读书笔记 Bioinformatics Algorithms Chapter5
Chapter5 HOW DO WE COMPARE DNA SEQUENCES
Bioinformatics Algorithms-An_Active Learning Approach
http://bioinformaticsalgorithms.com/

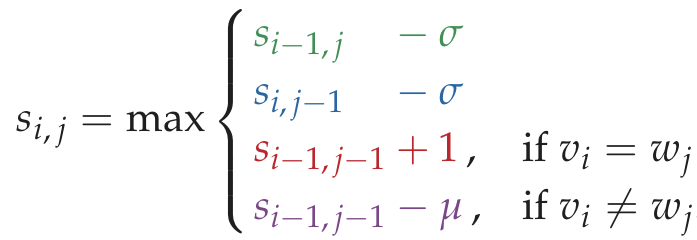
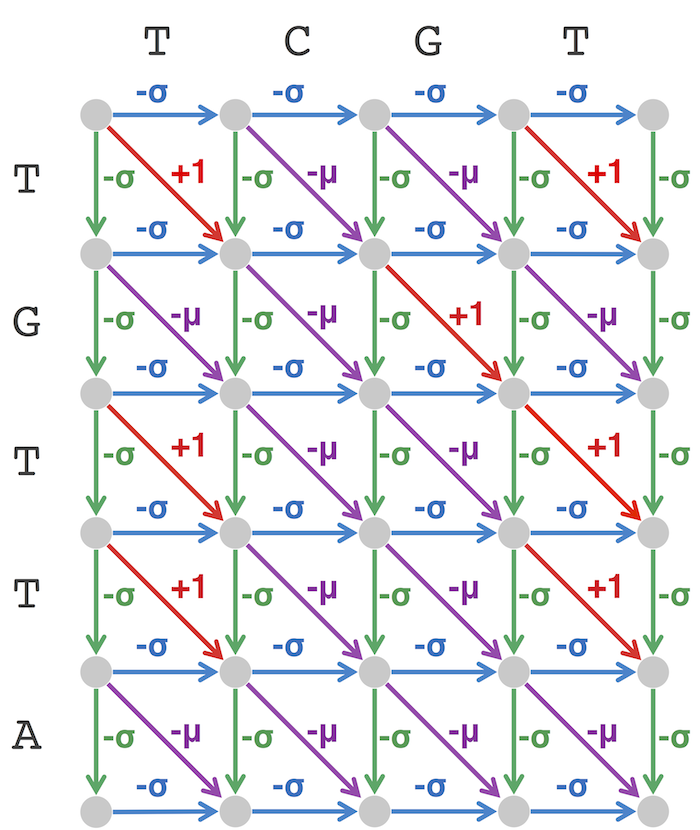
'''
Code Challenge: Solve the Global Alignment Problem.
Input: Two protein strings written in the single-letter amino acid alphabet.
Output: The maximum alignment score of these strings followed by an alignment achieving this maximum score. Use the
BLOSUM62 scoring matrix for matches and mismatches as well as the indel penalty σ = 5.
