPath.compile(expression).evaluate(xmlDocument, XPathConstants.NODE);About DOM:
The parser traverses the XML file and creates the corresponding DOM objects. These DOM objects are linked together in a tree structure.
The Node object is the primary data type for the entire DOM. Document不只包括树型元素结构,所以Element这种结构只是获取Document里的树型结构Document.getDocumentElement()。Document和Element都是Node interface的sub-interface。
A node can be an element node, an attribute node, a text node, or any other of the node types explained in the "Node types" chapter. Element is the only kind of node that can have child nodes and attributes.
DOM on the other hand is more robust - it reads the entire XML document into a tree, and is very efficient when you want to alter, add, remove data in that XML tree. XPath is useful when you only need a couple of values from the XML document, and you know where to find them (you know the path of the data, /root/item/challange/text).
如果你用DOM来获取元素:
Element rootElement = document.getDocumentElement();
NodeList nodes = element.getChildNodes();
for(int i=0; i<nodes.getLength(); i++){
Node node = nodes.item(i);
if(node instanceof Element){
//a child element to process
Element child = (Element) node;
String attribute = child.getAttribute("width");
}
}
A Node is a part of the DOM tree, an Element is a particular type of Node : e.g. <foo> This is Text </foo>
(I)Node
(I)Document (I)Element (I)Attr
You have a foo Element, (which is also a Node, as Element inherits from Node) and a Text Node 'This is Text', that is a child of the foo Element/Node
XPath为XML Path language: XPath包含一个标准函数库
XPath语法:
nodename 选取名为nodename节点的所有子节点
/ 从根节点选取
// 选取节点,所有,不管位置
@ 选取属性
Predicates:
例如 //tiltle[@lang] 选取所有属性lang的所有title节点
/bookstore/book[price>35]/title child::* 选取当前节点的所有子元素
//title| //price 选取若干路径"|" ancestor::book 选取当前节点的所有book先辈
XML Message Constructing in B-Puma:
<from uri="direct:default-order-record"/>
<transform>
<constant><xml/></constant>
</transform>
<to uri="xquery:com/barcap/eq/baths/core/puma/templates/DefaultOrderRecord.xml"/>
then Node.setAttribute(String name, String value);
Unit Testing or Component Testing:
1, To write a test with the JUnit 4.x/TestNG-6-3.1 framework you annotate a method with the @org.junit.Test/@org.testng.annotations.Test
annotation.
2, In TestNG, if you want to run multi-tests as a suite: define XML file with <suite> tag.
<suite><test><packages><package>...</>
Then in the test or base test, use annotation @BeforeSuite and @AfterSuite to initiate/close actors.
Other annotations: @BeforeGroups, @BeforeClass, @BeforeTest, @BeforeMethod.
3, Base class in B project:
extends AbstractTestNGSpringContextTests, part of spring-test-3.1.1, which integrates the Spring TestContext framework with testing support in a TestNG enrironment.
For example, at your base class, @ContextConfiguration(locations = {"/pApp-actors.xml"}), @ActiveProfiles({"SIT2"}).
4, Spring configuration files in test project:
====
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<import resource="spring/puma.xml"/>
<bean id="paul" p:pumaGuiUsername="${puma.user.name}" class="com.barcap.eq.baths.puma.framework.interactor.impl.PumaActorCamel"/>
<beans profile="SIT2">
<bean p:locations="classpath*:env/US-SIT2-*.properties" class="org.apache.camel.spring.spi.BridgePropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"/>
</beans>
====
Either to use <beans profile> in Spring xml and @ActiveProfiles annotation, to switch among profiles,
Or <profile> in Maven xml and mvn -P Profile1.
5, TestNG also include JUnit's Assert class, which lets you perform assertions on complex objects:
import static org.testng.AssertJUnit.*; assertEquals("Beust", m_lastName);
assertTrue(boolean value), assertFalse(boolean value), assertNull(object), assertNotNull(object), assertEquals(expected, actual).
6, TestNG DataProvider
A Data Provider is a method on your class that returns an array of array of objects. This method is annotated with @DataProvider:
@DataProvider(name = "test1")
public Object[][] createData() { return new Object[][] {{"Constance", new Integer(12)}, {"Roxy", new Integer(33)}};}
@Test(dataProvider = "test1")
public void verifyData(String name, Integer age) {System.out.println(name + " " + age);}
7, Mockito testing
The concept behind mock objects is that we want to create an object that will take the place of the real object. This mock object will expect a certain method to be called with certain parameters and when that happens, it will return an expected result.
http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/516360/Mockito-a-great-mock-framework-for-Java-developmen
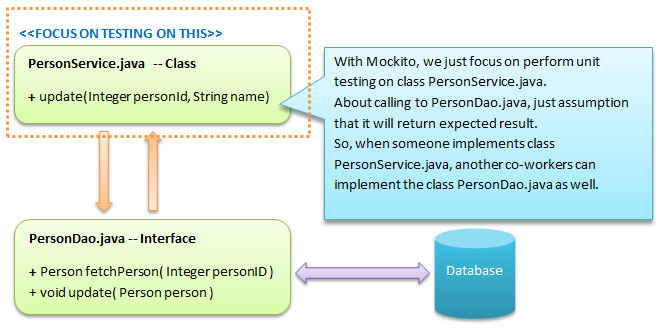
这里,没有PersonDao的具体implementation,只是为了test PersonService class,所以需要@Mock PersonDao personDao; 然后stub method calls, verify interations.
