大数据学习(26)—— Spark之RDD
做大数据一定要有一个概念,需要处理的数据量非常大,少则几十T,多则上百P,全部放内存是不可能的,会OOM,必须要用迭代器一条一条处理。
RDD叫做弹性分布式数据集,是早期Spark最核心的概念,是一种数据集合,它的核心就是迭代器。
创建方式
有两种创建RDD的方式:
- 在驱动程序中并行化现有集合
- 引用外部存储系统中的数据集
示例1:并行化集合
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,2,3,2,5))
示例2:引用外部文件
val file = sc.textFile("hdfs://mycluster/data.txt")
val rdd = file.flatMap(s => s.split(" "))
RDD操作
RDD 支持两种类型的操作:
- transformations,转换操作,从现有的数据集创建一个新的数据集。
- actions,执行操作,对数据集运行计算后返回一个值给驱动程序。
Spark 中的所有转换都是惰性的,因为它们不会立即计算结果。相反,他们只记住应用于某些基本数据集(例如文件)的转换。仅当操作需要将结果返回到驱动程序时才计算转换。这种设计使 Spark 能够更高效地运行。
转换操作
常用的转换操作如下表。很多转换操作传入的都是一个函数,这是Scala的语法,可以理解为Java的Lambda表达式。用多了就习惯了。
| Transformation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| map(func) | Return a new distributed dataset formed by passing each element of the source through a function func. |
| filter(func) | Return a new dataset formed by selecting those elements of the source on which func returns true. |
| flatMap(func) | Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items (so func should return a Seq rather than a single item). |
| mapPartitions(func) | Similar to map, but runs separately on each partition (block) of the RDD, so func must be of type Iterator<T> => Iterator<U> when running on an RDD of type T. |
| mapPartitionsWithIndex(func) | Similar to mapPartitions, but also provides func with an integer value representing the index of the partition, so func must be of type (Int, Iterator<T>) => Iterator<U> when running on an RDD of type T. |
| sample(withReplacement, fraction, seed) | Sample a fraction fraction of the data, with or without replacement, using a given random number generator seed. |
| union(otherDataset) | Return a new dataset that contains the union of the elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
| intersection(otherDataset) | Return a new RDD that contains the intersection of elements in the source dataset and the argument. |
| distinct([numPartitions])) | Return a new dataset that contains the distinct elements of the source dataset. |
| groupByKey([numPartitions]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, Iterable<V>) pairs. Note: If you are grouping in order to perform an aggregation (such as a sum or average) over each key, using reduceByKey or aggregateByKey will yield much better performance.Note: By default, the level of parallelism in the output depends on the number of partitions of the parent RDD. You can pass an optional numPartitions argument to set a different number of tasks. |
| reduceByKey(func, [numPartitions]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function func, which must be of type (V,V) => V. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. |
| aggregateByKey(zeroValue)(seqOp, combOp, [numPartitions]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, returns a dataset of (K, U) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given combine functions and a neutral "zero" value. Allows an aggregated value type that is different than the input value type, while avoiding unnecessary allocations. Like in groupByKey, the number of reduce tasks is configurable through an optional second argument. |
| sortByKey([ascending], [numPartitions]) | When called on a dataset of (K, V) pairs where K implements Ordered, returns a dataset of (K, V) pairs sorted by keys in ascending or descending order, as specified in the boolean ascending argument. |
| join(otherDataset, [numPartitions]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. Outer joins are supported through leftOuterJoin, rightOuterJoin, and fullOuterJoin. |
| cogroup(otherDataset, [numPartitions]) | When called on datasets of type (K, V) and (K, W), returns a dataset of (K, (Iterable<V>, Iterable<W>)) tuples. This operation is also called groupWith. |
| cartesian(otherDataset) | When called on datasets of types T and U, returns a dataset of (T, U) pairs (all pairs of elements). |
| pipe(command, [envVars]) | Pipe each partition of the RDD through a shell command, e.g. a Perl or bash script. RDD elements are written to the process's stdin and lines output to its stdout are returned as an RDD of strings. |