----------
Sample Input:
PLEASANTLY
MEANLY
----------
Sample Output:
8
PLEASANTLY
-MEA--N-LY
----------
@ Lo Kowngho 2018.9
'''
import numpy
from os.path import dirname def Grade(Symb1,Symb2):
Indx1 = symbolList[Symb1]
Indx2 = symbolList[Symb2]
return matrix[Indx1][Indx2] def Init_Graph_Global(l1,l2):
Graph = numpy.zeros([l2,l1])
for x in range(1,l2):
Graph[x][0] = Graph[x-1][0]-5
for y in range(1,l1):
Graph[0][y] = Graph[0][y-1]-5
return Graph def Init_Path(l1,l2):
Path = numpy.zeros([l2,l1])
for x in range(1,l2):
Path[x][0] = 1
for y in range(1,l1):
Path[0][y] = 2
return Path def buildGlobalAlignmentGraph(text1,text2): l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
Graph = Init_Graph_Global(l1, l2)
Path = Init_Path(l1, l2) for x in range(1,l2):
for y in range(1,l1):
Graph[x][y] = max(Graph[x-1][y]-5, Graph[x][y-1]-5, Graph[x-1][y-1]+Grade(text1[y],text2[x]))
if Graph[x-1][y]-5==Graph[x][y]:
Path[x][y]=1
elif Graph[x][y-1]-5==Graph[x][y]:
Path[x][y]=2
else:
Path[x][y]=3
return [Graph,Path] def OutputGlobalAligement(Path,Graph,text1,text2):
outT1 = ''
outT2 = ''
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
x = l2-1
y = l1-1
while(x!=0 or y!=0):
if Path[x][y]==1:
outT1 += '-'
outT2 += text2[x]
x -= 1
elif Path[x][y]==2:
outT1 += text1[y]
outT2 += '-'
y -= 1
else:
outT1 += text1[y]
outT2 += text2[x]
x -= 1
y -= 1
return [outT1[::-1],outT2[::-1]] def ImportScoreMatrix():
dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'BLOSUM62.txt').read().strip().split('\n')
symbolList = dataset[0].split()
for i in range(len(symbolList)):
symbolList[i]=[symbolList[i],i]
symbolList = dict(symbolList)
print(symbolList)
matrix = []
for i in range(1,len(dataset)):
matrix.append(dataset[i].split()[1:])
for l in range(len(matrix)):
for i in range(len(matrix[l])):
matrix[l][i]=int(matrix[l][i])
return [matrix,symbolList] if __name__ == '__main__': [matrix,symbolList] = ImportScoreMatrix() dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'dataset.txt').read().strip().split()
text1 = ''+dataset[0]
text2 = ''+dataset[1] [Graph,Path] = buildGlobalAlignmentGraph(text1, text2) [outT1,outT2] = OutputGlobalAligement(Path,Graph,text1,text2) print(int(Graph[-1][-1]))
print(outT1)
print(outT2)
全局比对 python
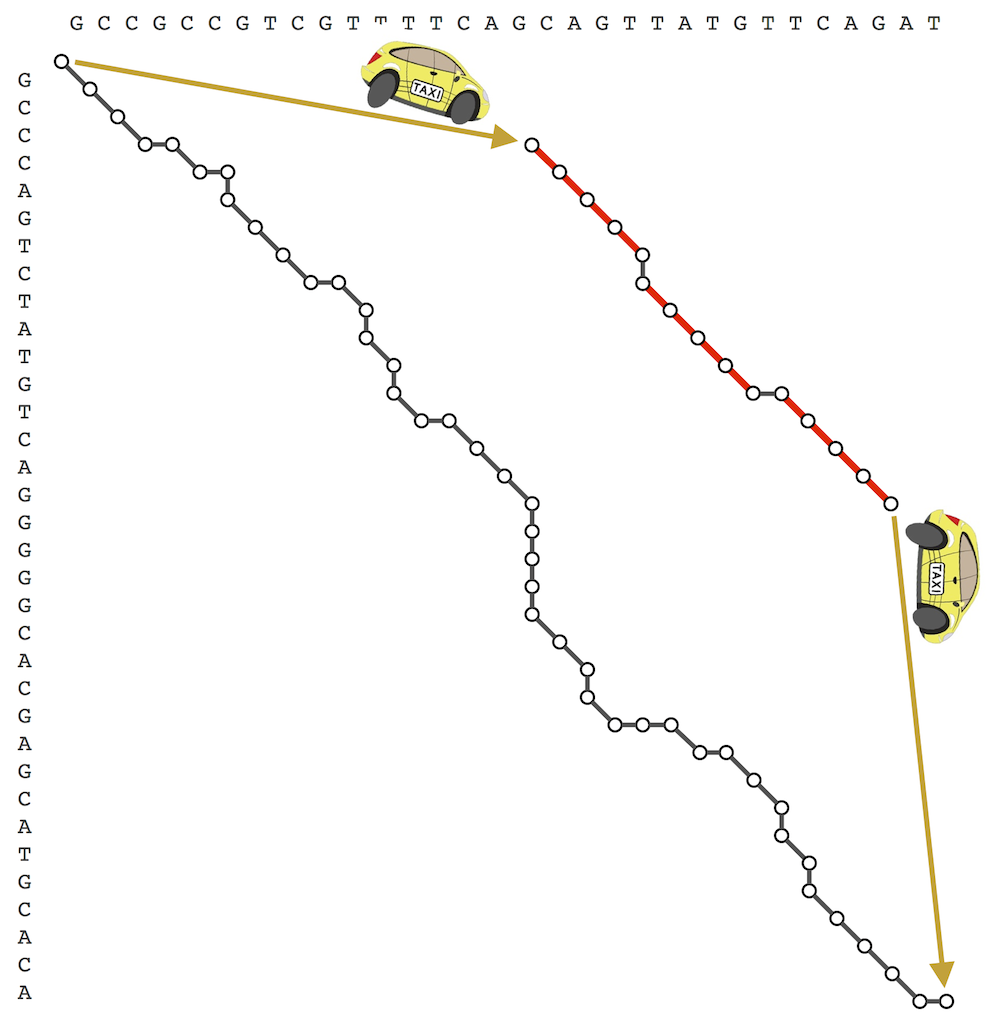
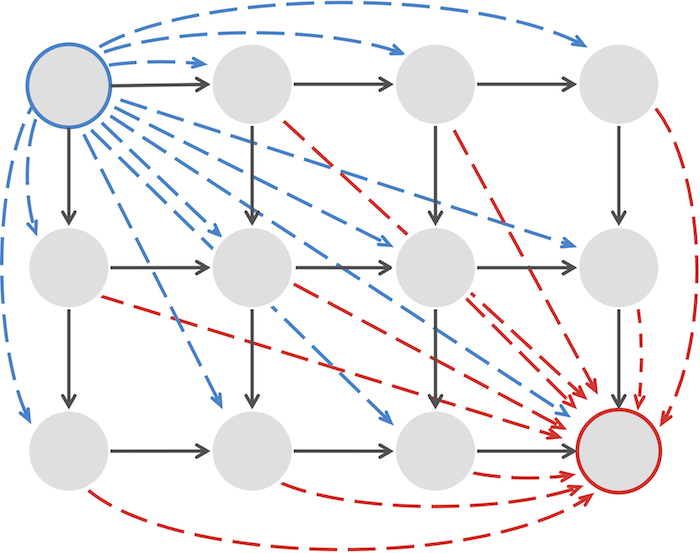
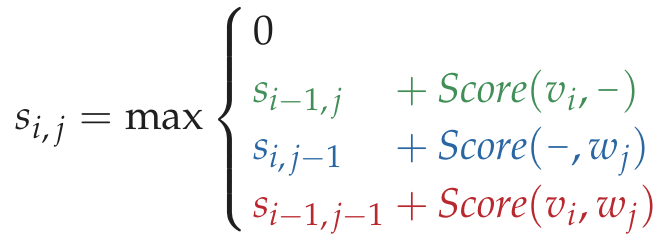
'''
Code Challenge: Solve the Local Alignment Problem.
Input: Two protein strings written in the single-letter amino acid alphabet.