public class PersonServiceTest
{
@Mock
private PersonDao personDAO;
private PersonService personService;
@Before
public void setUp()
throws Exception
{
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks( this );
personService = new PersonService( personDAO );
}
@Test
public void shouldUpdatePersonName()
{
Person person = new Person( 1, "Phillip" );
when( personDAO.fetchPerson( 1 ) ).thenReturn( person ); //Stub method calls
boolean updated = personService.update( 1, "David" );
assertTrue( updated );
verify( personDAO ).fetchPerson( 1 ); //verify interation
ArgumentCaptor<Person> personCaptor = ArgumentCaptor.forClass( Person.class );
verify( personDAO ).update( personCaptor.capture() );
Person updatedPerson = personCaptor.getValue();
assertEquals( "David", updatedPerson.getPersonName() );
// asserts that during the test, there are no other calls to the mock object.
verifyNoMoreInteractions( personDAO );
}
@Test
public void shouldNotUpdateIfPersonNotFound()
{
when( personDAO.fetchPerson( 1 ) ).thenReturn( null );
boolean updated = personService.update( 1, "David" );
assertFalse( updated );
verify( personDAO ).fetchPerson( 1 );
verifyZeroInteractions( personDAO );
verifyNoMoreInteractions( personDAO );
}
}
8, @Listeners annotation in TestNG
提供了一种改变TestNG behavior的方法,你create的listener class要implement ITestNGListener,比如在你的listener class里:
@Override
public void onConfigurationFailure(final ITestResult testResult) {
reporter.onConfigurationFailure(testResult);
}
9,JUnit 4里有expected = IllegalArgumentException.class,在testng里是expectedExceptions = {}。
[Java Basics3] XML, Unit testing的更多相关文章
- Java Unit Testing - JUnit & TestNG
转自https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/java/JavaUnitTesting.html yet another insignifican ...
- 10 Unit Testing and Automation Tools and Libraries Java Programmers Should Learn
转自:https://javarevisited.blogspot.com/2018/01/10-unit-testing-and-integration-tools-for-java-program ...
- Unit Testing of Classes in Java
Every class can have a main method. That is a handy trick for unit testing of classes. For example, ...
- C/C++ unit testing tools (39 found)---reference
http://www.opensourcetesting.org/unit_c.php API Sanity AutoTest Description: An automatic generator ...
- Unit Testing of Spring MVC Controllers: “Normal” Controllers
Original link: http://www.petrikainulainen.net/programming/spring-framework/unit-testing-of-spring-m ...
- Unit Testing of Spring MVC Controllers: Configuration
Original Link: http://www.petrikainulainen.net/programming/spring-framework/unit-testing-of-spring-m ...
- Javascript单元测试Unit Testing之QUnit
body{ font: 16px/1.5em 微软雅黑,arial,verdana,helvetica,sans-serif; } QUnit是一个基于JQuery的单元测试Uni ...
- Unit Testing a zend-mvc application
Unit Testing a zend-mvc application A solid unit test suite is essential for ongoing development in ...
- java对xml节点属性的增删改查
学习本文之前请先看我的另一篇文章JAVA对XML节点的操作可以对XML操作有更好的了解. package vastsum; import java.io.File; import java.io.Fi ...
随机推荐
- volatile关键字及编译器指令乱序总结
本文简单介绍volatile关键字的使用,进而引出编译期间内存乱序的问题,并介绍了有效防止编译器内存乱序所带来的问题的解决方法,文中简单提了下CPU指令乱序的现象,但并没有深入讨论. 以下是我搭建的博 ...
- Discuz! X论坛上传附件到100%自动取消上传的原因及解决方案
最近接到一些站长的反馈,说论坛上传附件,到100%的时候自己取消上传了.经查是附件索引表pre_forum_attachment表的aid字段自增值出现了问题,导致程序逻辑返回的aid值实际为一个My ...
- 后台接收前台传入的json 数据
引入JSONArray的类型为org.json而不是net.sf.json,笔者开始引入的是net.sf.json.JSONArray, 但JSONObject.fromObject(obj)时报错报 ...
- ArcMap Add-in插件开发中解决VS调试时断点不会命中的问题
在VS2010中进行ArcMap Add-in插件开发(ArcEngine10.1,ArcGIS10.1),运行时为.NET4.0,在程序中设置了断点进行调试,但是运行后程序并不会在断点处停止,且原来 ...
- MVC5 + EF6 完整入门教程三:EF来了
期待已久的EF终于来了 学完本篇文章,你将会掌握基于EF数据模型的完整开发流程. 本次将会完成EF数据模型的搭建和使用. 基于这个模型,将之前的示例添加数据库查询验证功能. 文章提纲 概述 & ...
- 解决ViewPager多次刷新后重叠问题
@Override public void destroyItem(ViewGroup container, int position, Object object) { ((ViewPager) c ...
- python3练习-杨辉三角/帕斯卡三角形
杨辉三角形式如下: 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 3 3 1 1 4 6 4 1 1 5 10 10 5 1 # 期待输出: # [1] # [1, 1] # [1, 2, 1] # [1, 3, 3, ...
- CodeForces #363 div2 Vacations DP
题目链接:C. Vacations 题意:现在有n天的假期,对于第i天有四种情况: 0 gym没开,contest没开 1 gym没开,contest开了 2 gym开了,contest没开 3 ...
- 繁星——JQuery选择器之层级
[ancestor descendant] 在给定元素下匹配所有后代元素.这个选择器的使用概率相当之高,使用示例如下: //HTML代码: <div id='div01'> <inp ...
- ADO.NET学习
ADO.NET重要的类 在.NET访问MySql数据库时的几点经验! string connstr=Setting.Instance().GetConnectionString("MySql ...