| coalesce(numPartitions) | Decrease the number of partitions in the RDD to numPartitions. Useful for running operations more efficiently after filtering down a large dataset. |
| repartition(numPartitions) | Reshuffle the data in the RDD randomly to create either more or fewer partitions and balance it across them. This always shuffles all data over the network. |
| repartitionAndSortWithinPartitions(partitioner) | Repartition the RDD according to the given partitioner and, within each resulting partition, sort records by their keys. This is more efficient than calling repartition and then sorting within each partition because it can push the sorting down into the shuffle machinery. |
执行操作
执行操作触发计算,返回结果。没有执行操作的RDD不会生成Job,没有实际意义。
| Action | Meaning |
|---|---|
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). The function should be commutative and associative so that it can be computed correctly in parallel. |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. This is usually useful after a filter or other operation that returns a sufficiently small subset of the data. |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset (similar to take(1)). |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, optionally pre-specifying a random number generator seed. |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. Spark will call toString on each element to convert it to a line of text in the file. |
| saveAsSequenceFile(path) (Java and Scala) |
Write the elements of the dataset as a Hadoop SequenceFile in a given path in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. This is available on RDDs of key-value pairs that implement Hadoop's Writable interface. In Scala, it is also available on types that are implicitly convertible to Writable (Spark includes conversions for basic types like Int, Double, String, etc). |
| saveAsObjectFile(path) (Java and Scala) |
Write the elements of the dataset in a simple format using Java serialization, which can then be loaded using SparkContext.objectFile(). |
| countByKey() | Only available on RDDs of type (K, V). Returns a hashmap of (K, Int) pairs with the count of each key. |
| foreach(func) | Run a function func on each element of the dataset. This is usually done for side effects such as updating an Accumulator or interacting with external storage systems. Note: modifying variables other than Accumulators outside of the foreach() may result in undefined behavior. |
洗牌
shuffle (洗牌)是 Spark 重新分配数据的机制。我们在学习MapReduce的时候,在reduce阶段,数据就是根据key值通过shuffle操作到达不同的分区。这个操作涉及到数据复制,代价很高。应通过合理的API调用或者调优,尽量避免发生shuffle。
在程序本地执行时,4040端口可以查看DAG,从图中能看出是否有shuffle发生。
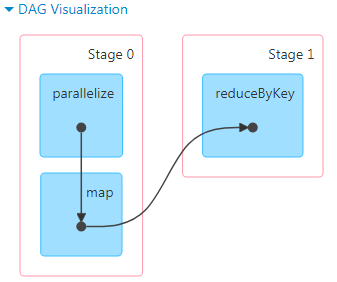
上图对应的代码如下
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("Test").setMaster("local")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
sc.setLogLevel("ERROR")
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,2,1,4,5,2))
val kv = rdd.map(x=>(x,1)).reduceByKey(_+_)
kv.foreach(println)
在调用reduceByKey时,作业产生了新的Stage1,这个过程就发生了shuffle,把相同key值的数据重新分区,计算出结果。
性能影响
发生shuffle时,它涉及到磁盘I/O,数据序列化和网络I/O,因此代价非常高。部分shuffle操作会用到相当多的堆内存,因为它在传输数据的过程中,会用到内存数据结构来组织数据。其中,reduceByKey和aggregateByKey这两个算子是在数据映射端创建内存数据结构,其他的byKey操作是在归约端创建。如果数据不适合放在内存里,Spark会将其溢写到磁盘上,从而导致额外的磁盘I/O开销和垃圾回收。
Shuffle还会在磁盘上生成大量中间文件。从 Spark 1.3 开始,这些临时文件会一直保留,直到相应的 RDD 不再使用并被垃圾回收。这样做是为了在重新计算血统时不需要重新创建 shuffle 文件。如果应用程序保留对这些 RDD 的引用或者 GC 不频繁启动,那长时间运行的 Spark 作业可能会消耗大量磁盘空间。
其他
Spark支持把数据持久化在内存中或者磁盘上,在性能调优的时候根据不同场景做出选择,这里不再赘述。
大数据学习(26)—— Spark之RDD的更多相关文章
- 大数据学习day23-----spark06--------1. Spark执行流程(知识补充:RDD的依赖关系)2. Repartition和coalesce算子的区别 3.触发多次actions时,速度不一样 4. RDD的深入理解(错误例子,RDD数据是如何获取的)5 购物的相关计算
1. Spark执行流程 知识补充:RDD的依赖关系 RDD的依赖关系分为两类:窄依赖(Narrow Dependency)和宽依赖(Shuffle Dependency) (1)窄依赖 窄依赖指的是 ...
- 大数据学习:Spark是什么,如何用Spark进行数据分析
给大家分享一下Spark是什么?如何用Spark进行数据分析,对大数据感兴趣的小伙伴就随着小编一起来了解一下吧. 大数据在线学习 什么是Apache Spark? Apache Spark是一 ...
- 大数据学习笔记——Spark工作机制以及API详解
Spark工作机制以及API详解 本篇文章将会承接上篇关于如何部署Spark分布式集群的博客,会先对RDD编程中常见的API进行一个整理,接着再结合源代码以及注释详细地解读spark的作业提交流程,调 ...
- 大数据学习笔记——Spark完全分布式完整部署教程
Spark完全分布式完整部署教程 继Mapreduce之后,作为新一代并且是主流的计算引擎,学好Spark是非常重要的,这一篇博客会专门介绍如何部署一个分布式的Spark计算框架,在之后的博客中,更会 ...