Output: The maximum score of a local alignment of the strings, followed by a local alignment of these strings achieving the maximum
score. Use the PAM250 scoring matrix for matches and mismatches as well as the indel penalty σ = 5.
---------------
Sample Input:
MEANLY
PENALTY
---------------
Sample Output:
15
EANL-Y
ENALTY
---------------
Lo Kwongho 2018.9
'''
import numpy
from os.path import dirname def Grade(Symb1,Symb2):
Indx1 = symbolList[Symb1]
Indx2 = symbolList[Symb2]
return matrix[Indx1][Indx2] def Init_Graph_Local(l1,l2):
Graph = numpy.zeros([l1,l2])
return Graph def Init_Path(l1,l2):
Path = numpy.ones([l1,l2])*-1
for x in range(1,l1):
Path[x][0] = 1
for y in range(1,l2):
Path[0][y] = 2
return Path def buildLocalAlignmentGraph(text1,text2):
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
Graph = Init_Graph_Local(l1, l2)
Path = Init_Path(l1, l2) for x in range(1,l1):
for y in range(1,l2):
Graph[x][y] = max(Graph[x-1][y]-5, Graph[x][y-1]-5, Graph[x-1][y-1]+Grade(text1[x],text2[y]),0)
if Graph[x-1][y]-5 == Graph[x][y]:
Path[x][y] = 1
elif Graph[x][y-1]-5==Graph[x][y]:
Path[x][y] = 2
elif Graph[x][y] == 0:
Path[x][y] = 0
else:
Path[x][y] = 3
maxVal = 0
maxIndx = [-1,-1]
for x in range(1,l1):
for y in range(1,l2):
if Graph[x][y]>maxVal:
maxVal=Graph[x][y]
maxIndx=[x,y] return [Graph,Path,maxIndx] def OutputLocalAligement(Path,Graph,text1,text2,maxIndx):
outT1 = ''
outT2 = ''
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
x = maxIndx[0]
y = maxIndx[1]
while(x!=0 or y!=0):
if Path[x][y]==1:
outT1 += text1[x]
outT2 += '-'
x -= 1
elif Path[x][y]==2:
outT1 += '-'
outT2 += text2[y]
y -= 1
elif Path[x][y]==3:
outT1 += text1[x]
outT2 += text2[y]
x -= 1
y -= 1
else:
x=0
y=0
return [outT1[::-1],outT2[::-1]] def ImportScoreMatrix():
dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'PAM250.txt').read().strip().split('\n')
symbolList = dataset[0].split()
for i in range(len(symbolList)):
symbolList[i]=[symbolList[i],i]
symbolList = dict(symbolList)
matrix = []
for i in range(1,len(dataset)):
matrix.append(dataset[i].split()[1:])
for l in range(len(matrix)):
for i in range(len(matrix[l])):
matrix[l][i]=int(matrix[l][i])
return [matrix,symbolList] if __name__ == '__main__':
[matrix,symbolList] = ImportScoreMatrix() dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'dataset.txt').read().strip().split()
text1 = ''+dataset[0]
text2 = ''+dataset[1] [Graph,Path,maxIndx] = buildLocalAlignmentGraph(text1,text2) [outT1,outT2]=OutputLocalAligement(Path,Graph,text1,text2,maxIndx)
print(int(Graph[maxIndx[0]][maxIndx[1]]))
print(outT1)
print(outT2)
局部比对 Python
'''
Code Challenge: Solve the Overlap Alignment Problem.
>>Input: Two strings v and w, each of length at most 1000.
>>Output: The score of an optimal overlap alignment of v and w, followed by an alignment of a suffix v' of v and a prefix w' of w.
achieving this maximum score. Use an alignment score in which matches count +1 and both the mismatch and indel penalties are 2.
-------------------
Sample Input:
PAWHEAE
HEAGAWGHEE
-------------------
Sample Output:
1
HEAE
HEAG
-------------------
coder: Lo Kwongho
''' import numpy
from os.path import dirname def Init_Graph_Overlap(l1,l2):
Graph = numpy.zeros([l1,l2])
for y in range(1,l2):
Graph[0][y] = Graph[0][y-1]-1
return Graph def Init_Path(l1,l2):
Path = numpy.ones([l1,l2])*-1
for x in range(1,l1):
Path[x][0] = 1
for y in range(1,l2):
Path[0][y] = 2
return Path def buildOverlapAlignmentGraph(text1,text2):
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
Graph = Init_Graph_Overlap(l1, l2)
Path = Init_Path(l1,l2)
for x in range(1,l1):
for y in range(1,l2):
if text1[x]==text2[y]:
Graph[x][y]=max(Graph[x-1][y-1]+1,Graph[x-1][y]-2,Graph[x][y-1]-2)
else:
Graph[x][y]=max(Graph[x-1][y-1]-2,Graph[x-1][y]-2,Graph[x][y-1]-2)
if Graph[x][y]==Graph[x-1][y]-2:
Path[x][y]=1
elif Graph[x][y]==Graph[x][y-1]-2:
Path[x][y]=2
else:
Path[x][y]=3 maxVal = 0
maxIndx = -1
for i in range(l2):
if Graph[l1-1][i]>maxVal:
maxVal=Graph[l1-1][i]
maxIndx=i return [Graph,Path,maxIndx,maxVal] def OutputOverlapAligement(Path,Graph,text1,text2,maxIndx):
outT1 = ''
outT2 = ''
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
x = l1-1
y = maxIndx
while(y!=0):
if Path[x][y]==1:
outT1 += text1[x]
outT2 += '-'
x -= 1
elif Path[x][y]==2:
outT1 += '-'
outT2 += text2[y]
y -= 1
elif Path[x][y]==3:
outT1 += text1[x]
outT2 += text2[y]
x -= 1
y -= 1
else:
x=0
y=0
return [outT1[::-1],outT2[::-1]] if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'dataset.txt').read().strip().split()
text1 = ''+dataset[0]
text2 = ''+dataset[1]
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
[Graph,Path,maxIndx,maxVal] = buildOverlapAlignmentGraph(text1,text2)
#print(Graph) [outText1,outText2]=OutputOverlapAligement(Path, Graph, text1, text2, maxIndx) print(int(maxVal))
print(outText1)
print(outText2)
Overlarp in python
'''
Fitting Alignment Problem: Construct a highest-scoring fitting alignment between two strings.