- 大数据学习day29-----spark09-------1. 练习: 统计店铺按月份的销售额和累计到该月的总销售额(SQL, DSL,RDD) 2. 分组topN的实现(row_number(), rank(), dense_rank()方法的区别)3. spark自定义函数-UDF
1. 练习 数据: (1)需求1:统计有过连续3天以上销售的店铺有哪些,并且计算出连续三天以上的销售额 第一步:将每天的金额求和(同一天可能会有多个订单) SELECT sid,dt,SUM(mone ...
- 大数据学习系列之六 ----- Hadoop+Spark环境搭建
引言 在上一篇中 大数据学习系列之五 ----- Hive整合HBase图文详解 : http://www.panchengming.com/2017/12/18/pancm62/ 中使用Hive整合 ...
- 大数据学习系列之七 ----- Hadoop+Spark+Zookeeper+HBase+Hive集群搭建 图文详解
引言 在之前的大数据学习系列中,搭建了Hadoop+Spark+HBase+Hive 环境以及一些测试.其实要说的话,我开始学习大数据的时候,搭建的就是集群,并不是单机模式和伪分布式.至于为什么先写单 ...
- 大数据学习系列之九---- Hive整合Spark和HBase以及相关测试
前言 在之前的大数据学习系列之七 ----- Hadoop+Spark+Zookeeper+HBase+Hive集群搭建 中介绍了集群的环境搭建,但是在使用hive进行数据查询的时候会非常的慢,因为h ...
- 大数据计算新贵Spark在腾讯雅虎优酷成功应用解析
http://www.csdn.net/article/2014-06-05/2820089 摘要:MapReduce在实时查询和迭代计算上仍有较大的不足,目前,Spark由于其可伸缩.基于内存计算等 ...
- 大数据实时处理-基于Spark的大数据实时处理及应用技术培训
随着互联网.移动互联网和物联网的发展,我们已经切实地迎来了一个大数据 的时代.大数据是指无法在一定时间内用常规软件工具对其内容进行抓取.管理和处理的数据集合,对大数据的分析已经成为一个非常重要且紧迫的 ...
随机推荐
- 对ES6中类class以及实例对象、原型对象、原型链之间关系的详细总结
1. 类 ES6 中新增加了类的概念,可以使用 class 关键字声明一个类,之后用这个类来实例化对象.即类的用途:实例化对象. // 创建一个Person类 class Person { } // ...
- Netty 框架学习 —— UDP 广播
UDP 广播 面向连接的传输(如 TCP)管理两个网络端点之间的连接的建立,在连接的生命周期的有序和可靠的消息传输,以及最后,连接的有序终止.相比之下,类似 UDP 的无连接协议中则没有持久化连接的概 ...
- sonarqube 8.9版本配置发信邮箱
admin登陆sonarqube系统 安装部署sonarqube 请参见我的安装博文: https://www.cnblogs.com/cndevops/p/14934434.html 配置邮箱 配置 ...
- 从零玩转人脸识别之RGB人脸活体检测
从零玩转RGB人脸活体检测 前言 本期教程人脸识别第三方平台为虹软科技,本文章讲解的是人脸识别RGB活体追踪技术,免费的功能很多可以自行搭配,希望在你看完本章课程有所收获. ArcFace 离线SDK ...
- 案例分享:Qt西门子机床人机界面以及数据看板定制(西门子通讯,mysql数据库,生产信息,参数信息,信息化看板,权限控制,播放器,二维图表,参数调试界面)
若该文为原创文章,转载请注明原文出处本文章博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq21497936/article/details/118685521 长期持续带来更多项目与技术分享 ...
- 2012年第三届蓝桥杯C/C++程序设计本科B组省赛 方阵旋转(代码填空)
方阵旋转 对一个方阵转置,就是把原来的行号变列号,原来的列号变行号 例如,如下的方阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 转置后变为: 1 5 9 13 2 ...
- spring集成flyway
最近给公司项目集成flyway,由于我们项目移动端使用的是spring框架,网上看了很多博客,感觉这方面的东西还是很少的,毕竟现在是springboot的天下,大多数都是springboot集成fly ...
- 用 SwiftUI 五天组装一个微信
GitHub 链接:SwiftUI-WeChatDemo 效果图 实装内容 4 个 Tab 页面 + 聊天界面,使用纯 SwiftUI 搭建而成 应用启动界面 Launch Screen 国际化及应用 ...
- 家庭账本开发day07
返回数据问题解决,需要按照规定的json数据进行返回. 利用jsonobejact或者GSON工具将对象ArrayList转化为json 格式.然后response.getWriter().write ...
- python 爬取网络小说 清洗 并下载至txt文件
什么是爬虫 网络爬虫,也叫网络蜘蛛(spider),是一种用来自动浏览万维网的网络机器人.其目的一般为编纂网络索引. 网络搜索引擎等站点通过爬虫软件更新自身的网站内容或其对其他网站的索引.网络爬虫可以 ...