>>Input: Strings v and w as well as a matrix Score.
>>Output: A highest-scoring fitting alignment of v and w as defined by the scoring matrix Score.
-------------------
Sample Input:
GTAGGCTTAAGGTTA
TAGATA
-------------------
Sample Output:
2
TAGGCTTA
TAGA--TA
-------------------
coder: Lo Kwongho
''' import numpy
from os.path import dirname def Init_Graph_Fiting(l1,l2):
Graph = numpy.zeros([l1,l2])
for y in range(1,l2):
Graph[0][y] = Graph[0][y-1]-1
return Graph def Init_Path(l1,l2):
Path = numpy.ones([l1,l2])*-1
for x in range(1,l1):
Path[x][0] = 1
for y in range(1,l2):
Path[0][y] = 2
return Path def buildFittingAlignmentGraph(text1,text2):
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
Graph = Init_Graph_Fiting(l1, l2)
Path = Init_Path(l1,l2)
for x in range(1,l1):
for y in range(1,l2):
if text1[x]==text2[y]:
Graph[x][y]=max(Graph[x-1][y-1]+1,Graph[x-1][y]-1,Graph[x][y-1]-1)
else:
Graph[x][y]=max(Graph[x-1][y-1]-1,Graph[x-1][y]-1,Graph[x][y-1]-1)
if Graph[x][y]==Graph[x-1][y]-1:
Path[x][y]=1
elif Graph[x][y]==Graph[x][y-1]-1:
Path[x][y]=2
else:
Path[x][y]=3 maxVal = 0
maxIndx = -1
for i in range(l1):
if Graph[i][l2-1]>maxVal:
maxVal=Graph[i][l2-1]
maxIndx=i return [Graph,Path,maxIndx,maxVal] def OutputFittingAligement(Path,Graph,text1,text2,maxIndx):
outT1 = ''
outT2 = ''
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
x = maxIndx
y = l2-1
while(y!=0):
if Path[x][y]==1:
outT1 += text1[x]
outT2 += '-'
x -= 1
elif Path[x][y]==2:
outT1 += '-'
outT2 += text2[y]
y -= 1
elif Path[x][y]==3:
outT1 += text1[x]
outT2 += text2[y]
x -= 1
y -= 1
else:
x=0
y=0
return [outT1[::-1],outT2[::-1]] if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'dataset.txt').read().strip().split()
text1 = ''+dataset[0]
text2 = ''+dataset[1]
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
[Graph,Path,maxIndx,maxVal] = buildFittingAlignmentGraph(text1,text2) [outText1,outText2]=OutputFittingAligement(Path, Graph, text1, text2, maxIndx)
#print(Graph)
print(int(maxVal))
print(outText1)
print(outText2)
Fitting Alignment in python



'''
Code Challenge: Solve the Alignment with Affine Gap Penalties Problem.
>>Input: Two amino acid strings v and w (each of length at most 100).
>>Output: The maximum alignment score between v and w, followed by an alignment of v and w achieving this maximum score. Use the
BLOSUM62 scoring matrix, a gap opening penalty of 11, and a gap extension penalty of 1.
---------------------
Sample Input:
PRTEINS
PRTWPSEIN
---------------------
Sample Output:
8
PRT---EINS
PRTWPSEIN-
---------------------
coder: Lo Kwongho
'''
import numpy
from os.path import dirname
negINFINITY = -999
#Penalties
gs = -10 #gap_Start
ge = -1 #gap_Extend
#
def Grade(Symb1,Symb2):
Indx1 = symbolList[Symb1]
Indx2 = symbolList[Symb2]
return matrix[Indx1][Indx2] def initGraph(l1,l2):
Graph = [numpy.zeros([l1,l2] ,dtype=int) for i in range(3)] Graph[1][0][0] = negINFINITY
Graph[2][0][0] = negINFINITY
for x in range(1,l1):
Graph[0][x][0]=negINFINITY
if x==1:
Graph[1][x][0]=ge+gs
else:
Graph[1][x][0]=Graph[1][x-1][0]+ge
Graph[2][x][0]=negINFINITY
for y in range(1,l2):
Graph[0][0][y]=negINFINITY
if y ==1:
Graph[2][0][y]=ge+gs
else:
Graph[2][0][y]=Graph[2][0][y-1]+ge
Graph[1][0][y]=negINFINITY
return Graph def Init_Path(l1,l2):
Path = [numpy.ones([l1,l2])*-1 for i in range(3)]
'''for x in range(1,l1):
Path[x][0] = 1
for y in range(1,l2):
Path[0][y] = 2'''
return Path def buildAlignmentGraph(text1,text2,l1,l2): Graph = initGraph(l1,l2)
#Path = #Init_Path(l1,l2)
for x in range(1,l1):
for y in range(1,l2):
# X ######
Graph[1][x][y]=max(gs+ge+Graph[0][x-1][y],gs+ge+Graph[2][x-1][y],ge+Graph[1][x-1][y]) # Y ######
Graph[2][x][y]=max(gs+ge+Graph[0][x][y-1],gs+ge+Graph[1][x][y-1],ge+Graph[2][x][y-1]) # M ######
Graph[0][x][y]=Grade(text1[x], text2[y])+max(Graph[0][x-1][y-1],Graph[1][x-1][y-1],Graph[2][x-1][y-1]) maxVal = 0
maxIndx = -1
for i in range(3):
if Graph[i][l1-1][l2-1]>maxVal:
maxVal=Graph[i][l1-1][l2-1]
maxIndx=i
return [Graph,maxIndx,maxVal] def trackBack(Graph,maxIndx,text1,text2):
x = len(text1)-1
y = len(text2)-1
otext1 = ''
otext2 = ''
Indx = maxIndx
while(1):
if Indx==0:
otext1 += text1[x]
otext2 += text2[y]
if x ==1:
break
if Graph[0][x][y]==Graph[1][x-1][y-1]+Grade(text1[x], text2[y]):
Indx = 1
elif Graph[0][x][y]==Graph[2][x-1][y-1]+Grade(text1[x], text2[y]):
Indx = 2
else:
Indx = 0
x -= 1
y -= 1
elif Indx==1:
otext1 += text1[x]
otext2 += '-'
if x == 1:
break
if Graph[1][x][y]==Graph[0][x-1][y]+ge+gs:
Indx = 0
elif Graph[1][x][y]==Graph[2][x-1][y]+ge+gs:
Indx = 2
else:
Indx = 1
x -= 1
else:
otext1 += '-'
otext2 += text2[y]
if y == 1:
break
if Graph[2][x][y]==Graph[0][x][y-1]+ge+gs:
Indx = 0
elif Graph[2][x][y]==Graph[1][x][y-1]+ge+gs:
Indx = 1
else:
Indx = 2
y -= 1 return [otext1[::-1],otext2[::-1]] def ImportScoreMatrix():
dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'BLOSUM62.txt').read().strip().split('\n')
symbolList = dataset[0].split()
for i in range(len(symbolList)):
symbolList[i]=[symbolList[i],i]
symbolList = dict(symbolList)
matrix = []
for i in range(1,len(dataset)):
matrix.append(dataset[i].split()[1:])
for l in range(len(matrix)):
for i in range(len(matrix[l])):
matrix[l][i]=int(matrix[l][i])
return [matrix,symbolList] if __name__ == '__main__':
[matrix,symbolList] = ImportScoreMatrix() # 打分矩阵 dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'dataset.txt').read().strip().split()
text1 = ''+dataset[0]
text2 = ''+dataset[1]
l1 = len(text1)
l2 = len(text2)
[Graph,maxIndx,maxVal] = buildAlignmentGraph(text1, text2, l1, l2)
#print(Graph) [output_text1,output_text2] = trackBack(Graph,maxIndx,text1,text2)
print(maxVal)
print(output_text1)
print(output_text2)
Alignment with Affine Gap Penalties
'''
Code Challenge: Implement LinearSpaceAlignment to solve the Global Alignment Problem for a large dataset.
>>>Input: Two long (10000 amino acid) protein strings written in the single-letter amino acid alphabet.
>>>Output: The maximum alignment score of these strings, followed by an alignment achieving this maximum score. Use the BLOSUM62 scoring matrix and indel penalty σ = 5.
------------
Sample Input:
PLEASANTLY
MEANLY
------------
Sample Output:
8
PLEASANTLY
-MEA--N-LY
------------
coder: Lo Kwongho in 2018.9
'''
from os.path import dirname
import numpy
#
indel = -5
negINF = -9999
#
#
def Grade(Symb1,Symb2):
Indx1 = symbolList[Symb1]
Indx2 = symbolList[Symb2]
return matrix[Indx1][Indx2] def ImportScoreMatrix():
dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'BLOSUM62.txt').read().strip().split('\n')
symbolList = dataset[0].split()
for i in range(len(symbolList)):
symbolList[i]=[symbolList[i],i]
symbolList = dict(symbolList)
matrix = []
for i in range(1,len(dataset)):
matrix.append(dataset[i].split()[1:])
for l in range(len(matrix)):
for i in range(len(matrix[l])):
matrix[l][i]=int(matrix[l][i])
return [matrix,symbolList]
#
def half_Alignment(v,w):
nv = len(v)
mw = len(w)
s = numpy.zeros(shape=(nv+1,2),dtype=int)
for i in range(nv+1):
s[i,0] = indel*i
if mw==0:
return s[:,0] #
for j in range(mw):
s[0,1]=s[0,0]+indel
for i in range(nv):
s[i+1,1]=max(s[i,1]+indel,s[i+1,0]+indel,s[i,0]+Grade(w[j],v[i]))
s[:,0]=s[:,1]
return s[:,1] def midEdge(v,w):
nv = len(v)
mw = len(w)
mid = int((mw-1)/2)
wl = w[:mid]
wr = w[mid+1:]
pre = half_Alignment(v,wl)
suf = half_Alignment(v[::-1],wr[::-1])[::-1]
hs = [pre[i]+suf[i]+indel for i in range(nv+1)]
ds = [pre[i]+suf[i+1]+Grade(w[mid],v[i]) for i in range(nv)]
maxhs = max(hs)
maxds = max(ds)
if maxhs>maxds:
return ( (hs.index(maxhs),mid) ,(hs.index(maxhs),mid+1) )
else:
return ( (ds.index(maxds),mid) ,(ds.index(maxds)+1,mid+1) ) def build_Alignment_track(v,w):
vn = len(v)
wm = len(w)
if vn==0 and wm==0:
return []
elif vn==0:
return ['-']*wm
elif wm==0:
return ['|']*vn
((x1,y1),(x2,y2)) = midEdge(v,w)
if x1==x2:
edge = ['-']
else:
edge = ['\\']
wleft = w[:y1]
wright = w[y2:]
vupper = v[:x1]
vbotm = v[x2:] upper_left_track = build_Alignment_track(vupper,wleft)
bottom_right_track = build_Alignment_track(vbotm,wright)
return upper_left_track+edge+bottom_right_track def trackToString(v,w,track):
vi = 0
wj = 0
outv = ''
outw = ''
score = 0
for i in track:
if i == '|':
outv += v[vi]
outw += '-'
score += indel
vi += 1
elif i == '-':
outv += '-'
outw += w[wj]
score += indel
wj += 1
else:
outv += v[vi]
outw += w[wj]
score += Grade(v[vi], w[wj])
vi += 1
wj += 1 return [score,outv,outw] def LinearSpaceAlignment(v,w):
track = build_Alignment_track(v,w)
[score,outv, outw] = trackToString(v,w,track)
print(score)
print(outv)
print(outw) if __name__ == '__main__':
dataset = open(dirname(__file__)+'dataset.txt').read().strip().split()
[matrix,symbolList] = ImportScoreMatrix()
v = dataset[0]
w = dataset[1]
LinearSpaceAlignment(v,w)
Linear-Space Alignment
读书笔记 Bioinformatics Algorithms Chapter5的更多相关文章
- 笔记 Bioinformatics Algorithms Chapter7
一.Lloyd算法 算法1 Lloyd Algorithm k_mean clustering * Centers to Clusters: After centers have been selec ...
- 笔记 Bioinformatics Algorithms Chapter2
Chapter2 WHICH DNA PATTERNS PLAY THE ROLE OF MOLECULAR CLOCKS 寻找模序 一. 转录因子会结合基因上游的特定序列,调控基因的转录表达,但是在 ...
- 笔记 Bioinformatics Algorithms Chapter1
Chapter1 WHERE IN THE GENOME DOES DNA REPLICATION BEGIN 一. ·聚合酶启动结构域会结合上游序列的一些位点,这些位点有多个,且特异,并且分布 ...
- 读书笔记-Coding faster(英文版)
读书笔记-Coding faster(英文版) Getting More Productive with Microsoft visual Studio Author: Zain Naboulsi S ...
- 读书笔记-实用单元测试(英文版) Pragmatic Unit Testing in C# with NUnit
读书笔记-实用单元测试(英文版) Pragmatic Unit Testing in C# with NUnit Author: Andrew Hunt ,David Thomas with Matt ...
- 强化学习读书笔记 - 02 - 多臂老O虎O机问题
# 强化学习读书笔记 - 02 - 多臂老O虎O机问题 学习笔记: [Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, Richard S. Sutton and An ...
- 【读书笔记】《Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface》(1)
笔记前言: <Computer Organization and Design: The Hardware/Software Interface>,中文译名,<计算机组成与设计:硬件 ...
- The Pragmatic Programmer 读书笔记之中的一个 DRY-Don’t Repeat Youself
The Pragmatic Programmer读书笔记之中的一个 DRY-Don't Repeat Youself 尽管自己买了非常多软件project方面的书,可是由于时间的问题.一直没有静 ...
- 《Unix编程艺术》读书笔记(1)
<Unix编程艺术>读书笔记(1) 这两天開始阅读该书,以下是自己的体会,以及原文的摘录,尽管有些东西还无法全然吃透. 写优雅的代码来提高软件系统的透明性:(P134) Elegance ...
随机推荐
- sourceTree git的一些命令
经常使用的三个命令 1.添加修改过的文件到缓冲区 git add. 2.commit到本地 git commit -am ' 更改描述' 3.如果是多人开发的话,中间可能会有别人先提交的这是就需要先把 ...
- Oracle高级查询之OVER
注释:为了方便大家学习和测试,所有的例子都是在Oracle自带用户Scott下建立的 oracel的高级用法:rank()/dense_rank() over(partition by ...orde ...
- linq join用法
单条件: var query = from person in people join pet in pets on person equals pet.Owner select new { Owne ...
- IE7下面踩得坑
bug1.position:fixed:z-index:99; 出现了z-index:2的层级跑到他上面了, 为什么?会出现这问题??? 检查: 1你的固定定位的容器是不是被其他容器包裹,你包裹得容器 ...
- Informatica_(6)性能调优
六.实战汇总31.powercenter 字符集 了解源或者目标数据库的字符集,并在Powercenter服务器上设置相关的环境变量或者完成相关的设置,不同的数据库有不同的设置方法: 多数字符集的问题 ...
- linux 管道符与通配符
###管道符 *命令格: 命令1 | 命令2 //命令1的正确输出作为命令2的操作对象 ll | more netstat -an | grep xxx 通配符 类似于正则表达式 ? 一个以上 [] ...
- hdu 5532 (LIS) Almost Sorted Array
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5532 题意大致是一组数中去掉一个数后问剩下的数是否构成非严格单调序列 正反各跑一遍最长非严格连续子序列,存在长度 ...
- swift 要点
swift 基本语法注意点 通常来说,编程语言教程中的第一个程序应该在屏幕上打印“Hello, world”.在 Swift 中,可以用一行代码实现 print("Hello, world! ...
- python中装饰器使用
装饰器是对已有的模块进行装饰(添加新功能)的函数. 现有一段代码: import time def func1(): time.sleep(3) print("in the func1&qu ...
- jquery Nestable 获取改变排序后的json数据 拖动排序
<script type="text/javascript"> jQuery(function($){ $('.dd').nestable(); $('.dd-hand ...
